The Nervous System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Last updated 9:04 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
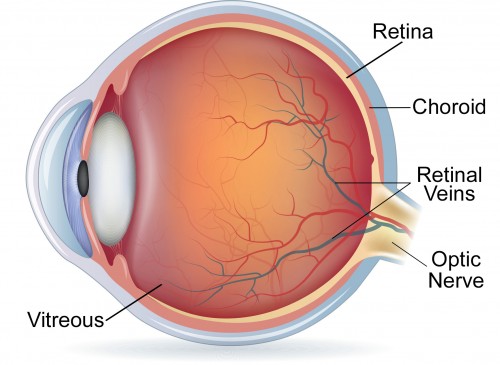
Retina
Contains light receptors and processes image being captured
2
New cards
Cornea
Made of connective tissue; protects eye
3
New cards
Vitreous Humor
Begins to focus image; bends light
4
New cards
Optic Nerve
Sends images between the eyes and the brain
5
New cards
Sclera
Helps maintain eye's shape
6
New cards
Choroid
Provides retina with blood suply
7
New cards
Pupil
Allows light into and out of the eye
8
New cards
Lens
Bends and focuses light on retina
9
New cards
Iris
Muscle that opens and closes pupil to regulate light
10
New cards
Blind Spot
No rods or cones so no image can be focused
11
New cards
Ciliary Body
A part of the middle layer of the wall of the eye. Found behind the iris and includes the ring-shaped muscle that changes the shape of the lens when the eye focuses.
12
New cards
Anterior Chamber
Focuses the rays of light that penetrate the eye on the retina.
13
New cards
Posterior Chamber
Structure involved in production and circulation of aqueous humor
14
New cards
Vitreous Chmaber
Contains a thick, gel-like fluid called _______ humor or _____ gel. These two fluids press against the inside of the eyeball and help the eyeball keep its shape.
15
New cards
Optic Disk
The start of the optic nerve where messages from cone and rod cells leave the eye via nerve fibres to the optic centre of the brain.
16
New cards
Aqueous Humor
Carries nutrient from blood to eye and nourishes the lens and maintains pressure within the eye.
17
New cards
Nervous Cell structure and function
Responsive for sending electrochemical messages
18
New cards
Nervous Cells found in
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
19
New cards
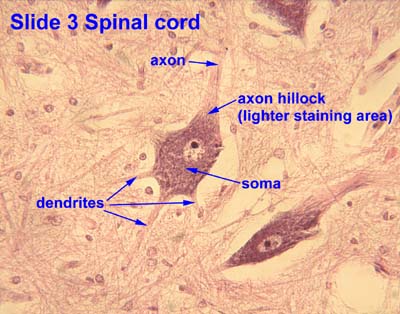
Cell processes
Branches (Axon and Dendrites)
20
New cards
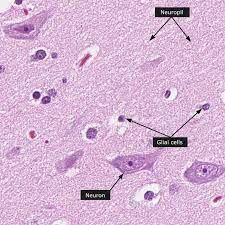
Glial cells
cells surrounding and supporting the neuron
21
New cards
Arbor vitae
It brings sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum.
22
New cards
Cerebellum
helps coordinate and regulate a wide range of functions and processes in both your brain and body.
23
New cards
Cortex
involved in higher processes in the human brain, including memory, thinking, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, consciousness and functions related to your senses.
24
New cards
Corpus Callosum
ensures both sides of the brain can communicate and send signals to each other.
25
New cards
Frontal Lobe
voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions.
26
New cards
Hypothalamus
keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis
27
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
helps control vital processes like your heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure.
28
New cards
Midbrain
vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation (auditory and visual information)
29
New cards
Occipital Lobe
responsible for visual perception, including colour, form and motion
30
New cards
Olfactory tract/nerve
enables your olfactory system and sense of smell
31
New cards
Optic Chiasm
allow for the crossing of fibers from the nasal retina to the optic tract on the other side
32
New cards
Parietal Lobe
vital for sensory perception and integration, including the management of taste, hearing, sight, touch, and smell.
33
New cards
Petuitary gland
regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the hormones that it produces.
34
New cards
Pons
handles unconscious processes and jobs, such as your sleep-wake cycle and breathing
35
New cards
Pons
send motor commands from the brain to the body, send sensory information from the body to the brain, and coordinate reflexes.
36
New cards
Temporal Lobe
processing auditory information and with the encoding of memory
37
New cards
Thalamus
your body's information relay station
38
New cards
Cerebrum
initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature.
39
New cards
Brainstem
responsible for regulating most of the body's automatic functions that are essential for life.