Amino Acids: Structure, Classification, and Biological Roles in Proteins and Neurotransmission
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are amino acids?
Building blocks of proteins; linear heteropolymers of amino acids.
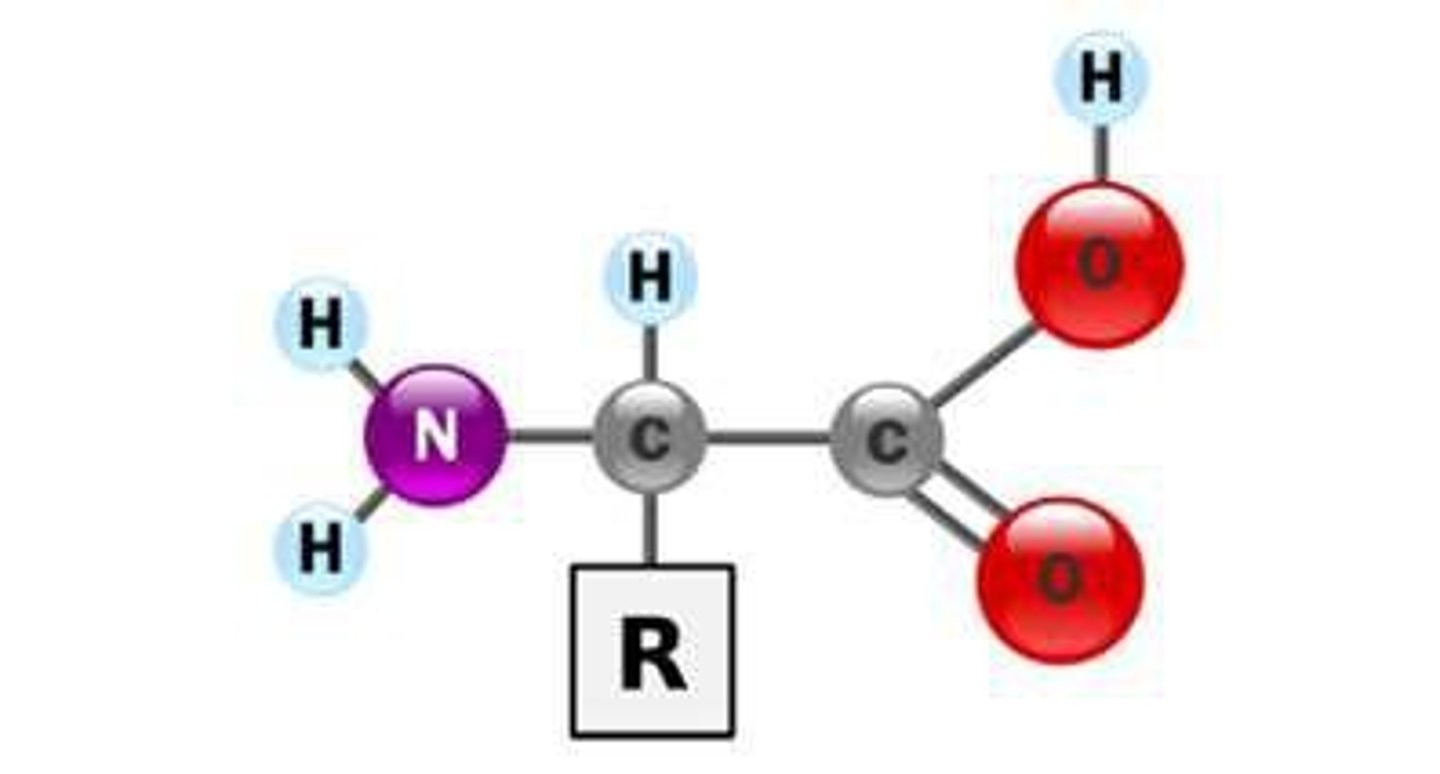
How many different amino acids are there?
20 different amino acids.
What is the significance of the zwitterion form of amino acids?
Amino acids exist as zwitterions at physiological pH (7.4), having both positive and negative charges.
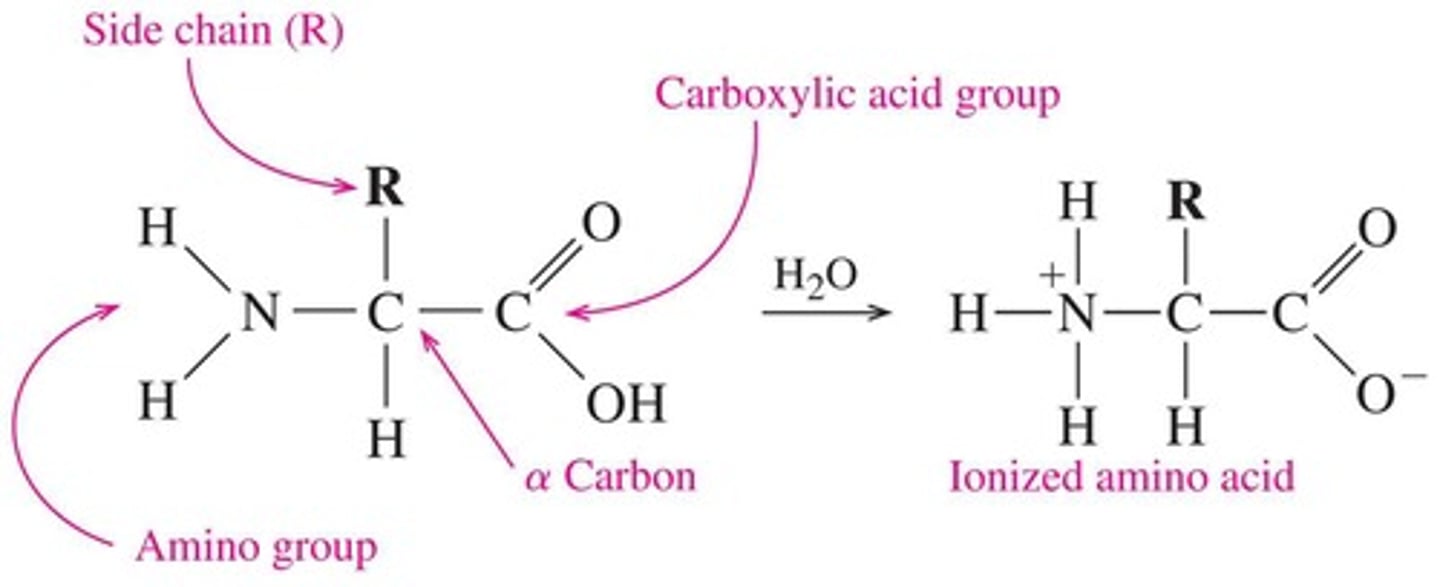
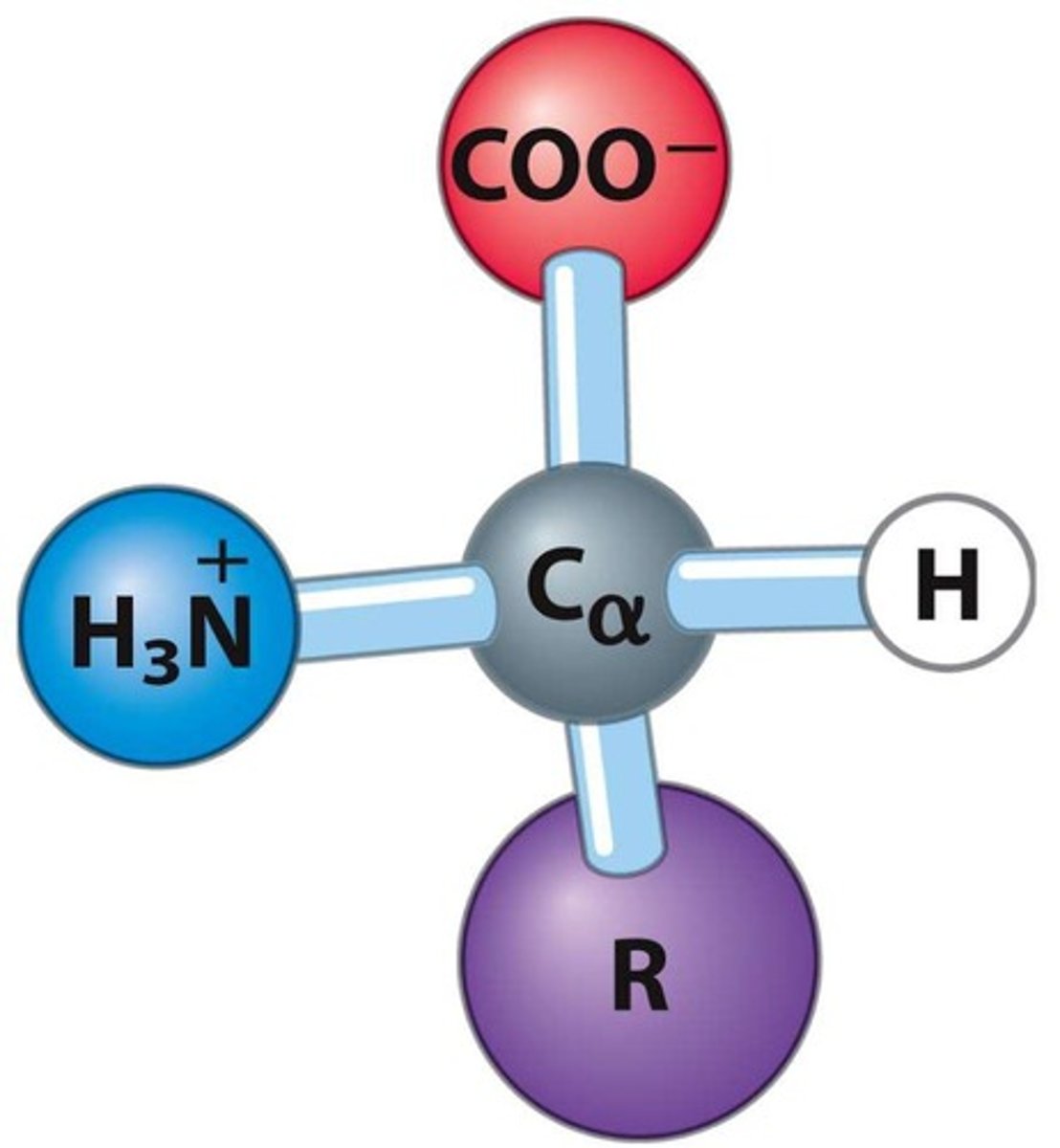
What functional groups are attached to the α carbon of amino acids?
A carboxylic acid group, an amino group, and a hydrogen atom, along with a side chain (R group).
What are the five basic groups of amino acids based on their side chains?
Nonpolar aliphatic, aromatic, polar uncharged, positively charged, and negatively charged.
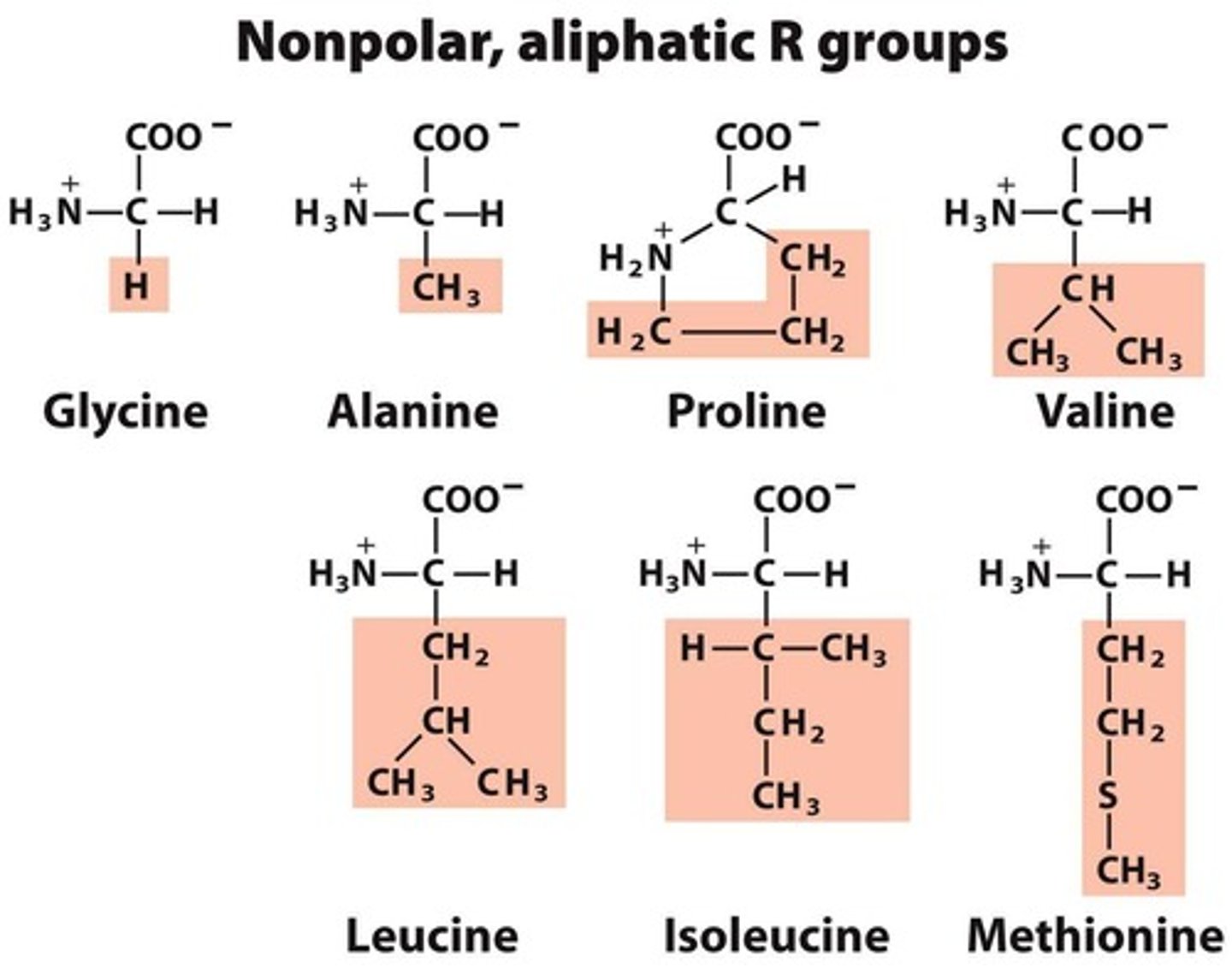
Which amino acid is not chiral?
Glycine (R group is hydrogen).
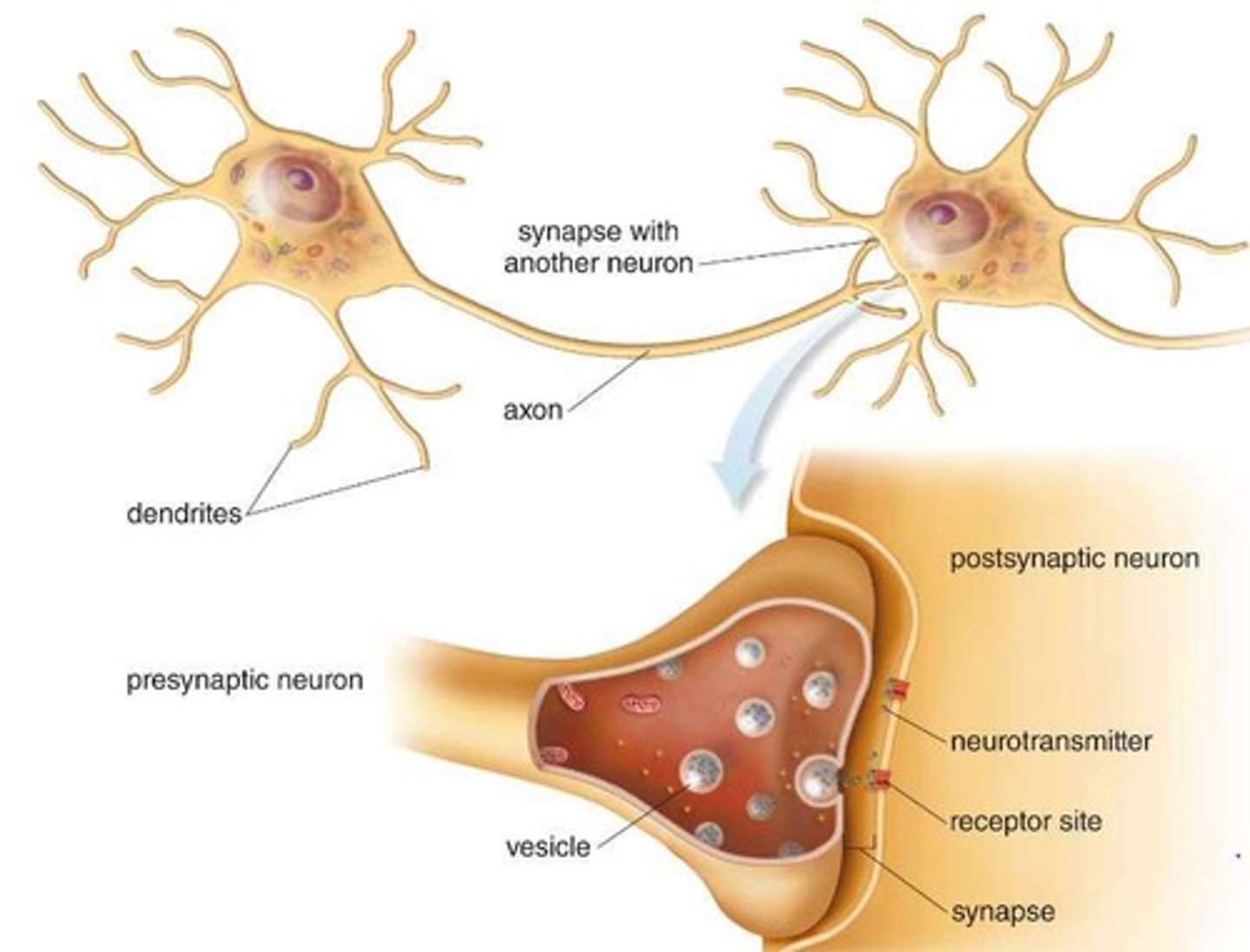
What role do amino acids play in neurotransmitter synthesis?
Amino acids are precursors to important neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate.
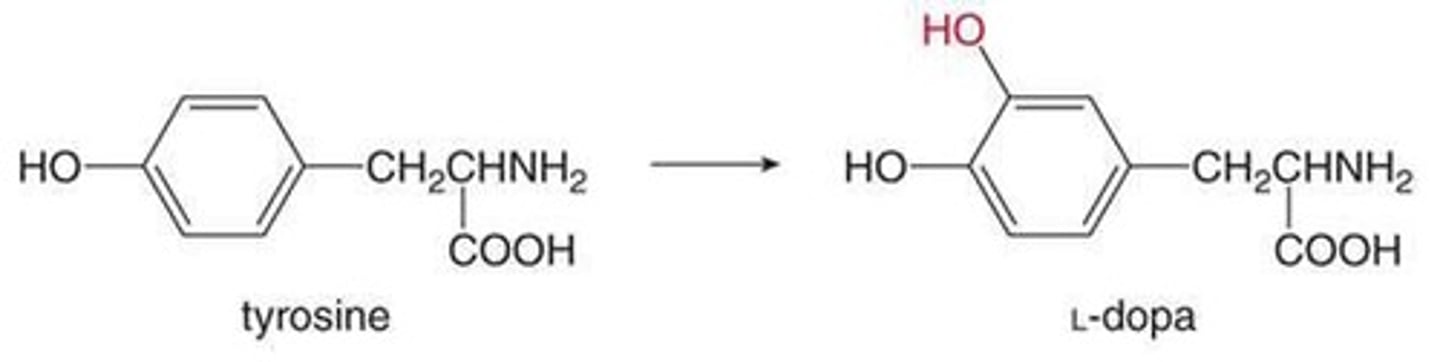
What is dopamine synthesized from?
Tyrosine.
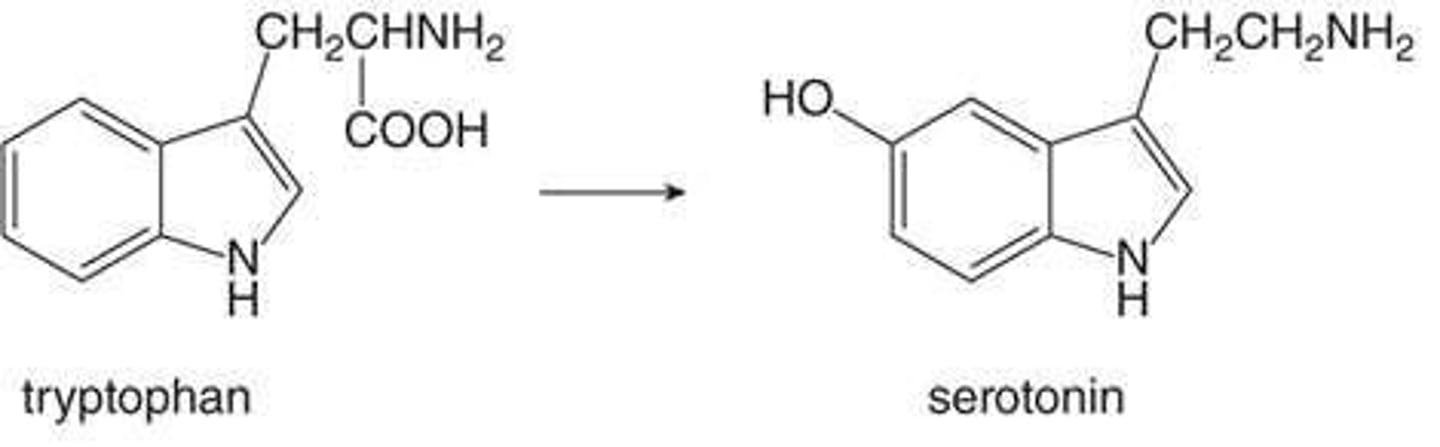
What is the function of serotonin?
Regulates mood, emotion, sleep, temperature, and activity levels.
What is GABA derived from?
Glutamate.
What is the role of norepinephrine and epinephrine in the body?
They are involved in the body's fight-or-flight response to stress.
What is histamine derived from?
Histidine.
What is the function of histamine in the immune response?
Regulates the immune response to bacteria, parasites, and allergens.
What is the role of amino acids in nucleotide synthesis?
They provide carbon and nitrogen atoms for the synthesis of nucleotide bases.
What are the UV light absorption characteristics of certain amino acids?
Amino acid side chains can absorb UV light at 270-280 nm.
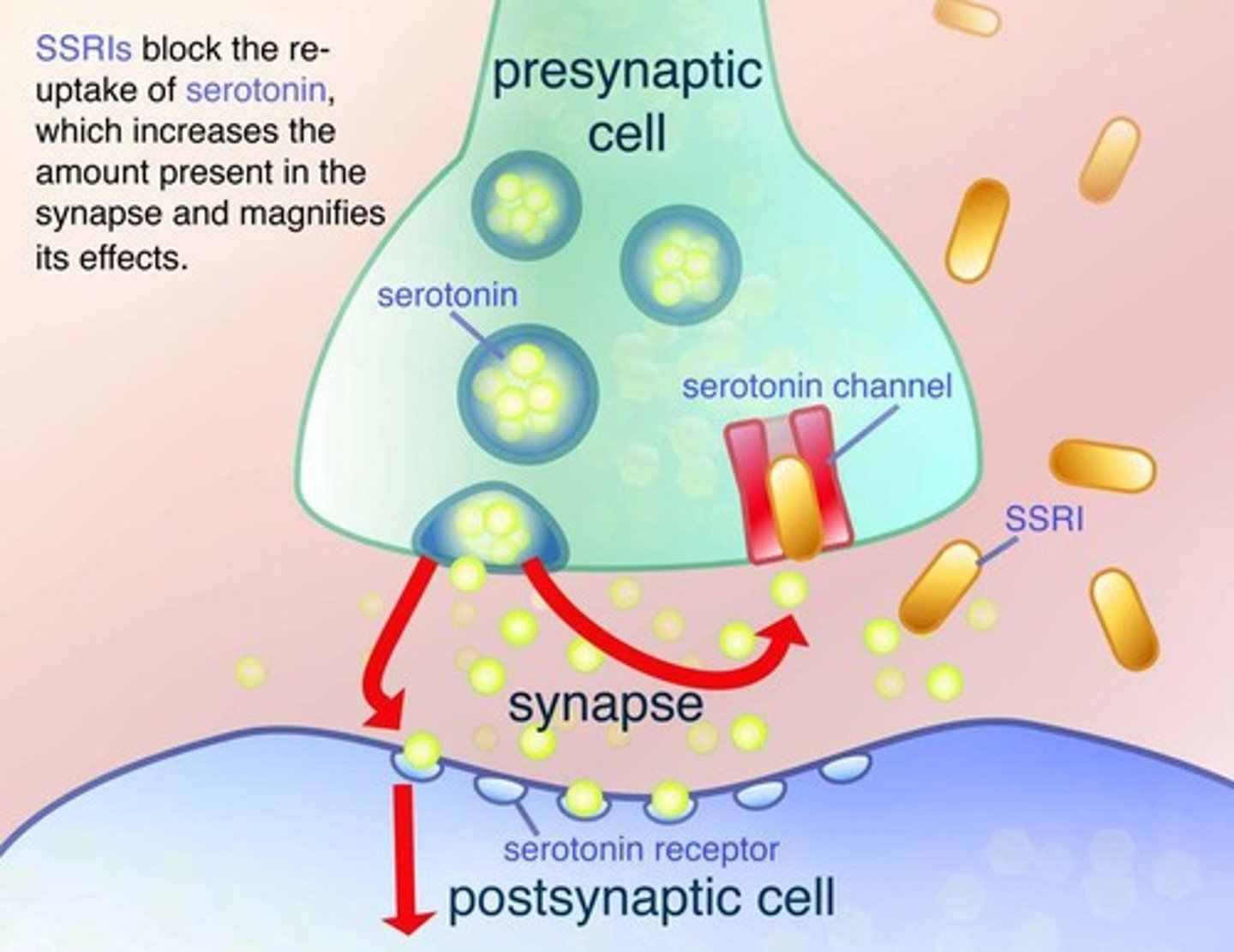
What is the effect of SSRIs on serotonin levels?
SSRIs block the reuptake of serotonin, allowing it to remain longer in the synapse.
What is the significance of the fight-or-flight response?
It prepares the body to respond to danger or stress by releasing hormones like epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What are the effects of elevated dopamine levels?
Can lead to conditions such as schizophrenia.
What neurotransmitter is associated with feelings of well-being?
Serotonin.
What is the primary function of glutamate in the brain?
It is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter, playing key roles in cognitive functions.
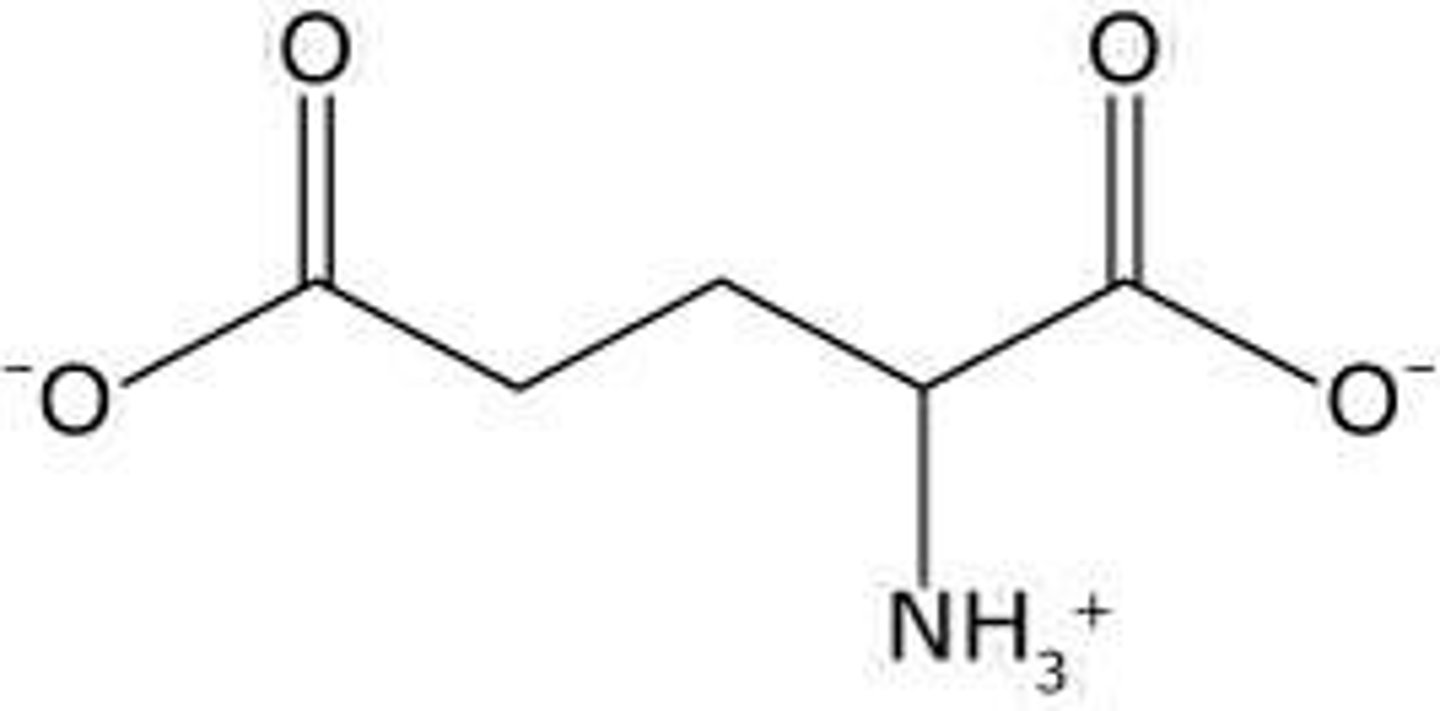
What can an imbalance of glutamate levels lead to?
Conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, seizures, and autism.