Biology Edexcel Topic 3 (Inheritance)
1/30
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a chromosome?
A long coiled molecule of DNA that carries genetic information in the form of genes
What is a gene?
A length of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids which forms a protein
What is a genotype?
An organism's genetic composition (describes all alleles)
What is a phenotype?
An organism's observable characteristics due to interactions of the genotype and the environment
Define homozygous
Having two identical alleles of a gene - FF or ff
Define heterozygous
Having two different alleles of a gene - Ff
What is a dominant allele?
An allele that is always expressed in the phenotype - represented with a capital letter (e.g. F)
What is a recessive allele?
An allele that is only expressed in the phenotype in the absence of a dominant allele - represented with a small letter (e.g. f)
What is monohybrid inheritance?
The inheritance of a single gene
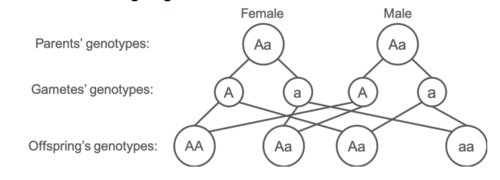
Imagine if parents who are both heterozygous for sickle cell anaemia (Aa) have a child. Draw a genetic diagram to illustrate this single gene inheritance
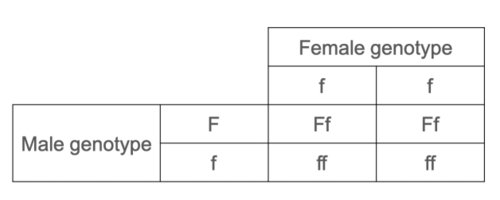
A female who is homozygous recessive for cystic fibrosis (ff) has a child with a heterozygous male (Ff). Draw a Punnett square to illustrate this single gene inheritance
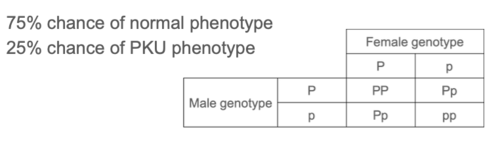
PKU is a recessive condition. Two heterozygous parents (Pp) have offspring. Predict the proportion of offspring that will have PKU
What is the problem with single gene crosses?
Most characteristics are controlled by multiple alleles rather than just one
What are sex chromosomes?
A pair of chromosomes that determine sex
What sex chromosomes do males have?
An X and a Y chromosome
What sex chromosome do females have?
Two X chromosomes
Why does the inheritance of a Y chromosome mean that an embryo develops into a male?
Testes development in an embryo is stimulated by a gene present on the Y chromosome
A couple have a child. Using a Punnett square, determine the probability of having offspring that is female
Other than using a Punnett square, how else can monohybrid inheritance be represented?
Using a family pedigree
What is a sex-linked characteristic?
A characteristic that is coded for by an allele found on a sex chromosome
Why are the majority of genes found on the X chromosome rather than the Y chromosome?
The X chromosomes is bigger than the Y chromosome so more genes are carried on it
Why are men more likely to show the phenotype for a recessive sex-linked trait than women?
Many genes are found on the X chromosome that have no counterpart on the Y chromosome - women have two alleles for each sex-linked gene whereas men often only have one allele so only one recessive allele is required to produce the recessive phenotype in males whereas females need two recessive alleles
Haemophilia is a recessive X-Iinked condition. A carrier female and a normal male have a son. What is the probability of the child having haemophilia?
Give an example of a characteristic that is determined by more than one allele
Blood group determined by 3 alleles: I^A, I^B, I^O
Name the four different blood groups
A, B, AB, O
What are codominant alleles?
Alleles that equally contribute to an organism's phenotype. They are expressed to an equal extent
Describe codominance in blood groups
I^A and I^B are codominant - I^A I^B gives the blood group AB
Why does I^A I^O only give blood group A?
I^O is recessive to I^A - I^A is dominant and is expressed in the phenotype giving blood group A
What are the possible genotypes for blood group B?
I^B I^O and I^B I^B
What is the genotype for blood group O?
I^O I^O
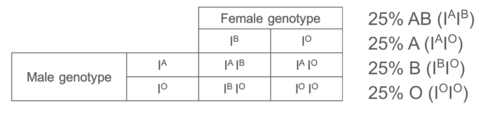
A female with genotype I^B I^O and a male with genotype I^A I^O have a child. Use a Punnett square to predict the potential phenotypes of the offspring