353 - fractures, joint replacement, arthritis
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
didnt do arthritis yet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
whose at risk for fractures?
age, athletes, diet (poor vitamin D and calcium intake, excessive alcohol intake)
gender: 1 out of 2 women, 1 out of 4 men
genetics, trauma, co-morbidities such as bone cancer, osteoporosis, HIV, hyper and hypothyroidism
types of fractures
segmental, displaced, non-displaced, pathological
fragments: segmental
large fragments separate from main bone
fragments: displaced
separated, not aligned
fragments: non-displaced
separated but aligned
aligned = much easier to heal
fragments: pathological
just sort of happens, indicates underlying illness
result of non-traumatic forces
fractures defined by: bone
incomplete vs complete
incomplete: goes through part of bone
complete: goes through entire bone
fractures defined by: skin
closed (simple) vs open (compound)
close or simple: skin remained closed or intact
open or compound: skin is open, greater infection risk
fractures: spiral
twisting of bone (not normally from a fall)
fractures: comminuted
lots of small pieces, multiple fractures
harder to heal
fractures: avulsed
piece pulled away
KIDs only: fractures
torus & greenstick
torus: buckles in on itself (spongy)
greenstick: think young stick that won’t break completely
fractures - diagnostic tests
x-ray: easiest way to look at bones, first choice
CT scan/MRI if occult
bone scan to determine complications: delayed healing, infection
General Assessments of Fracture
deformity, edema, pain, crepitus
spasms (may cause more pain than actual fracture)
ecchymosis, loss of function, abnormal ROM
circulatory compromise
neurovascular assessment/concerns split into
early ~ 3Ps: pain (unrelieved w meds), paresthesia (THINK nerve damage), pallor (cap refill > 3sec)
late ~ 3Ps: polar (cold fingers, toes), paralysis, pulses (doppler-only, or none)
early 3Ps are serious, late 3Ps are super severe
fracture - treatments are
determined by type/location
more stable fracture → external immobilization
less stable fracture → internal immobilization
more stable fracture
external immobilization
casts, splints, traction
less stable fracture
internal immobilization
if more conservative treatment fails OR
immobilization risk is greater than surgical risk
skeletal traction ~ external fixator ~ internal fixation (ORIF) ~ bone grafting
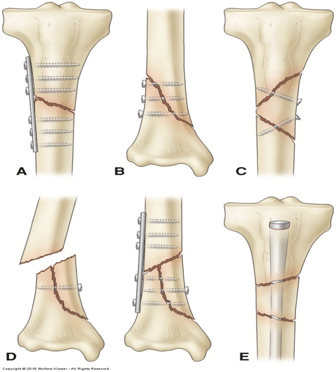
fracture repair
hardware - for life
fix above and below fracture
immobilization - casts
rigid, external immobilizing device
uses: immobilize a reduced fracture, correct deformity, apply uniform pressure to soft tissues, support to stabilize a joint
joints proximal and distal are included
reduced fracture
pieces put back to where they should be (in its proper place)
cast materials
fiberglass: lightweight, durable, waterproof (colorful, for younger pt)
plaster: heavier, break apart when wet, require 24+ hrs to dry
cast assessments: pt
skin, neurovascular, edema/swelling
cast assessments: the cast itself
dry, intact, no rough edges
cast education - BEFORE
purpose/goals of cast, expectations during casting process (will feel heat)
do not scratch or stick under cast, cushion rough edges
activity and mobility options
cast education - AFTER
should feel better - control of edema/pain
exercises (muscle shrinks in cast - atrophy), safe use of devices
s/s to report: persistent pain, swelling, changes in sensation/movement/color/temp, signs of infection, burning or itching at pressure areas
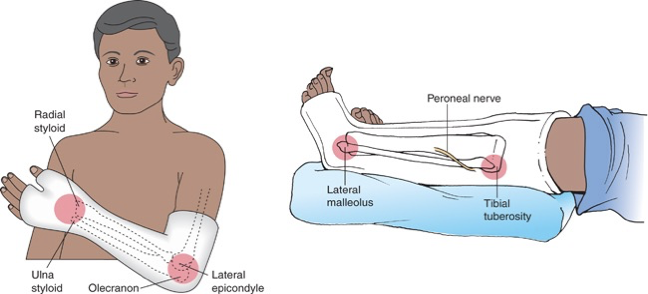
cast - common pressure points
leg cast: monitor for peroneal nerve damage which can cause foot drop

body and spica cast encases
trunk and portions of 1 or 2 extremities
requires multiple ppl to position pt
perineal opening for hygiene
cast syndrome
in pt with body and spica cast
claustrophobia, anxiety
compression of blood flow may lead to this
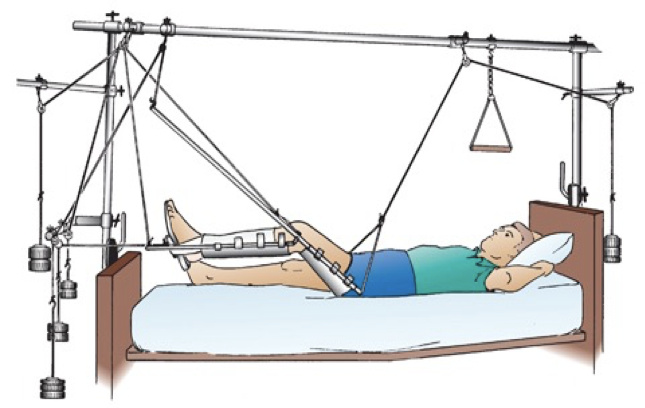
skeletal traction
immobility, blood clots, pneumonia?
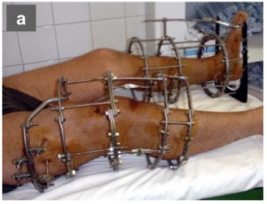
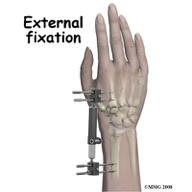
external fixators
pins going into person’s bones, used if pt has infection in area
the frankenstein things
fractures - traction: nursing responsibilities
hydration/nutrition, back rubs, float heels, reposition, avoid shearing (skin)
minimize calf pressure (proper body alignment)
monitor pulses, sensation (circulation, infection)
position feet to avoid (peroneal nerve)
plantar flexion, inversion, eversion
pin care
immobilization: traction’s purpose
reduce muscle spasms, deformity
reduce, align, and immobilize fractures
increase space btwn opposing forces
skin traction is a short-term intervention
skeletal traction can be used as treatment
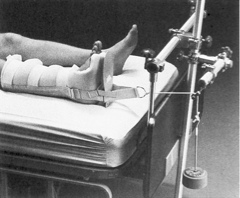
manual (aka skin) traction
used before surgery, can be intermittent, wt limit maximums
you have a pulley and weight pulling back on boot (buck traction)
5-10 lbs of wt max
skeletal traction
continuous, pins are screwed through bones
treatment - pole in skeleton is pulling
INTERNAL immobilization
pin care
specific to skeletal traction/external fixators
goal: prevent infection of skin, soft tissue, bone
inspect sites q shift for infection, crusting may occur (normal)
pt education about performing this at home
pin care: initially
first 48 hrs: insertion sites may be covered by sterile non-stick dressing
pin care: later
use betadine, water/saline solution as ordered/per policy
clean inner to outer
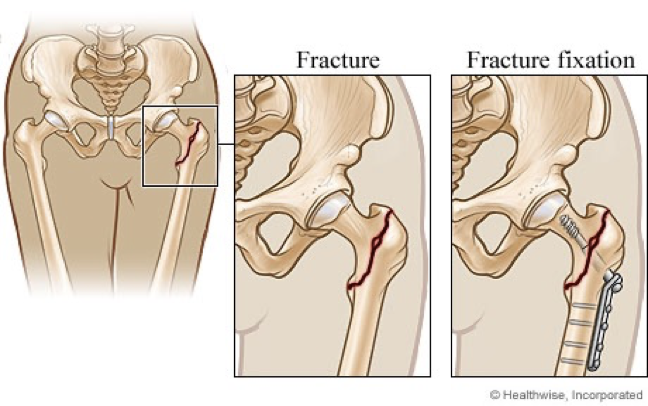
open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)
open body and put pieces back where they belong
internal fixation with nails and plains
surgical procedure to help fracture w internal hardware
open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): nursing responsibilities
routine post-op care
administer IV antibiotics, wound care as ordered
elevate extremity if possible
assess neurovascular status frequently (q4h)
monitor for signs of infection
assess for safety
complications of a fracture
compartment syndrome
fat emboli
DVT
osteomyelitis
avascular necrosis/non-union
localized infection at pin site
complication of fracture: compartment syndrome
reperfusion swelling → increase pressure within muscle compartments → compression of nerves and blood vessels
emergency situation - within 4 to 6 hrs, necrosis, neuromuscular damage, death (severe)
dx of compartment syndrome
measure pressure (intra-compartmental pressure monitor)
human response: PAIN!!!
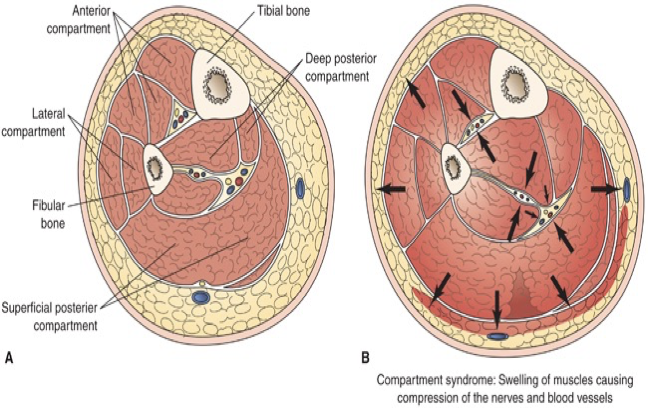
compartment syndrome
A. normal
B. swelling of muscles, edema, possible bleeding
arrows are where pressure is pushing out
compartment syndrome - nursing interventions
FIRST - be aware of risk profile, clinical picture
human response: pain, edema, anxiety
intervention: analgesics as ordered, elevate extremity, educate/answer qs
compartment syndrome - medical treatment
control/reduce swelling (elevate extremity)
release restrictive dressing/cast
fasciotomy: remains open (to decrease pressure), covered w moist + sterile dressing for 3-5 days
retention sutures
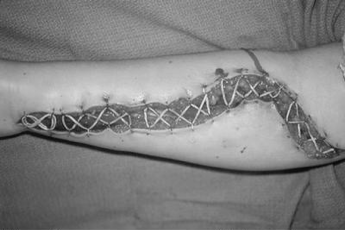
interventions for fasciotomy - pain
analgesics as ordered, elevate extremity
interventions for fasciotomy - risk for infection
maintain moist, sterile dressing
monitor incision, labs (WBCs), VS (pulse, temp)
antibiotics as ordered
interventions for fasciotomy - post op status
diet for healing, routine post-op care
complication of fracture: fat emboli syndrome (FES)
pt profile: young, casted (not ORIF), closed fracture, long bone/hip fracture, necrosis of bone marrow, trauma
no treatment - supportive, prevention
fat emboli syndrome - preventative care
recognize profile, increased risk
maintain adequate oxygen, ventilation
stable hemodynamics, hydration/nutrition, early ambulation (prevents fat from escaping)
prophylaxis (prevention) of stress-related GI bleeding
monitor labs, VS, ABGs
fat emboli syndrome - clinical presentation
24-72 hrs after fracture/trauma
respiratory compromise
cerebral dysfunction, confusion
petechiae
fat emboli syndrome - respiratory comprimse
seen in 75% and will progress to failure in 10%
human response: tachypnea, dyspnea, cyanosis, elevated T, decreased hematocrit, hypoxemia may be detected hrs before onset of respiratory complaints
fat emboli syndrome - cerebral dysfunction
human response: acute confusion, drowsiness, rigidity, convulsions, coma
fat emboli syndrome - petechiae
blockages in small vessels → small pin-point hemorrhages; in upper torso but can also affect eyes
within 24-36 hrs, disappears within week
human response: nonpalpable petechial rash in chest, axilla, neck, reddened conjunctiva
FES - diagnosis
clinical pic, risk factors
rule out alt pathologies: increase ICP, PE, pneumonia
blood gases: hypoxia w paO2 < 60 mmHg AND hypocapnia (low CO2) w respiratory alkalosis
chest x-ray: fluffy white shadows
schonfeld’s criteria
score > 5 = increased probability of FES
petechiae (5 = MOST pts), chest-xray change, diffuse alveolar infiltrates
hypoxia, fever, tachycardia, tachypnea
FES - nurse things - supportative
telemetry (monitor heart rhythm for warnings of emboli in circulation)
ventilation via face mask or mechanical ventilator (maintain resp, function)
nutrition (via TPN or feeding tube if needed)
adequate hydration (IV fluids), foley cath (accurate I&O(
SCDs (prevent venous stasis in lower extremities)
air mattress (good skin care), good eye care (keep moist)
track progress w ongoing dxs
fracture complication - DVT
MOST common complication following trauma, surgery or disability
can progress to a pulmonary embolism so
prevention is better than treatment…
OOB, leg/ankle exercises, adequate hydration
DVT - human response + nursing responsibilites
pain → analgesia
swelling → assess pulses, pain, swelling
decreased pedal pulse → report to PCP
fracture complication - osteomyelitis
inflammation of bone d/t penetrating organisms - Staph aureus most common
at risk: pt w diabetes mellitus, pt undergoing orthopedic surgery (placement of prostheses, management of open fractures, history of osteomyelitis)
osteomyelitis - risk reduction
open fractures receive antibiotics within 6 hrs of injury and prompt surgical treatment (get to OR)
avoid health care associated osteomyelitis, with careful attention to intravascular and urinary caths, surgical incisions, other wounds
osteomyelitis - s.s,
bone pain worse w movement
elevated WBC, temp
dx: biopsy and culture
osteomyelitis - treatment
long term antibiotic therapy (3 months), surgery, debridement, amputation
osteomyelitis - complications
abscess formation, sepsis, bone deformity, limited ROM, motor and sensory deficits
20-30% will experience recurrence within 2 yr, even w treatment
osteomyelitis - nurse things
recognize profile, increased risk
inspection of surgical site/pin site - note change in COCA, REEDA
administer antibiotics as ordered
monitor VS, labs
note complaints of worsening pain w movement
maintain separation from potential infectious agents (keep clean from dirty pts)
fracture complication - non union
poor healing, dx through clinical picture/X-ray
treatment: internal fixation (surgery), bone grafting, electrical bone stimulation
may or may not need surgery
fracture complication - avascular necrosis
disruption of blood flow to fracture site → bone necrosis
dx: clinical pic, x-ray
treatment: repair vascular compromise, surgical joint replacement
common in hips, blood vessels need to communicate so if damaged, need to give hip replacement instead of saving
joint replacement
reconstructive normal joint with artificial or aftermarket parts
arthro -
prefix meaning joint
arthroscopy
repair of joint problems through operating arthroscope or through open joint surgery
using a scope to look inside joint (can be dx or surgery)
arthroplasty
forming a new joint
technical term for joint replacement
hemiarthroplasty
replacement of one of articular surfaces
ex: half a hip joint
osteotomy
surgical cutting of the bone
ex: bone has spurs (overgrowth), cut a little to restore function
prosthesis
artificial substitute of missing part of body or as replacement
most common replaceable parts (joints)
hip, knee, finger joints
less frequently: shoulder, elbow, wrist, ankles
THA - total hip arthroplasty
total hip replacement (THR)
TKA - total knee arthroplasty
total knee replacement (TKR)
who gets joint replacements
pts with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (significant pain, decreased mobility and function)
osteo more common in older; rheumatoid in younger
pt who sustained trauma: hip fractures (in trochanter area, cut off blood supply → joint replacement NOT joint repair w hardware)
congenital deformity: functional joint damage, worn down as they age
hip dysplasia: not formed properly
tumors: can invade bone and cause death of bone
avascular necrosis: w/o blood supply (ex: sickle cell anemia), bone cannot supply
joint replacement: why?
increase mobility, use, joint stability
relieve pain, mobility, functionality, comfort
joint replacement: when?
after conservative therapies have failed (after PT, meds, joint injections, weight loss, activity modification - cane)
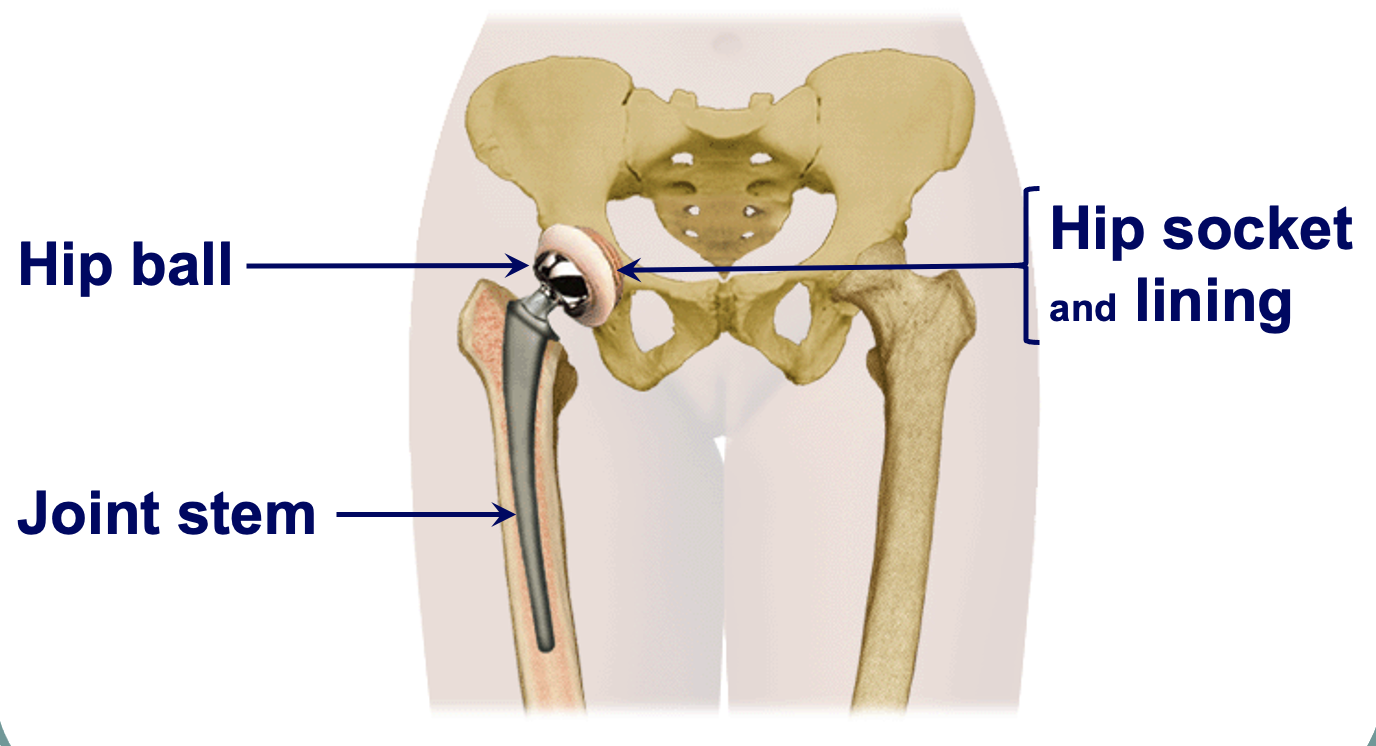
(R) hip prosthesis
hip ball - end of joint stem, fits into socket (cup)
can replace all these elements, entire native hip with artificial pieces
different pts need different size of joint stem
component materials - hip replacement
plastic (polyethylene - often in cup for ball to rotate)
cobalt-chrome or titanium metals (joint stems)
ceramic (metal oxide for ball of new hip, lasts long)
cement: old method, filling compound to hold parts in place (trend is to move away from this, for better fitting pieces)
can dry and flake off, loosening of parts
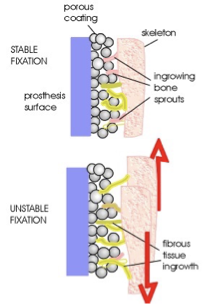
cementless hip prosthesis
avoids cement issues (loose, jiggly), minimal prosthesis-bone bond loss
prosthesis is hammered into more precisely bored hole in femur
porous coating - healthy bone grows/sprouts, allow for stable joint
requires good circulation
ppl do extremely well w this prosthesis
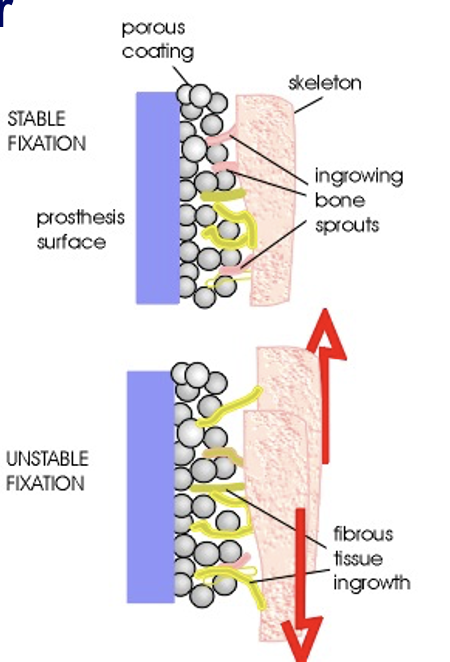
cementless hip prosthesis: disadvantages
risk of bone marrow chunks in circulation during shaft placement
potential weight-bearing restrictions in place
thigh pain (larger prosthesis)
loosening of fibers from porous coated surface
requires good circulation
cemented hip prosthesis
don’t need as much skill to place (surgical skill deviations)
prosthesis placed into bored opening in femur, surrounded by bone cement (opening doesn’t need to be precise)
early weight-bearing, smaller + lighter prosthesis
cost effective
cemented hip prosthesis: disadvantages
circulatory interruptions d/t cement
with age, cement can crack → bonding loss btwn prosthesis and bone → joint instability
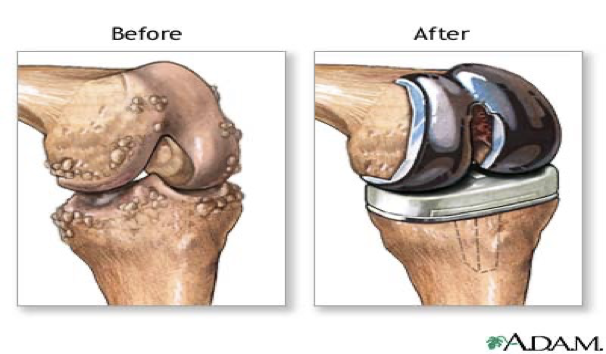
knee prosthesis - before
loss of joint space
bone on bone contact → painful
bulging things → bone spurs, excessive growth
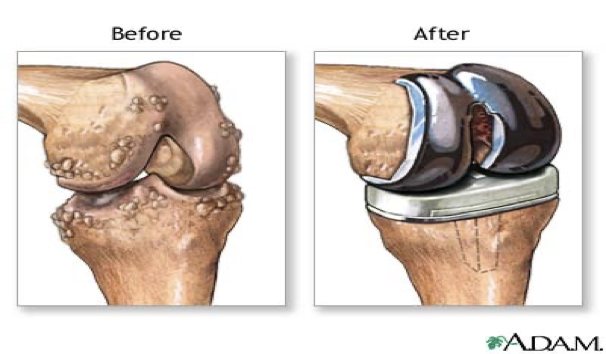
knee joint prosthesis
smooth base on bottom portion
metallic piece fit over femur to allow for smooth bending on base
complications of joint replacement
dislocation/loosening (osteolysis) of artificial joint - don’t have the normal connecting structures in native join
infection at surgical site
thromboembolism - blood clot could become lsoe and move
complications of immobility
complications of joint replacement - long term
heterotopic ossification - extensive bone growth in odd places
avascular necrosis - lack of blood supply
loosening of joint
nursing goals for joint replacement
minimize discomfort/pain
prevent infection of surgical site (leave it closed in sterile dressing for couple days, don’t peek and change often)
minimize negative consequences of immobility
prevent dislocation/loosening of prosthesis
post-op nursing responsibilites for joint replacement
vs/neurovascular checks as ordered (q1-2 hr)
control pain: meds (IV, PO, PCA, nerve block*)
monitor incision: infection, bleeding, record drainage/drain output, maintain clean, dry dressing
prevent DVT: thrombus-preventive therapy - Lovenox/Coumadin/aspirin
AE hose, SCDs, activity and weight-bearing as allowed by surgeon, OOB w order
active ROM
maintain body/limb alignment
respiratory toilet - C-DB, IS
assess skin integrity: investigate itching, burning (especially heels), redness of bony prominence
nutrition/hydration: balanced diet for healing, energy for PT/activity
home health/social service for rehab referrals
joint replacement: pain control
PCA - patient controlled analgesia, moving away from this
nerve blocks - local anesthetic, common in knee replacement, more likely to progress better
individualize strategies: reposition
neurovascular assessment/concerns
same as fractures
early 3Ps - pain, paresthesia, pallor
late 3Ps - polar, paralysis, pulses
dislocation of hip prosthesis
dislocates more readily
human response: increased pain, swelling, immobilization, shortening of affected leg, abnormal rotation, restricted movement, popping sensation of affected hip
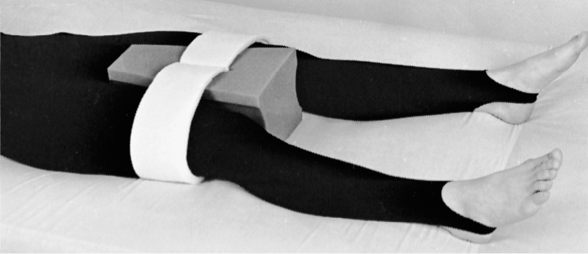
prevent hip prosthesis dislocation
proper positioning: maintain abduction for some replacements
abductor pillow keeps legs apart
posterior approach
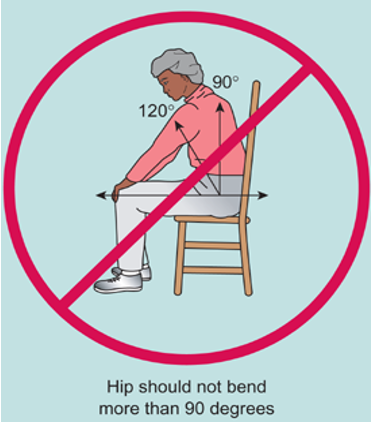
prevent prosthesis dislocation
sometimes, hip should not bend more than 90 degrees (leaning forward is a nono) - hip should be higher than knee
affected leg should not turn inward
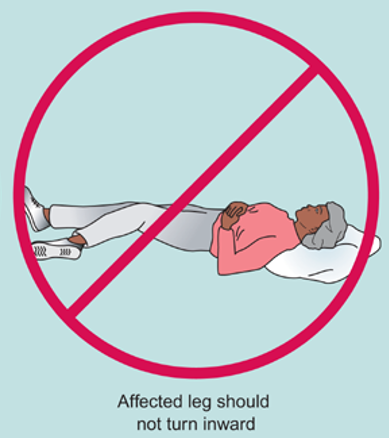
hip dislocation - risk
greatest during 3 months post-op
other factors: age, bone loss, RA, cognitive impairment, implant issues
important to know specific PRECAUTIONS FROM SURGEON (depends on surgical approach)
give printed literature with pictures to patient and review before discharge
dislocation of knee prosthesis
human response: pain or swelling after moving, obvious deformity of knee, numbness or no pulses in foot