Overview of Injections for Optometry (Part II)
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Landgraf's FOSD II UMSL School of Optometry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Intradermal
What type of injection used to be done more frequently and is similar to intralesional?
Intralesional
Local infiltrative
Subconjunctival
What are the 3 perioribital types of injections?
Intralesional
What type of injection is performed on chalazions?
intradermal
Out of the following injections (IM, IV, SC, Intradermal), which one is performed most tangential to the skin?
IM
Out of the following injections (IM, IV, SC, Intradermal), which one is performed at 90 degrees from the skin?
Anaphylaxis to IV NaFl
Pre- or post-IVFA for nausea & vomiting
Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
What are 3 ophthalmic indications for an IM injection?
IM Benadryl
IM Epinephrine
What 2 medications can be given for anaphylaxis to IV NaFl? Include type of injection before.
IM Promethazine 25 or 50 mg/mL
What medication can be given for pre- & post-IVFA for nausea and vomiting? Include type of injection before the medication as well as dosage.
IM Promethazine
IV Mannitol
What 2 medications can be given for acute angle closure glaucoma? Include type of injection before the medication.
True
True/False: Epinephrine can be administered intramuscularly through the clothes if necessary.
2-5 cc
What range of syringe volume should be used for epinephrine injection?
20 gauge; 1-2”
What gauge of needle should be used for epinephrine injection? What length?
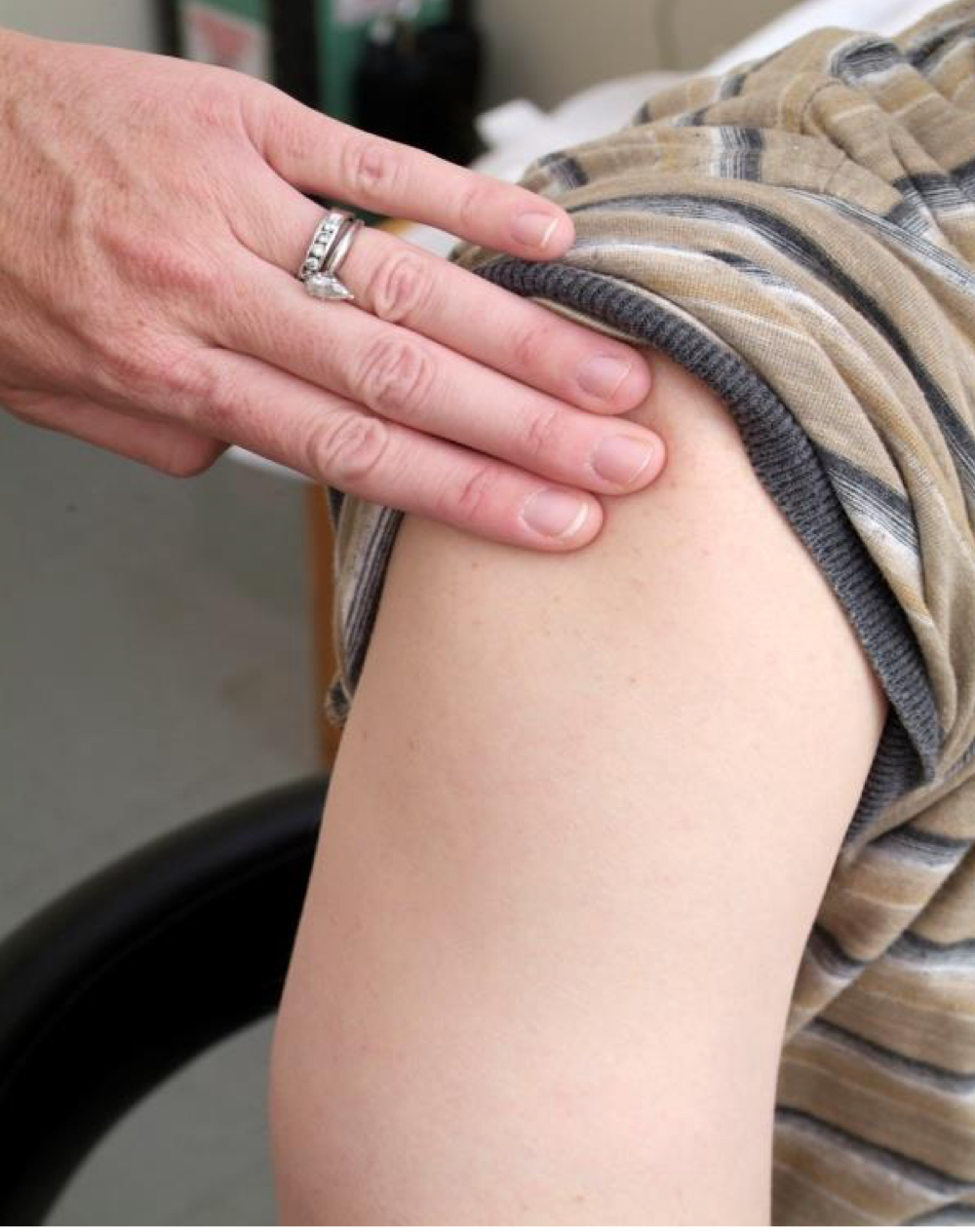
2-3 finger widths below acromion process of the deltoid
What is the primary site in which epinephrine should be administered if injected with IM epinephrine via syringe?
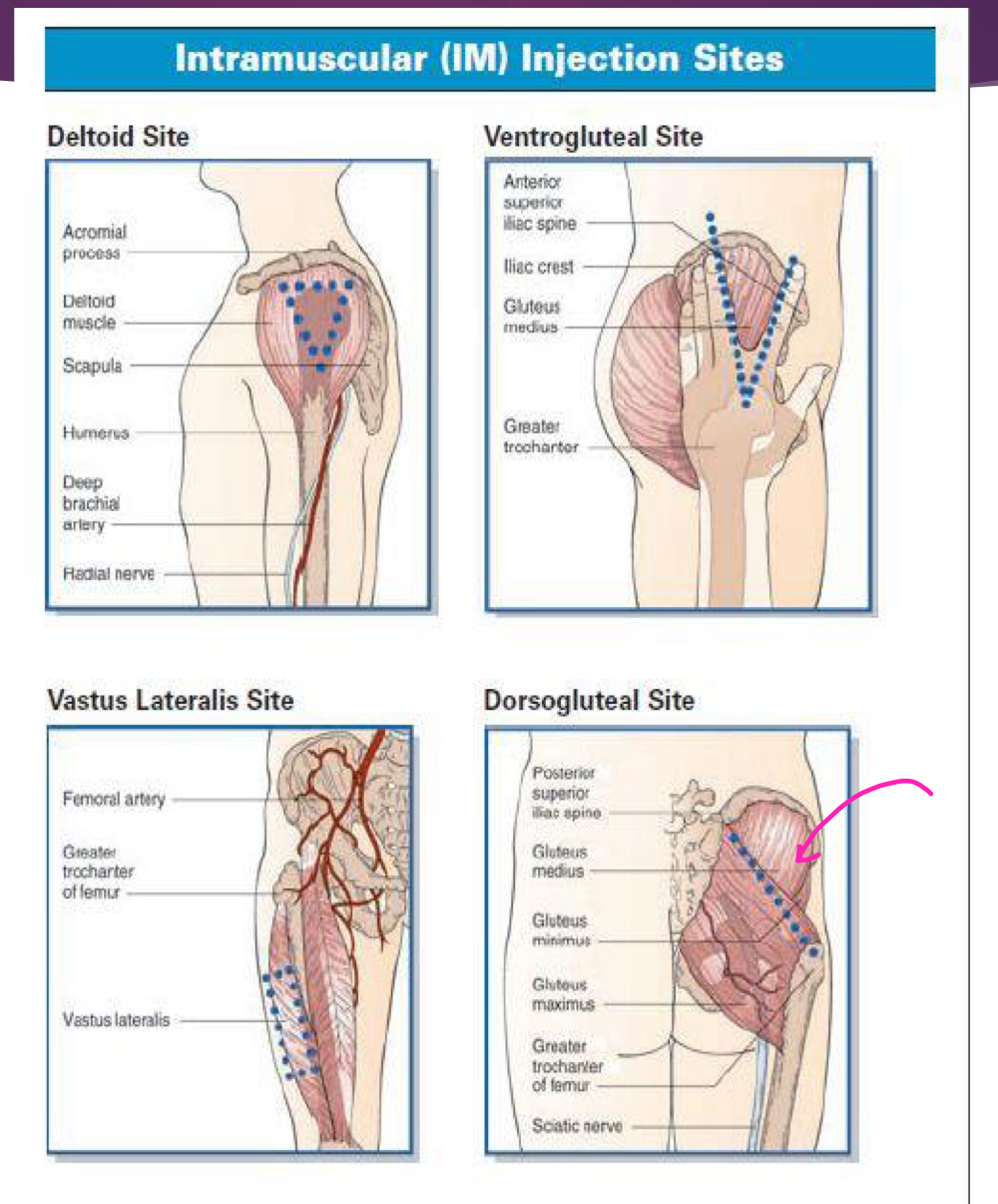
Dorsogluteal
Ventrogluteal
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis
Besides the deltoid muscle, what 4 other muscles are a potential site for epinephrine administration IM via syringe?
Dorsogluteal
What injection site do we need to be wary of sciatica when injecting IM epinephrine?
Stretch & Bunch
What technique should be done for IM epinephrine injection into the deltoid?
45-90 degrees; less painful
At what angle range should you attempt to jab the patient with for an IM epinephrine injection? Why?
False—bury the needle
True/False: For an IM epinephrine injection via syringe, it is important to only jab the needle about halfway to avoid hitting a blood vessel.
True—you don’t want blood
True/False: you should aspirate for blood with an IM injection.
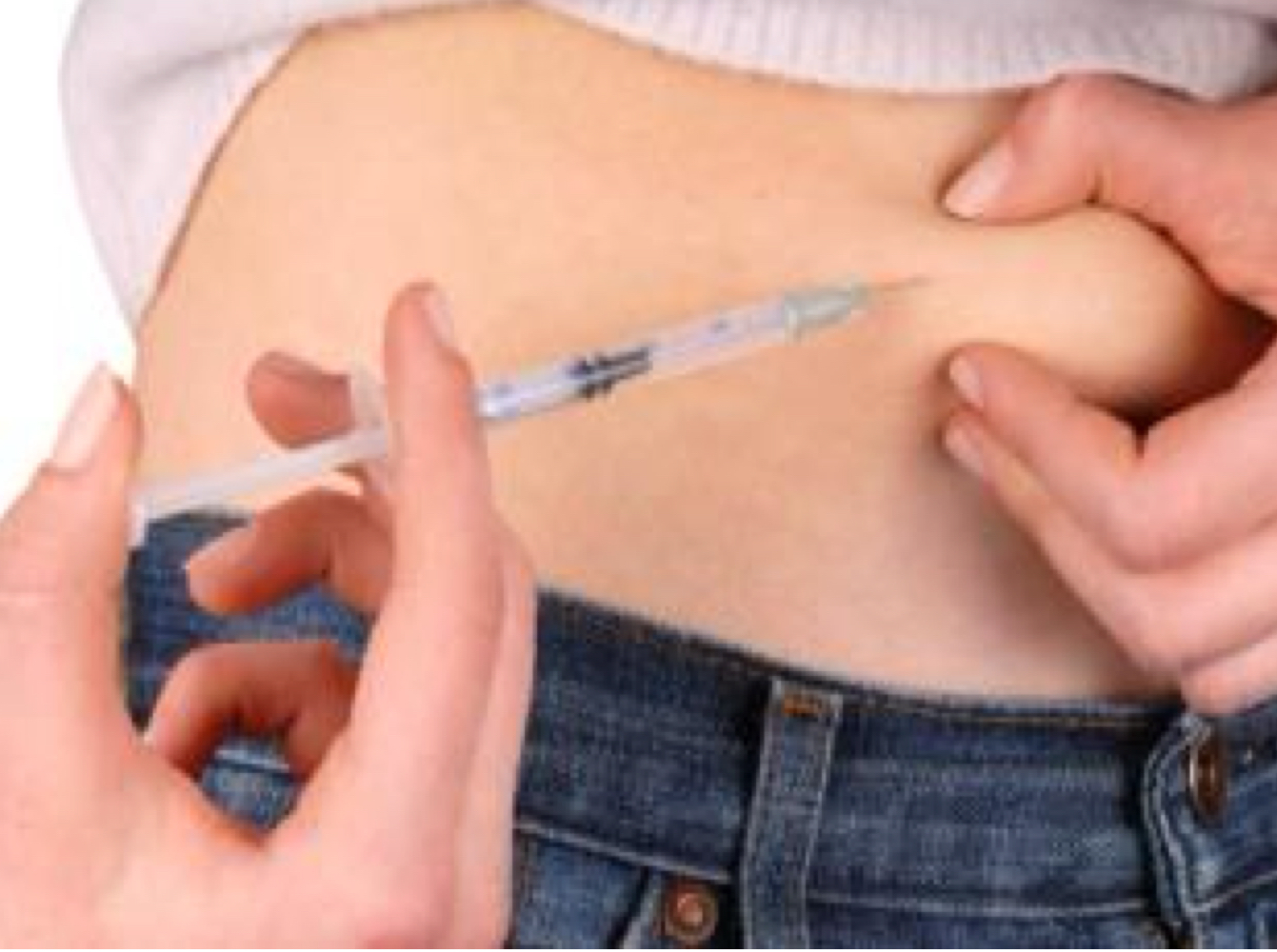
Subcutaneous (SQ)
What type of injection is indicated for slow absorption of numerous medications?
3/8 - 5-8”
What needle lengths are used for Subcutaneous injections?
25-27 g
What needle gauges are used for subcutaneous injections?
< 1 mL
What injection volume is often necessary for SQ injections?
To deliver local anesthesia with Xylocaine prior to various procedures
What is an ophthalmic indication for subcutaneous injections?
Subcutaneous
What type of injection is used to deliver local anesthesia prior to an ophthalmic procedure?
Local infiltrative
Intradermal
What are 2 types of subcutaneous injections?
Local infiltrative
What type of SQ injection is utilized prior to cyst removal or drainage within the eyelid?
Local infiltrative
What type of subcutaneous injection is utilized prior to incision & cutterage of chalazion?
Local infiltrative
What type of SQ injection is utilized prior to eyelid lesion removal or papilloma?
1% Xylocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine
What medication (include dosage) is used for local infiltrative procedures of the eyelid?
Lidocaine
What is the Brand Name of Xylocaine?
4%; 0.5-2%
What concentration of Xylocaine is utilized when used topically? Injectable?
4-6 minutes; 1 hour (2 hours with epinephrine)
How long does it take for injectable Xylocaine to take effect? How long does it take to wear off?
Liver
Where is Xylocaine metabolized when given as an injectable?
Liver disease
What disease should you ensure patients do not have before injecting Xylocaine SQ?
Xylocaine SQ
What medication reversibly blocks nerve conduction & temporarily paralyzes sensory and motor function with loss of sensation? Include type of injection.
Epinephrine
What medication is a vasoconstrictor to prolong anesthesia, decreases the rate of systemic absorption, and decreases local bleeding?
Epinephrine
What medication keeps Xylocaine in the area?
Hypersensitivity to amide anesthetics
Sites with active injection, bony prominences, large nerves
Peripheral, cerebro- disease
Immunocompromised?
Nerve Blocks?
What are 5 contraindications of Xylocaine?
Keratitis
Corneal edema
Lacrimation
Allergic conjunctivitis
What are the 4 ocular side effects of Xylocaine
Tingling
Numbness
Hypertension
Tachycardia
CNS Stimulatory effects (early)
CNS Depression effects (late)
What are the 6 systemic side effects of Xylocaine?
Delayed wound healing
Necrosis
Vasoconstriction
What are the 3 main side effects of epinephrine?
Vasoconstriction
What side effect of epinephrine can be beneficial when used with anesthesia?
Liver disease
Cardiovascular disease
Before using injectable Xylocaine + Epinephrine, what 2 systemic conditions are most important to ask about during your history?
27-30 g
What size needle should be used for SQ injections?
20 g; 27-30g
What gauge of needle are you supposed to draw up medication with for subcutaneous injections? What gauge needle are you supposed to switch to for subcutaneous injections for the actual injection?
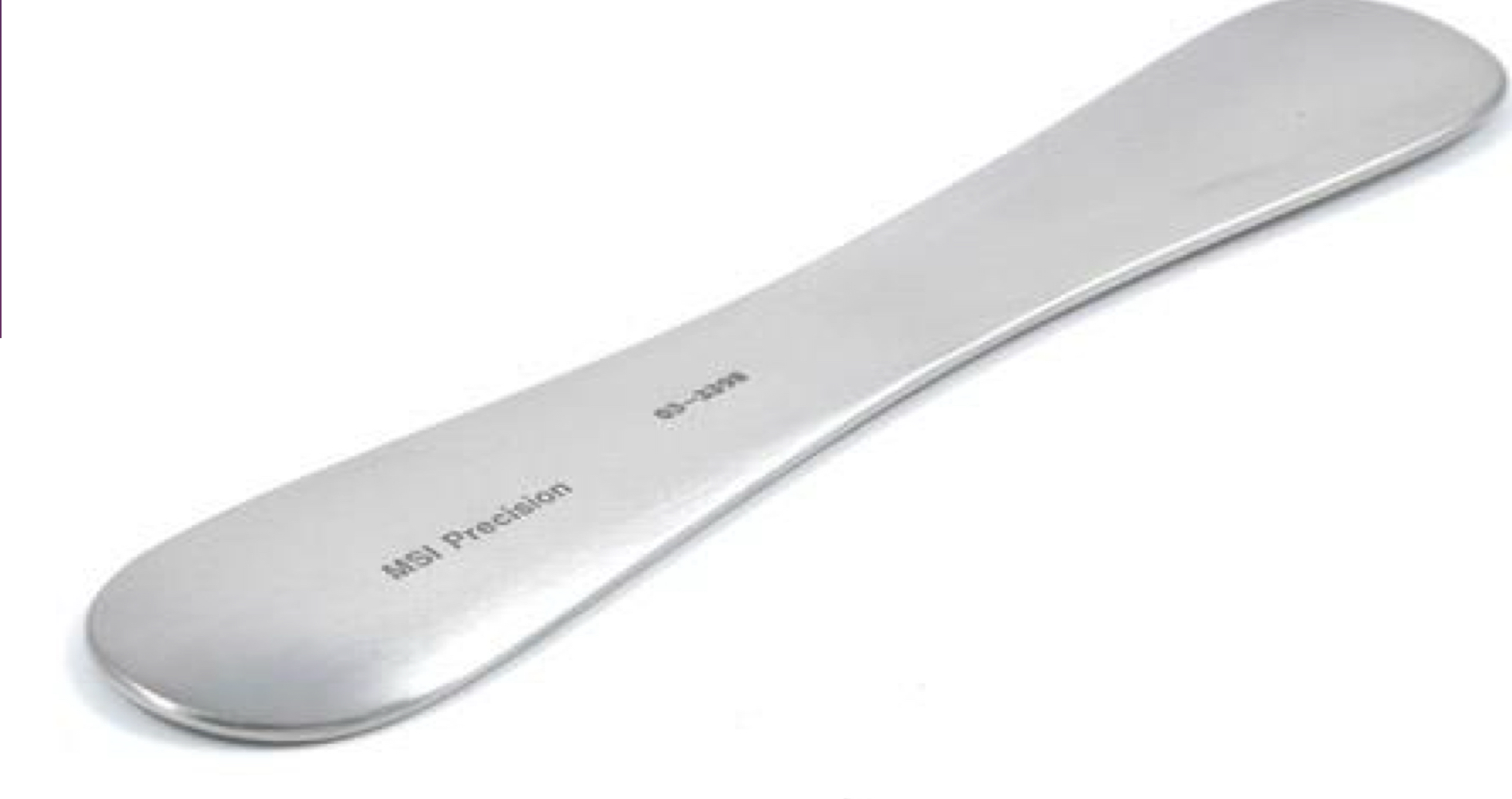

Jaeger plate
What equipment used for subcutaneous injection is used to prevent injury from going through the lid into the globe?
bevel up
How should the needle be oriented for a subcutaneous injection?
15-30 degrees
What angle should a SQ injection be given?
Intravenous (IV)
What type of injection is indicated for large volumes, meds specified for this type of injection, and medical emergencies?
FLAN & ICG —> IV NaFl & ICG
Anaphylaxis Treatment (IV epinephrine)
Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma (IV Mannitol)
Rule-out Myasthenia Gravis (IV Tensilon)
What are 4 ophthalmic indications for IV injection use?
Serious systemic side effect
Why isn’t IV Tensilon administered much anymore via IV to rule out Myasthenia Gravis?
5 mL; 2 mL
What is the dosing of IV NaFl at a concentration of 10%? 25%?
80-90%
What percent of IV NaFl is bound to plasma albumin?
Nausea & Vomiting
Extravasation (ice packs)
Dizziness & fainting
Pruritis & Utricaria
What are 4 milder effects of IV NaFl?
Anaphylaxis
Syncope
Myocardial Infarction
What are 3 serious side effects of IV NaFl?
Visualize a hidden subretinal neovasulcar membrane
What is the purpose of performing an IV ICG injection (Indocyanin Green)?
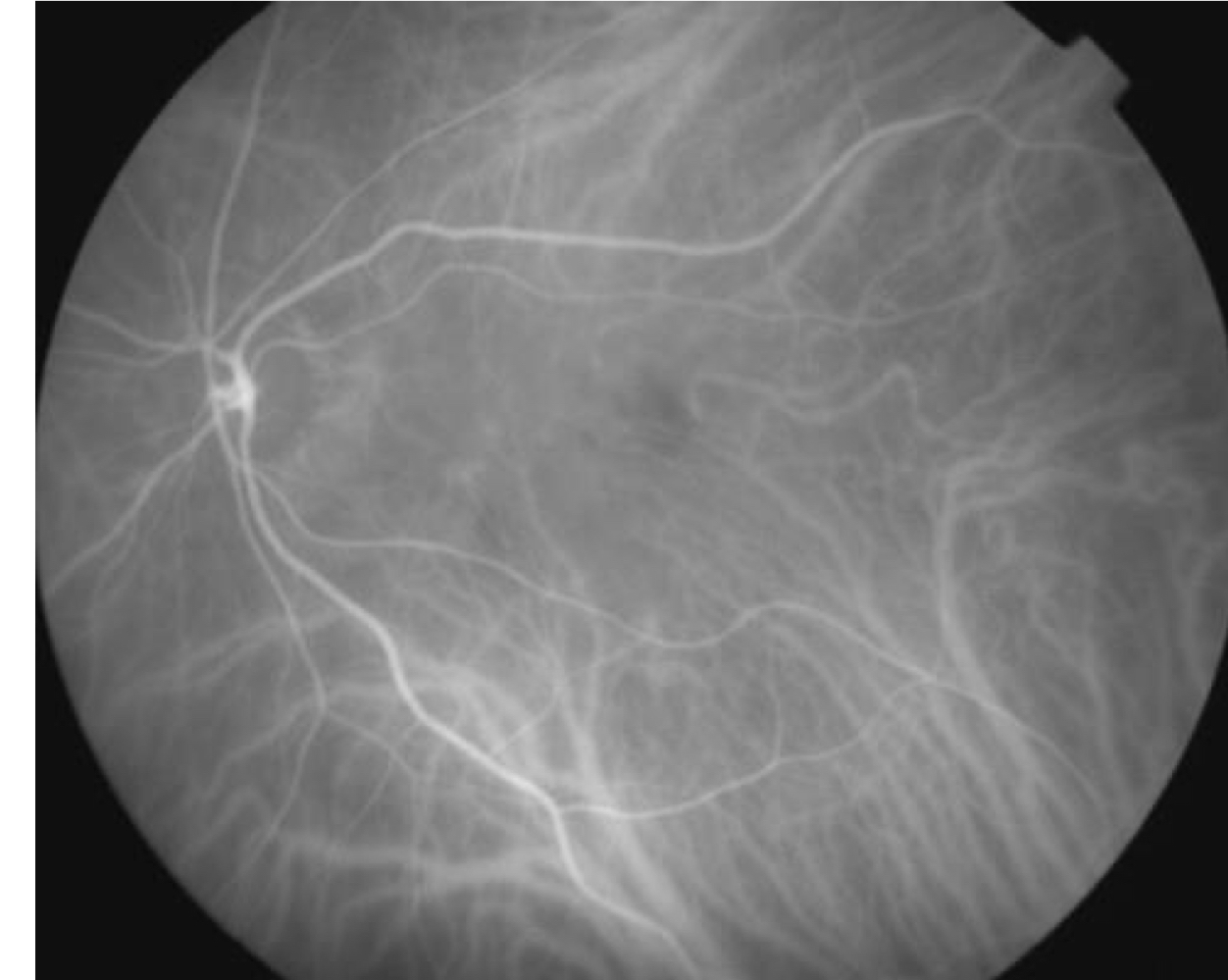
choroid
What retinal structure can be better visualized with IV ICG?
True
True/False: Pigment & hemes fluoresce through Indocyanin Green.
True
True/False: ICG IV is relatively non-toxic and safe.
Intravenous (IV)
What type of injection requires a tourniquet?
25-27 gauge butterfly needle
What type of needle & gauge is often used for IV injections?
Epi-Pen
IM Benadryl (pre-loaded)
Promethazine
Supplemental oxygen
Defibrillator
What 5 additional equipment must be around when injecting an IV injection?
Dorsum of hands
Forearm
Inner aspect of elbow
What are the 3 main sites of IV injections?
Veins
Which is easier to feel for IVs—arteries or veins?
Have patient open & close fist
Tap skin overlying vein
Stroke the arm below the expected site
Apply tourniquet
What are 4 helpful tips to help find vein of choice for IV injection?
20 g
What gauge of needle should be used for IV?
Bevel up
How should the needle be oriented for IV injection?
15-45 degrees
What angle should IV injections be administered?
Extravasation
After removing the tourniquet for an IV injection, what should you check for at the site of injection?
30 minutes after
How long should you observe a patient for following FLAN IV injection?
Chalazion management
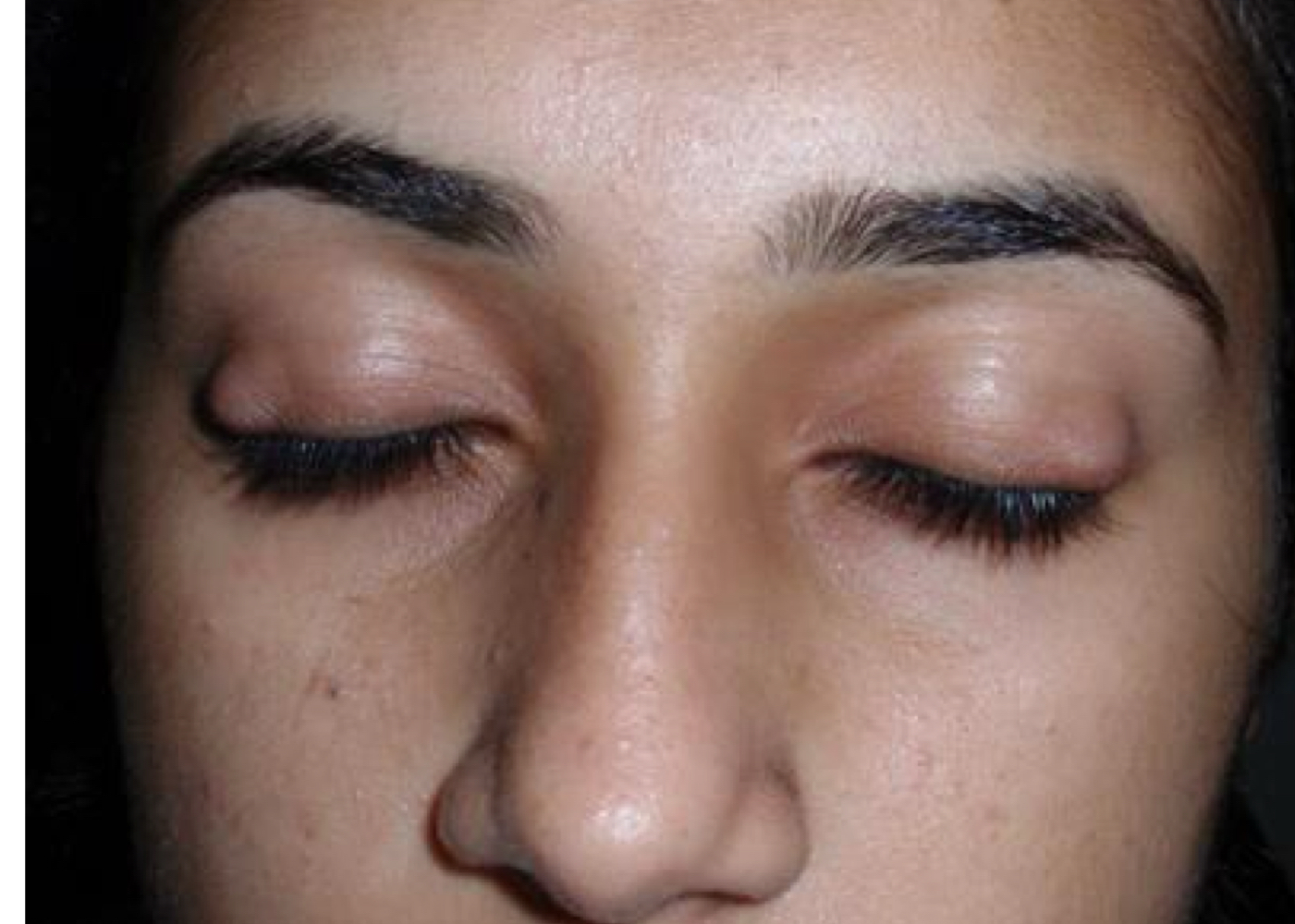
What is a major indication for intralesional (IL) injections?
Kenalog-10 (10 mg/ml)
Kenalog-40 (40 mg/ml)
Triamcinolone acetonide suspension
What 3 main steroids are used for intralesional injections, often for chalazions?
40%; 80%; 90%; 100%
What percent of chalazions will treated with hot compresses & digital massage? Injections alone? Injections + massage? Incision + curettage?
Chalazion
Chronic inflammatory bags with steroid-sensitive histiocytes, multinucleate giant cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, PMNs, eosinophils
True
True/False: Chalazions may require a 2nd injection if > 6mm & takes longer than 6 months to heal.
False—usually steroid injection
True/False: Antibiotic-Steroid Drops are often very effective for chalazion management.
Pain on injection
Depigmentation of eyelid at injection site
Bruising
Ptosis (from steroid)
Vasovagal syncope
Temporary skin atrophy
Retinal & Choroidal vascular occlusion
Increased IOP
Subcutaneous abscess / white steroid deposits
What are 9 complications of intralesional injections?
Known hypersensitivity
Internal hordeolum
Sebaceous cell carcinoma
What are 3 contraindications for intralesional injections?
Use an oral antibiotic first to treat
Why should you avoid intralesional injection for an internal hordeolum?
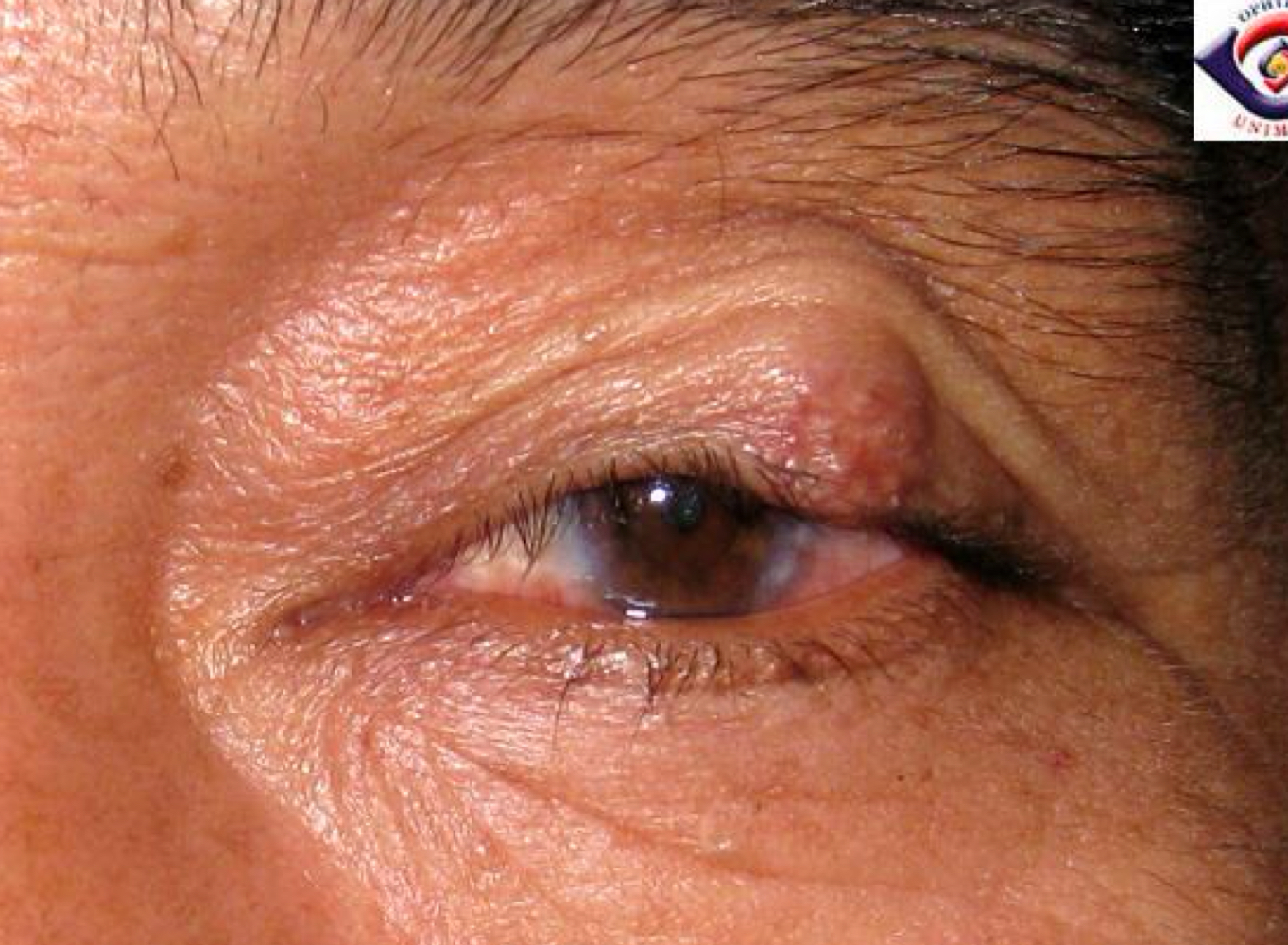
25-27 g
What gauge needle should be used for intralesional injections?
1 cc syringe
What volume of syringe should be used for intralesional injections?
Chalazion clamp
Jaeger plate
What 2 pieces of equipment may be used for intralesional injections to better navigate the injection?
True
True/False: You should draw up medication for intralesional injections before applying the injection.
Evert the lid
What should you do prior to the administering an intralesional injection if the chalazion is on the conjunctiva side of the lid?
Bevel Up
How should a needle be oriented for an intralesional injection?
0.1-0.3 cc
What volume of medication should be injected for intralesional injections?
RTC 1 month
How soon should you follow up after an intralesional injection for a chalazion?
Delivery of increased concentration vs. topicals
Prolonged tissue exposure
Avoid adverse systemic effects
Eliminate compliance issues
What are 4 considerations of Subconjunctival injections?
1-2 weeks
How long does medication delivery last after subconjunctival injection?
Refractory uveitis
Cystoid Macular Edema Post-Op
Scleritis
Corneal Ulcers
Trabeculectomy (post and failing)
What are 5 indications of subconjunctival injections?
Methylprednisone or Kenalog; subconjunctival (SC)
What medication should be administered for refractory uveitis? What type of injection?
Subconjunctival (SC)
What type of injection should be administered for corneal ulcers?
Peripheral Corneal Ulcers
What ocular anomaly is shown here?
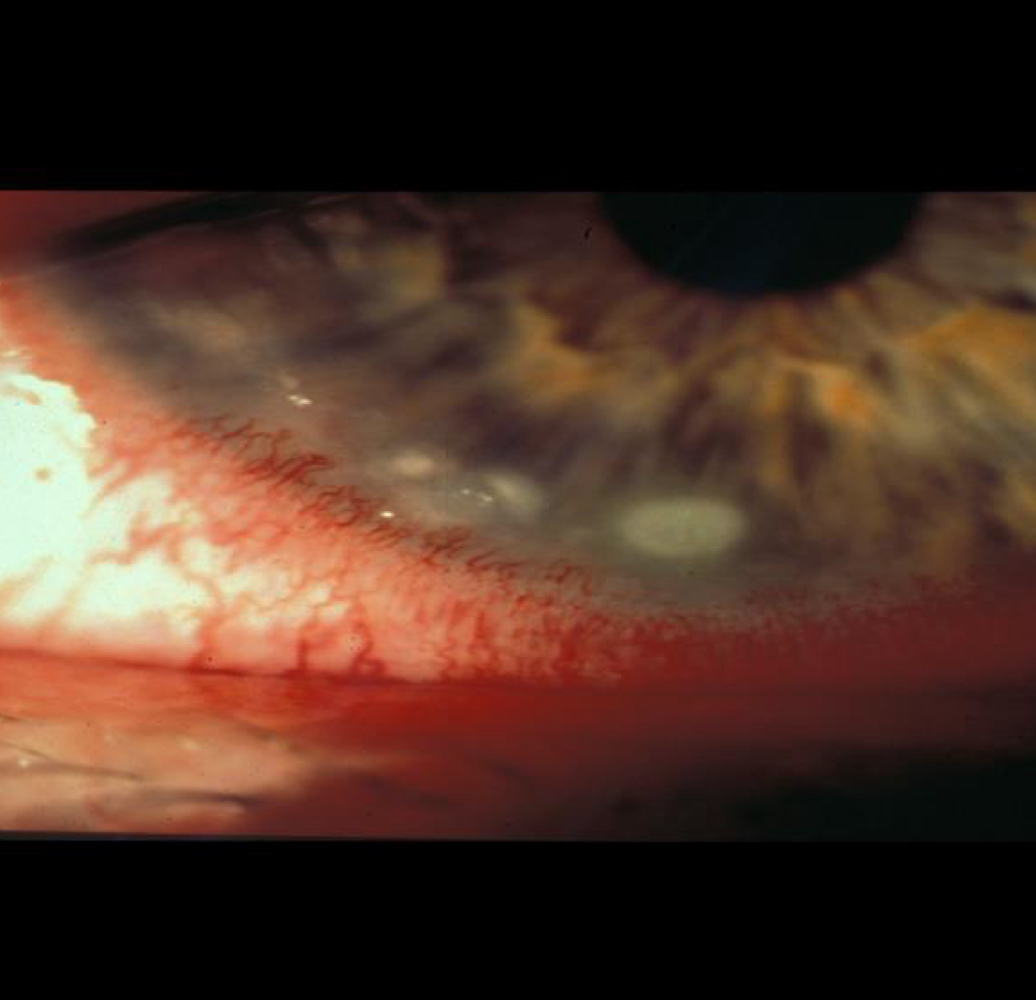
Known hypersensitivity
Steroid responders
Infectious etiology if using steroids
What are 3 contraindications of Subconjunctival injections?
Discomfort
Subconjunctival heme
Subconjunctival steroid deposits
Increased IOP
Vasovagal syncope
Globe penetration
What are 6 complications of subconjunctival injections?
Bevel down
How should you orient the needle for a subconjunctival injection?
Subconjunctival heme; subconjunctival injection
What ocular complication is shown here? What type of injection has this as a complication?
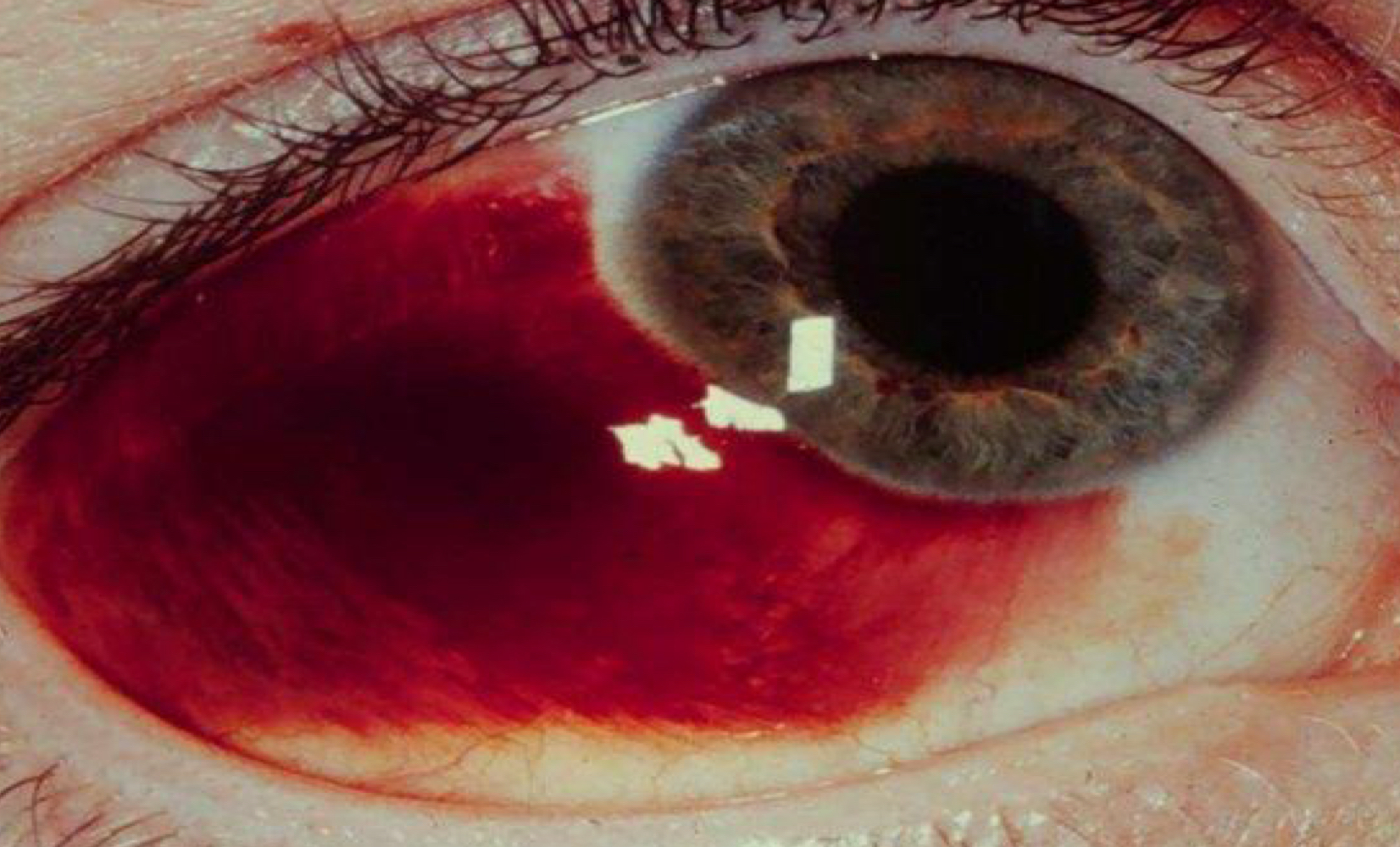
27-30 g; 1 cc syringe
What diameter of needle is used for subconjunctival injections? What volume of syringe?
Forceps
What equipment should you use to lift the conjunctiva up into a “tent”?