HBS TEST 2.1.3 - 2.1.4
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Neuron
A specialized cell that transmits nerve impulses
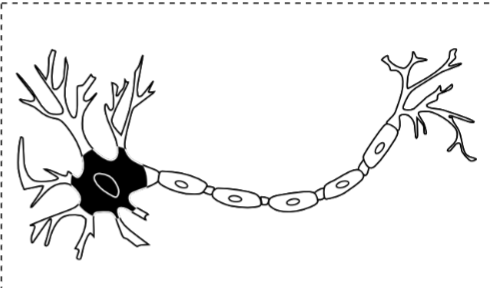
Cell body
The central part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and is the main structural component of gray matter.
Axon
the long thread-like part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells.
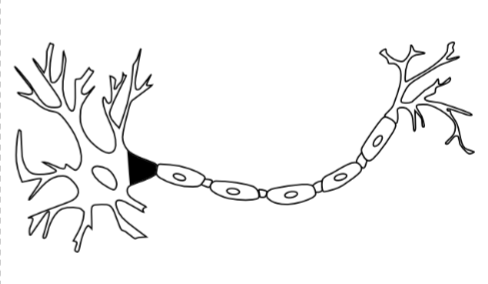
Axon Hillock
A specialized part of the cell body (or soma) of a neuron that connects to the axon.
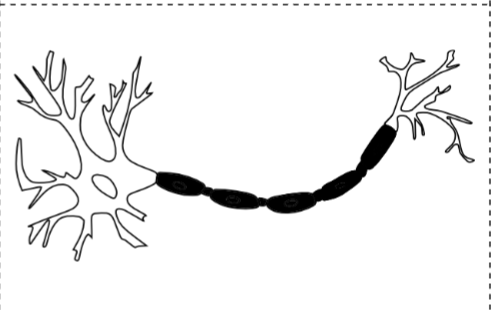
Nodes of Ranvier
The gaps in the myelin sheath of a nerve, between adjacent Schwann cells.
Myelin Sheath
A wrapping of myelin around certain nerve axons, serving as an electrical insulator that speeds nerve impulses to muscles and other effectors.
Synapse
a junction between two nerve cells, consisting of a minute gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neuro transmitter
Synaptic Cleft
the space between neurons at a nerve synapse across which a
nerve impulse is transmitted by a neurotransmitter
presynaptic neuron
the neuron that is SENDING the signal
postsynaptic neuron
the neuron RECEIVING the signal
neurotransmitters
a substance that transmits nerve impulses across a synapse
vesicles
a small sac containing neurotransmitters enclosed by a lipid bilayer
Action Potential (word form)
The change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell
axon terminals
The end of a neuron. The part of the neuron that sends the signal
dendrites
The part of the neuron that receives the signal from another neuron.
Cell membrane
A semi-permeable membrane made of phospholipids that surrounds the cytoplasm of cells; found in all cell types
Nucleus (cells)
The organelle found in all eukaryotic cells that contains all of the chromosomal DNA of the cell.
Schwann Cell
Cell that produces the myelin sheath
Passive transport
high to low
moves with the gradient
does not require atp
Simple diffusion
passive transport
molecules moving directly across a cell membrane without the assistance of any proteins
Facilitated Diffusion
passive transport
requires specific transport proteins embedded in the membrane to help molecules move across
Active transport
low to high
requires atp
moves against the gradient
Action Potential (words)
a brief electrical impulse that travels across the axon of the neuron
Neuromuscular Junction
a synapse where a motor nerve connects to a muscle fiber and transmits electrical impulses to cause muscle contraction
Experimental Research
comes first
basic medical research & includes animal experiments, cell studies, biochem, genetic, and physiological investigations
Clinical research
comes second
determines the safety and other effects on medications, their devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens
protein channels
allow potassium ions to pass in or out of the cells
Sodium Channels
allow sodium or Na+ ions to pass it around
Protein pump (Na / K pumps)
pumps 3 “Na” ions out and pumps 2 “K” ions in
Multipolar Neurons
CNS and effernt PNS
Most common form of neurons, make up 99% of all types
3 or more processes extend out of the cell body
Bipolar Neurons
found in the CNS. specialized sensory neurons for the transmission of senses (smell, sight, and hearing)
Relatively Rare
Two extensions, one axon and one neuron
Pseudounipolar
CNS and afferent division of the PNS
Only occurs as a sensory neuron, Fairly common
Unipolar
afferent division of the PNS
common in invertebrates, but rare in vertebrates
large cell body with axon pointing in only one direction.
Axon appears shorter in this type of neuron
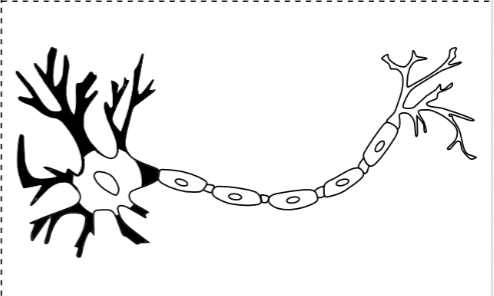
Neuron (nerve cell)
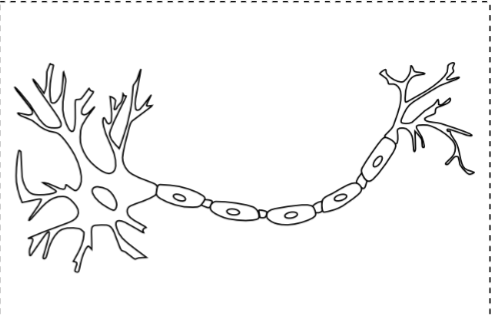
Cell body
Axon
Axon Hillock
Nodes of ranvier
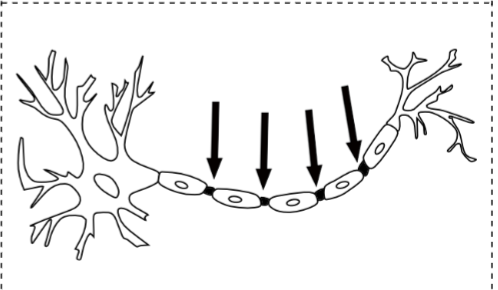
Myelin Sheath
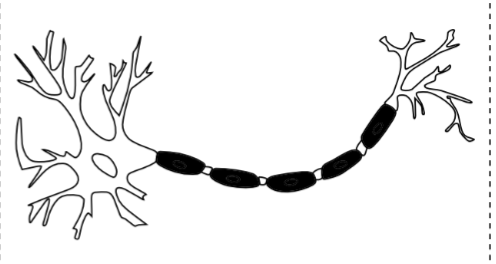
Synapse
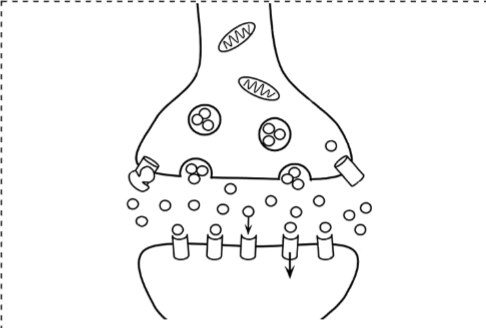
Synaptic Cleft
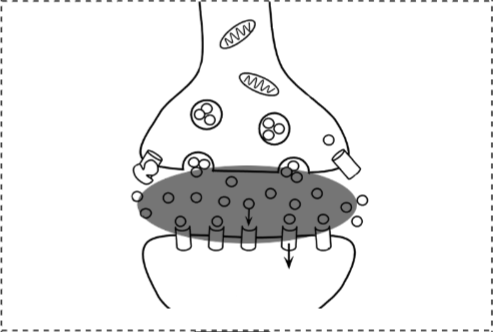
Presynaptic Neuron
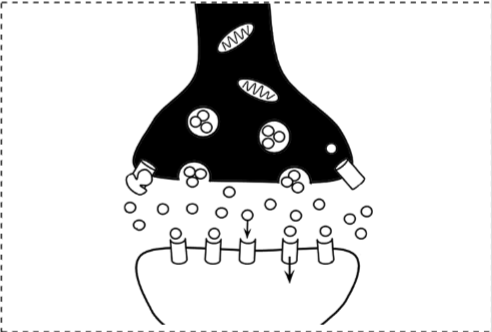
Postsynaptic Neuron
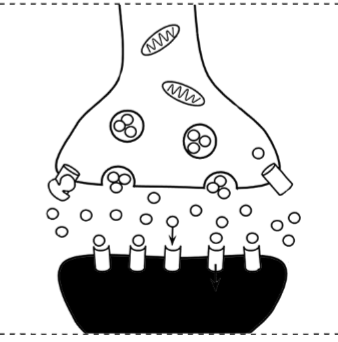
Neurotransmitters
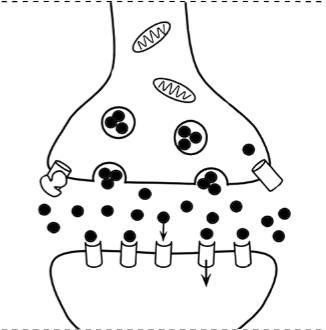
Vesicles
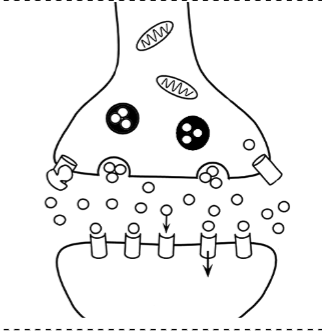
Action Potentials (picture)
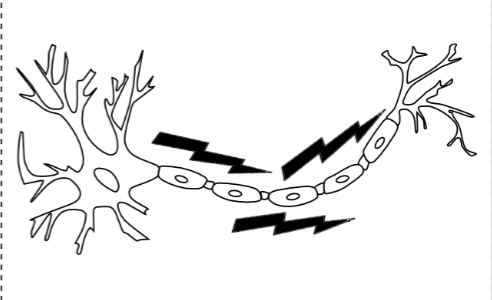
Axon Terminals
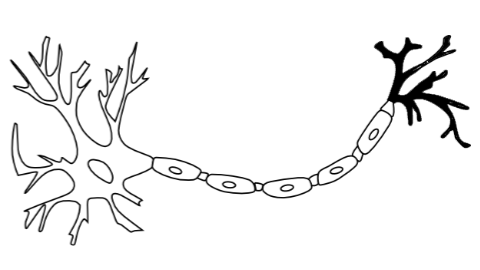
Dendrites
What is an action potential?
A signal that is sent through your body. It has 4 stages.
An action potential acts like a
wave, where one section is triggered and then another, till it reaches the synapse
Na+ and K+ are both
Ions, or elements with a positive (or negative) charge
If there is a concentration gradient, what does that mean
There is more ions on one side of the neuron cell then the other
What is the concentration gradient at resting potential
Na+ are outside the cell and K+ are inside the cell
What is resting potential also known as
on switch
what is an excitatory signal
A signal that stimulates a neuron while an inhibitory signal prevents a neuron from sending a message
what happens to cause the neuron to be more positive, and the line on the graph to go up
Na+ (sodium) enters the nueron
What caused the graph to increase in charge so much
Na+ concentration gradient was eliminated, now most + charged ions are all inside the cell.
What happens to repolarize the neuron?
Na+ channels close and K+ channels open
Which way is K+ going to flow, now that the channels for it are open?
Out of the cell, because there are more K+ inside the cell.
What is happening to the charge of the cell during repolarization?
The cell is getting more negative because it is losing positive charges.
What would happen if the Na+ channels opened right now with the cell looking as it does? (nothing is moving)
Na+ wouldn't move into or out of the cell, as there isn't a concentration gradient.
How does the cell restore the concentration gradients for K+ and Na+?
sodium potassium pump
Which structure of a neuron receive information from other neurons to be processed by your brain?
dendrites
Which structure of a neuron transmits signals from the cell body to other neurons?
axon
What is the signal called that the neuron sends down the axon?
action potential
What is the main purpose of the myelin sheath in the neurons?
speed up the action potential
What is the gap between the end of the axons and the dendrites of the other neuron called?
synaptic cleft
Which structure brings information into the neuron?
dendrites
Where is information processed in the neuron?
cell body
Which structure insulates the neuron and speeds up the action potentials?
myelin sheath
Which structure conducts the action potential signal to other neurons?
axon
What are the spaces between each myelin sheath that allow signals to jump from one node to another?
nodes of ranvier