Large scale structures and case studies part 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Upwelling
Movement of water from deep, underlying masses to the surface
What is an upwelling result from what?
The divergence of surface waters from the coast or other water masses
Upwelling features
-Cold
-Nutrient rich
What is the amount of fish production of one upwelling?
44,700 mg C m-2y-1
-Most productive of all marine environments
What is the stereotype of upwellings
-Short food chains
-High transfer efficiency
-Well matched
-High f-ratio
-Oversimplified
Equatorial upwellings
Winds drive rotational currents in the surface ocean, anticlockwise in the north, clockwise in the south, both heading inwards
-When they meet, these pulls surface water apart, drawing water from below
Despite equatorial pacific upwelling having rich NO3- water what does it have low of?
Chlorophyll a
-High Nitrate Low Chlorophyll (HNLC)
What is expected from eqatorial pacific upwelling?
-Low PP
-Phytoplankton cells < 2 nanometres
-Phytoplankton (cyanobacteria & picoeukaryotes)
-Grazing dominated by microzooplankton
-Phytoplankton too small for mesozooplankton
-Low f-ratio
Where is Galapogas Plume situated?
Equatorial Pacific
Galapogas Plume features
-High chlorophyll a
-Volcanic rock below ocean & volcanic dust from land
-Fertilise water with Fe
When does coastal upwellings occur?
Longshore equatorward winds, offshore currents drag up deep, nutrient rich water to surface
Causes for upwelling
Variability in weather
Example of upwelling affected by different sources of variability in weather:
Arabian Sea
-Seasonal → Monsoon winds
Peru
-El Nino
Benguela
-Frequent changes wind stress
What was the focus of ARABESQUE Cruise
August-September cruise leads to waning of Southwest monsoon
(ARABESQUE Cruise) Upwelling Region features
-Diatoms: Porosira sp (large)
-High phytoplankton biomass
-Large mesozooplankton population
-Low microzooplankton biomass
-Characterisitcs upwelling system
(ARABESQUE Cruise) Offshore Region features
-Phytoplankton: Synechoccocus
-HNAN dominated by zooplankton
-Low mesozzoplankton
-Characteristics oceanic system
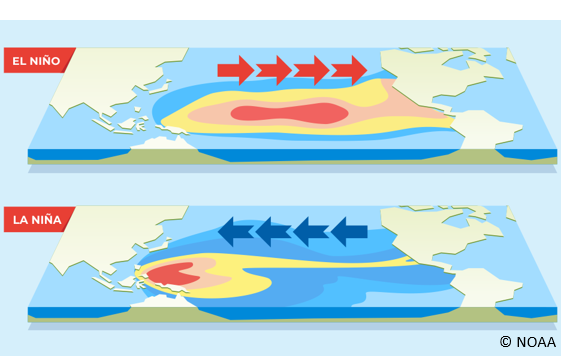
El Nino/La Nina (ENSO)
-Easterly winds drive warm surface waters to the west
-Water level ‘piles up’ on the west
-Wind structures can change resulting in the potential energy in this pile being released and flowing back to East (El Nino)
-Major weather and biological impacts
Benguela current (Benguela Upwelling Zone:Case Study 3)
-Massively productive upwelling region
-Variable system based on weather changes supported by Ekman transport
Why is Benguela important? (Benguela Upwelling Zone:Case Study 3)
Supports a commercially important demersal & pelagic fishery
-Anchovy & Pilchard
Benguela features (Benguela Upwelling Zone:Case Study 3)
-Strongly influenced by physical environment
-Upwelling contains South-eastern stress, austral summer
-Tongues cold upwelled water move offshore and northwards
-Mix with warm aged upwelled or oceanic water
What did Painting et al (1993) investigated
Investigated changes in planktonic food web structures by following plume of upwelled water
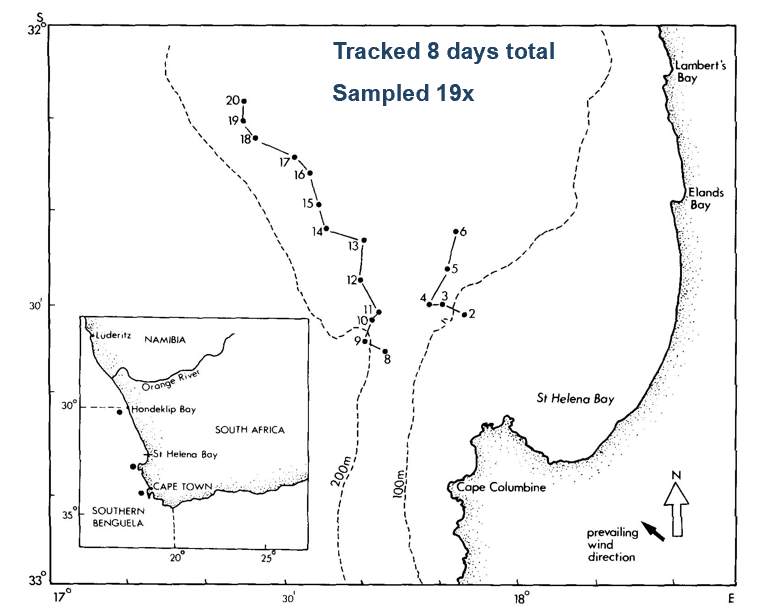
What did Painting et al (1993) ecounter in his investigation?
3 distinct water masses
-Age identified from temperature & NO3- data
What were the 3 distinct water masses Painting et al, (1993) found?
-Initial Maturing Upwelled Water
-Intermediate Maturing Upwelled Water
=Aged Maturing Upwelled Water
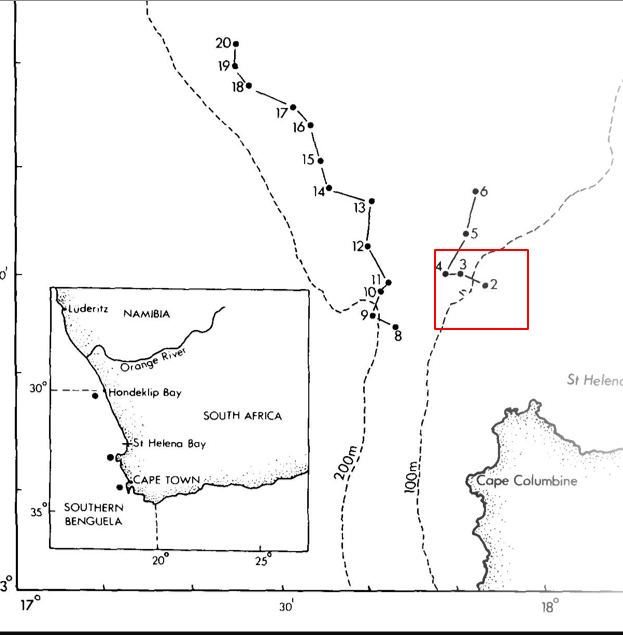
Initial Maturing Upwelled Water features
-Cold & high NO3-
-High chlorophyll a and PP
-Diatoms dominated phytoplankton (Skeletonema)
-High bacterial biomass
-Classical food chain
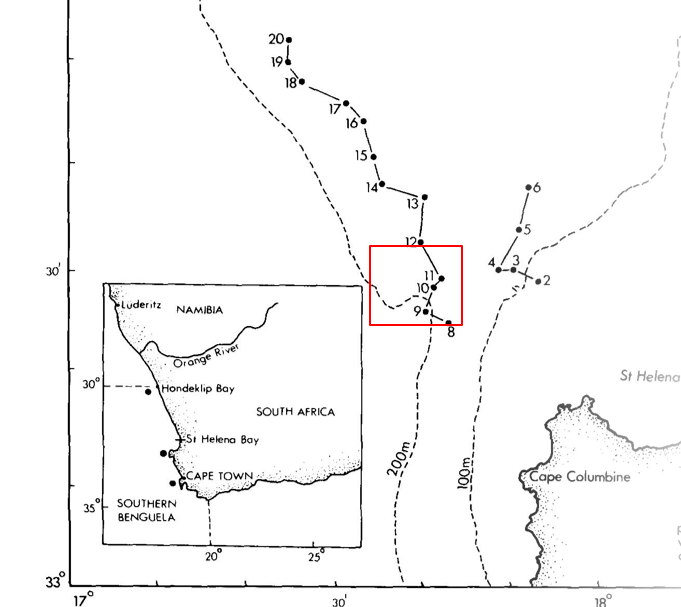
Intermediate Maturing Upwelled water features
-Higher temperature
Low NO3-
-Lower PP & chlorophyll a
-Diatoms → Nanoflagellates
-Highest bacterial biomass
Aged Maturing Upwelled Water features
-Higher temperatures
-Lower NO3-
-Low chlorophyll a and PP
-Nanoflagellates
-Lowest bacterial biomass
-Microbial food web
What did Probyn (1985) investigate
This study examines nitrogen uptake by different size-fractionated phytoplankton populations in the southern Benguela upwelling system. Researchers investigated how oceanic, continental shelf, and inshore waters influence nitrogen assimilation across various phytoplankton size classes
What were the key findings of Probyn (1985)
Size-Based Nitrogen Uptake
-Microplankton (>10 µm) showed higher nitrate uptake, dominating nitrogen assimilation in shelf waters.
-Nanoplankton (<10 µm) relied more on ammonium and urea, particularly in oceanic regions.
Environmental Influence
-Upwelling zones provided high nitrate concentrations, supporting larger phytoplankton.
-More stable offshore waters favored nanoplankton dominance, with regenerated nitrogen sources playing a key role.
Nitrogen Cycling & Ecosystem Impact
-The study highlights how different phytoplankton groups contribute to nitrogen cycling, shaping primary production.
-Understanding these dynamics is crucial for predicting ecosystem responses to environmental changes.
What were the F-ratios recorded for diatom bloom and annual average by Probyn, 1985?
Diatom bloom=0.7
Annual average=0.2-0.3
What is the least productive upwelling system?
Benguela
-Upwelling pulses are episodic which equals to mismatch
What wasthe recent increase in Benguela upwelling system?
Increase mesozooplankton due to favourable wind stress
-Mesozooplankton increased 100 fold over 50 years