AH Exam 1 (Prehistoric, Near-Eastern, Egyptian)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Prehistoric
Before written history, hunter-gatherer societies.
Paleolithic
The "Old Stone Age", a long period of human development before the development of agriculture. Began 40,000 BC
Neolithic
The "New Stone Age", associated with the ancient Agricultural Revolution. Domesticated crops and animals, honoring dead important. Began earlier in Near East than Europe.
Bronze Age
a period of human culture between the Stone Age and the Iron Age, characterized by the use of weapons and implements made of bronze.
Sumerian Culture (Bronze Age)
3500-2300 BC
Akkadian Culture (Bronze Age)
2300-2150 BC
Neo-Sumerian Culture (Bronze Age)
2150-2000 BC
Old Babylonian Culture (Bronze Age)
1780 BC
Hittite Culture (Bronze Age)
1400 BC
Iron Age
the period following the Bronze Age; characterized by rapid spread of iron tools and weapons.
Assyrian Culture (Iron Age)
900-600 BC
Neo-Babylonian (Iron Age)
600-540 BC
Ancient Egyptian Culture, Pre Dynastic
3500-3000 BC
Ancient Egyptian Culture, Old Kingdom
2600-2100 BC
Ancient Egyptian Culture, New Kingdom
1550-1070 BC
Twisted perspective
form depicted in a way that combined profile and frontal perspectives. Two views at the same time.
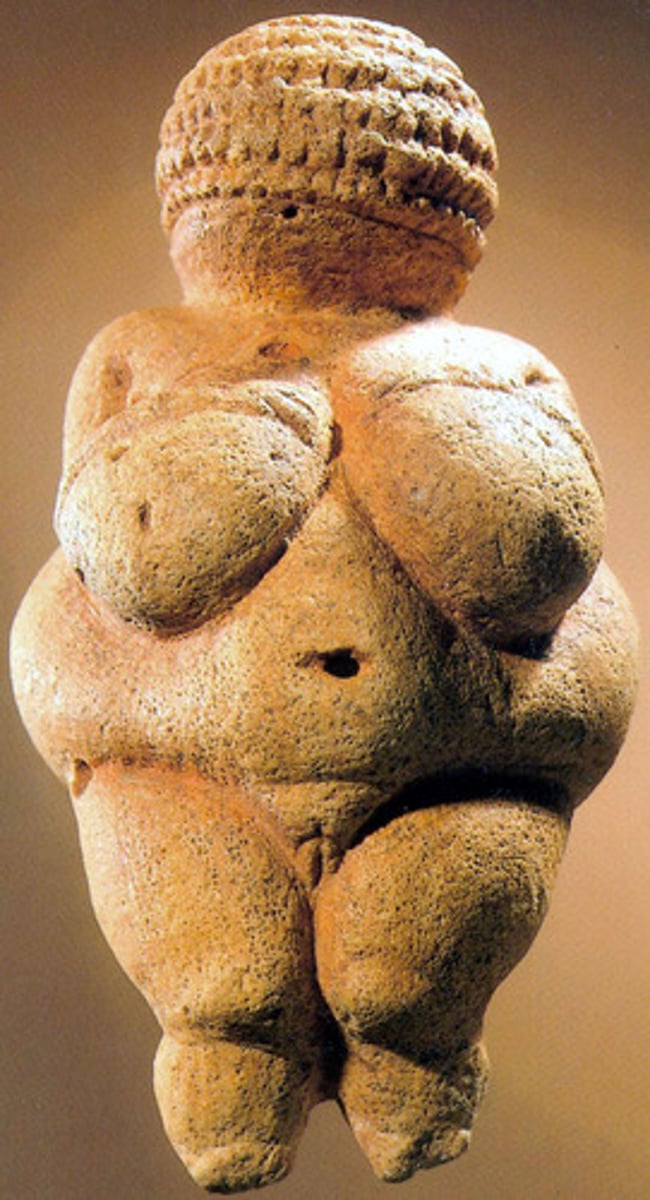
Venus of Willendorf
Paleolithic, Willendorf, Austria. Exaggerated female features, perhaps about fertility. Small arms and feet show low agency. Small size and smoothness suggest held often.

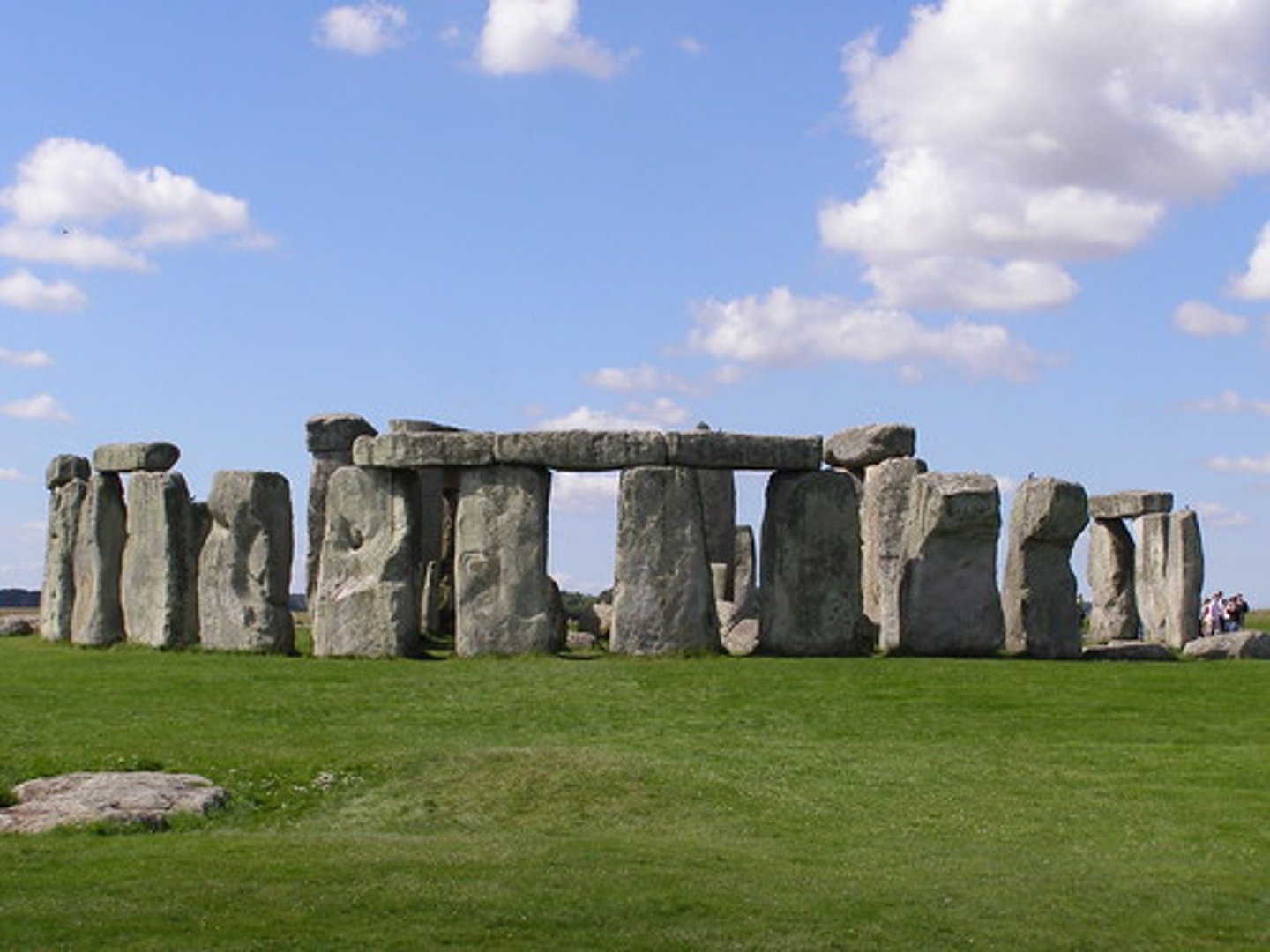
Stonehenge
Neolithic, 2,000 BC. Wiltshire, England. Multiple uses as it was built in many stages. At one point, calendar functions, summer solstice. Cut from far away, and shipped. Smoothly dressed stones.

Post and Lintel System
A method of construction that uses posts to support a crossbeam that can bear the weight of the roof.
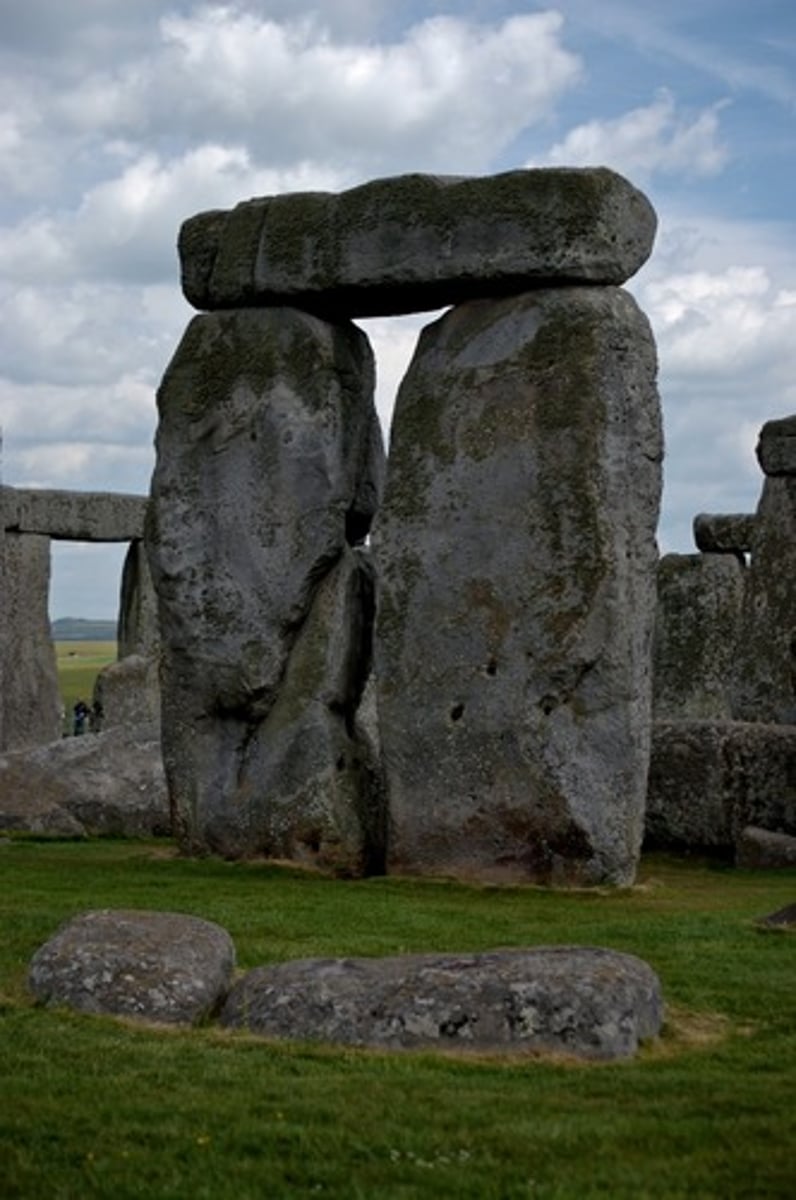

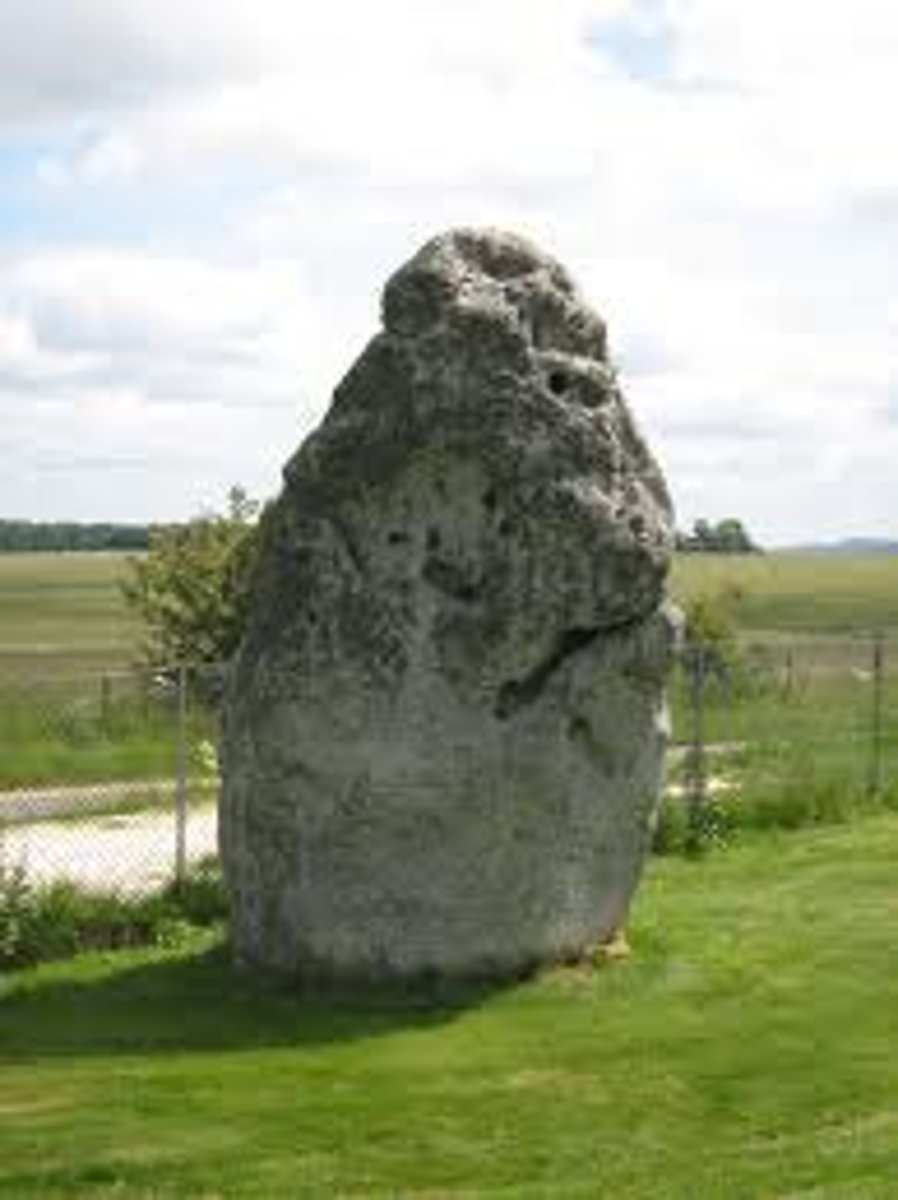
Heel Stone
Neolithic, 2,000 BC. Wiltshire, England. The monolith set outside the stone circle of Stonehenge along an axis which marked the rising of the sun on June 21st the mid-summer solstice.

Bent-axis vs. axial approach
Bent-axial- turns required to face/reach central feature. Axial approach- access along a straight central route.
Nave/Cella
Inner main chamber, central part.
Horned crown
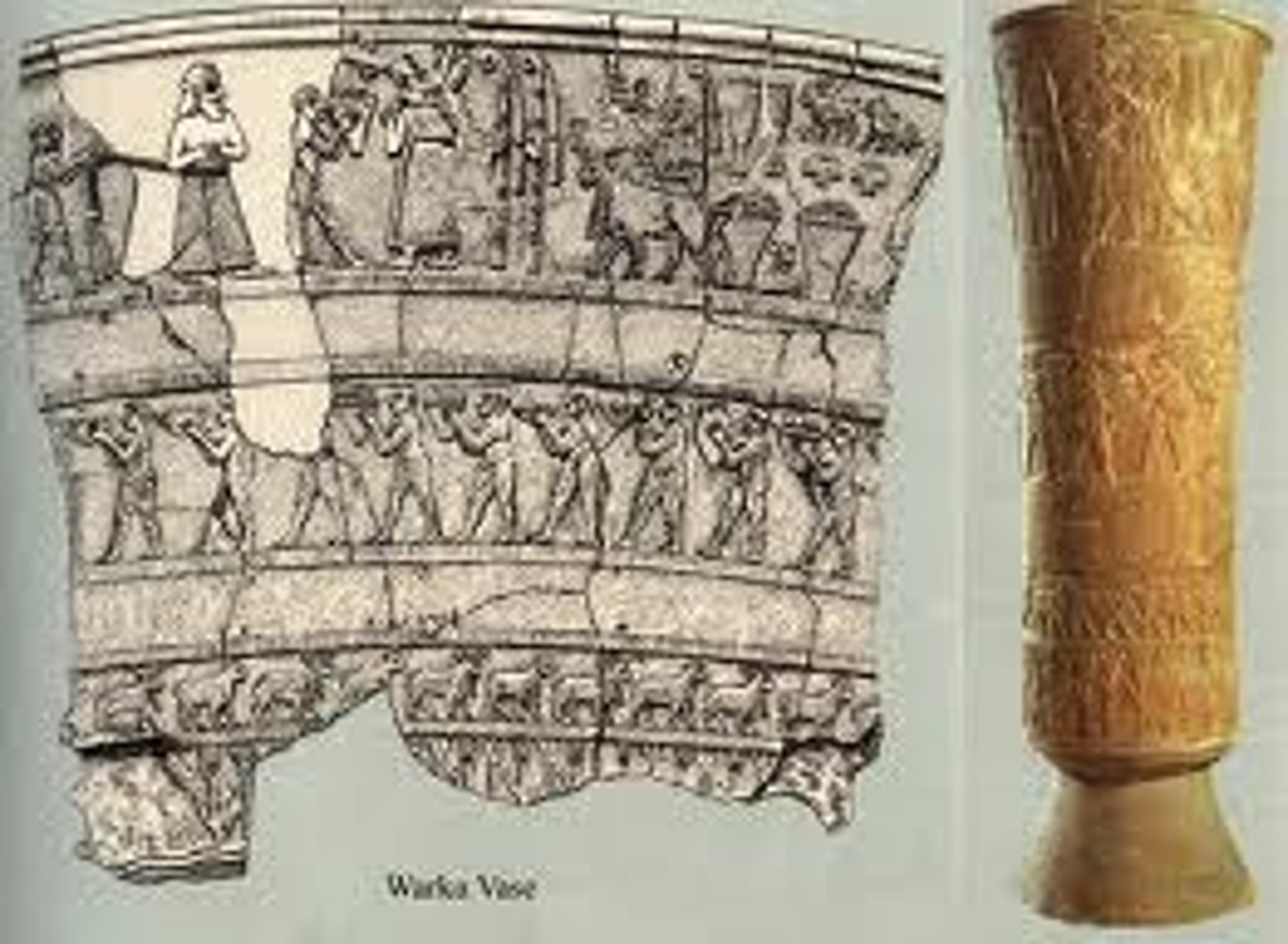
From the Warka Vase, Sumerian 3500-2300 BC, Iraq. 3 registers showing a ceremony honoring Inanna, goddess of fertility. Tall horned headless is the symbol of Inanna.
Relief (sculpture)
Relief sculpture is a type of art in which figures or forms project from a flat, two-dimensional background, remaining attached to a supporting surface rather than being freestanding.
Naturalism
A style and theory of representation based on the accurate depiction of detail.
Shamash
Sun god of Babylon.
Rod and ring
Symbolizes authority. In Mesopotamian art history, the rod and ring is a symbol held by gods and goddesses, appearing on stelae, reliefs, and cylinder seals from the Sumerian to the Neo-Assyrian periods. While its exact meaning remains a subject of scholarly debate, it is widely interpreted as a symbol of divine authority, royal power, or justice.
Citadel
(n.) a fortress that overlooks and protects a city; any strong or commanding place
Composite animal
Composite creatures are mythical beings that combine elements from various animals or humans, often seen in prehistoric art and sculptures.
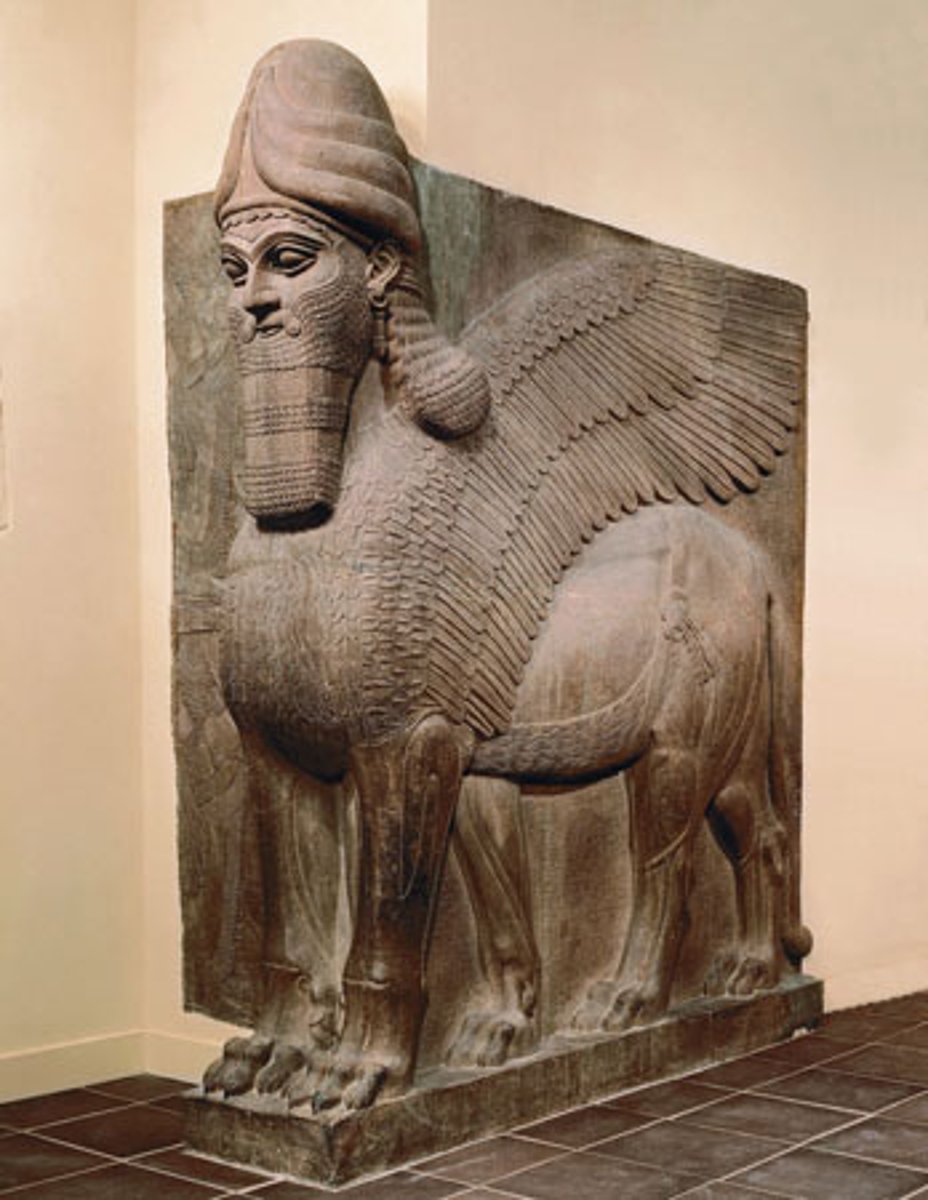
Lamassu
Iraq, 721-705 BC. Assyrian royal complexes guarded by lamassu, such as this one from the citadel of Sargon II. Front view in rest and side view in motion. Monster man-headed winged bulls.

Stylized/stylization
In art history, stylized art depicts subjects in a non-naturalistic way by emphasizing or simplifying certain features to convey specific ideas, emotions, or cultural significance, moving away from strict realism. Artists focus on specific forms, shapes, or lines, sometimes to an exaggerated degree.
Nebuchadnezzar II
Babylonian king who constructed Babylon's Ishtar Gate and the Marduk ziggurat. Restored Babylon.
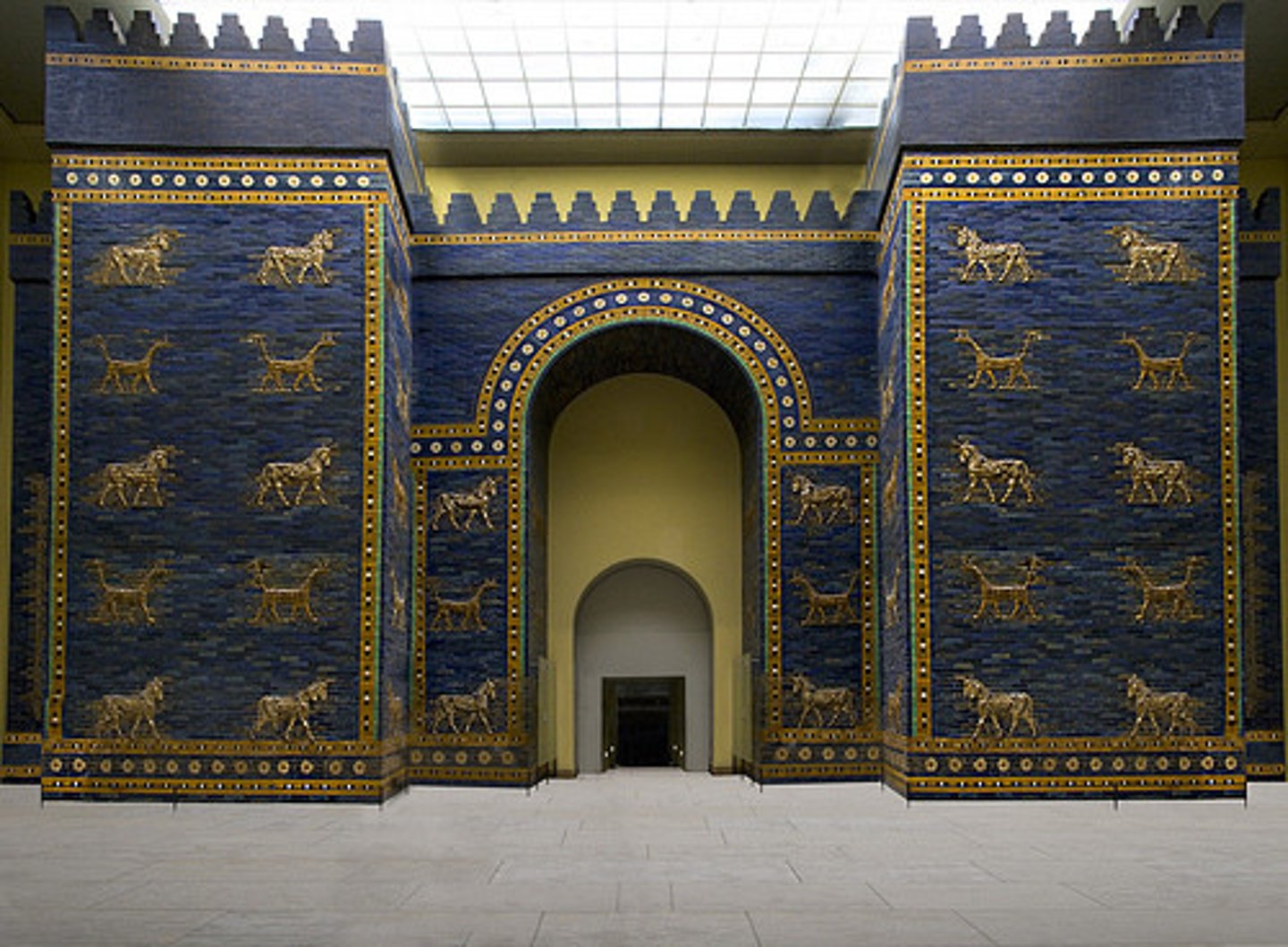
Ishtar Gate
Babylon, Iraq, Neo-Babylonian, 600-540 BC. Made out of glazed brick. Blue/gold palette. Animals reference to power, such as dragons and bulls.

Daniel
Person and book of the Bible recounting king Nebuchadnezzar II and his actions.
Upper Egypt
Southern, upstream part of ancient Egypt. Grasslands that encouraged hunting.
Lower Egypt
Northern Egypt, where the rich soil of the Nile Delta islands promoted agriculture and animal husbandry.
Nile River
Made Egyptian area very fertile. Annual floods helped create rich soils for crops, and marshlands supplied habitat for animals that the Egyptians hunted.
Hathor
Goddess of fertility.
Horus
Falcon god and god of upper Egypt.
Cartouche
An emblem with the name of a pharaoh or deity. Shown on the Palette of Narmer.
Mastaba
Egypt, Old Kingdom, 2600-2100 BC. Meaning bench in Arabic. For upper class burials. Burial chamber is underground. Housed body, portrait statues, and offerings. Often decorated with scenes of everyday life.
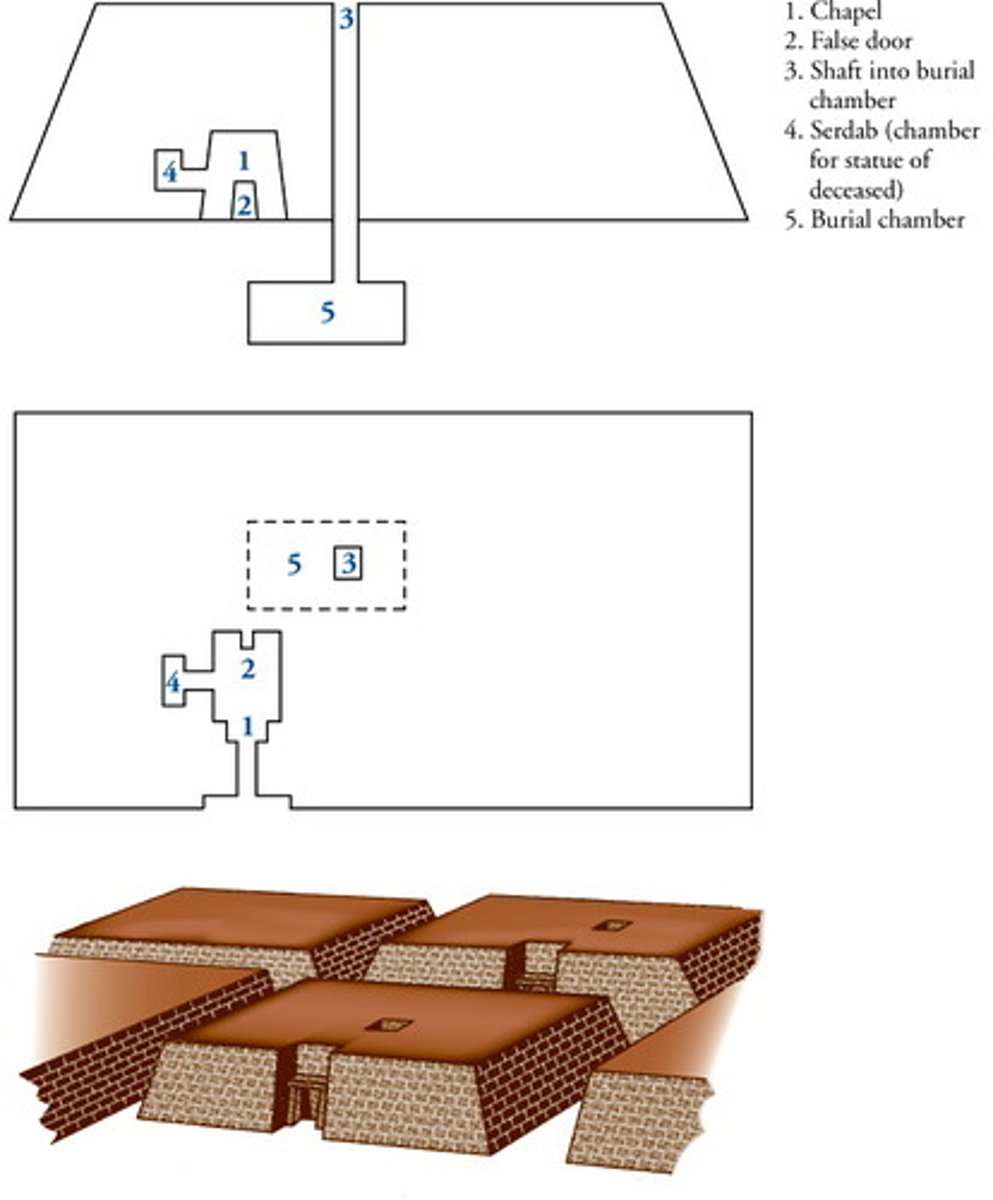
Section v Plan v reconstructed view
Plan View: A "plan" is a drawing of an object or space as if viewed from directly above. In architecture, a floor plan is a plan view showing the layout of a building.
Section View: A "section" is a drawing that cuts vertically through an object or space to reveal what is inside. It shows the internal construction, materials, and vertical relationships.
Reconstructed View: A "reconstructed view" is a computer-generated image created from data collected from different angles or slices. For example, a medical CT scan takes many cross-sectional images that are then computationally "reconstructed" into a full 3D view.
Stepped pyramid
Egypt, Old Kingdom 2600-2100 BC. Built by master builder Imhotep for King Djoser. Resembles a series of stacked mastabas. Pyramid was the center of a massive underground funerary complex.
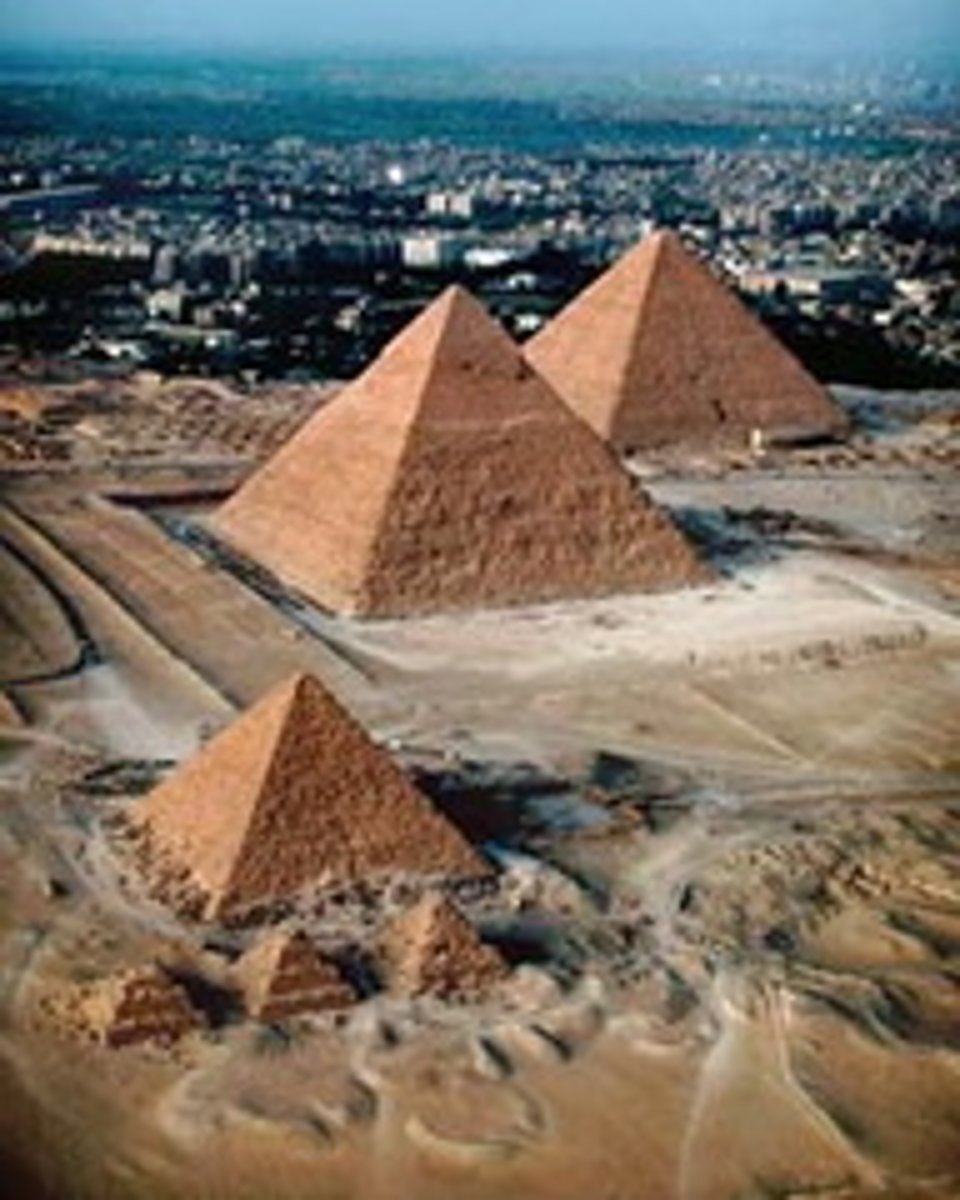
Pyramid of Khufu
Gizeh, Egypt, Old Kingdom 2600-2100 BC. Complex of the Great Pyramids. Largest and oldest pyramid at Gizeh.
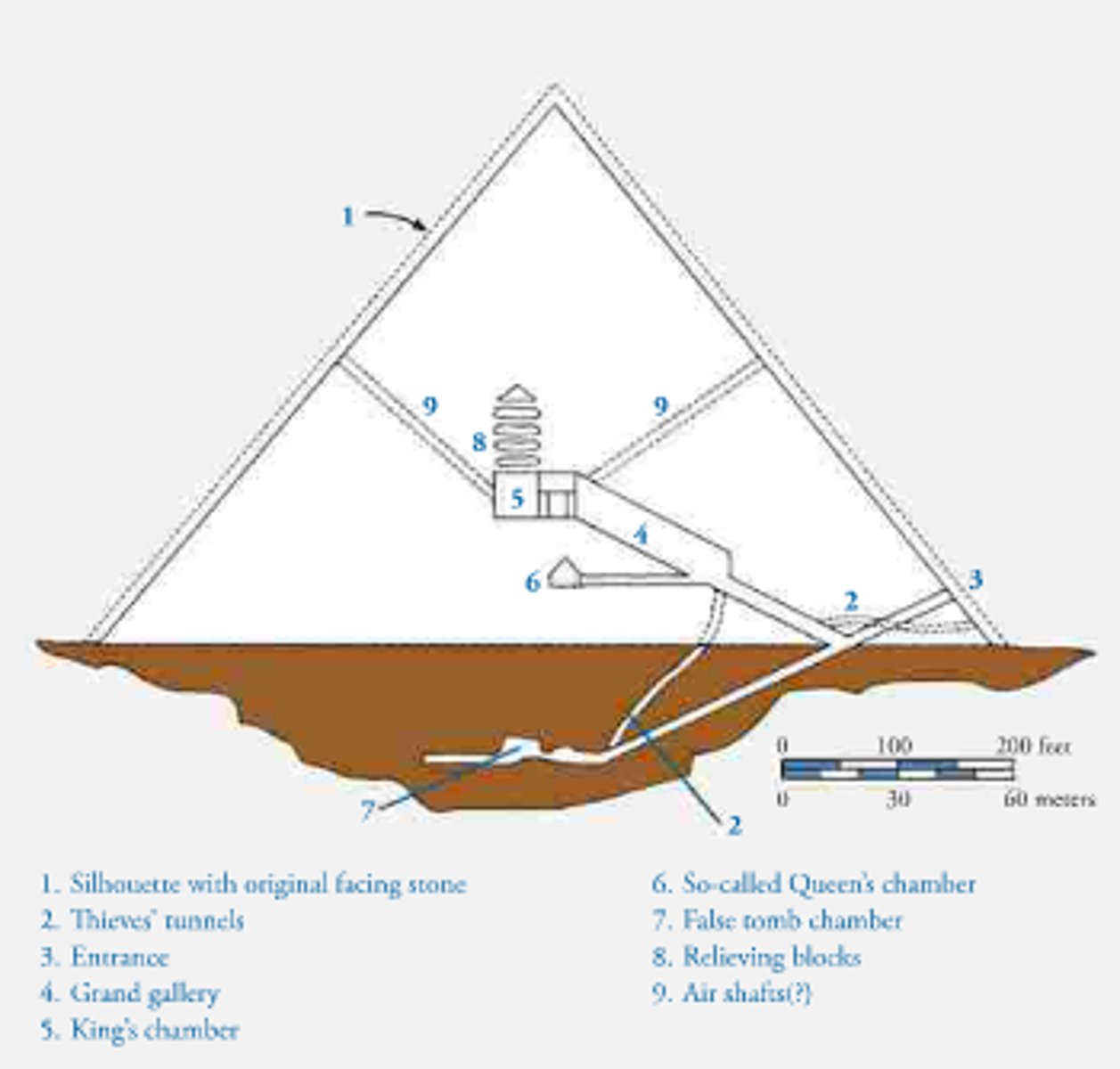
Pyramid of Khafre
Gizeh, Egypt, Old Kingdom 2600-2100 BC. Complex of the Great Pyramids. Great Sphinx located here, and valley temple with statue of Khafre. Some casing stones still at the peak.

Pyramid of Menkaure
Gizeh, Egypt, Old Kingdom 2600-2100 BC. Complex of the Great Pyramids.

Valley temple
The temple closest to the Nile River associated with each of the Great Pyramids at Gizeh in ancient Egypt. Funerary complex. Containing the statue of Khafre.

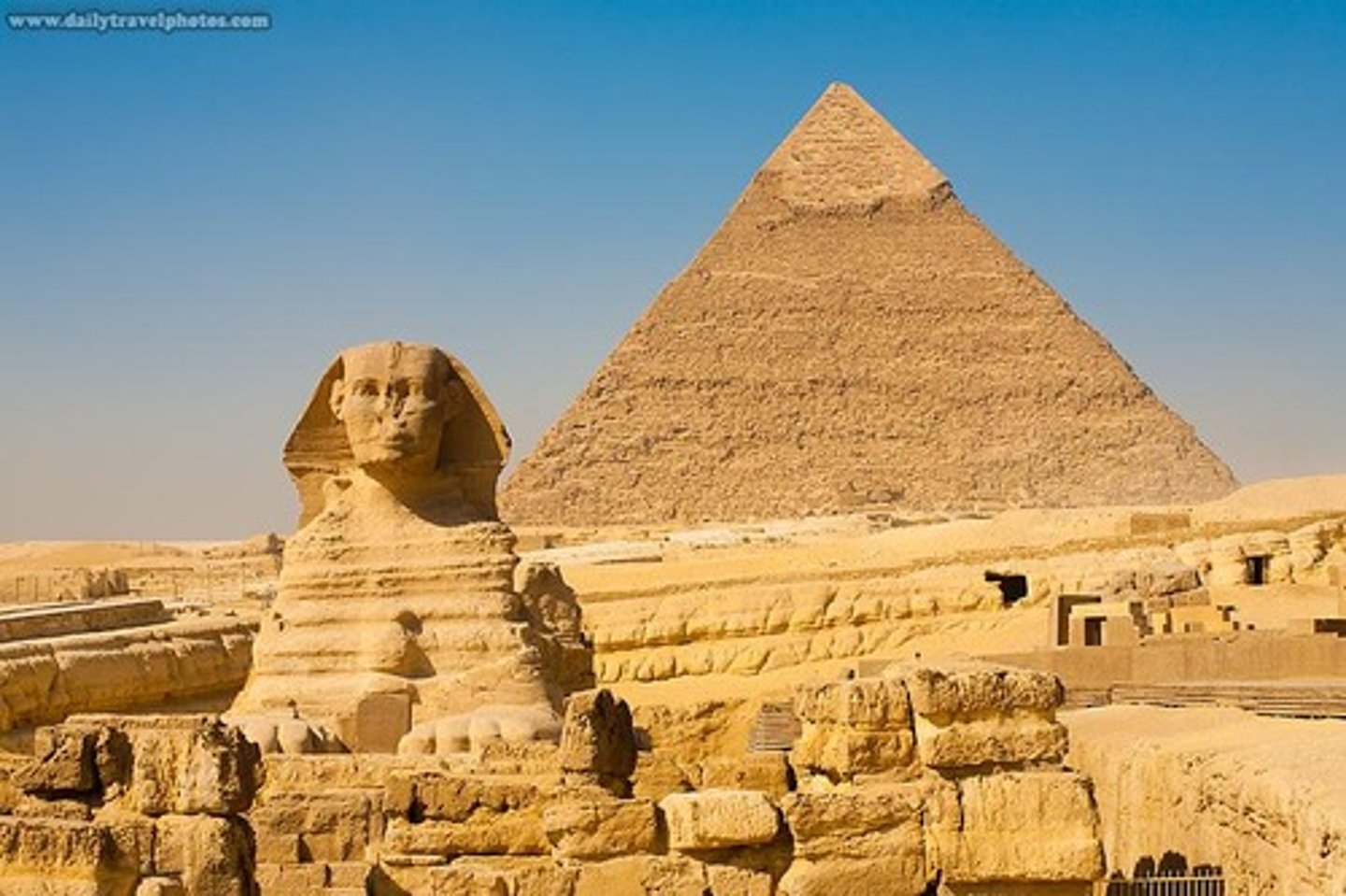
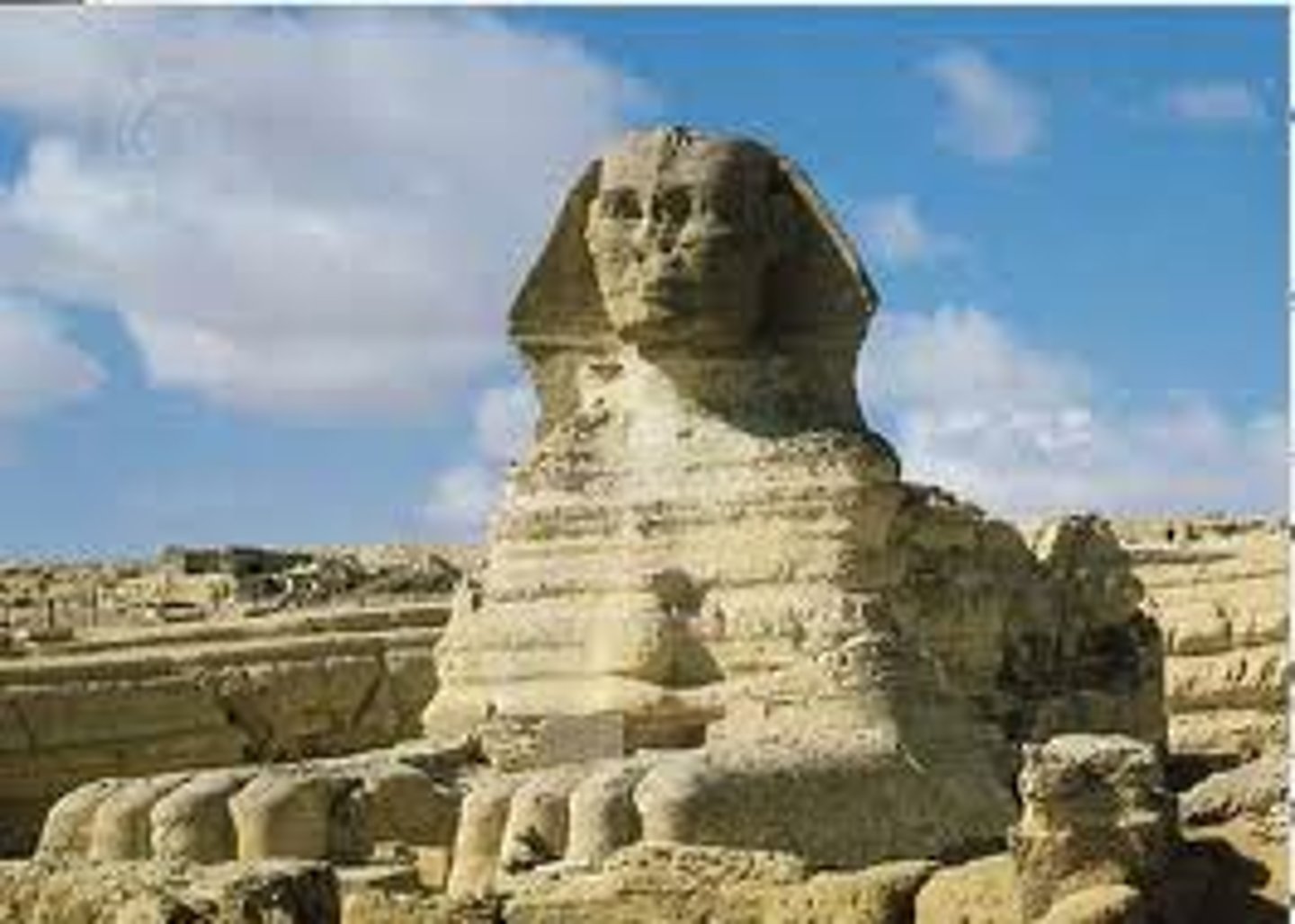
Sphinx
Gizeh, Egypt. Predynastic period, 3500-3000 BC. Used to be colored. Found in the Great pyramid complex. Person head and lion body, hence composite human-animal. Human intelligence with animal strength fit for a king.

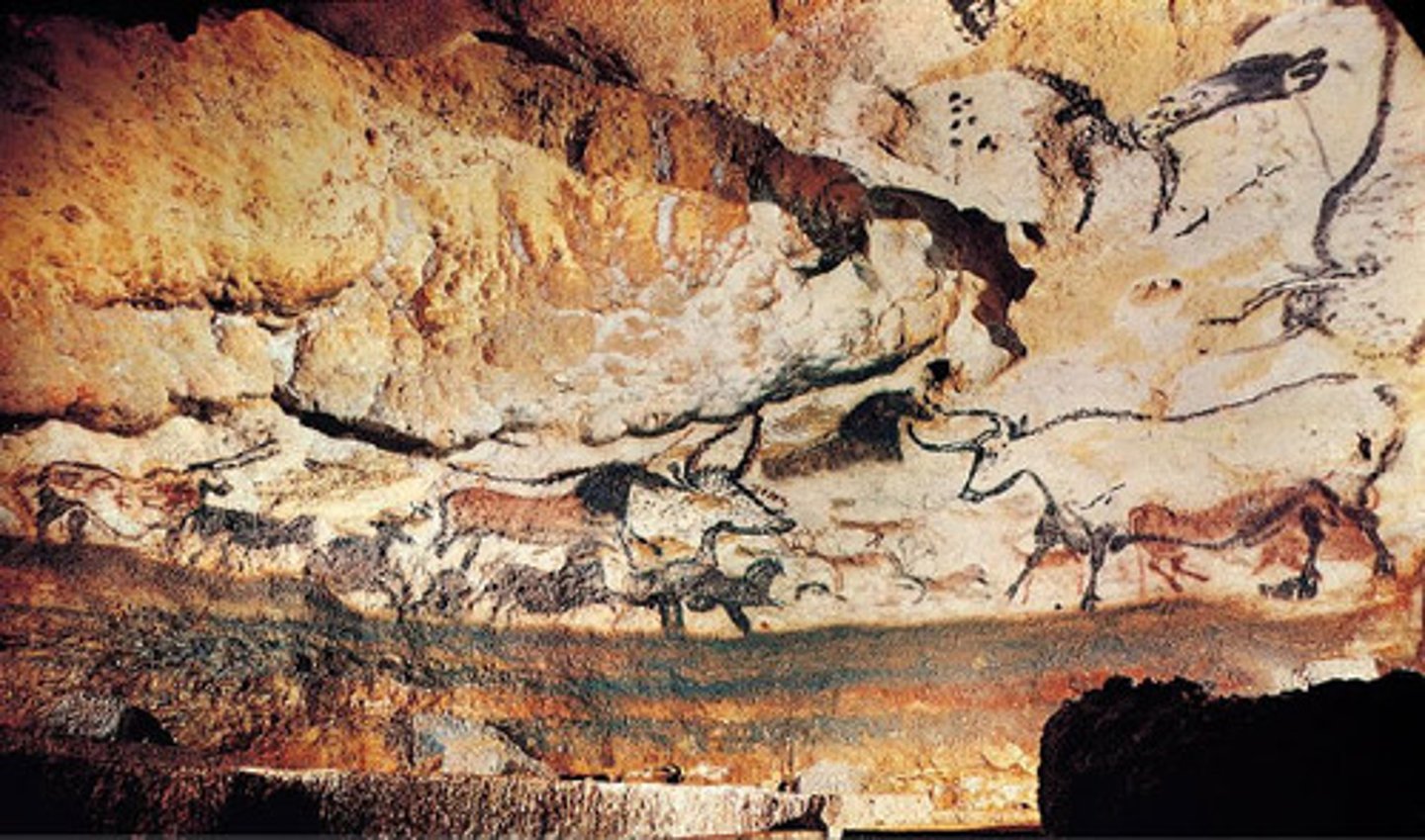
Hall of The Bulls
Lascaux, France. Some of the most studied caves with layers of cave paintings of animals.

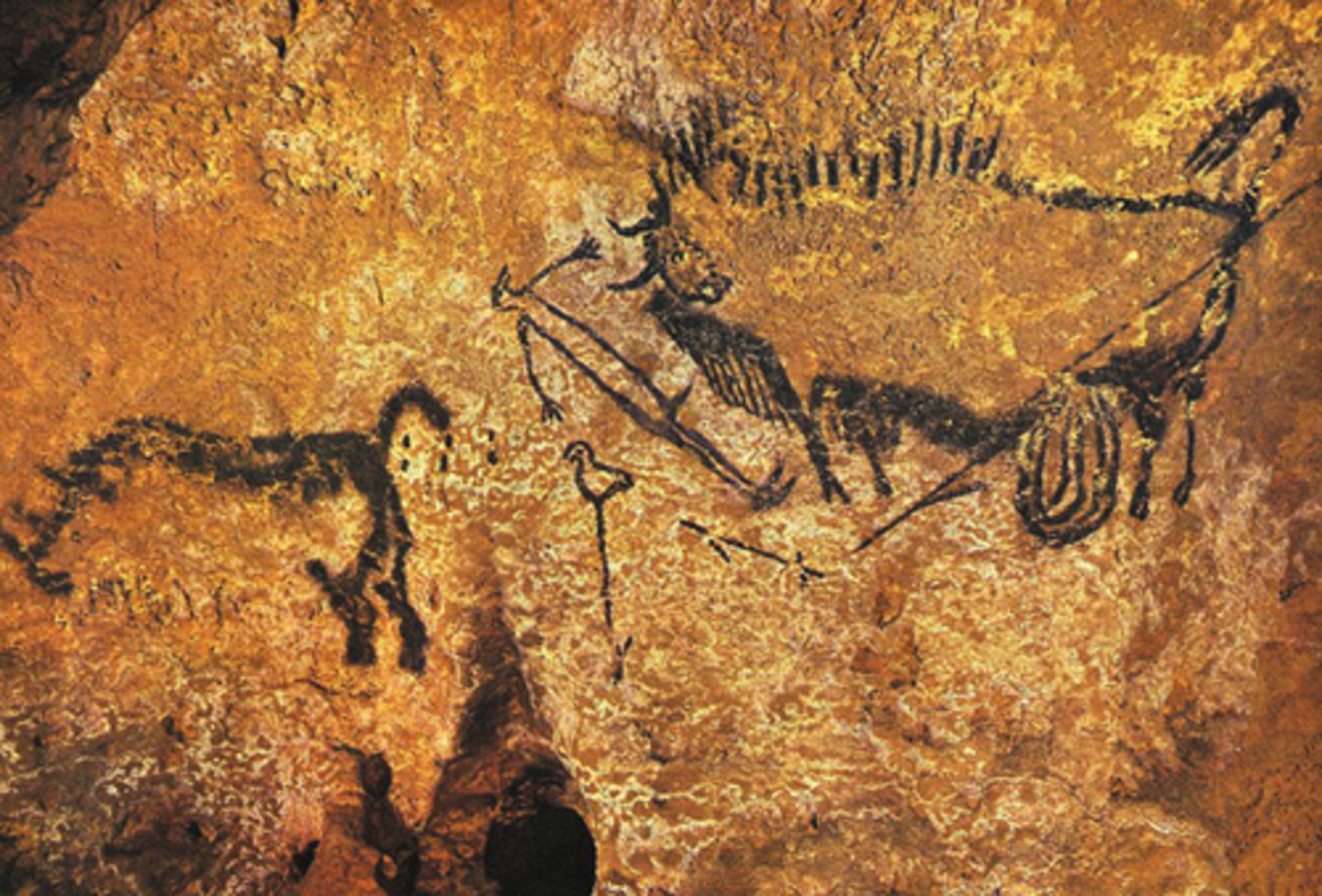
Rhino, bison, and wounded man
Lascaux, France. Paleolithic. Usually only animals, but man shown, perhaps with bird mask. Disemboweled bison. Perhaps early signs of narrative art, perhaps spiritual?

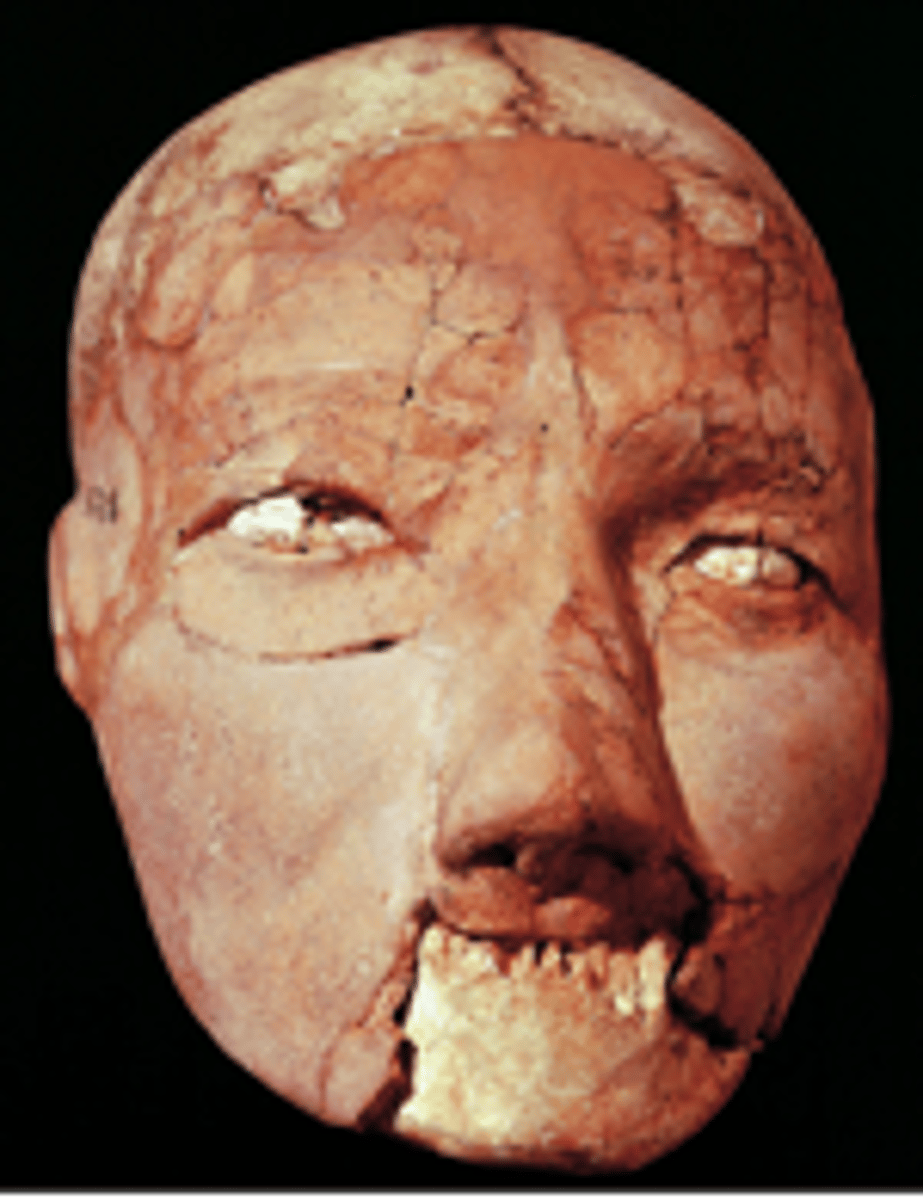
Human skull
Jericho, Israel, Neolithic, 7200-6700 BC. Filled with plaster with shells for eyes. Kept in yard or home. Potential ancestor worship.
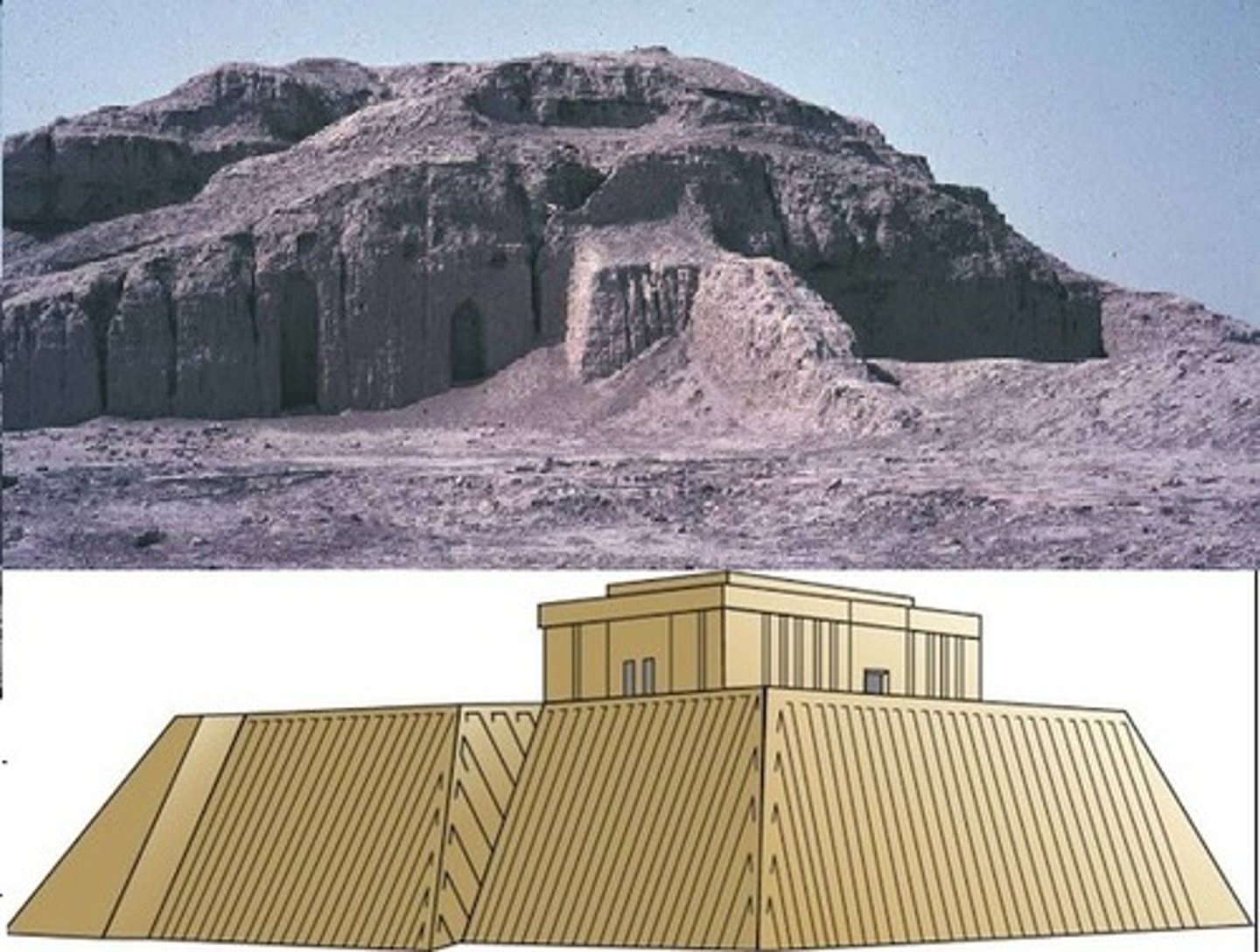
White temple and ziggurat
Iraq, Sumerian, 3500-2300 BC. Made out of mud brick, hence not much remains. Elevated platform, dedicated to Anu, the sky god. Bent axis approach.
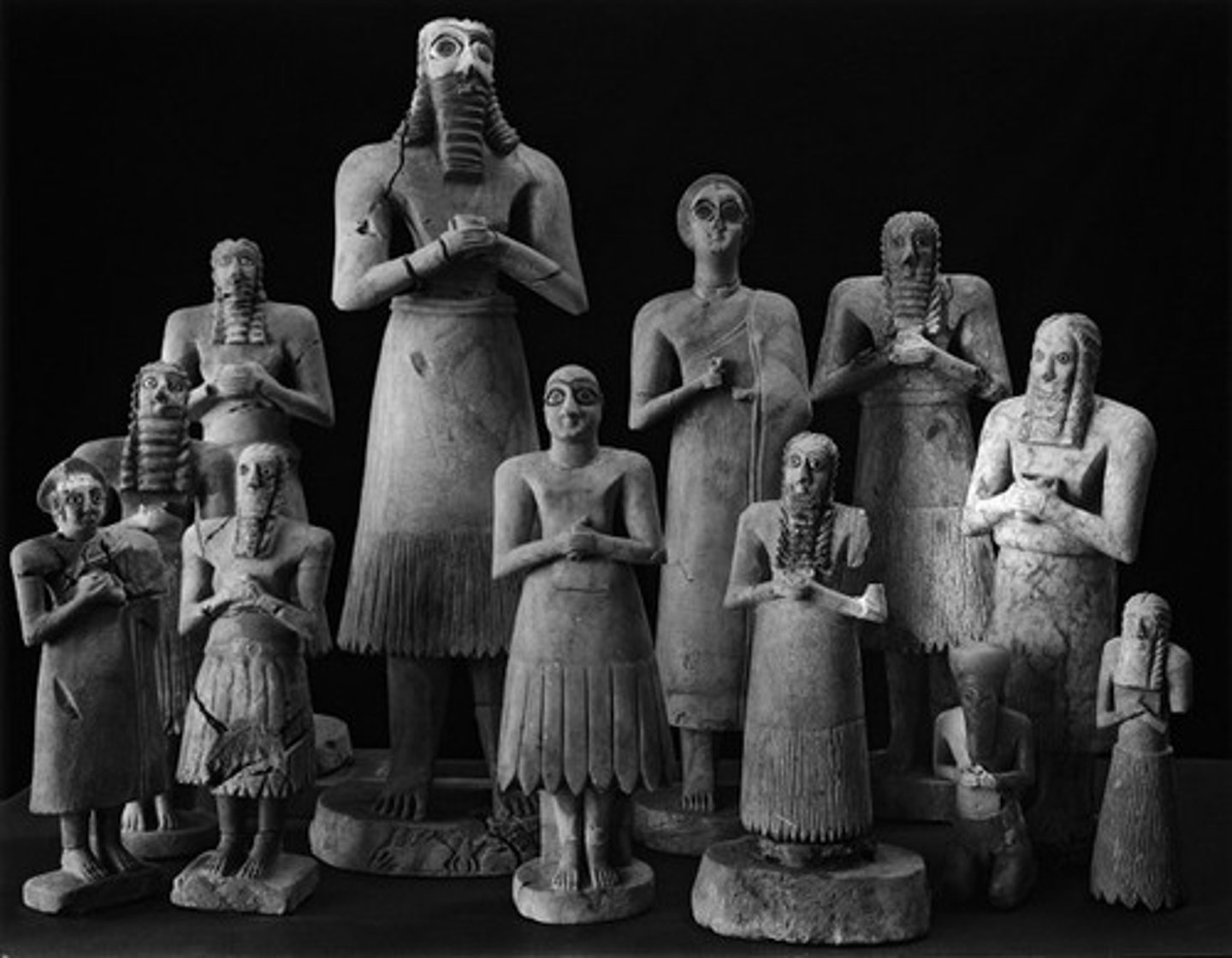
Statuettes of worshippers
Iraq, Sumerian, 3500-2300 BC. Placed around altar in temple of Abu. Always praying to the gods, hence wide open eyes. Varying sizes could reflect wealth.

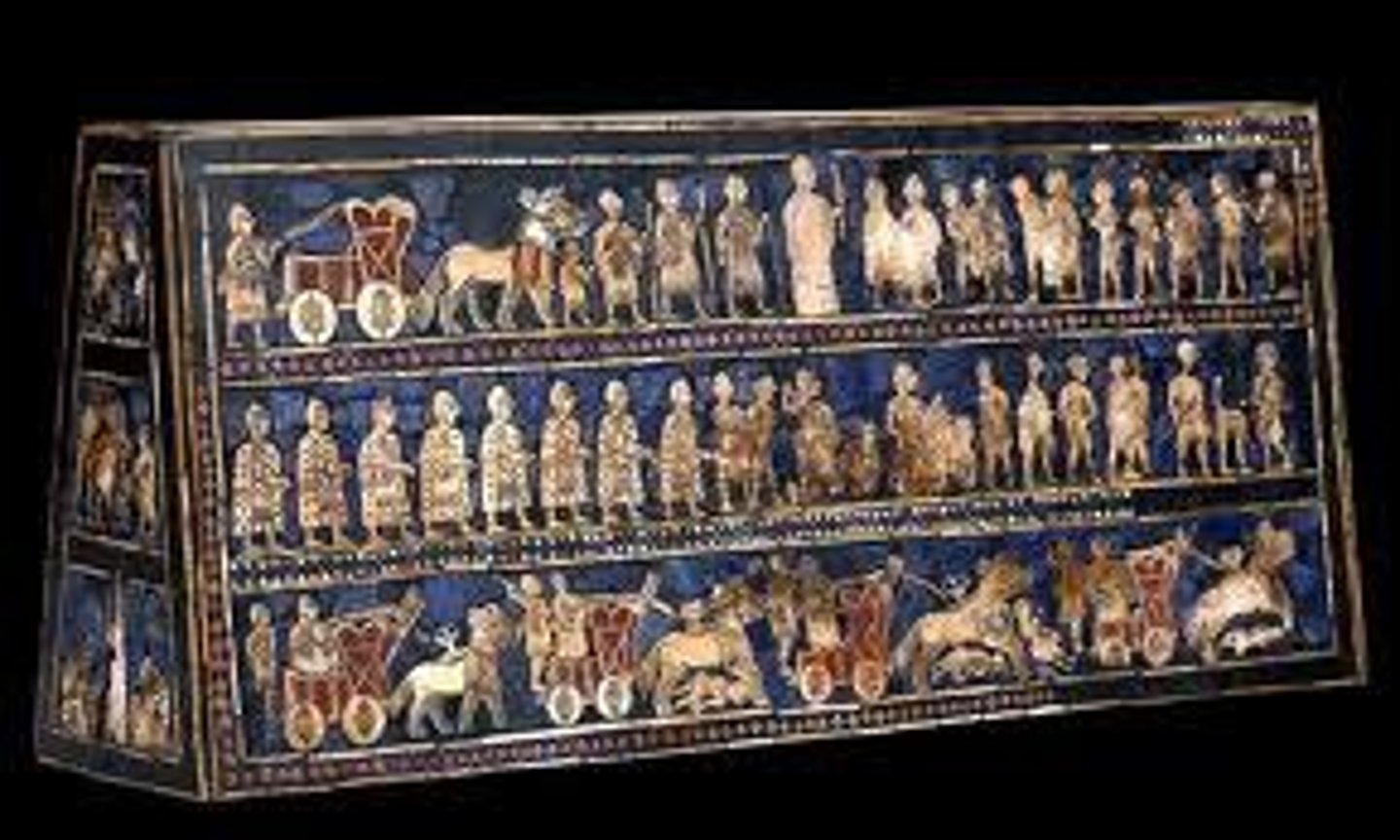
Standard of Ur
Iraq, Sumerian, 3500-2300 BC. Scenes of war and peace. Three registers. Twisted perspective. Mosaic image. Lapis lazuli. Found in "Royal Cemetery".

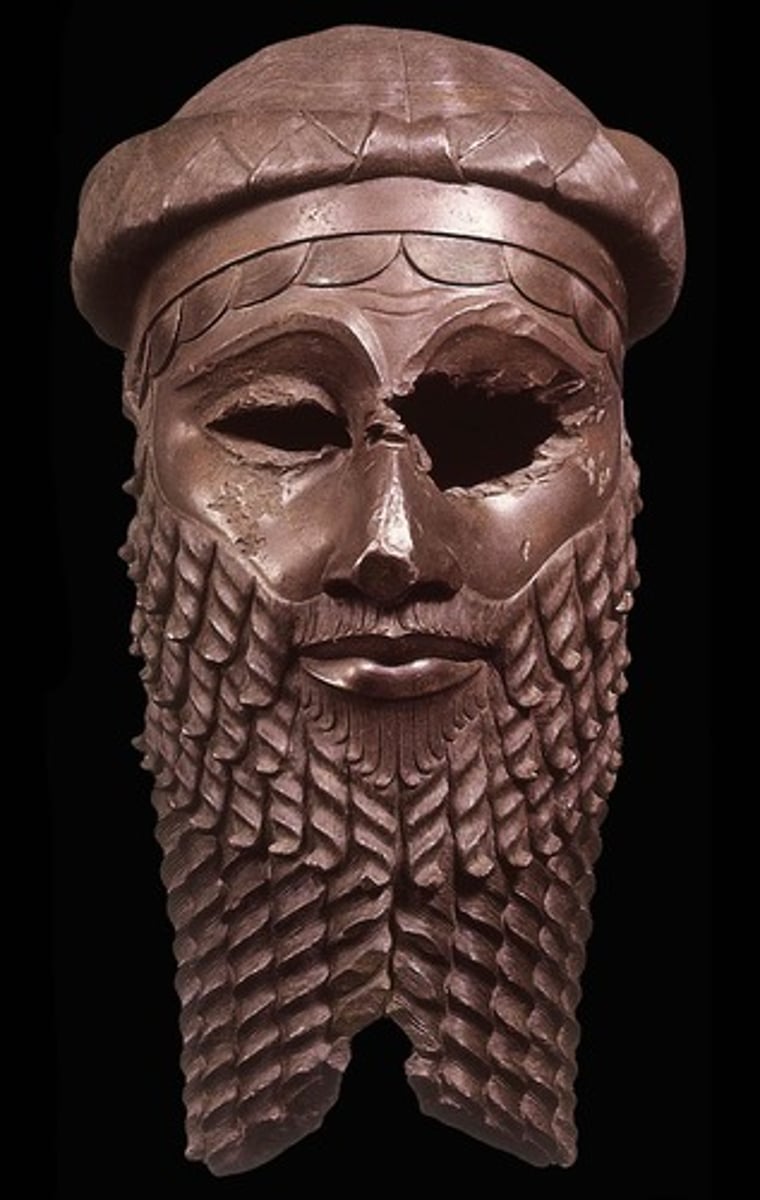
Head of Akkadian ruler
Ninevah, Iraq, Akkadian, 2300-2150 BC. Made of copper. Beard represents high status. Damage from enemies. Could be Sargon.

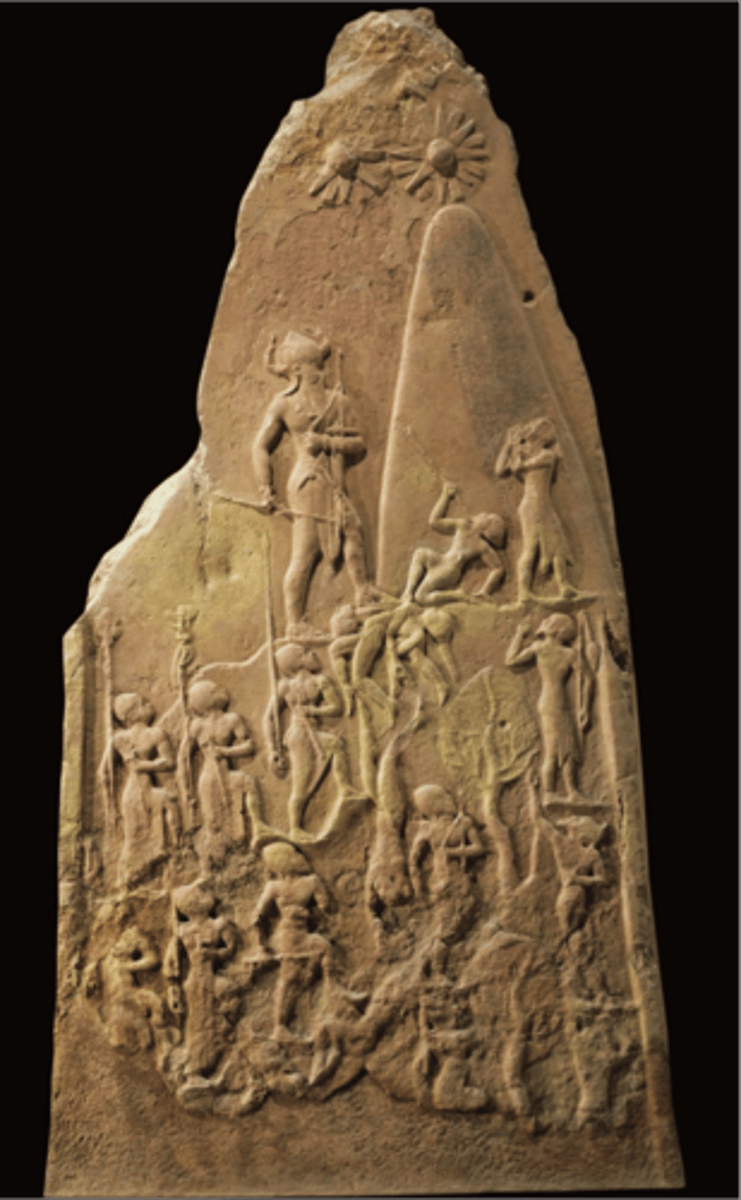
Victory Stele of Naram-Sin
Iran, Akkadian, 2300-2150 BC. Sloping registers, king climbing a mountain conquering enemies. Shows Akkadian power and military might. Stars at the top represent divinity.

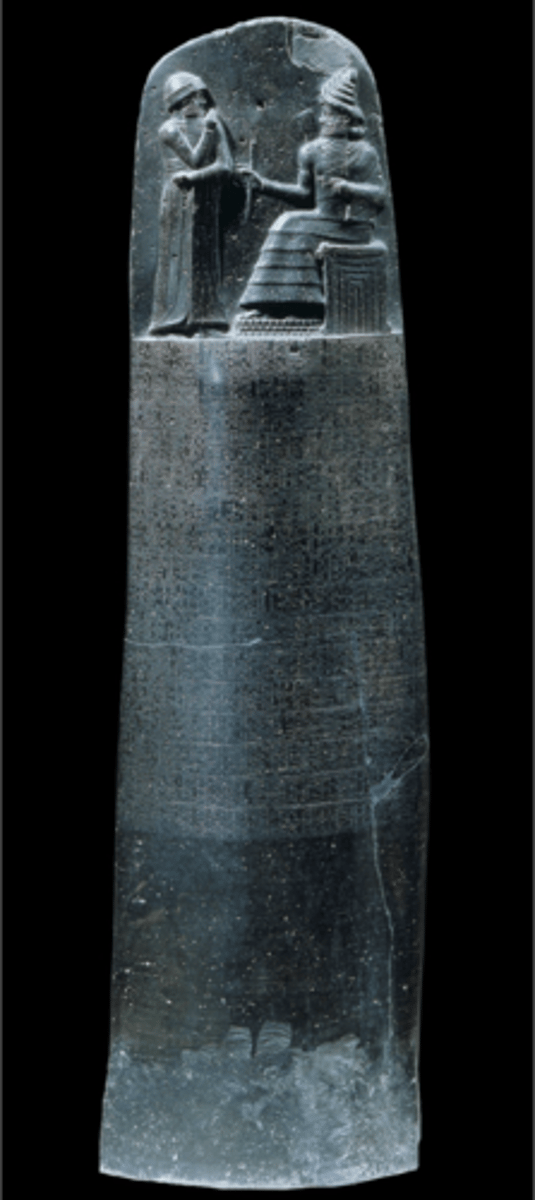
Stele with laws of Hammurabi
Iran, Old Babylonian, 1780 BC. Shamash (sun and justice god of Mesopotamia) sitting on temple, stone upright with written elements. Law codes governing all aspects of life. Hammurabi raising hand in respect as sun god hands builder's tools to him, signifying his capacity to build social order.

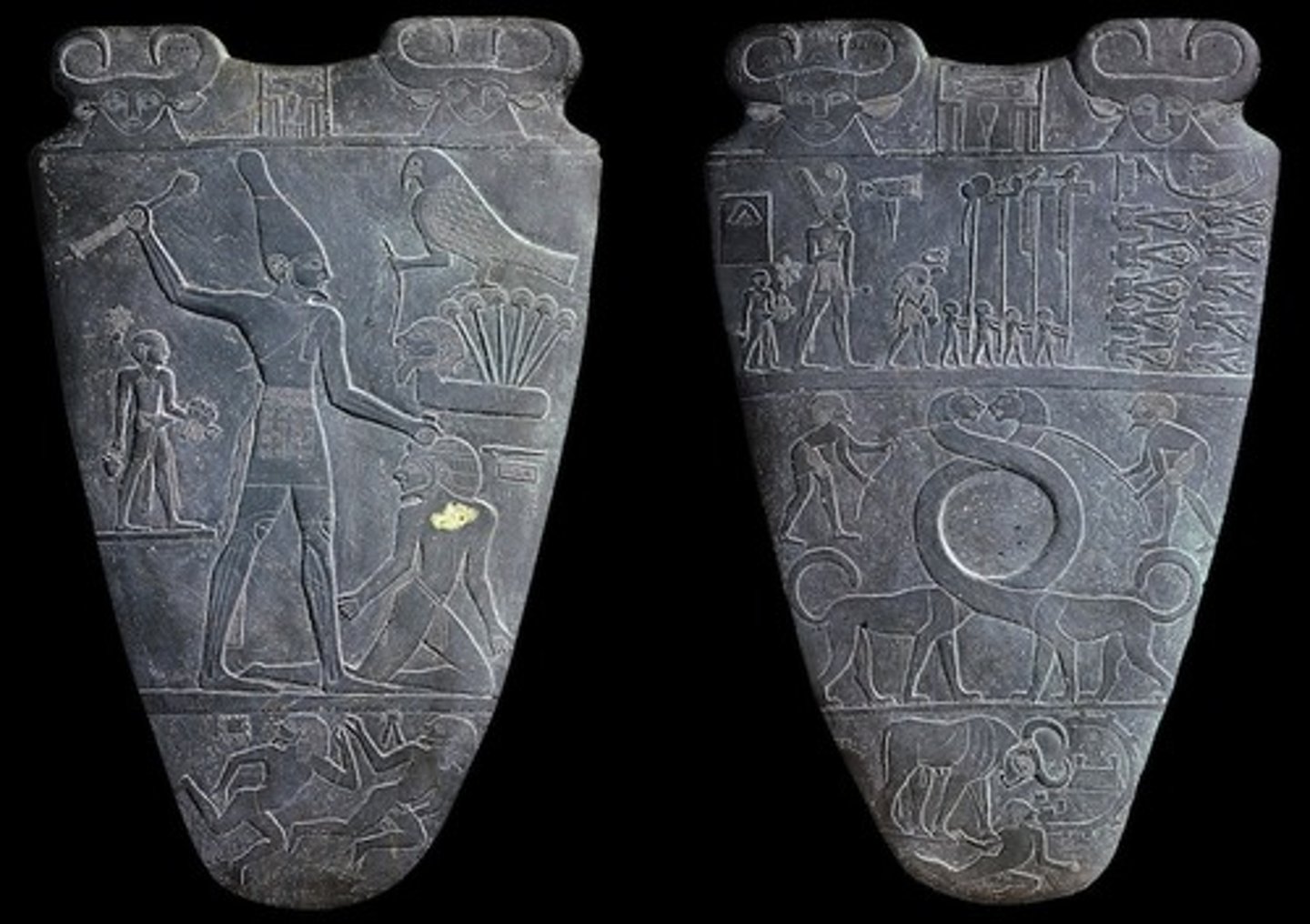
Palette of King Narmer
Predynastic Egypt, 3500-3000 BC. Possible represents unification under Narmer. King in smiting pose. Hathor (fertility god) and Horus (falcon god and god of upper Egypt) shown. Malachite crushed in palette used as medicine? Cartouche emblem, organized in registers.

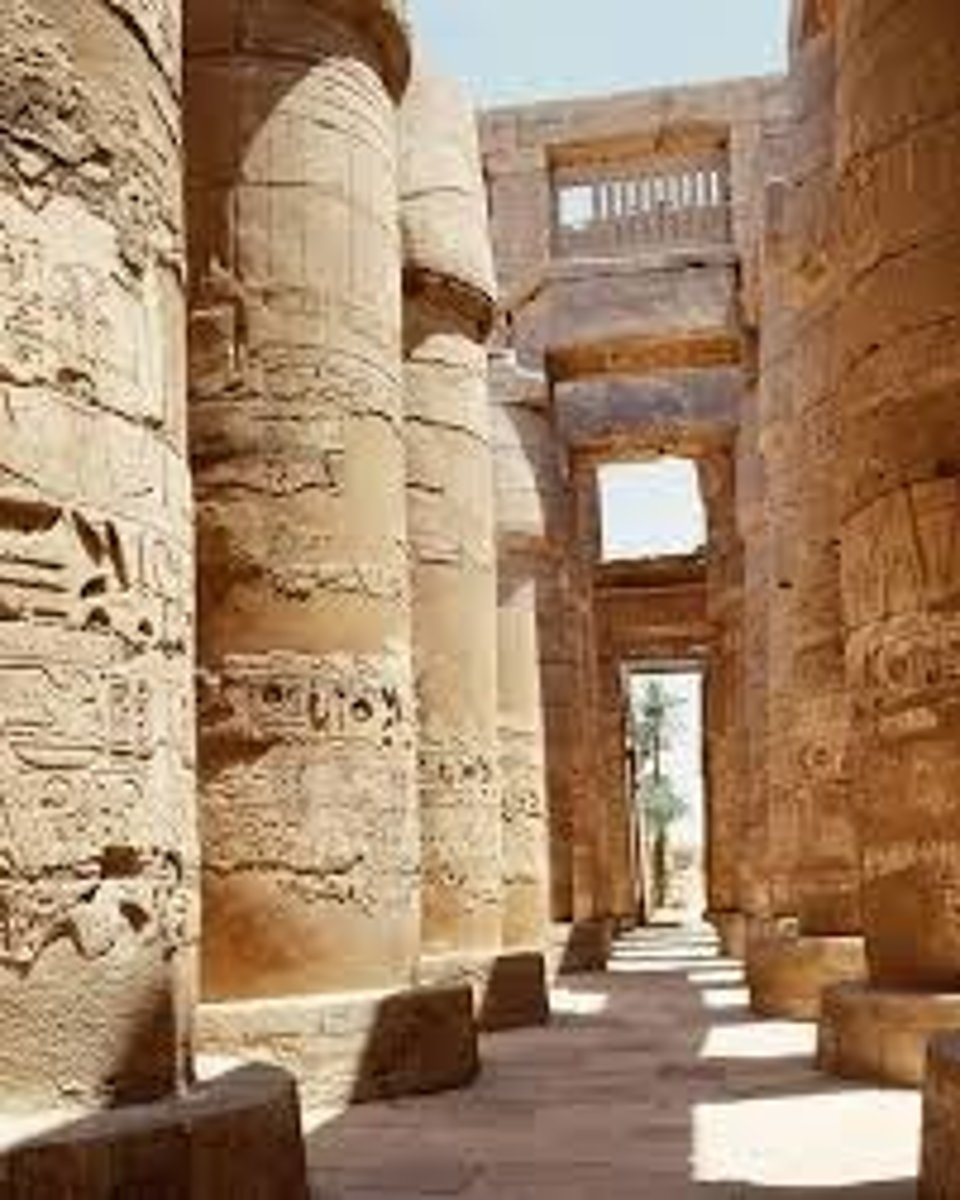
Temple of Amen-Re
Karnak, Egypt, New Kingdom 1550-1070. Hypostyle Hall of columns. Built entirely of stone. Inclusion of windows. Dedicated to Amen-Re, the sun god. Axial entrance. Pylon (thick wall at entrance).
