IB Bio Endocrine System
5.0(3)Studied by 47 people
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:14 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
endocrine system
body system made up of glands & hormones they produce
2
New cards
all hormones are ligands but…
not all ligands are hormones
3
New cards
glands
maintain homeostasis (constant environment) & regulate development
4
New cards
hormones
transported throughout body by blood
5
New cards
blood acts as a…
highway
6
New cards
what amount of hormone is needed to have significant influence on target tissues?
minute amounts of hormone
7
New cards
target tissues
tissues where its cells have receptors that bond to hormone
8
New cards
hormones can be what?
* steroids
* peptides
* modified amino acids
* peptides
* modified amino acids
9
New cards
non-endocrine glands
make other substances besides hormones
10
New cards
example of non-endocrine glands
sweat glands
11
New cards
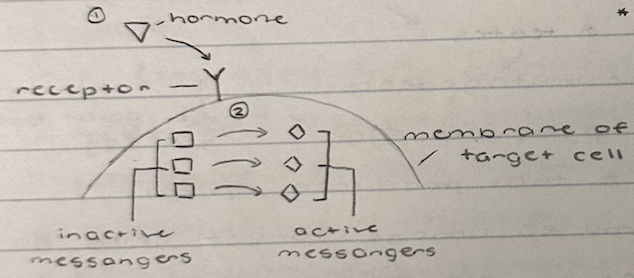
how do hormones cause coupled reaction?
1. hormone bonds to receptor on membrane of cells in target tissue
2. inactive messengers become active messengers
12
New cards
what happens to effect of hormone in coupled reaction?
effect of hormone = amplified
13
New cards
why is pituitary gland called “master gland”?
b/c acts as target tissue of some hormones released by other glands
14
New cards
pituitary gland consists of?
* anterior (front) pituitary gland
* posterior (back) pituitary gland
* posterior (back) pituitary gland
15
New cards
hypothalamus relationship w/ pituitary gland
hypothalamus sends signals that tells pituitary to secrete certain hormones
16
New cards
hormones in posterior pituitary gland
* ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
* oxytocin
* oxytocin
17
New cards
what makes ADH & oxytocin?
neurosecretory cells of hypothalamus
18
New cards
ADH function
* increases reabsorption of H2O in kidneys (takes H2O out of blood to store in kidneys)
* determines whether kidneys absorb or release H2O into blood? (\*\*clarify)
* determines whether kidneys absorb or release H2O into blood? (\*\*clarify)
19
New cards
oxytocin function
stimulates release of milk from mammary glands
20
New cards
how does the nervous system and endocrine system differ?
* nervous: made up of neurons, faster
* endocrine: made up of glands & hormones they produce, slower, causes developmental changes.
* endocrine: made up of glands & hormones they produce, slower, causes developmental changes.
21
New cards
posterior pituitary gland function
controls body parts, not other glands
22
New cards
anterior pituitary gland function
regulates hormone production of other endocrine glands
23
New cards
what is anterior pituitary gland affected by?
affected by releasing hormones made by neurosecretory cells of hypothalamus
24
New cards
what do releasing hormones in the anterior pituitary gland stimulate?
stimulate release of tropic hormones
25
New cards
tropic hormones
hormones whose target cells are other endocrine glands
26
New cards
hormones in anterior pituitary gland
* TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
* ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
* FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
* LH (luteinizing hormone)
* PRL (prolactin)
* GH (growth hormone)
* ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
* FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
* LH (luteinizing hormone)
* PRL (prolactin)
* GH (growth hormone)
27
New cards
non tropic hormones
hormones whose target cells do not make up other endocrine glands
28
New cards
two non tropic hormones
PRL & GH
29
New cards
TSH function
affects thyroid by secreting T3 & T4
30
New cards
ACTH function
affects adrenal cortex by secreting glucocorticoids
31
New cards
FSH function
affects ovaries by regulating oogenesis
32
New cards
LH function
affects testes by regulating spermatogenesis
33
New cards
oogenesis
meiosis that produces eggs
34
New cards
spermatogenesis
meiosis that produces sperm
35
New cards
PRL function
helps mammary glands regulate milk production
36
New cards
GH function
stimulates muscle & bone cell growth
37
New cards
how does pancreas produce antagonistic hormones?
by having bundles of glucocorticoids w/ alpha & beta cells
38
New cards
how does liver store sugar?
by converting glucose → glycogen for storage
39
New cards
alpha cells
* produce glucagon
* increases blood glucose level in liver
* glycogen in liver → released into blood as glucose
* increases blood glucose level in liver
* glycogen in liver → released into blood as glucose
40
New cards
beta cells
* produce insulin
* decreases blood glucose level in liver, muscle & fat cells
* glucose leaves blood → stored in liver as glycogen
* decreases blood glucose level in liver, muscle & fat cells
* glucose leaves blood → stored in liver as glycogen
41
New cards
pancreas (diagram)
blood---------liver
glucose → glycogen (using insulin/beta cells)
glucose
glucose → glycogen (using insulin/beta cells)
glucose
42
New cards
adrenal gland parts
medulla & cortex
43
New cards
hormone in medulla
epinephrine (adrenalin)
44
New cards
epinephrine function
* affects blood vessels, liver, & heart
* causes increase in blood glucose, blood vessel constriction, & fight or flight response
* causes increase in blood glucose, blood vessel constriction, & fight or flight response
45
New cards
hormones in cortex
* glucocorticoids (ex: cortisol)
* mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
* mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
46
New cards
glucocorticoids function
* affect entire body
* help increase blood glucose
* greater in long-term stress
* help increase blood glucose
* greater in long-term stress
47
New cards
mineralocorticoids function
* affect kidney
* increases rate of reabsorption of Na+ & K+
* increases rate of reabsorption of Na+ & K+
48
New cards
hormones in thyroid
* T4 (thyroxin)
* T3 (triiodothyronine calcitonin)
* calcitonin
* T3 (triiodothyronine calcitonin)
* calcitonin
49
New cards
T4 & T3 function
causes body to increase cellular metabolism
50
New cards
cellular metabolism
sum total of all chem reactions in organism
51
New cards
calcitonin function
causes bones to absorb Ca2+ from blood
52
New cards
where is parathyroid?
within thyroid
53
New cards
hormone in parathyroid
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
54
New cards
PTH function
causes bones to release Ca2+ into blood
55
New cards
PTH works antagonistic to…
to calcitonin
56
New cards
as women grow older…
calcium in body decreases b/c calcitonin decreases or PTH increases
57
New cards
hormone in testes
testosterone
58
New cards
testosterone function
* affects testes & to lesser extent, rest of body
* affects spermatogenesis & secondary sexual characteristics
* affects spermatogenesis & secondary sexual characteristics
59
New cards
hormone in ovaries
* estrogen
* progesteron
* progesteron
60
New cards
estrogen function
* affects uterus & to lesser extent, rest of body
* affects menstrual cycle & secondary sexual characteristics
* affects menstrual cycle & secondary sexual characteristics
61
New cards
progesterone function
* affects uterus & to less extent, rest of body
* affects menstrual cycles & pregnancy
* affects menstrual cycles & pregnancy
62
New cards
pineal gland location
in brain
63
New cards
hormone in pineal gland
melatonin
64
New cards
melatonin function
* affects entire body
* helps regulate circadian rhythms
* disrupted during spring forward
* helps regulate circadian rhythms
* disrupted during spring forward
65
New cards
how does adipose tissue store glucose?
excess glucose gets stored in the liver as glycogen or, w/ help of insulin, converted into fatty acids, circulated to other parts of the body, & stored as fat in adipose tissue
66
New cards
what is fight or flight response?
automatic physiological reaction to an event perceived as stressful or frightening & is triggered by release of hormones