Lecture 11: Circulation of Blood
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not much to know...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are the 2 major factors that determines the flow (F) of blood from point A to point B? 𝛥
Pressure difference between A and B (𝛥P) / Resistance to flow (R)
What is the equation for flow of blood?
F = 𝛥P / R
What is the Darcy’s law?
Flow of a fluid through a porous medium
What is the terminology for the physics of blood flow?
Haemodynamic
What is haemodynamic?
The physics of blood flow
What are all the factors affecting friction and vascular resistance?
Vessel length / blood viscosity / vessel radius
What would dramatically affect tissue blood flow?
Small changes in arteriole diameter
What would cause high viscosity in blood flow?
High RBC or protein content
What is η in the Hagen-Poiseuille formula?
Blood viscosity
The flow of blood is directly proportional to what on the vessel?
r^4
If a blood pressure is read as 120 / 70, what is the 120 showing?
Systolic pressure
If a blood pressure is read as 120 / 70, what is the 70 showing?
Diastolic pressure
What is the numerical range of ideal systolic pressure?
90-120
What is the numerical range of ideal diastolic pressure?
60-80
How do you work out the pulse pressure?
Systolic - diastolic pressures
How do you work out the mean arterial pressure?
Diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure
What does the cardiac conduction system do?
Rapidly carries electrical impulses across the heart, initiating contraction / relaxation
What does ECG stand for?
Electrocardiogram
What does ECG do?
Detect electrical activity (ionic movement) across the heart
What is the first wave in an ECG?
P wave
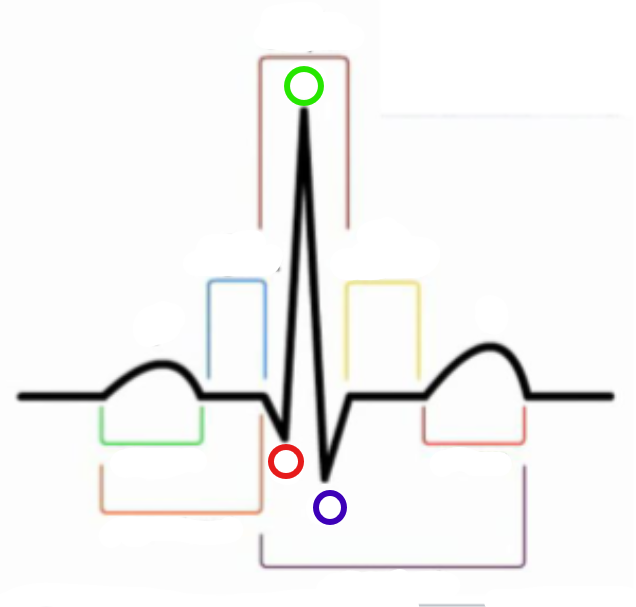
What is the green compartment?
P wave
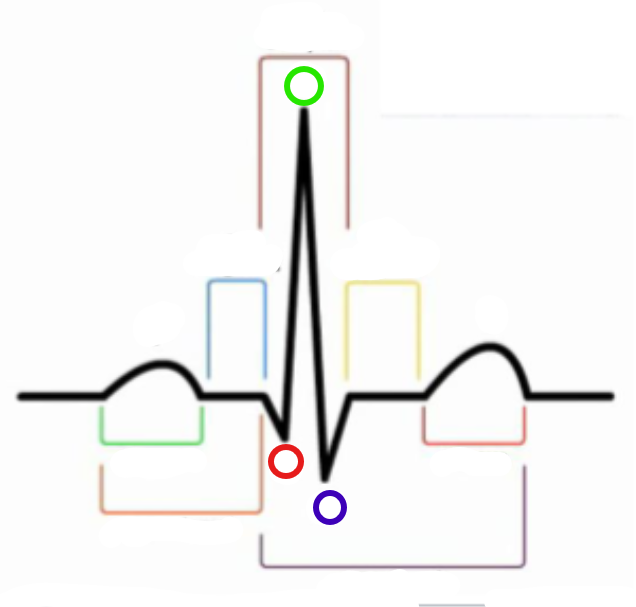
What is the red compartment? (RHS)
T wave
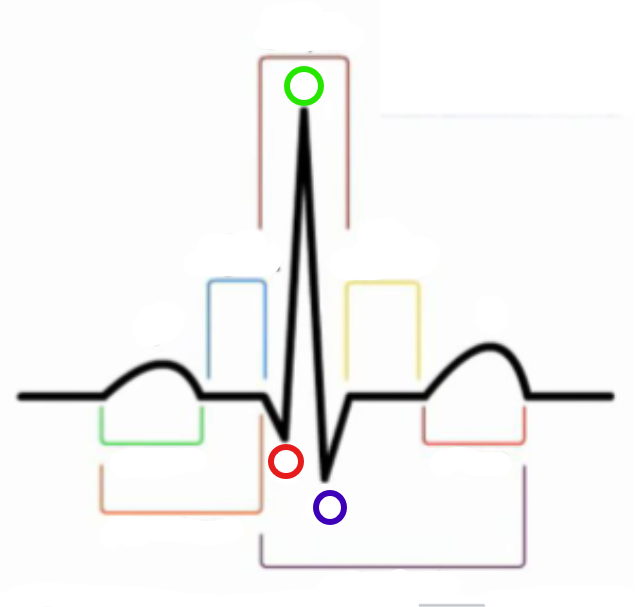
What is the blue compartment?
PR segment
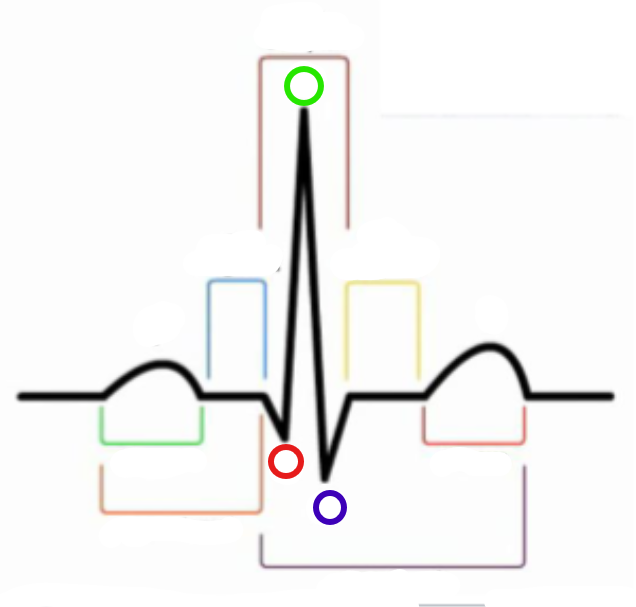
What is the yellow compartment?
ST segment
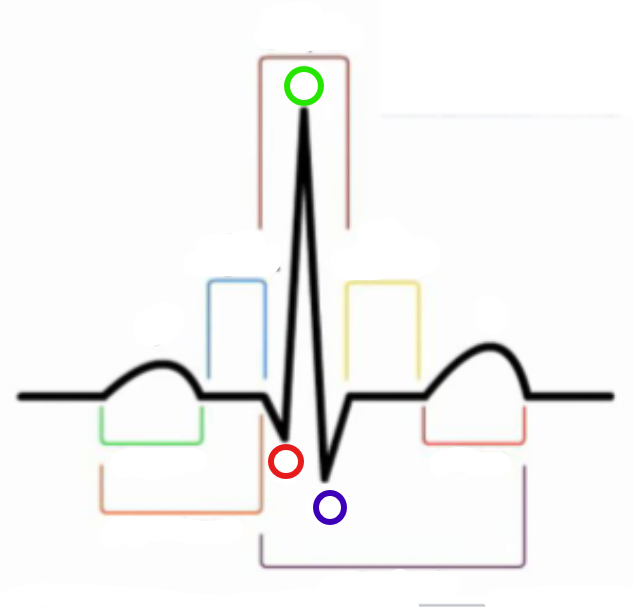
What is the orange compartment? (LHS)
PR interval
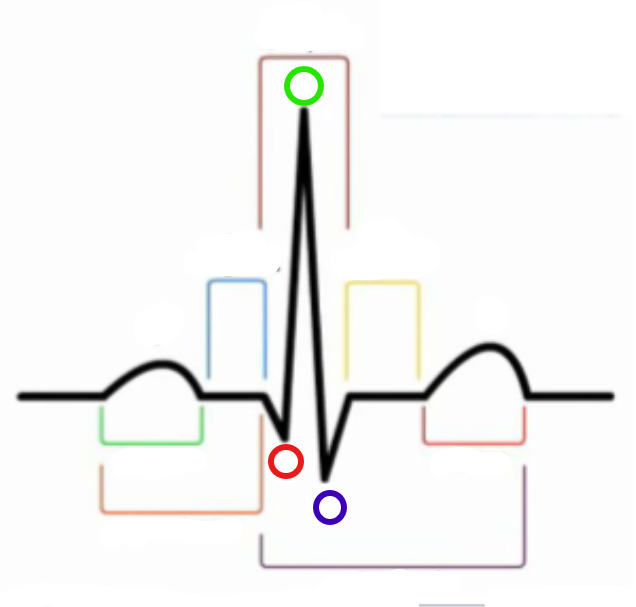
What is the brown compartment? (top)
QRS complex
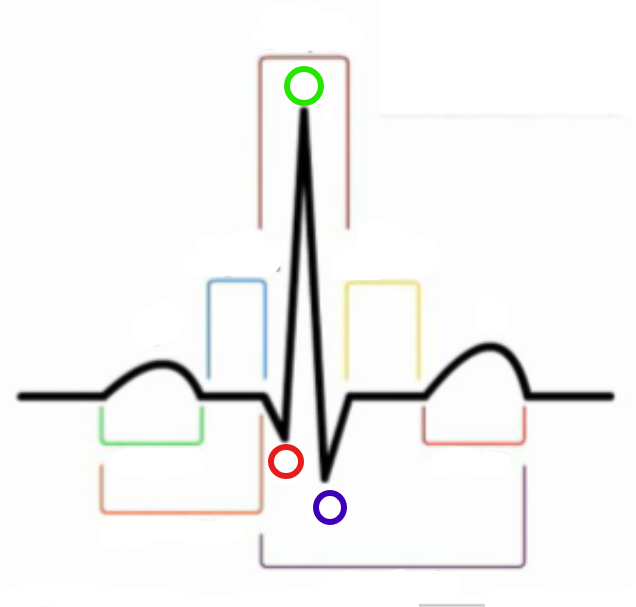
What is the purple compartment?
QT interval
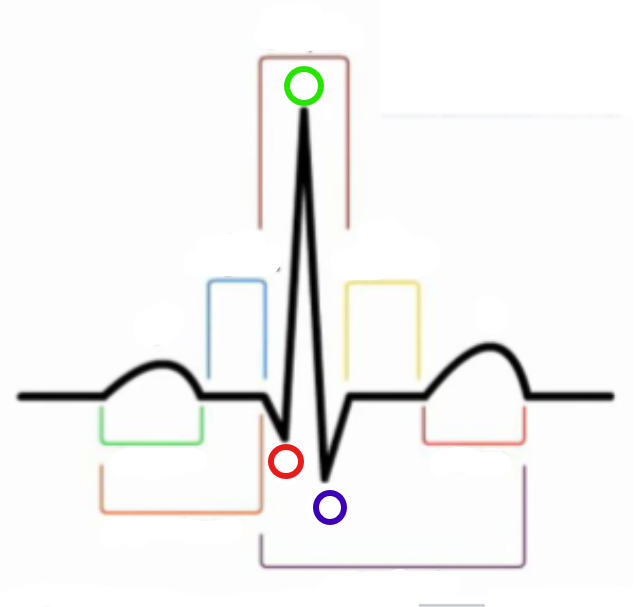
What is the green circle?
R
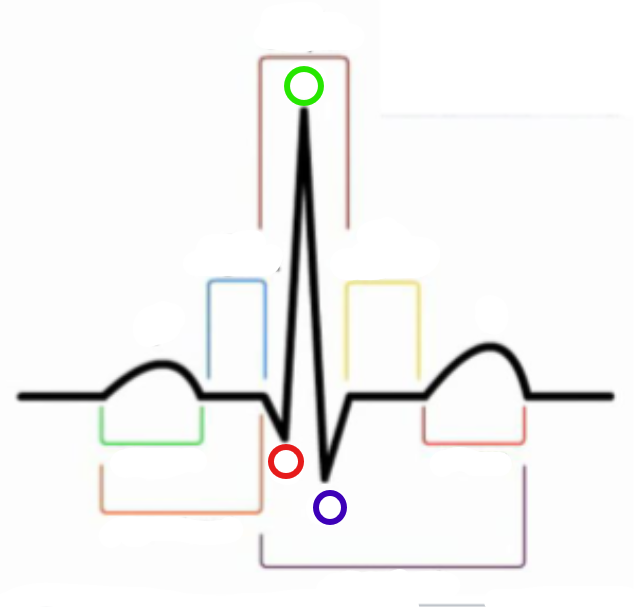
What is the red circle?
Q
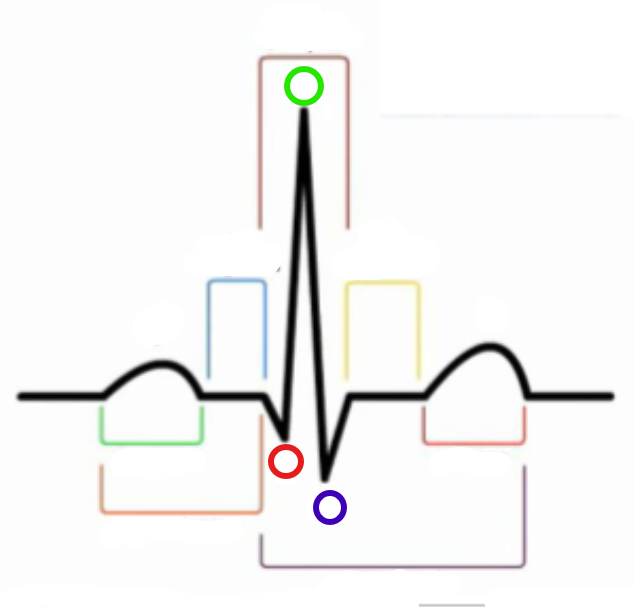
What is the blue circle?
S
What does the P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization → contraction
What follows the P wave?
QRS complex
What does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization → contraction / atrial repolarization → relaxation
What follows the QRS complex?
T wave
What does the T wave represent?
Ventricular repolarization