Regulation of phosphorus balance
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
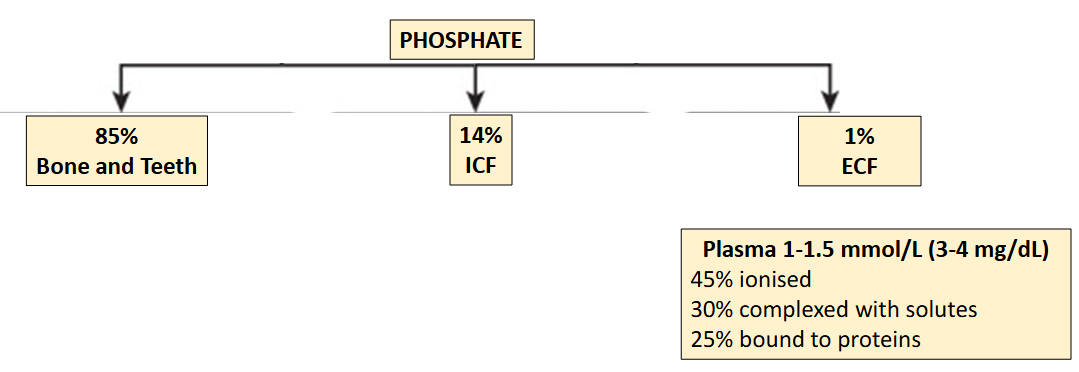
Where is phosphorous found in the body?
Phosphate homeostasis
Plasma phosphate is determined by
(1) intestinal absorption
(2) storage in bone
(3) excretion by the kidneys
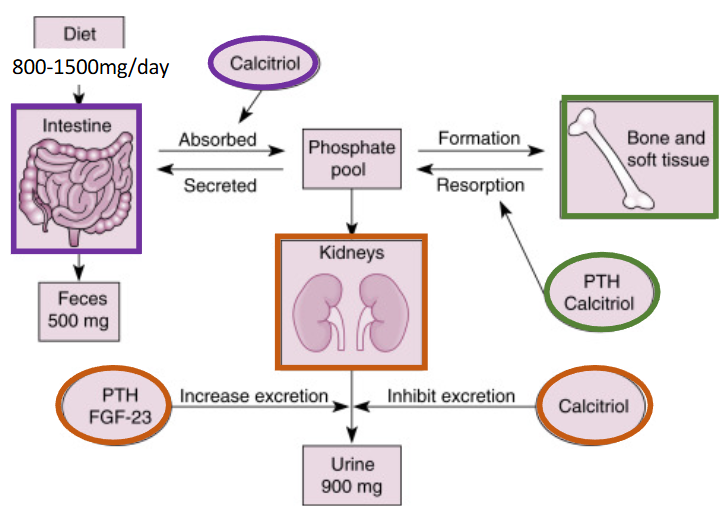
Where is phosphate reabsorbed?
primarily by the proximal tubule
What stimulates PTH secretion and what does it do?
Hypocalcaemia
stimulates bone resorption
increases urinary Pi excretion
decreases urinary Ca ++ excretion
stimulates production of calcitriol
** Increases plasma [Ca ++ ] while having little effect on the plasma [Pi ]
What stimulates calcitriol secretion and what does it do?
Hypocalcaemia (via PTH) and hypophosphatemia
stimulates Ca ++ and Pi absorption by the intestine
acts with PTH to release Ca ++ and Pi from the bone
decreases Ca ++ excretion by the kidneys
** Increase the plasma [Ca ++ ] and [Pi ]
What increases PCT reabsorption?
Metabolic alkalosis and phosphate depletion
What decreases PCT reabsorption?
PTH, FGF-23, metabolic acidosis, phosphate loading
Main cause of Hypophosphatemia
reduced renal phosphate excretion
eg. acute renal failure
