AQA GCSE Business Unit 6 - Finance (WIP)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Reasons for needing finance
start up capital
to cover outflows
to expand
Short Term Sources of Finance
Government grants - strict critera but dont need to be repaid
Trade Credit - not paying immediately for purchased resources, with a large fee if not paid in time
Overdrafts - allow the firm to go into the negatives in their bank account. Higher interest rates than loans
Long Term Sources Of Finance
Loans
Bank loans easy to take out but repaid with interest over a set period of time
Mortgages - loans used to finance purchasing property, with the property being used as collateral if the firm were to default on their payments
Hire purchases - when a firm purchases something buy paying a deposit then paying the rest in instalments
Sources of Finance for Established Businesses
Retained Profits - profits that the owners have put into the business after theyve paid themselves a dividend
Fixed assets - the selling of asstes thay a business has kept long term, such as machinery
Share Issue - a Public limited company can issue and sell shares, shares are parts of the business which means selling shares reduces control of the business
Investments
an investment is something a business outs money into in order to make profit
some examples of investments are
new machinery
new buildings
new vehicles
spending money is risky because if there isnt a ROI (Return On Investment) the business may lose lots of money
Average Rate of Return
Average annual Profit
ARR(%)= —————————— X100
Initial Investment
Break even Analysis
Breaking even is when your total revenue = your total costs
When total costs are higher than revenue the busmess is making a Loss
when revenue is higher than total costs, a business is making rpofit
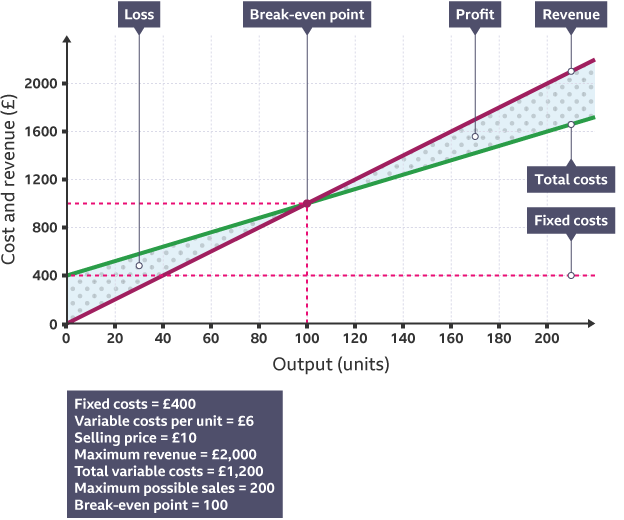
Margin of Safety
The margin of safety is how many less units a business could produce and sell and still break even.
If the break even output for a business was at 1000 Units, and the business was producing 1800 Units, the margin of safety would be 800 Units (1800-1000=800)
Advantages of Break even analysis
easy to work out
allows business to predict how changes in output may affect revenue costs and profit
can be used in cohesion with a business plan to get a loan
Disadvantages of Break even analysis
break even analysis assumes all products sre sold and there are no returns
can be complicated with more than one product
doesnt predict how much a business WILL sell
Cash Flow Forecasts
a cashflow forecast is a way of predicting when a firm my face a liquidity problem
the firm will see when or if they are scheduled to go into the red
the forecast needs to be monitored to see the impact of unexpected cash flows
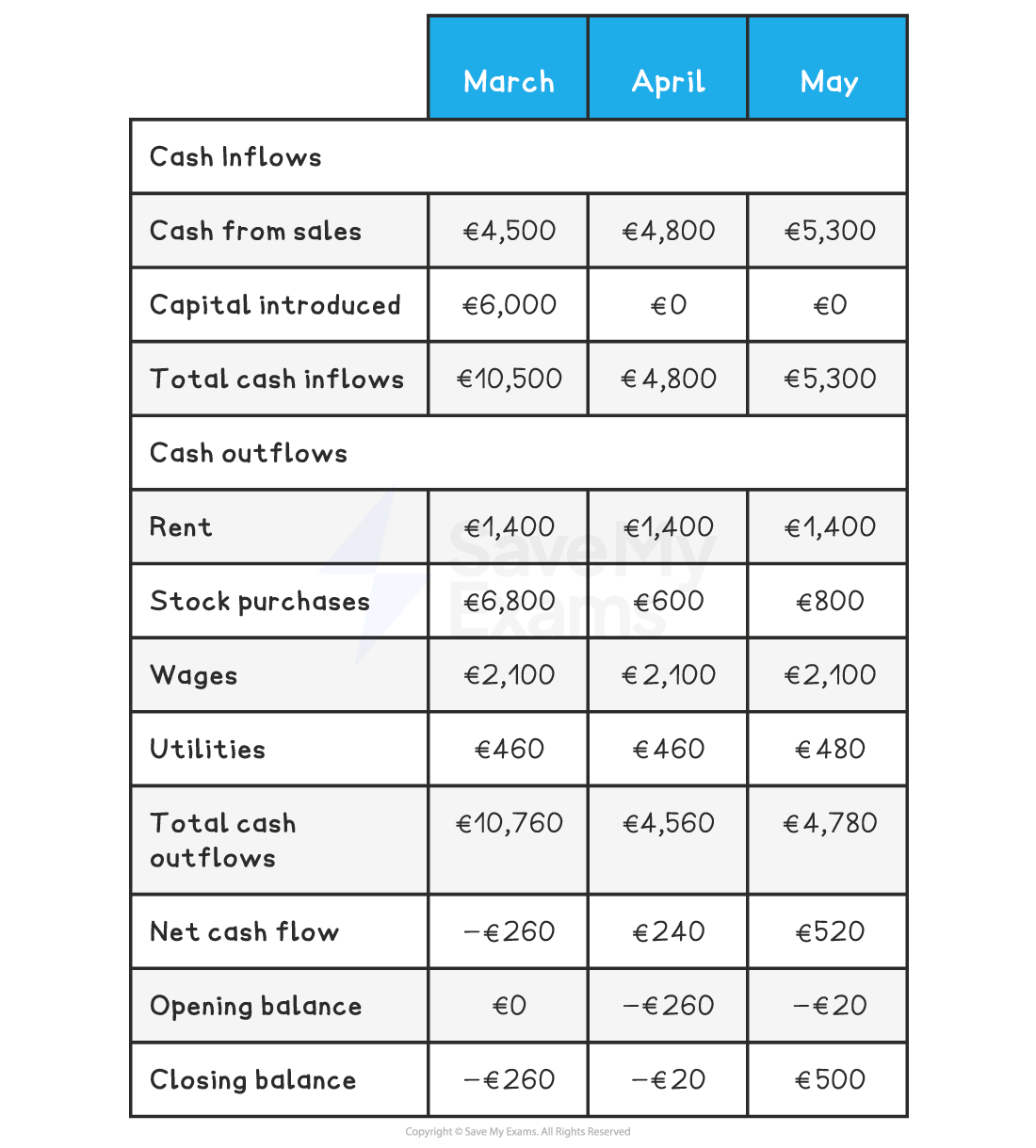
Cash Flow - Credit
credit terms tell you how long after a purchase a customer has to pay
if a business gives two months credit, customers must pay within two months of purchase
this changes cash flow diagrams as even though the sals may be registered in a certain month the inflows are only marked at the end of the credit term
Poor Cash Flow
Having poor cash flow is one of the major problems that can kill a business
The main reasons for poor cashflow are
Poor sales - lack of demand from consumers
Overtrading - taking on too many orders and not being able to fulfill them
Poor business descisions - e.g. expanding into a new market which doesnt give the revenue forcasted
Improving Cash Flow
Rescheduling payments
giving customers less time to pay
Reducing cash outflow
laying off worker or selling their retained surplus of products
arranging an overdraft
finding new sources of finance
increasing inflows e.g. increasing selling price
Income Statements
an income statement is a financial statement showing how income has changed over time
There are three parts to an Income statement
Trading account
Profit and Loss account
Appropriation account
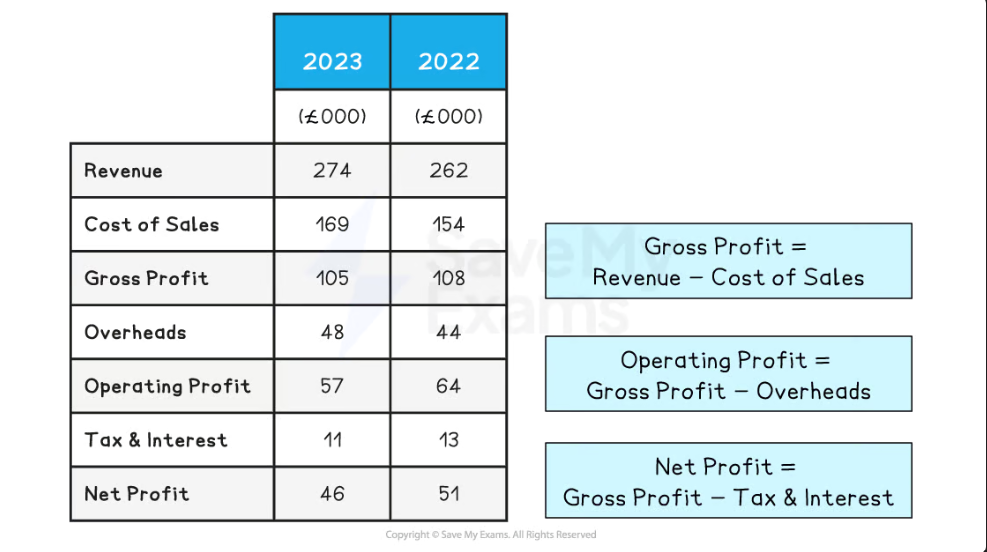
Parts of an Income Statement
The trading account shows the gross profit/loss, the revenue and the cost of sales
the Profit and Loss Account shows the indirect costs of running a business, such as wages or rent. it also coveres depreciation, which is how much the value of an asset decreases
The appropriation account is unique to Limited companies and records where the profit has gone e.g. to the government, to shareholders or being kept as retained profit
Profit Margins
Gross profit margin is the fraction of every pound spent by customers that doesnt go directly towards making a product and it ignores indirect costs
Gross Profit Margin + gross profit / sales revenue * 100