GG101 FINAL EXAM
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
geographic themes
location, place, human environment, interaction, movement, region
Systems Theory
model/representation of a portion of the natural or human landscape
Open system
energy CAN flow in/out
matter CAN flow in/out
photosynthesis
Closed System
Energy and matter CANNOT flow in/out
Steady State of Equilibrium
overtime it changes, but it remains a steady state
Dynamic state of equilibrium
when there is a major change, something that makes it jump
Threshold or Tipping Point of equilibrium
means it can no longer maintain its own character
Sea ice
frozen ocean water
Positive Feedback
encourages change in the system
Albedo
amount of k down that is reflected or scattered from the surface and or the atmosphere
How do you calculate albedo?
albedo = Kup/Kdown x 100 = % value
ex:
200up/300down= 0.666 × 100% = 66%
What type of surfaces have high albedo ?
any surfaces that are light in colour (light colours reflect more light)
snow
sand if light coloured
mirror
concrete
water CAN be unless its dark underneath
What type of surfaces have a low albedo
tar
dirt
asphalt roads
Negative feedback
discourages change in the system
abiotic spheres
atmosphere : thin layer surrounding earth
hydrosphere : sum of water on earth
cryospehre : frozen portion of hydrosphere
lithosphere : earths crust and a portion of the upper mantle below the crust
biotic spheres
biosphere: interconnected web that links organisms with their physical environment
systems in geosystem
energy-atmosphere system
water, weather and climate system
earth-atmosphere interface
soils. ecosystems and biomes
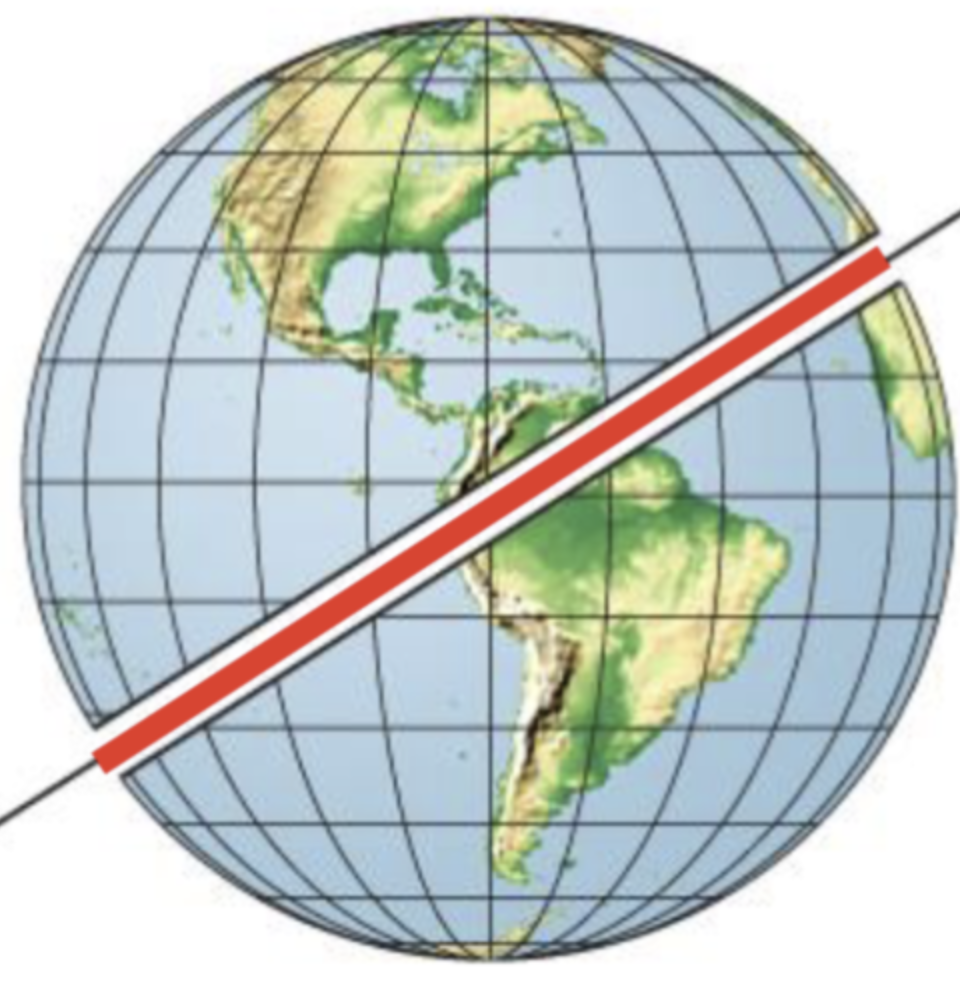
Great Circle
line traced on the surface of the sphere when a plane passes though its centre
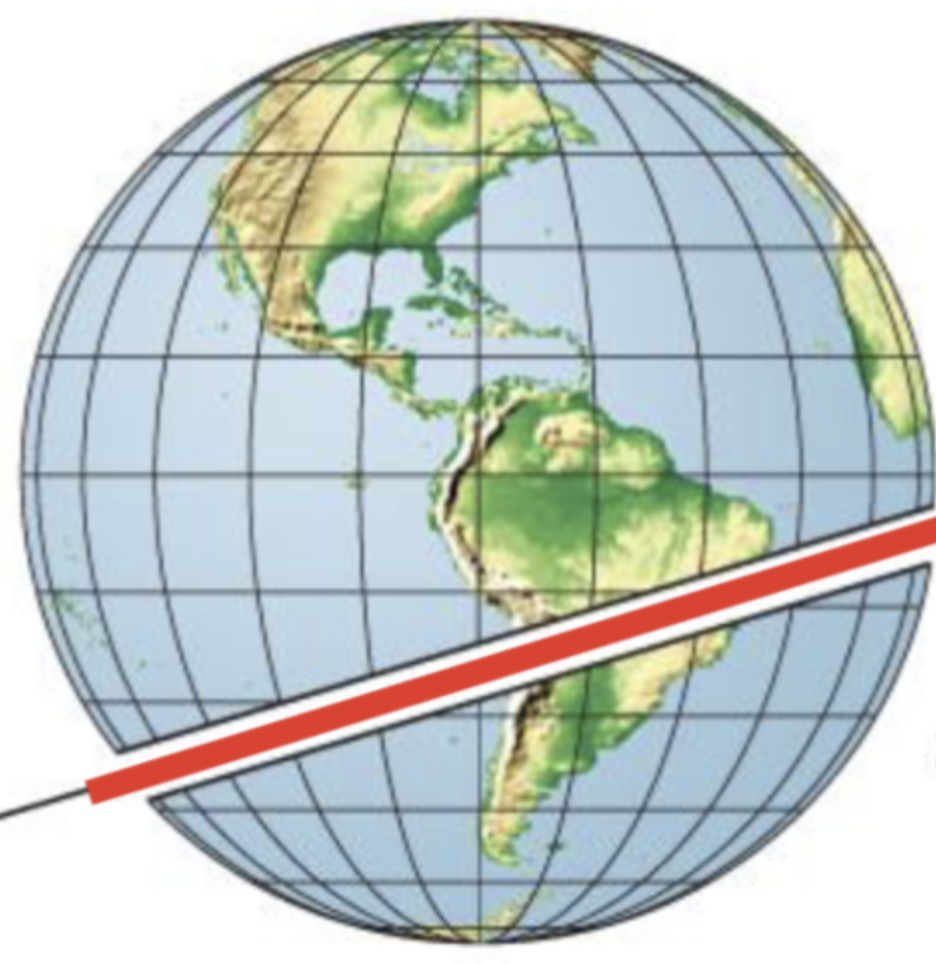
Small Circle
line traced on the surface of a sphere that DOES NOT pass through the centre
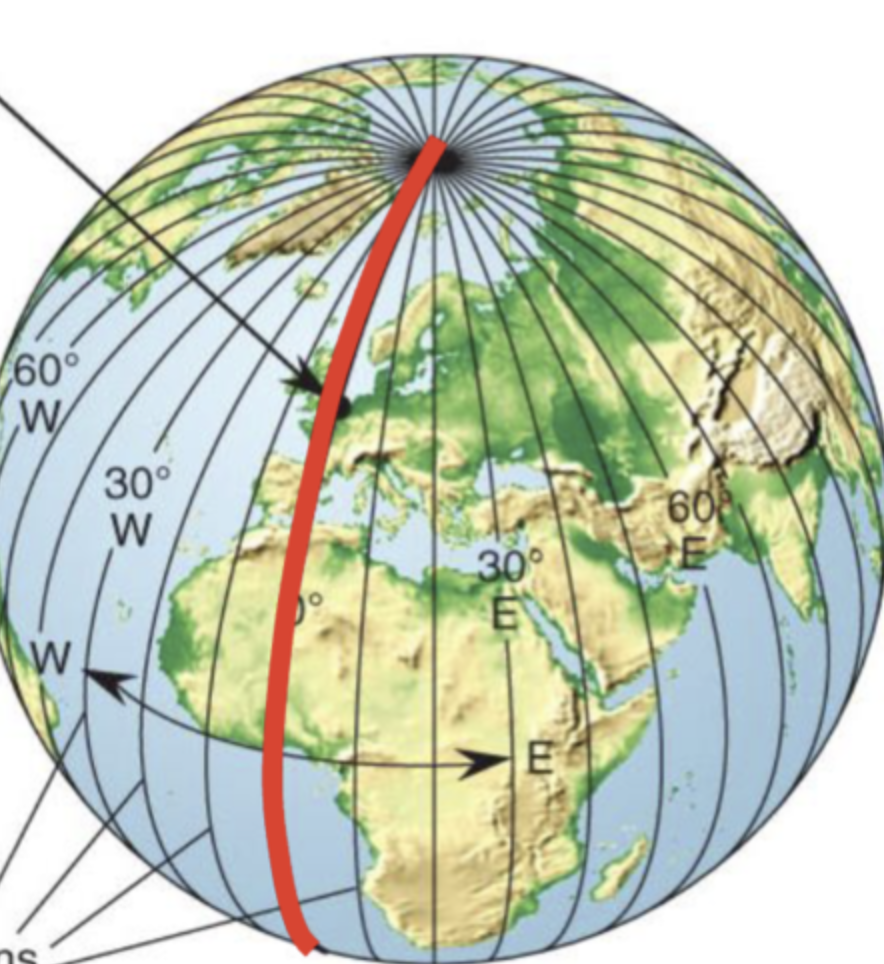
Meridians
aka Longitude
line that runs North-South (connecting poles)
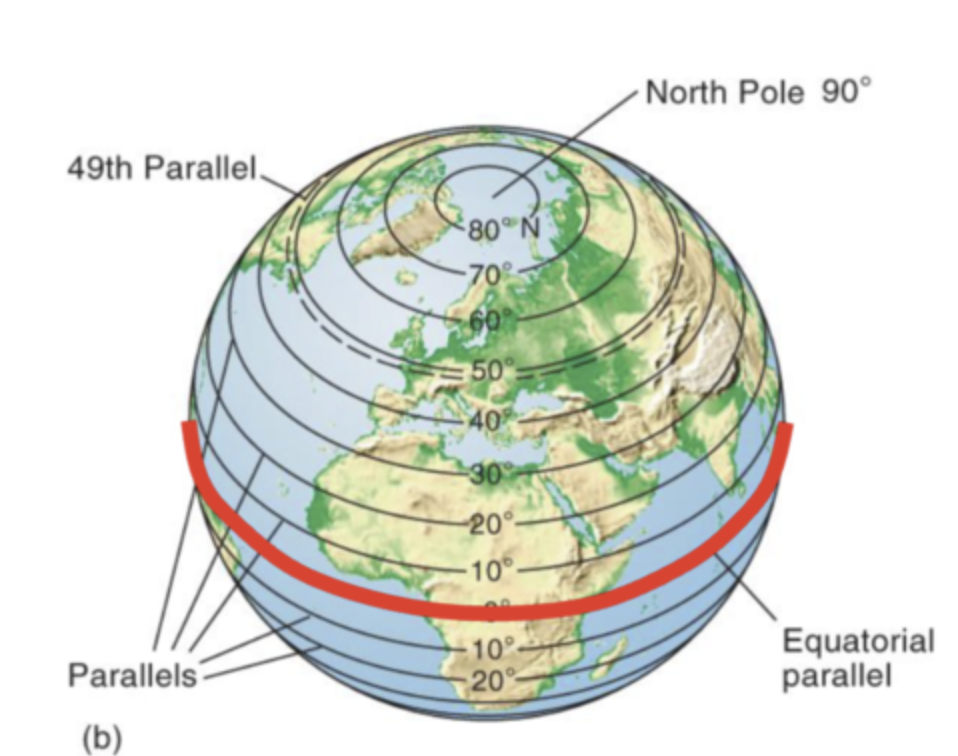
Parallels
aka Latitude
lines that run East-West, parallel to or along the equator
To locate objects, use a network of
meridians and parallels
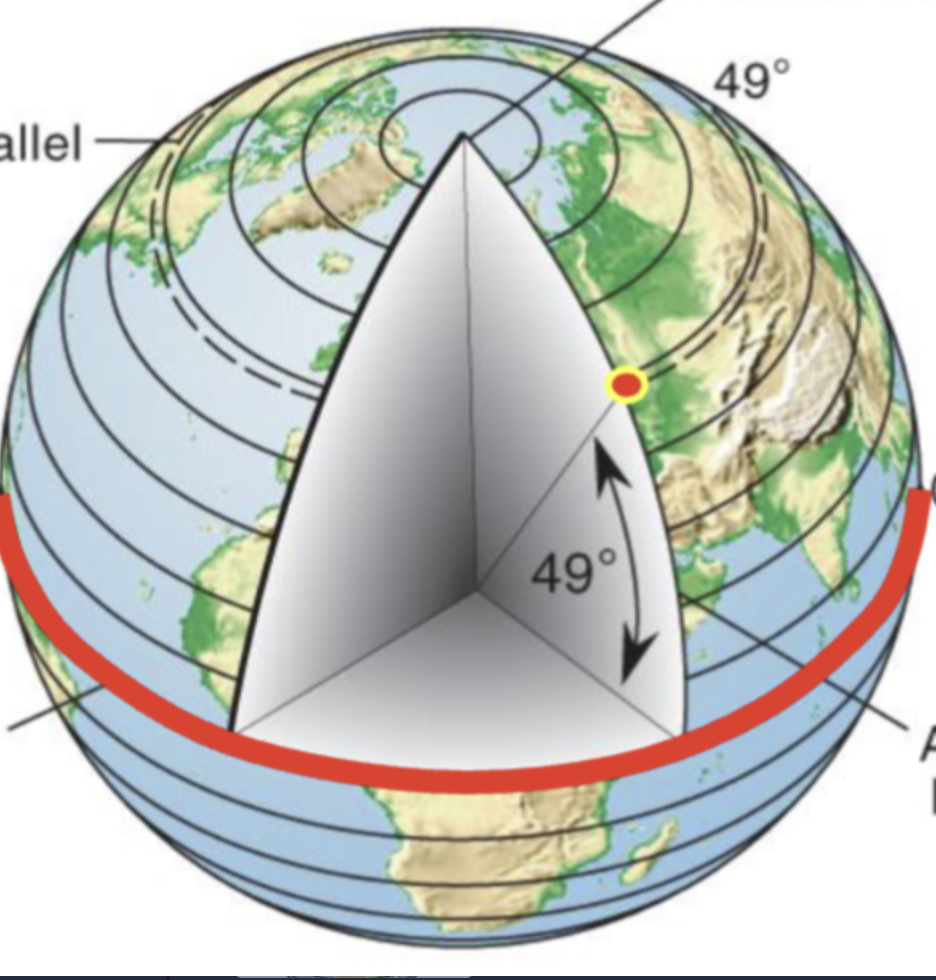
Latitude
horizontal line
distance from north or south of the equator measured from the center
Longitude
vertical line
distance from east or west of a fixed point to line (prime meridian) measures from the centre of the earth
Higher Latitude
those nearer the poles
Lower Latitude
those nearer the equators
Equator is assigned a value of …
zero
values range from 0 degrees to 90 degrees or south of the equator
How do you read lat/long
90 degrees NORTH of the equator is the north pole
90 degrees SOUTH of the equator is the South Pole
Prime Meridian is a datum from which ___ is determined
longitude
Map projections
shape (conformal)
area (equal area, equivalence)
azimuth (true direction)
equidistance (true distance)

What does each letter represent
A/D: energy sources
sun and satellite orbiting earth, info being sent out
B: energy through atmosphere
transfers though atmosphere
C: interactions at surface
D: Record at sensor
E: Transmit data
F: analyses of data
G: product
Passive system
measure reflected sunlight emitted from the sun
ex: using a camera without flash. the camera is not sending the light out, it uses naturally emitted light from the sun. without the sun, there would be no passive remote sensing
Active system
has their own light/illumination
sends a pulse out and measures the backscatter reflected to the sensor
example: when you take a picture with flash, the camera sends its OWN source of light. then the camera captures the reflected light back into the lens
Radar
radio waves being sent out and bouncing back
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Data processing tool for gathering, manipulating and analyzing geographic information
Use of GIS
Automate mapping of features
analyze distributions (areas, connections, routes)
examine spatial relations
Electromagnetics Radiation
energy that propagates though space, in the form of an advancing disturbance in electric and magnetic fields
What colour is the shortwave and long wave
shortwave - blue
longwave - red
heat is also long wave
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
the HIGHER the objects temperature
the GREATER the amount of radiation emitted per unit of surface area
HOTTER = MORE
RADIATION/ENERGY
Wien’s Displacement Law
the higher an objects temperature, the shorter the wavelength of maximum radiant emission
HOTTER = EMIT SHORTER WAVELENGHTS
K down is
sun emitting energy (incoming energy)
incoming
K up is
outgoing (reflected) shortwave radiation
outgoing
L up is
longwave radiation emitted from the surface
outgoing
L down is
longwave radiation reaching the surface from the atmosphere or other object
incoming
Net Radiation (Q*)
balance of incoming and outgoing radiation
Net radiation (Q*) equation
Q*= incoming - outgoing
Q* = (K down + L down) - (K up - L up)
Axial Tilt
earth rotates on its polar axis (23.5 degrees from the vertical)
Sun Sets/rises in which direction
sun sets at the west
rises in the east
Atmosphere
mixture of gases and suspended liquids and solids
Aerosols
liquids and solids (but not water or ice) that are suspended in the atmosphere
What happens with MASS as we increase height (altitude) on the atmosphere?
as we move upward, the density decreases (mass per unit volume)
What happens with PRESSURE as we increase height (altitude) in the atmosphere?
as we increase height in the atmosphere, pressure decreases
Four layers of temperature
thermospehre
mesospehre
stratosphere
troposphere
Troposphere
1st layer of the atmosphere
0-17 km above Earth's surface
- contains most atmospheric water vapor. (temperature decreases with increasing altitude, pressure decreases)
tropopause is the boundary between troposphere and stratosphere
Stratosphere
2nd layer of the atmosphere
15-50km above troposphere
ozone layer
temperature increases
Mesosphere + Troposphere
Mesosphere
3rd layer
50-80km
temperature decreases
Mesopause between mesosphere and thermosphere
Thermosphere
4th layer
temperature increases
Ionosphere
absorbs gamma and x-ray radiation
Ozonospehre
a region in the upper stratosphere where ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION IS ABSORBED
What is Energy Balance
shortwave coming from sun
some is direct
some is diffuse
Solar radiation that is reflected off of the earths surface back to space is called:
outgoing shortwave (reflected not absorbed)
Possible outcomes of Electromagnetic radiation contact with matter
Transmission (goes through an object)
Refraction (reflected off of things)
changes of light speeds which the angle
reflection (like a mirror)
Sensible heat
heat we can feel, measure with thermometer, sense
Latent Heat
the heat required to convert a solid into a liquid or vapor, or a liquid into a vapor, without change of temperature
What happens to shortwave radiation absorbed at the surface?
The atmosphere emits longwave radiation, much directed towards the surface (L↓)
The longwave radiation is absorbed at the surface and the process repeats
What does the sun radiate?
thermal infra-red
is continental climate influenced by large bodies of water
no
is marine climate influenced by large bodies of water
depends of proximity
What decreases with altitude
pressure, density and temperature
Pressure gradient force
drives air from High air pressure to Low air pressure
stronger where the pressure gradient is steep
Coriolis force (effect)
crosses isobars at right angles
Coriolis force produces Coriolis effect
Friction Force
friction acts on wind when the air approaches th surface
slows the wind speed by exerting drag
Friction causes the geostrophic wind to..
slow, which reduces the Coriolis force and therefore the wind turns in the direction of the PGF
Humidity measures
hygrometer or psychomotor
specific humidity (q)
mass of water vapour in grams per kg of air
absolute humidity
mass of water vapour in grams per kg
mixing ratio
mass of water vapour in kg per kg mass of dry air
Vapour pressure (e)
partial pressure of water vapour
stability
refers to the tendency of a parcel off air to rise in the atmosphere
an unstable air parcel rises
ELR (Environmental Lapse rate)
rates at which air temperature changes with heigh in the atmosphere
DALR (Dry adiabatic lapse rate)
rate at which a dry (unsaturated) parcel of air cools or warms with height
Unstable example 15 degrees
air parcel is hotter, keeps rising
Stable example 3 degrees
parcel is colder, more dense, sinks
Conditional example 8 degrees
conditional i.e. is it dry or saturated
dry air will sink (stable)
saturated will rise (unstable)
Lifting condensation level (LCL)
the level at which an air parcel becomes saturated (100% rH)
3 basic forms of clouds
stratiform (stratus)
cumuliform (cumulus)
cirroform (cirrus)
four altitudinal classes
high
middle (alto)
low
vertically developed
Cloud classification: Low
up to 2000 m
made of water
stratus, stratocumulus, nimbostratus
Cloud classification : Middle
more than 6000 m
made of ice and water
altostratus, altocumulus
Cloud Classification: High
more than 6000m
made of ice
cirrus, cirrostratus, cirrocumulus
Cloud classification : vertical
surface to 13,000
made of water and ice
cumulus, cumulonimbus
How does fog form?
air temperature must drop to the dew point (saturated air)
commonly formed when moist air cools to its dew point under calm condition
advection fog
warm moist air moving over colder land
radiation fog
clear nights, lots of heat escapes the cold ground, reach Td
Evaporation Fog (aka sea smoke)
water evaporating into colder air above
4 ways that air rises into the atmospehre
convergent (comes from left and right and goes up the middle)
convectional (same as convergent but exponential)
orographic (follows the shape of the hill)
frontal (cold air and warm air collide and bounce back)
cold front
cold air mass moves into warmer air mass
warm front
warm air mass moves unto cooler air mass
cyclone
an enclosed area of low pressure with air circulation in a spiral or vortex
wave cyclone
system of the mid and high latitudes
a moving vortex with warm and cold air masses
runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground