atomic bonding and the periodic table
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Mixture
2 or more substances that are not chemically combined (elements or compounds) → separated by physical means, with no fixed composition and variable mp/bp
Compound
Require a chemical reaction to separate elements, has a fixed ratio of elements present, fixed mp/bp
Isotope
Atoms of the same element which have different number of neutrons but the same protons and electrons
Ions
Electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons
Separation example 1
Solvent+solute=solution
Separation example 2
Salt+water=evaporation/filtration/sieving
Separation example 3
Iron filings+sulfur=a magnet
Separation example 4
Ethanol+water=boiling+condensing tube
Atomic history
Democritus → found everything was made of particles surrounded by empty space
John dalton → elects had their own atoms that could not be divided or split
Jj Thompson → plum pudding model and found charges
Ernest Rutherford → alpha scattering experiment
Niehls Bohr→ electrons at set distances
James Chadwick → discovered the neutron, its mass and its charge
Column/ group
How many electrons in outer shell
Down/ period
How many electron shells
Atomic number
Number of protons
Atomic mass
Number of protons + number of neutrons
Dmititri Mendeleev
Created modern periodic by organising them into groups and periods of similar structure and increasing mass, leaving gaps for protected unfound elements based on properties
Element
Substances that only contain the same type of atom (same number of protons)
Atom
The smallest part of a chemical element that can exist
Electronic structure
Distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbits
Physical properties of metal (7)
Conductor (heat+electricity)
Malleable
High mp/bp
Sonorous
Ductile
High density
Shiny
Metal ion notes
Tend to have 3 or less outer electrons, so they give away their electrons to other atoms, becoming positively charged ions
Noble gases physical properties
Unreactive as full outer shell
Inflammable
Exist on their own
Non metals
Low densities
Group 8 trends
Going down:
Mp/bp increase
Density increase
Size increase
Alkali metals trends
Group 1:
Attempt to lose electron and become positively charged
Solid but soft at room temperature
Going down:
Reactivity increase
Density increase
Mp/bp decrease
Because number of electron shells increase so attraction weakens and bonds are easier to break
Equation 1
Metal + water (H²O) → hydrogen(g) [acidic] + metal hydroxide (OH) [alkaline]
alkali reactions examples (water)
Lithium: fizzes on top of water + produces hydrogen
Sodium: turns spherical + fuzzes diagonally + produces hydrogen
Potassium: burns with lilac flame + fizzes + produces hydrogen
Chlorine: flame + white smoke + solid form + colour fades
Halogen trends
Group 7 (non metals) going down:
Size of atom increase
Mass of atom increase
Density increase
Mp/bp increase
they are highly reactive so only used in small amounts and are diatomic molecules meaning they join with each other (Cl², Br², At²)
Transition metal notes
Similarities:
Conduct electricity in solid+liquid form
Shiny when first cut
Differences:
Higher mp/bp
Higher densities
Greater strength
Greater hardness
Compare transition metals and group 1
Group 1= reacts vigorously with cold water
Tm= reacts slowly, if at all
Group 1= reacts vigorously with halogens
Tm= same but not all also react
Group 1= reacts quickly with air
Tm= reacts slowly, if at all
Alpha scattering experiment
Rutherford passed positively charged alpha particles through gold foil. As some of them succeeded in passing through, he concluded the mass must’ve been concentrated in the centre of the atom. But as some were deflected he decided the atom’s nucleus was positively charged.
Isotope example
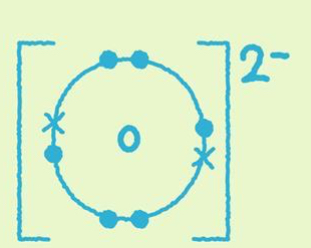
Monatomic
E.g. gold
Consisting of one atom/ exists on its own
Diatomic
E.g. hydrogen
Consisting of 2 atoms/ comes in pairs