Biology and Behavior/Sensation and Perception/Consciousness
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:07 AM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
1
New cards
dendrites
fiber-like cells that come out of the cell body; take information and pass it on to the soma (cell body)
[part of neuron]
[part of neuron]
![fiber-like cells that come out of the cell body; take information and pass it on to the soma (cell body)
[part of neuron]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3c4828d37d0941eca67c151233522ffe.png)
2
New cards
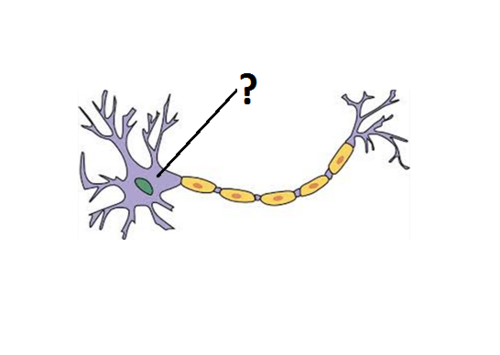
cell body
provides the energy for the nerve cell and houses the nucleus; power plant
3
New cards
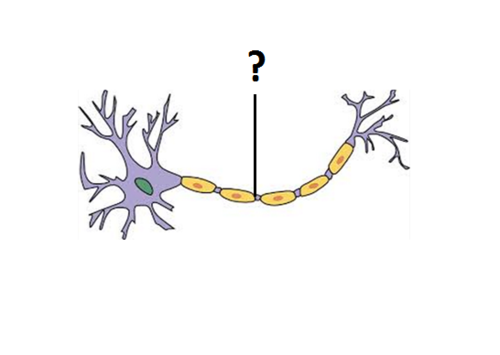
axon
carries information away from the cell; consists of myelin sheaths, nodes of Ranvier, and Schwann's cells
4
New cards
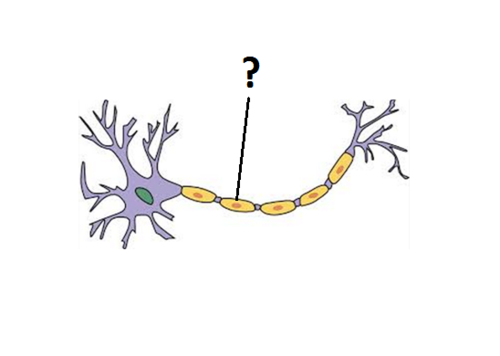
myelin sheath
acts as insulation; allows signal to run fast and uninterrupted from cell body to axon terminals; protects axon from damage; each bubble has a cell called Schwann's cell
5
New cards
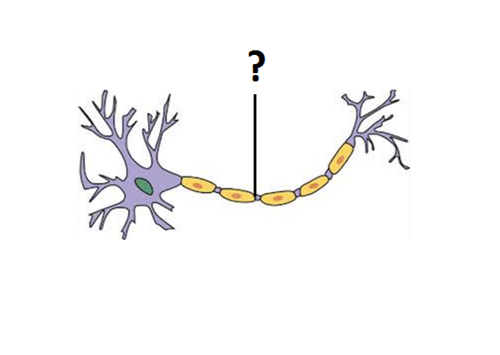
node of Ranvier
where action potential occurs; in between two myelin sheaths
6
New cards
Schwann's cell
produces and maintains the myelin shell
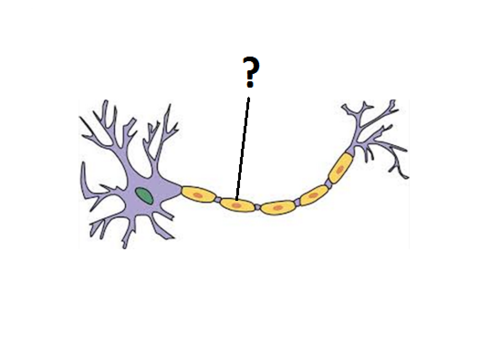
7
New cards
axon terminal
where information is released from the nerve cell
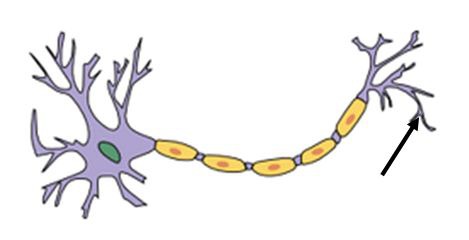
8
New cards
synapse
gap between two nerve cells; makes you who you are
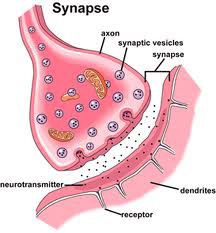
9
New cards
input of information
handled by afferent (aka sensory) neurons that bring information to the brain
[one of the three functions of neurons]
[one of the three functions of neurons]
10
New cards
interneuron
process information; all in the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system)
[one of the three functions of neurons]
[one of the three functions of neurons]
11
New cards
output of information
efferent (aka motor) neurons neurons that handle information sent from the brain to the body
[one of the three functions of neurons]
[one of the three functions of neurons]
12
New cards
threshold
minimum amount of stimuli needed to trigger a neural impulse; genetic; referred to as tolerances
ex | pain tolerances
ex | pain tolerances
13
New cards
ascending track
afferent neurons sending information from the body to the brain
(northbound on I-95)
(northbound on I-95)
14
New cards
descending track
efferent neurons sending information from the brain to the body
(southbound on I-95)
(southbound on I-95)
15
New cards
excitatory response
nervous system fires at faster than normal rate
[one of two events that occurs when a reflex is triggered]
[one of two events that occurs when a reflex is triggered]
16
New cards
inhibitory response
nervous system fires at slower than normal rate
[one of two events that occurs when a reflex is triggered]
[one of two events that occurs when a reflex is triggered]
17
New cards
excitatory overrules inhibitory
ex | Thursday night - party, Friday morning - major test
- lie to yourself and say you'll study until you have to leave; too busy thinking about party
- lie to yourself and say you'll only stay a little while, flash forward to 3 am and you're still there
- say you'll study in the morning but end up sleeping through alarm and rushing to class
- lie to yourself and say you'll study until you have to leave; too busy thinking about party
- lie to yourself and say you'll only stay a little while, flash forward to 3 am and you're still there
- say you'll study in the morning but end up sleeping through alarm and rushing to class
18
New cards
action potential
neural signal moving down the axon from node of Ranvier to node of Ranvier; caused by positive and negative ions rubbing against each other
19
New cards
neurotransmitters
communicators of the nervous system; talk through chemicals
20
New cards
Goldilocks principle
"just right"; perfect amount of neurotransmitters equals normal behavior
21
New cards
abnormal behavior
oversupply/undersupply of neurotransmitters
22
New cards
illicit drugs
temporarily create an undersupply or oversupply of neurotransmitters
23
New cards
lock and key
type of relationship between neurotransmitters and receptor sites; if all receptor sites are used, then the message is received
24
New cards
characteristics of a neurotransmitter
- work quickly
- serve a specific function
- released next to an adjacent nerve cell
- serve a specific function
- released next to an adjacent nerve cell
25
New cards
ACh
primary neurotransmitter for memory and learning
undersupply - Alzheimer's
undersupply - Alzheimer's
26
New cards
serotonin
primary neurotransmitter with mood, hunger, and sleep
undersupply - depression
oversupply - mania
undersupply - depression
oversupply - mania
27
New cards
dopamine
primary neurotransmitter with muscle movement and mood
undersupply - Parkinson's
oversupply - Schizophrenia
undersupply - Parkinson's
oversupply - Schizophrenia
28
New cards
glutamate
primary neurotransmitter for excitatory responses; speeds up nervous system
oversupply - migraines
oversupply - migraines
29
New cards
GABA
inhibitory neurotransmitter; slows down nervous system
30
New cards
PEA
what causes people to find other people attractive; breathing and heart beat accelerate, pupils dilate; only lasts between 90 days and 6 months
(works with oxytocin)
(works with oxytocin)
31
New cards
oxytocin
produces feelings of love
(works with PEA)
(works with PEA)
32
New cards
reuptake
releases more neurotransmitters than we have receptor sites for; extra unused neurotransmitters are recycled to the axon terminal to be used later; makes sure you always have enough to keep things moving; replenishing now doesn't have to occur constantly
33
New cards
undersupply of neurotransmitters
reuptake didn't happen, and all these molecules are sitting there, waiting to be used
34
New cards
oversupply of neurotransmitters
reuptake was too quick and the message wasn't fully received
to fix: you want to block reuptake
to fix: you want to block reuptake
35
New cards
central nervous system
where interneurons are located and process information
- spinal cord is protected by vertebrae, disks, and spinal fluid
- brain is protected by skull and spinal cerebral fluid
- spinal cord is protected by vertebrae, disks, and spinal fluid
- brain is protected by skull and spinal cerebral fluid
36
New cards
peripheral nervous system
brings information to brain and allows the brain to send information back to the body
- SNS
- ANS
- SNS
- ANS
37
New cards
SNS
controls voluntary muscle movement; you have to think to do it
ex | running, walking, talking, writing
ex | running, walking, talking, writing
38
New cards
ANS
controls smooth muscles and heart; everything that your body does unconsciously
ex | breathing, blinking, heart beating
- sympathetic
- parasympathetic
ex | breathing, blinking, heart beating
- sympathetic
- parasympathetic
39
New cards
sympathetic
uses energy; runs fight/flight responses; helps release adrenaline
40
New cards
parasympathetic
makes sure you're never burning more energy than necessary so you have energy for fight/flight
41
New cards
lesion
permanently destroys part of the brain so you can understand what it controls
ex | Phineas Gage - railroad pipe through the frontal lobe; changed his personality completely
ex | Phineas Gage - railroad pipe through the frontal lobe; changed his personality completely
42
New cards
lobotomy
probe shoved through eye and hammer hits it against frontal lobe, it gets wiggled around and supposedly cures mental illnesses
43
New cards
EEG
captures electrical activity in the brain
Strength: shows brain activity; non-invasive
Weakness: cannot show detail such as structure
Strength: shows brain activity; non-invasive
Weakness: cannot show detail such as structure
44
New cards
CT scan
slice by slice 3D X-ray
Strength: shows detail
Weaknesses: doesn't show activity; uses radiation, invasive
Strength: shows detail
Weaknesses: doesn't show activity; uses radiation, invasive
45
New cards
PET Scan
measures brain activity by looking at blood flow
Strength: shows higher level of activity
Weaknesses: requires radioactive isotopes, invasive; cannot show structure, no good picture; doesn't last long
Strength: shows higher level of activity
Weaknesses: requires radioactive isotopes, invasive; cannot show structure, no good picture; doesn't last long
46
New cards
MRI
uses radio waves that produce an image once sent back
Strengths: highly detailed image, shows soft tissues; non-invasive; can spend hours in the machine
Weaknesses: can't show activity; cannot have reactive metal
Strengths: highly detailed image, shows soft tissues; non-invasive; can spend hours in the machine
Weaknesses: can't show activity; cannot have reactive metal
47
New cards
fMRI
first machine to show both activity and structure; looks at how oxygen moves through body
48
New cards
DTI
studies blood flow on a microscopic level
49
New cards
TMS
uses electromagnetic waves to create temporary lesion in the brain
50
New cards
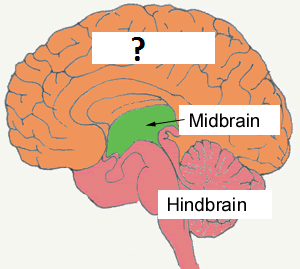
hindbrain
back, bottom part; most primitive part of the brain; takes care of the most basic functions; consists of medulla, pons, cerebellum, and reticular formation
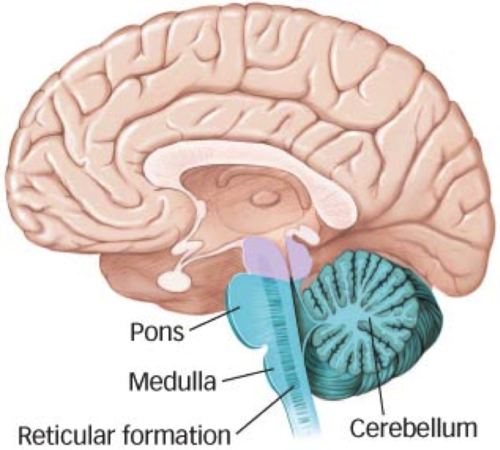
51
New cards
medulla
controls breathing, heart rate, pulse and reflexes; essential function
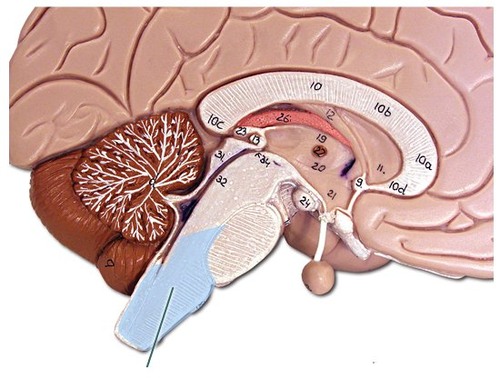
52
New cards
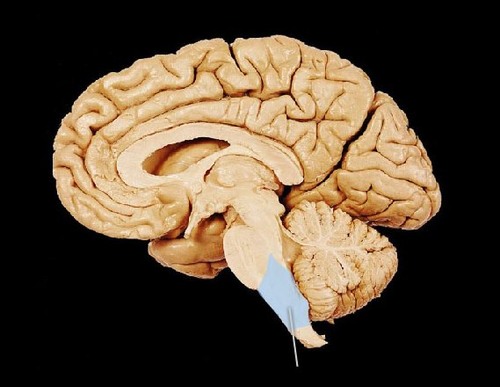
pons
regulates sleep; bridge connecting lower and upper brain
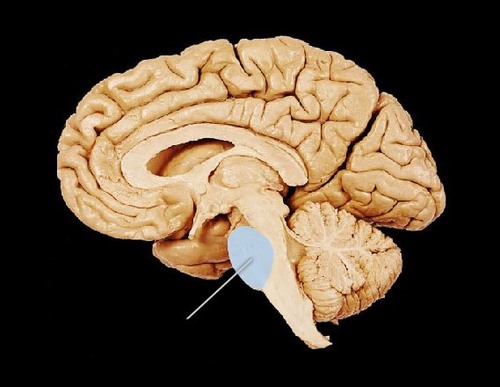
53
New cards
cerebellum
posture, balance, memory, ability to perform controlled activities
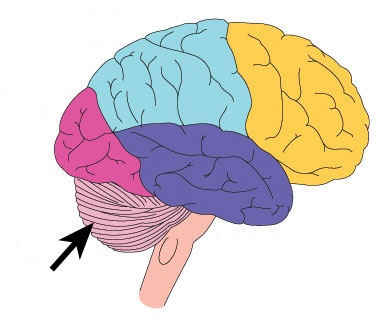
54
New cards
reticular formation
controls alertness and arousal; like alarm system in house; active while sleeping, only inactive when in coma or death; brain processes unimportant information while sleeping by dumping it in dreams
55
New cards
midbrain
integrates and coordinates sensory information; helps tie it together and make it work together
ex | hear a noise and turn your head to try to find out where it came from
ex | hear a noise and turn your head to try to find out where it came from
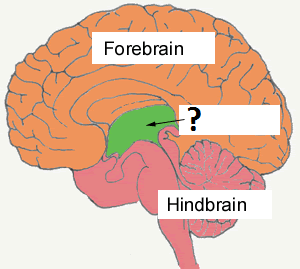
56
New cards
forebrain
where complexities start; higher order operations
57
New cards
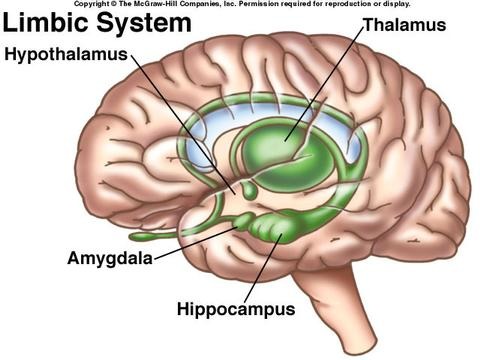
limbic system
inner core of the brain; second oldest part of the brain; control motivation and emotion
58
New cards
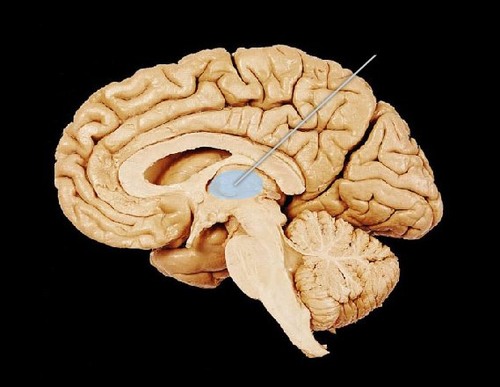
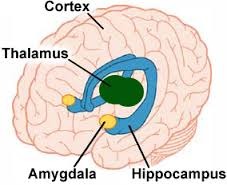
thalamus
sensory switchboard; all incoming sensory information goes here, and it directs it to the correct part of the brain to be processed; except for smell
59
New cards
hypothalamus
the brain's pleasure center; runs human pleasures and directs pituitary gland
four human pleasures: food, drinks, body heat, sex
four human pleasures: food, drinks, body heat, sex
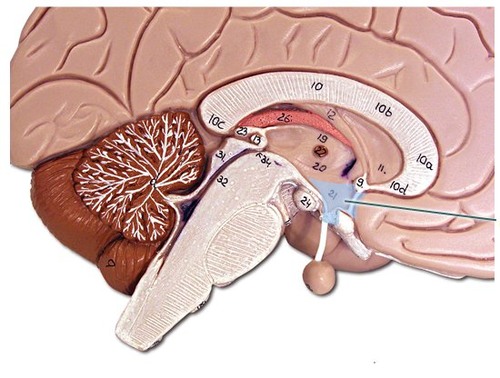
60
New cards
hippocampus
in charge of memory, helps coordinate it; Function 1A - make short-term memory long-term and Function 2B - long-term memory short-term
61
New cards
retrograde amnesia
forget everything; entire life is erased and have to start over
62
New cards
antrograde amnesia
cannot make any new memories; stuck in time only remembering events that occurred prior to event causing the brain damage (50 First Dates)
63
New cards
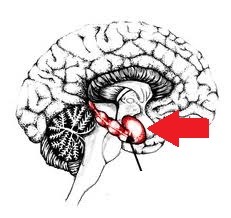
amygdala
in charge of fear, anger, and impulsive thinking; makes decisions during fight/flight; makes decisions because it seems fun at the time, without thinking of consquences; if all your friends jump off a cliff, you would too
64
New cards
singular cortex
bridge between thoughts and emotions
65
New cards
cerebrum
upper part of the brain; right and left hemisphere, same four lobes on each hemisphere; functions can be hemisphere-specific
66
New cards
left hemisphere
language, analytical thinking, and controls right side of the body
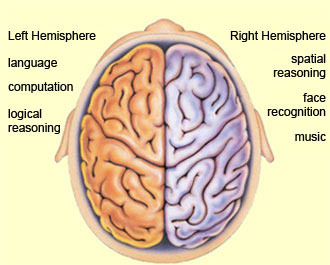
67
New cards
right hemisphere
creativity, spatial thinking, holistic, and left side of the body
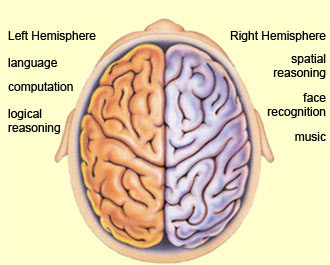
68
New cards
corpus callosum
connects hemispheres together; allows information to go back and forth between them
- females have larger ones, which is believed to make them better at empathy and nonverbal communication/language
- females have larger ones, which is believed to make them better at empathy and nonverbal communication/language
69
New cards
cerebral cortex
upper covering of brain; where all higher order learning occurs and where personality is; makes you who you are; part of the brain that becomes "brain dead"; the higher your level of education, the thicker this will be
70
New cards
occipital lobe
smallest of the lobes; where visual information is processed; 70% of brain's energy is used for it
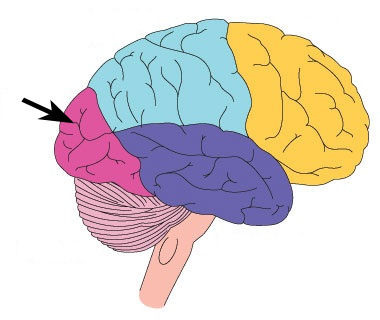
71
New cards
parietal lobe
where body senses (touch and taste) are; larger part because it codes a large area
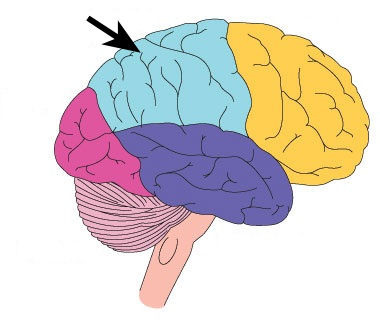
72
New cards
temporal lobe
hearing, language, emotions, memory, and human faces
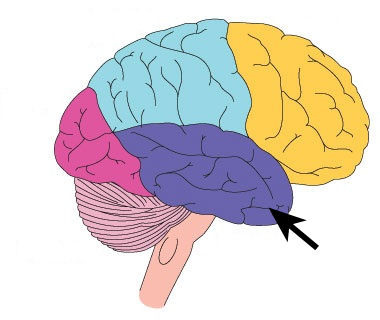
73
New cards
frontal lobe
takes 22 to 23 years to develop; where organization and planning occurs; most sophisticated part of us is the cerebral cortex on our frontal lobe (pre-frontal cortex)
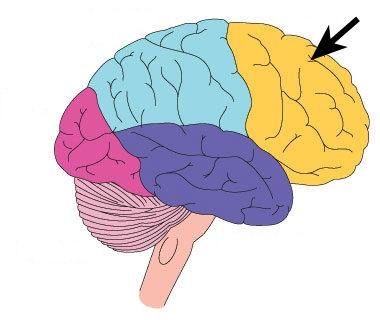
74
New cards
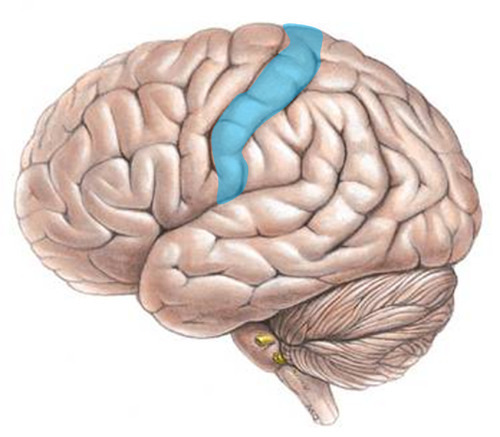
somatosensory cortex
very front of parietal lobe; where all incoming touch information goes; hands and mouth are most sensitive
75
New cards
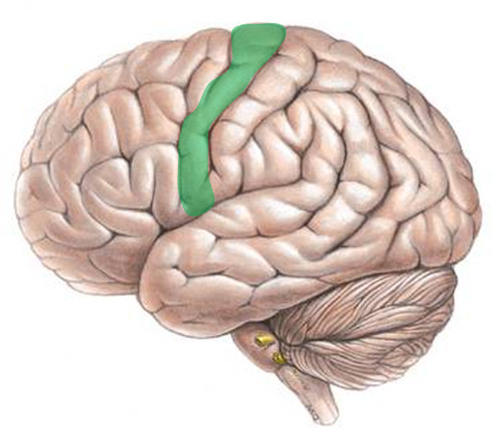
motor cortex
back of the frontal lobe; controls movement
76
New cards
association areas
neural cluster/network that performs a unique and specific function
77
New cards
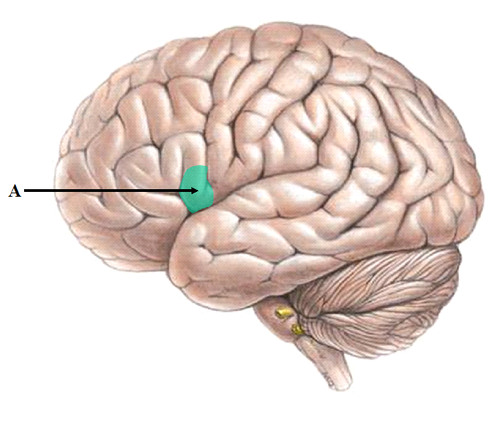
Broca's area
left frontal lobe; controls speech production; if damaged, Broca's aphasia will occur - know what you want to say but are unable to physically communicate it
78
New cards
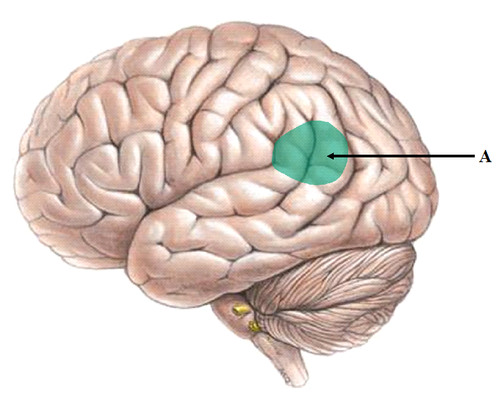
Wernicke's area
understanding; if damaged, you could speak but it wouldn't make sense
79
New cards
split-brain operation
cut the corpus callosum in half; right brain and left brain that don't that don't talk to each other anymore; treats fatal epilepsy
80
New cards
hemispherectomy
done when right side is having seizure activity that is life-threatening; cuts out right hemisphere
81
New cards
hormones
messengers of the endocrine system
- very slow
- carried by bloodstream
- last longer and affect a much broader area of the body
- very slow
- carried by bloodstream
- last longer and affect a much broader area of the body
82
New cards
pituitary gland
master gland; controls other glands and tells them to start secreting hormones; right under hypothalamus
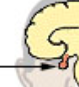
83
New cards
pineal gland
produces/secretes melatonin (sleep)
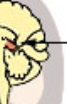
84
New cards
thyroid gland
produces/secretes thyroxine
85
New cards
hypothyroidism
too little thyroxine is used; weight gain
86
New cards
hyperthyroidism
too much thyroxine is used; weight loss
87
New cards
adrenal gland
makes three hormones: adrenaline (opens up airways and rushes blood to muscles), noradrenaline (brings body's functioning back to normal), and cortisol (retains energy for fight/flight; stores calories; also releases from stress and causes weight gain)
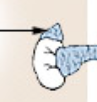
88
New cards
ovary
produces estrogen and progesterone; regulates fertility cycle; develop secondary sex characteristics in females (puberty); retain and shave fat; cycles sync when females cohabitate; these characteristics start at puberty and run up until menopause

89
New cards
testes
testosterone is regulated within 28 seconds; can be made higher by having women treat him rudely and can be made lower by handing him a baby; drives sexual behavior and creates secondary sex characteristics (facial hair and deepening of voice)
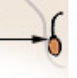
90
New cards
sensation
raw information/stimuli taken in by senses; governed by sensory system
91
New cards
perception
how sensation is organized into something meaningful; governed by interneurons
experiences - memory
expectations - what you think will be there
experiences - memory
expectations - what you think will be there
92
New cards
accessory structure
anything that modifies or enhances incoming stimuli
ex | lens of eye - focuses image on retina
ear - funnels sound into the ear canal
ex | lens of eye - focuses image on retina
ear - funnels sound into the ear canal
93
New cards
transduction
all about brain and its function; turns outside stimuli into electrical activity so the brain can enhance it
94
New cards
receptors
specialized cells in which transduction is caused
95
New cards
adaptation
when an incoming stimuli is constant and unchanging, we stop responding to it
positive: weight of clothes
negative: when it occurs in the eye
ex | driving down a long country road and hit a cow because you don't see it
positive: weight of clothes
negative: when it occurs in the eye
ex | driving down a long country road and hit a cow because you don't see it
96
New cards
absolute threshold
minimum amount of stimuli you can accurately detect 50% of the time
97
New cards
Signal Detection Theory
at or near the absolute threshold, there are two or more competing stimuli and you have to to tell the difference between them
ex | thinking someone in a crowd looks like someone you know from far away but as you get closer you realize it's not them
competing stimuli - the faces in the crowd vs. the face of the person you know
ex | thinking someone in a crowd looks like someone you know from far away but as you get closer you realize it's not them
competing stimuli - the faces in the crowd vs. the face of the person you know
98
New cards
Just Noticeable Difference
the smallest amount of distance needed to detect a difference
99
New cards
sight
dominant sense; overrules every sense except smell
100
New cards
sight
dominant sense; overrules every sense except smell