Chapter 22: Metabolism単語カード | Quizlet
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are the eating control centers (hypothalamic centers) in the CNS?
CNS feeding Center
CNS satiety center
The CNS feeding center is _______ active and the CNS satiety center stops food intake by inhibiting the __________ center.
Tonically
Feeding
The cortex detects ____________ in the body
hunger
What are the CNS and GI peptides?
Ghrelin
Leptin
CCK
CRH
What is the function of Ghrelin? Where is its source?
Increases hunger
Stomach
What is the function of Leptin? Where is its source?
Increase satiety
Adipose Tissue
What is the function of CCK? Where is its source?
Increase satiety
Small intestine
What is the function of CRH? Where is its source?
Increase satiety
Hypothalamus
Glycogenesis
Glucose to glycogen
Glycogenolysis
Glycogen to glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Amino acids to glucose
Lipogenesis
Glucose/FA to fat stores
Lipolysis
Fat stores to FA & glycerol
Summarize the Metabolic conversion of nutrients
You eat 3 macros:carbs, fats, protein
FATS:
break down into FA+ glycerol and go into the free fatty acid pool for metabolism. Excess FA is stored.
ANY EXCESS NUTRIENTS ARE STORED AS FAT.
CARBS:
break into glucose and excess is stored as fat. Rest enters the glucose pool to be used for brain metabolism, excess is stored as fat, stored at glycogen, used in metabolism in tissues or excreted in urine.
PROTEINS:
breaks into AA, and goes into the AA pool. Excess is converted to glucose. AA pool is used to make proteins, and when they are broken down they contribute back into the AA pool
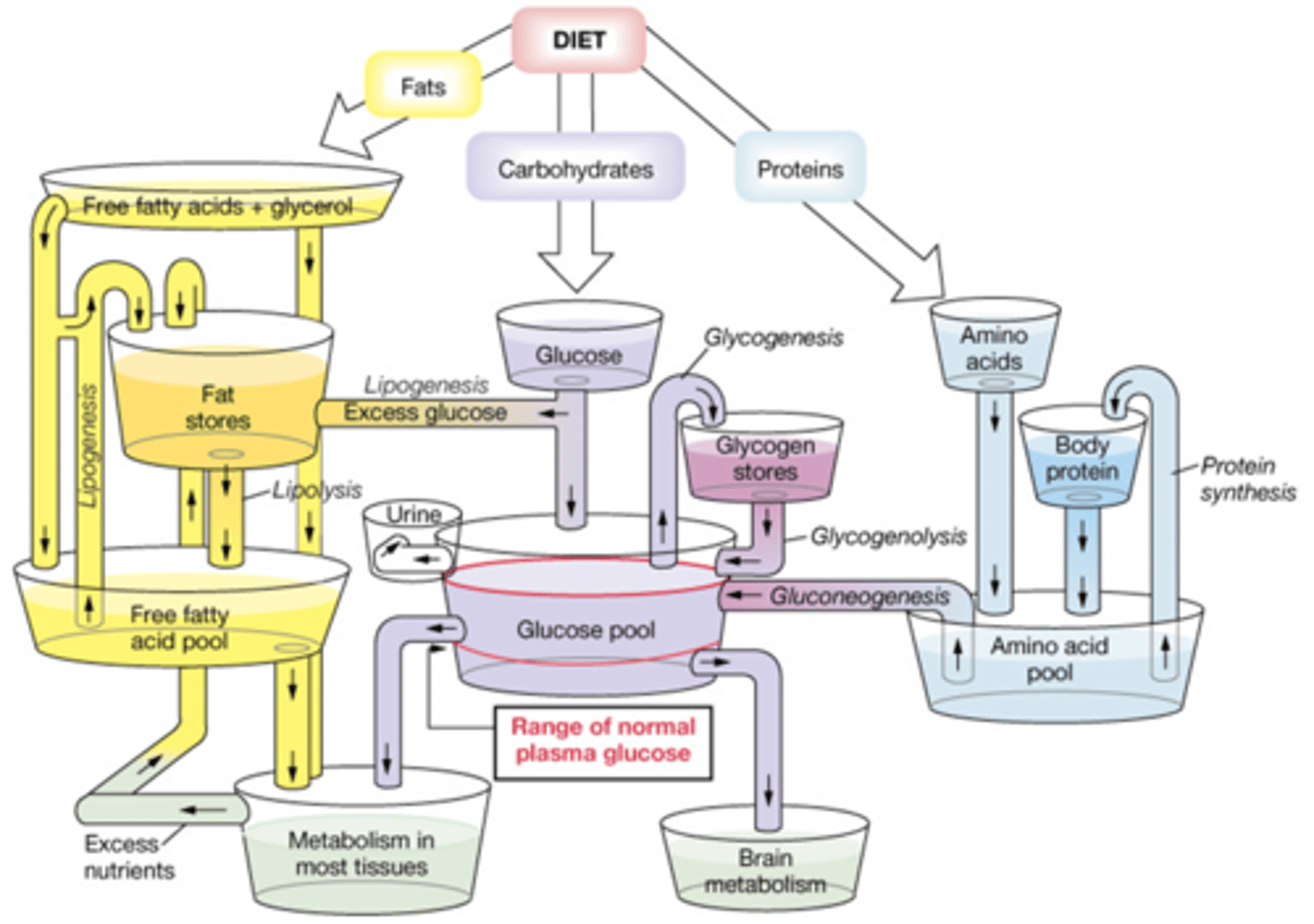
In the Fed state the bodies reversible pathways switch to ___________ process.
anabolic
During the Fed state, carbs are used for ___________ or ____________.
Metabolism
Stored
During the Fed state, AA are used to make __________ and ___________.
Proteins
Stored
During the Fed state, FA are turned into ____________ so they can be ___________.
Triglycerides
stored
In most cells, Fatty acids undergo ________________ ____________ for energy. Or they enter _________ and are reassembled into triglycerides for storage.
Beta-oxidation
Adipose cells (If you want to access the FA you can break down the TG via lypolysis)
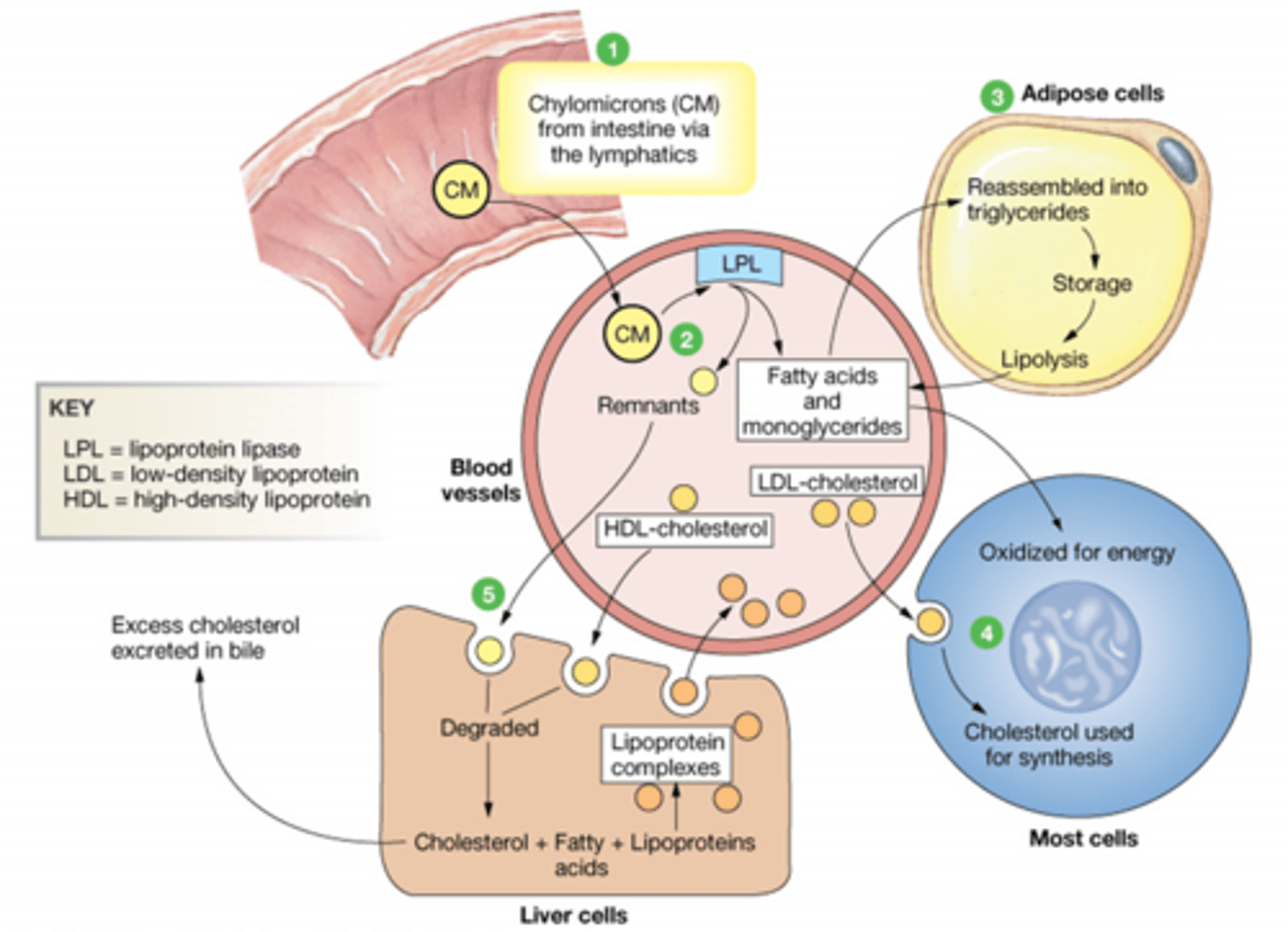
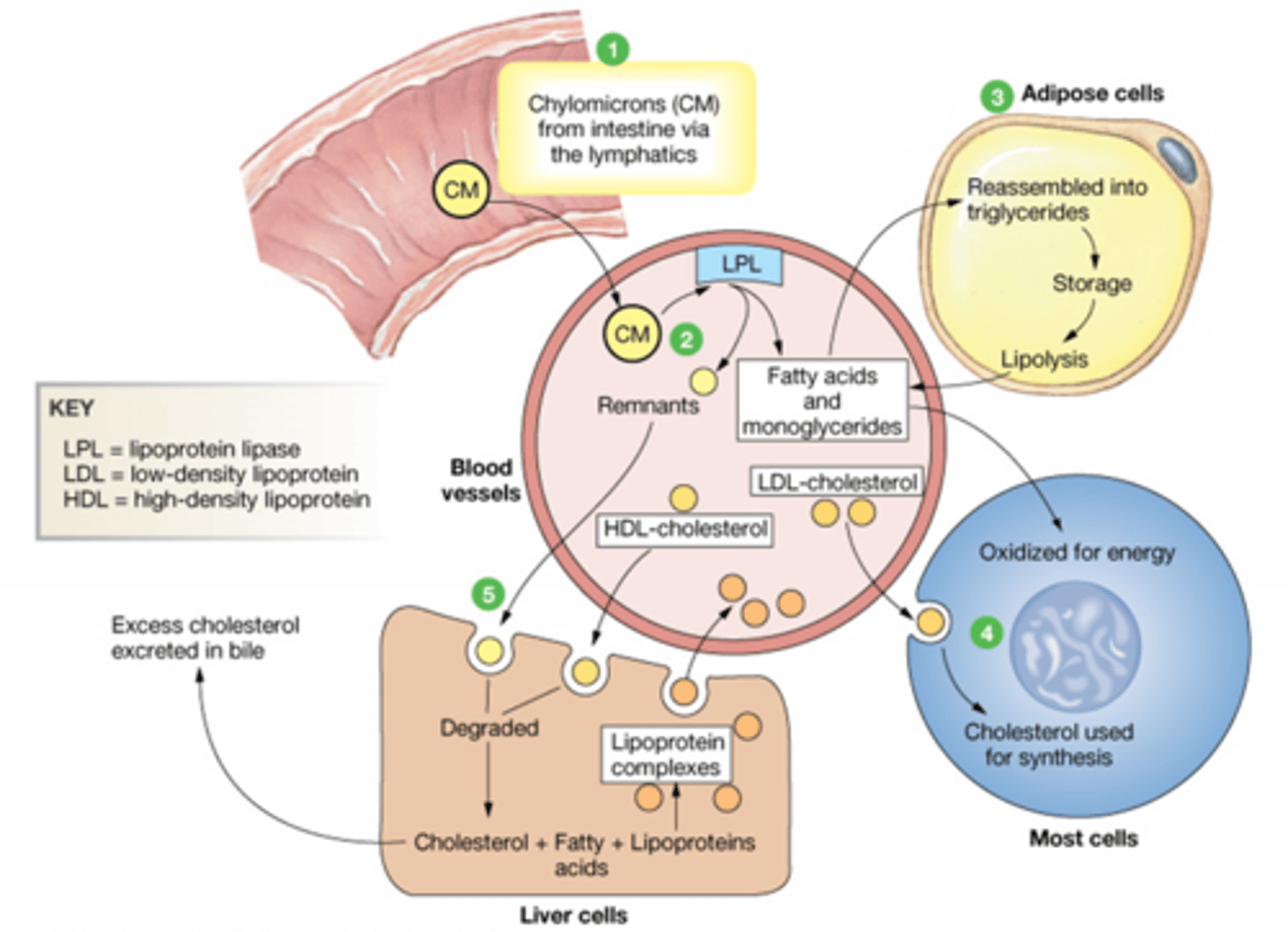
Describe the transport of Lipoproteins in the Fed state
CM enter from instestine, and interact with Lipoprotein lipase. This splits the CM into FA+Monoglyceride and CM remnant. The remnant goes to the Liver to be degraded.

Lipoprotein complexes are made in the
Liver
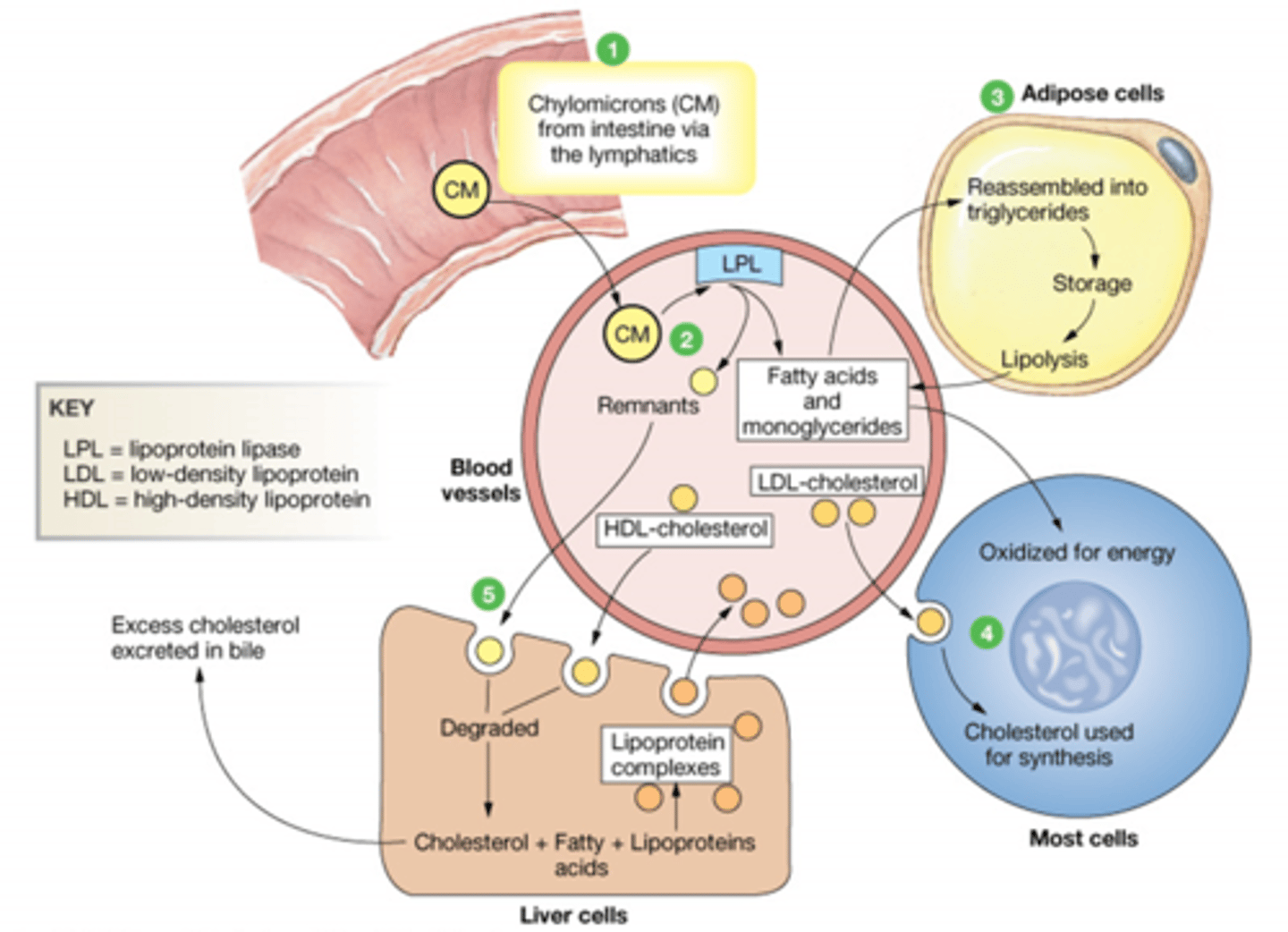
The liver has what 3 kinds of fats?
Cholesterol
FA
Lipoproteins

What happens to HDL once it leaves the liver?
It travels around the body picking up cholesterol and returning it to the liver. Once its done it is degraded.
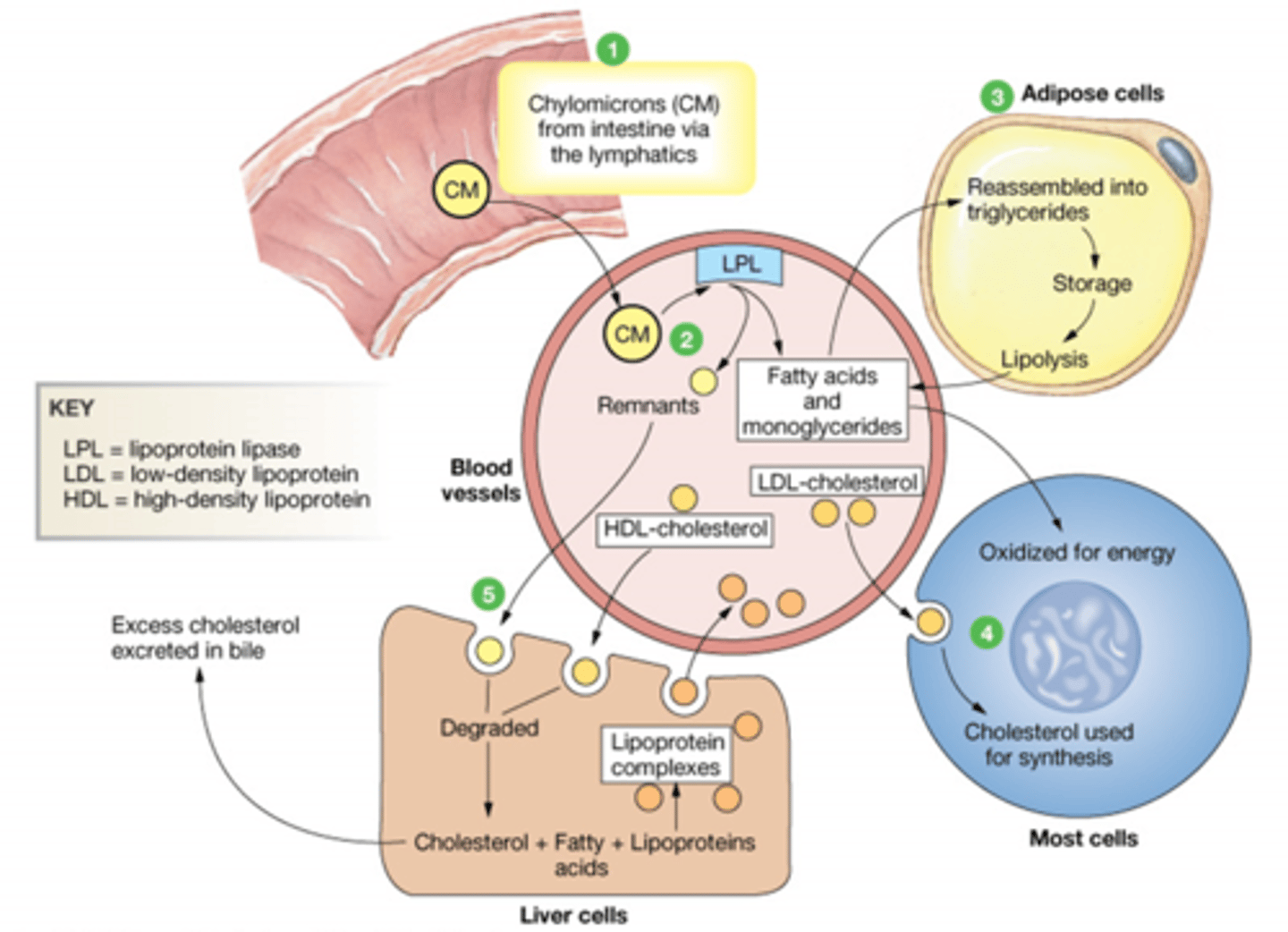
Excess cholesterol in the liver can be excreted in the ____________
Bile
During the fasting state the pathway shifts to _____________ to maintain energy levels needed for metabolism
catabolism
How does glucose reach cells during the fasted state?
Glycogen (stored glucose) - Glycogenolysis
Glucose in the blood to reach organs in need
Describe the fasted metabolism?(Liver, Muscle, Brain,Adipose cells)
Liver - glycogen becomes glucose
Brain - use only glucose and ketones for energy
Muscle - glycogen can be used for energy (convert to pyruvate) Muscle also can be use FA and break down their proteins to AA that enter the blood
Adipose cells-
Triglycerids becomes free FA+glycerol

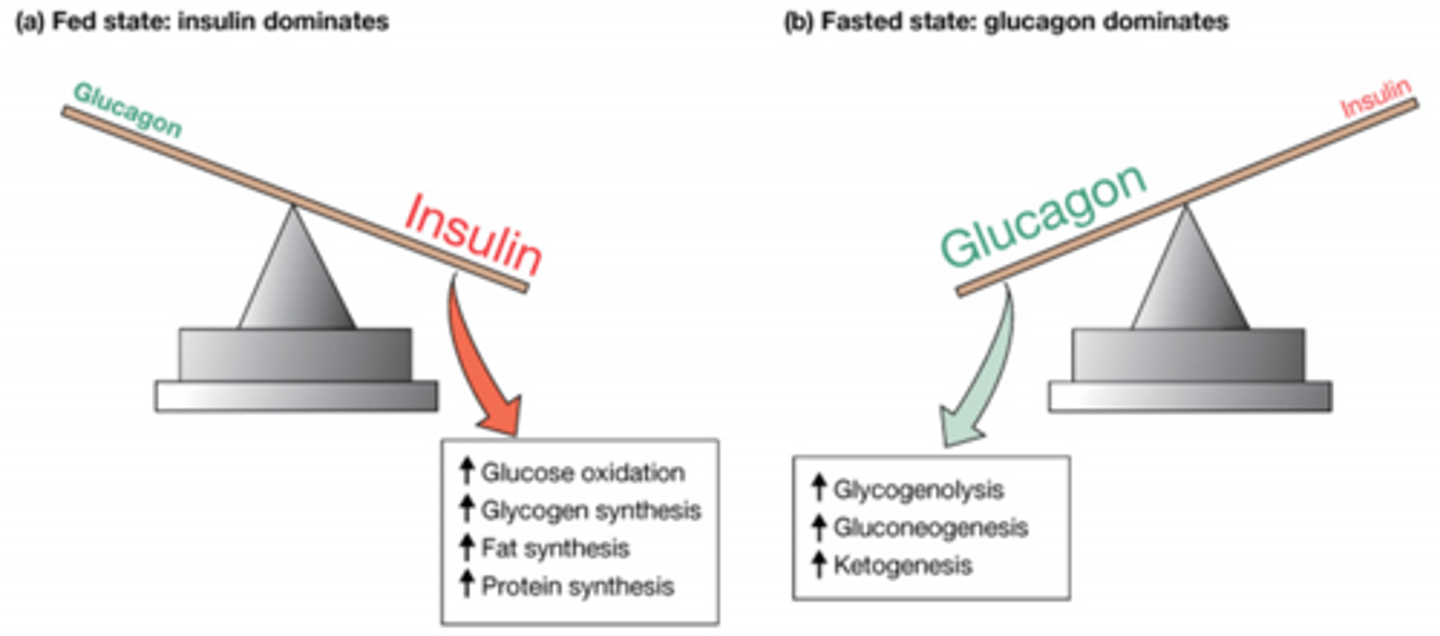
How does the ratio of insulin to glucose change as we go from fed to fasted state?
Fed: more insulin than glucagon
Fasted state: more glucagon than insulin
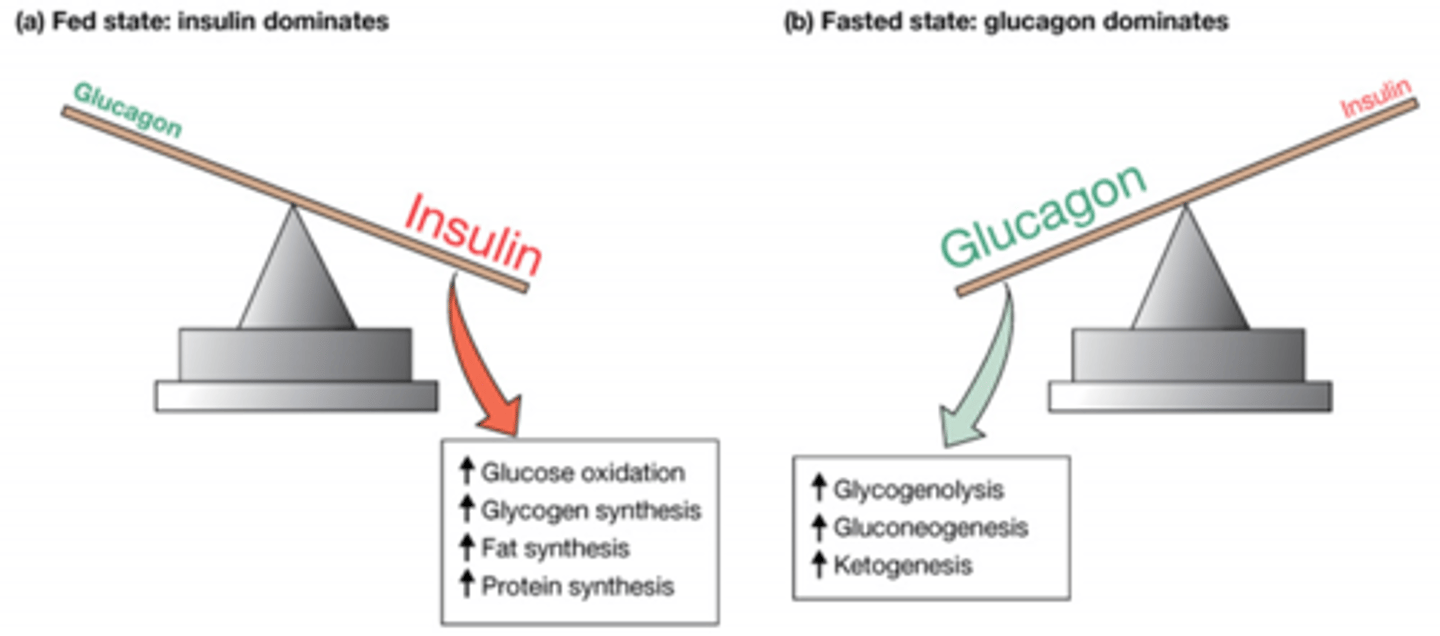
Insulin increase which glucose, glycogen, fat and protein pathways?
Glucose oxidation (cell respiration)
Glycogen synthesis
Fat synthesis
Protein synthesis
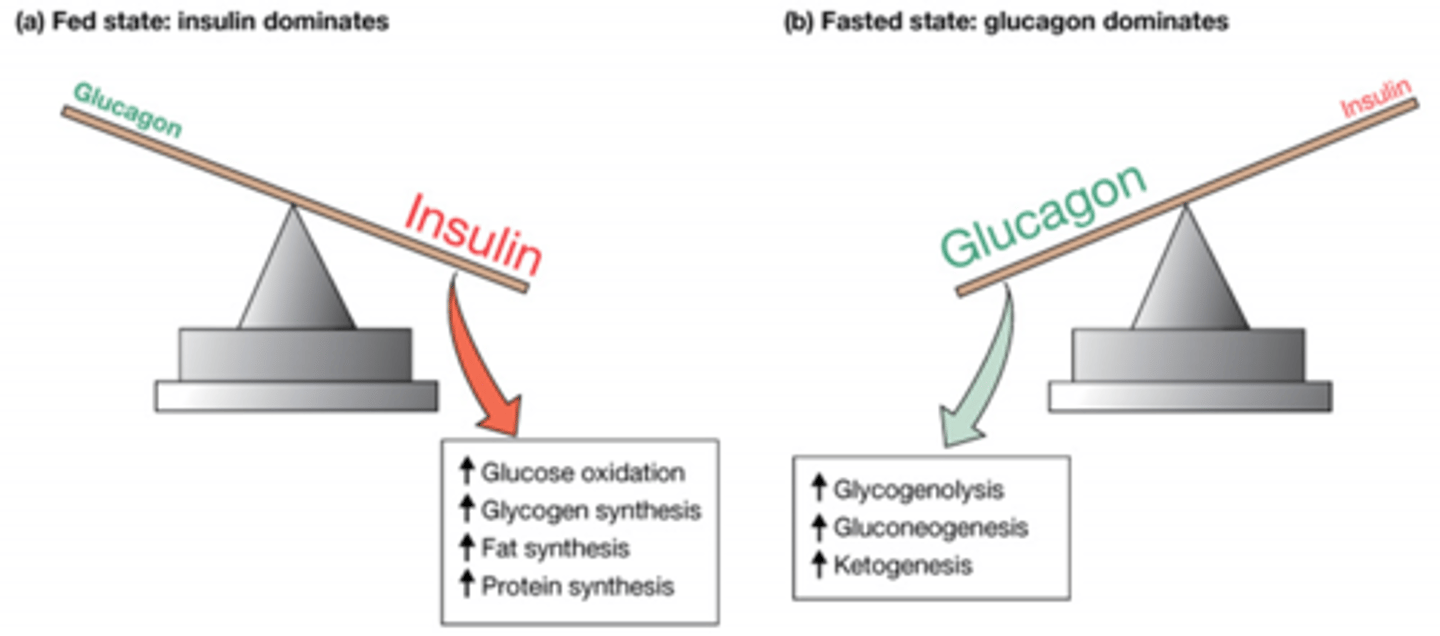
Glucagon increase which Glycogen, glucose, and keto pathways?
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Ketogenesis
What cells produce insulin?
beta cells of pancreas.
What is the purpose of insulin
To increase cellular uptake of glucose
What cells produce glucagon?
alpha cells of pancreas.
What is the purpose of Glucagon?
Increase blood glucose
What do D cells in the pancreas secrete?
somatostatin (inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion)
Glycogen and glucose synthesis during the fed and fasted state
Fed: more Glycogen
Fasted: more glucose
______________ (hormone) dominates in the Fed state
Insulin
____________ is not necessary for glucose uptake in active muscle, which makes it another avenue by which diabetics can regulate their glucose
Insulin
Describe the process by which insulin causes the cell to uptake glucose (increase transport activity)
Insulin binds to a tyrosine receptor
Which changes the shape of the receptor into a dimer which activates second messenger pathways
2nd messengers: alter protein synthesis and existing proteins
Metabolism is changed
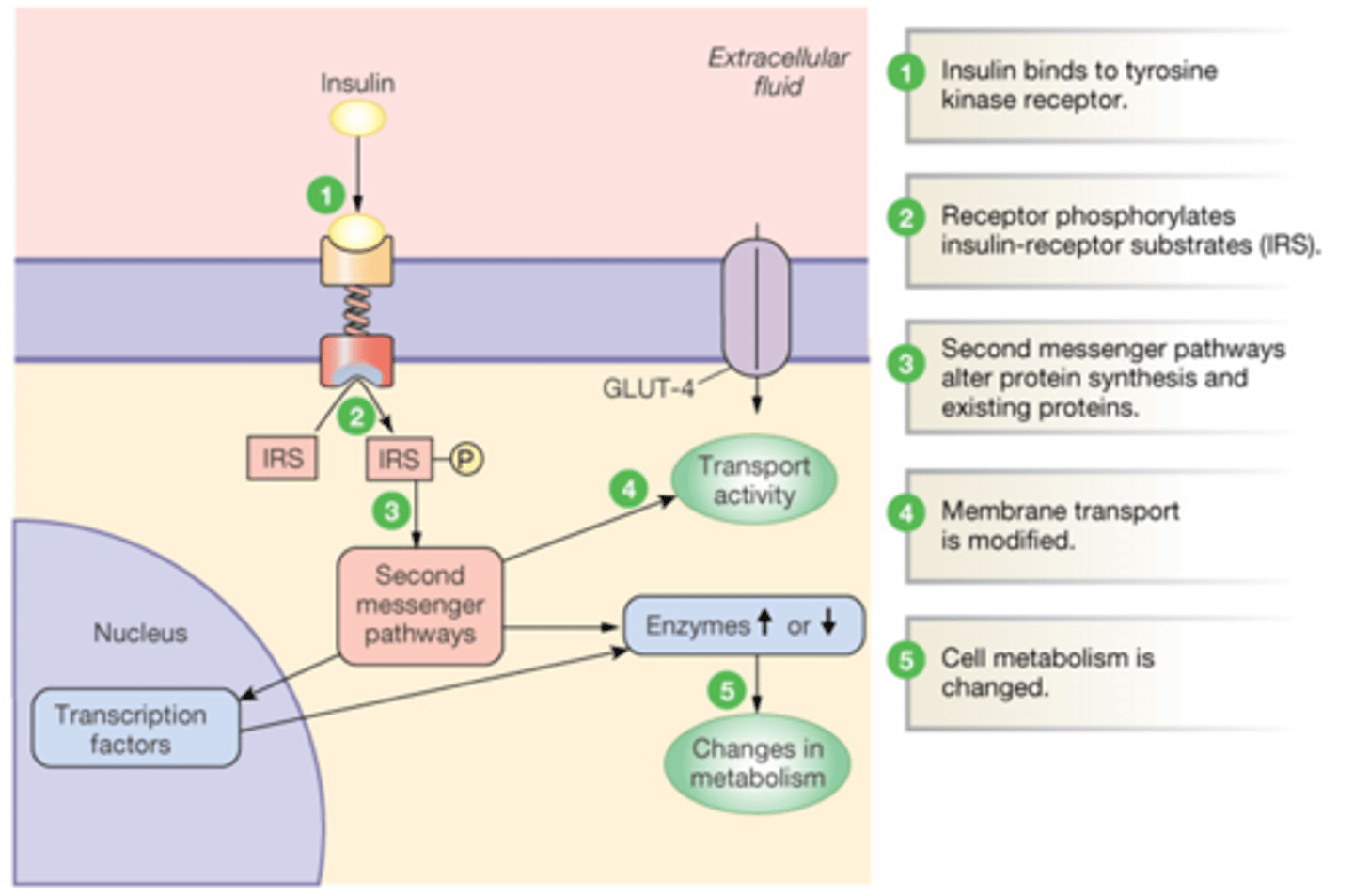
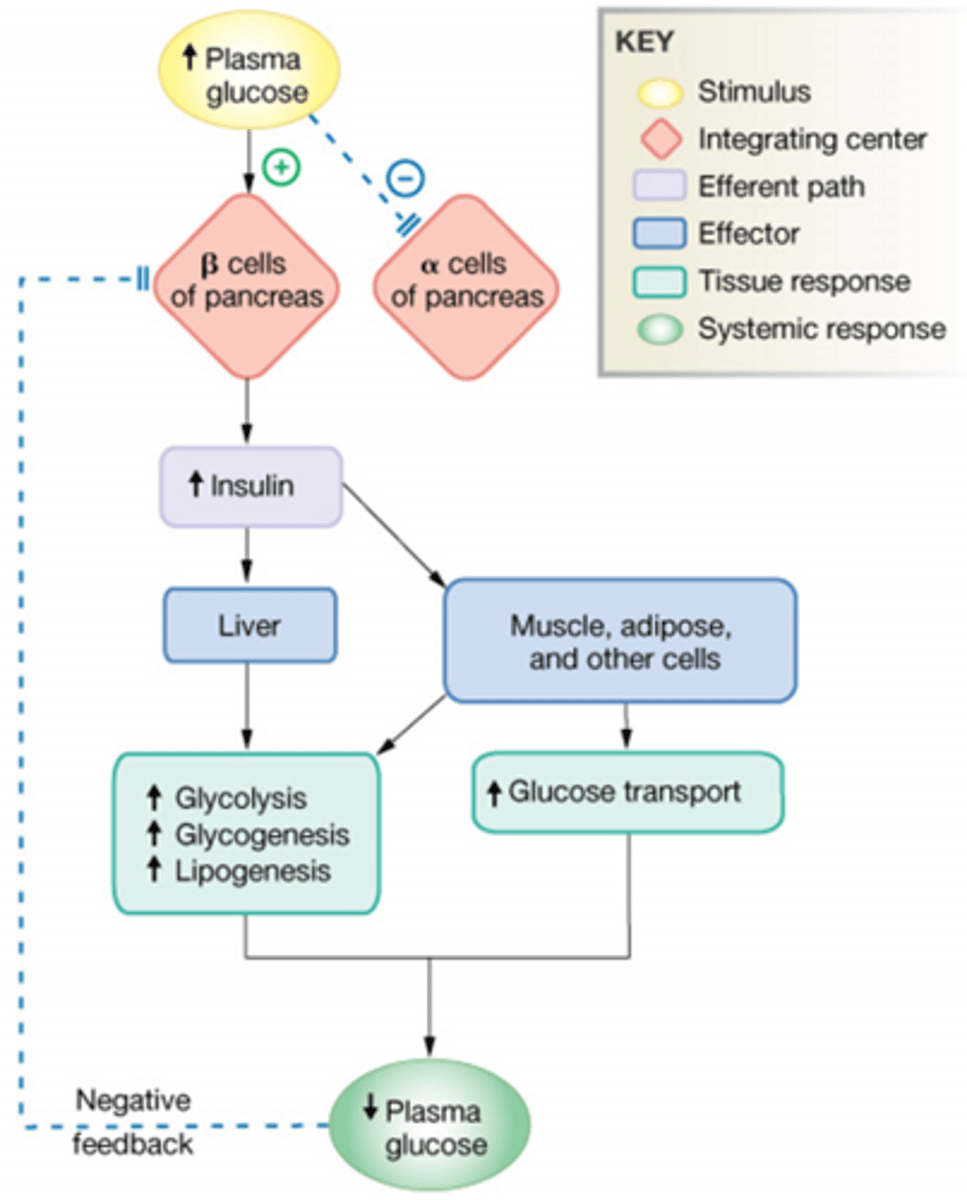
Summarize the cascade of events during the fed state
Increased Plasma glucose
Inhibits Alpha cells, B-cells are stimulated
Alpha stimulates insulin, goes tot he liver increases several sythesis and decrease plasma glucose.
______________ (hormone) dominates in fasting metabolism
Glucagon
Glucagon prevents _____________________/comma by increasing the plasma glucose.
hypoglycemia
_________ is the primary target to maintain blood glucose levels
Liver
Summarize how the process of increasing plasma glucose when plasma glucose decreases
Alpha cells are stimulated, increase glucagon, to liver, increases the production of some products.
diabetes insipidus
lack of vasopressin (ADH)
What is the consequence of diabetes insipidus?
Extreme thrist and urination, so you have a high volume being excreted with a low osmolarity.
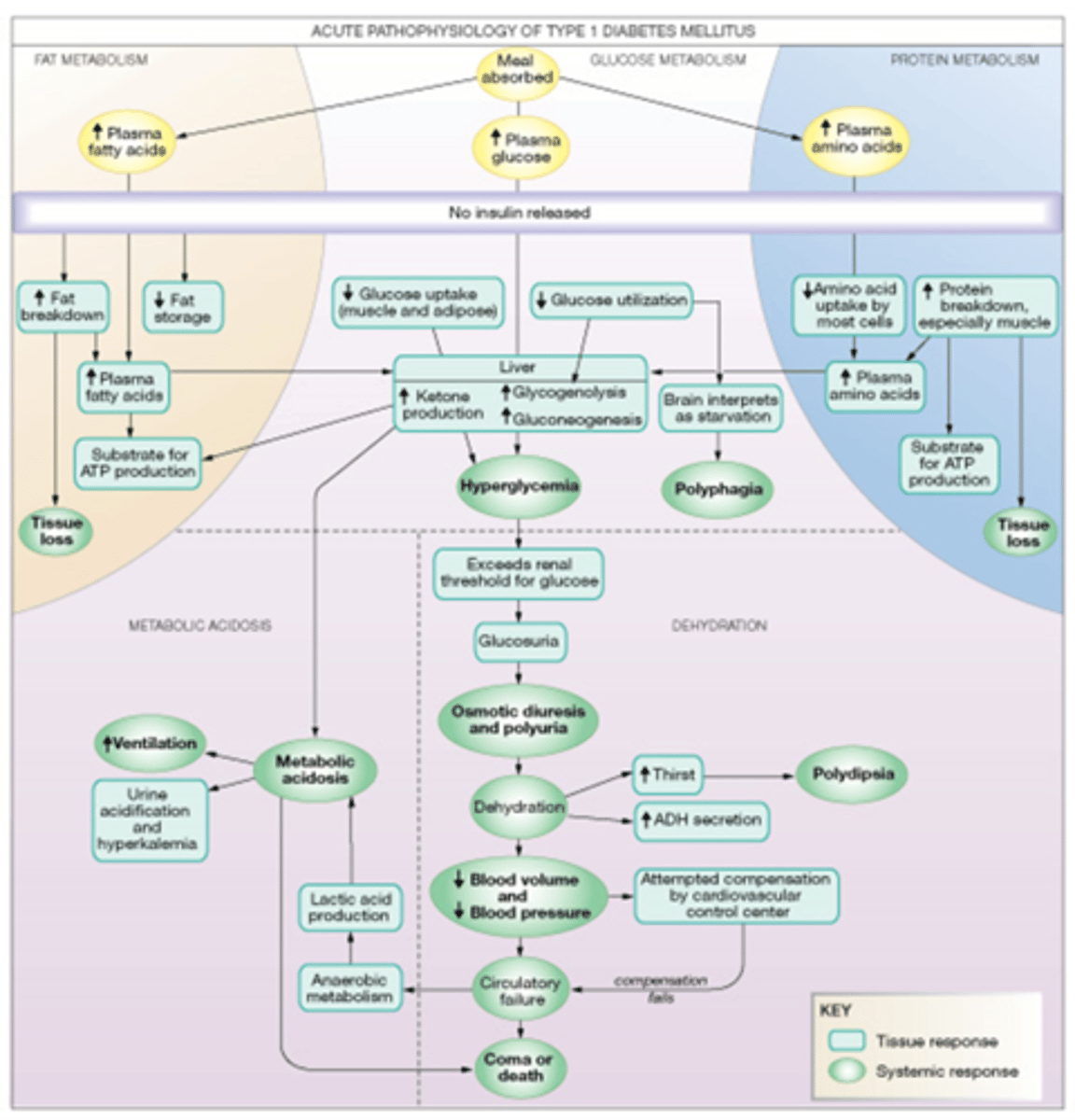
In Type 1 Diabetes there is no secretion of ____________ meaning that the ______cells have been destroyed
insulin
Beta
Of all diabetes, ___________% have type 1
10
Type 1 diabetics get what 5 consequences without proper treatment
Ketosis
Glucosurea
Diuresis
Acidosis
Coma
Summary of Type 1 diabetes
90% of diabetics are what type?
Type 2
Type 2 diabetics have insulin_____________ which keeps the glucose in the blood _______
insulin
high
Type 2 diabetes maybe due to issues in the _______ or ________ transduction
receptor
signal
What are the chronic complications of Type 2 diabetes?
Atherosclerosis
Renal Failure
Blindness (retina pulled out of place)
Blood vessels become fragile
Gangrene
The fasting plasma glucose of a diabetic is ____________ than a normal subject. What happens after eating
higher
increases for a significant amount of time