microbiology exam 3 material
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
are viruses living things?
no
- cannot reproduce on their own
- requires host
viroids
RNA molecules that infect plants
- have no protein capsid
- are replicated by host RNA polymerase
example of viroid
potato spindle tuber disease
t/f: viroids do the same thing as viruses in terms of replication
true
one difference: viroids do not contain proteins
example of prion
mad cow disease, creutzfeldt-jakob disease
prions
proteins that infect animals
- no nucleic acid component
what is the ideal virus structure?
maximizing capacity while minimizing the required number of genes
primary distinctions of viruses
genome composition (RNA or DNA)
route used to express messenger RNA (mRNA)
what traits are used to organize viruses? (2)
conformation (ss/ds) and genome (DNA/RNA)
aka Baltimore classification of viral genomes
group I virus
double-stranded DNA
group II virus
single-stranded DNA
Group III virus
dourble-stranded RNA
group IV virus
(+) single stranded RNA
group V virus
(-) single stranded RNA
antisense
group VI virus
RNA retroviruses
group VII virus
DNA pararetroviruses
RNA bacteriophage
- found in bacteria
- many are in the (+) configuration
once in the cell, viruses must make (2)
1. genetic material (genome)
2. proteins needed for capsid coats
RNA replicase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
reads RNA template, makes RNA compliment to it
ss DNA bacteriophages
- some contain ss DNA in (+) configuration
- first step is to make complimentary (-) strand
bacteriophage T7
- ds DNA
- infects E. coli (common)
- genome always enters host cell in same orientation
what is one problem with linear ds-DNA replication?
how do eukaryotes and bacteria handle this differently?
DNA gets shorter everytime
- bacteria doesn't have telomeres
- concatemer: numerous genomes join together and prevent DNA shortening
T4 bacteriophage replication
- early genes are transcribed by host RNA polymerase
- rolling-circle replication: phage T4 genome is synthesized within the host cell
- late genes are induced, produce capside and tail proteins
---> late genes also encode lysozyme
t/f: the viruses that infect archaea resemble those that infect enteric bacteria
true
t/f: only ds DNA viruses can infect archaea
false
only ds DNA viruses have been identified so far, but it is not exclusive
plant RNA virus type
(+)-strand RNA virus
what does tobacco mosaic virus cause?
necrosis of plants
enlarges cymplasm
(+) strand RNA viruses of animals
replication requires conversion of the genome into a (-) strand intermediate
(+) strand RNA virus example
Covid-19, poliovirus, Hep C(liver)
RNA replicase can go back up to make (-) strand --> can make another (+) strand
(-) strand RNA viruses of animals
(-) strand RNA viruses are complementary to the mRNA; copied into mRNA by an enzyme present in the virion
RNA polymerase travels WITH the virus (not made in host)
(-) strand RNA virus examples
Rhabdovirus (rabies)
t/f: both (+) and (-) strand RNA viruses effect only Eukarya
false
only (-) strand RNA viruses are known to infect Eukarya
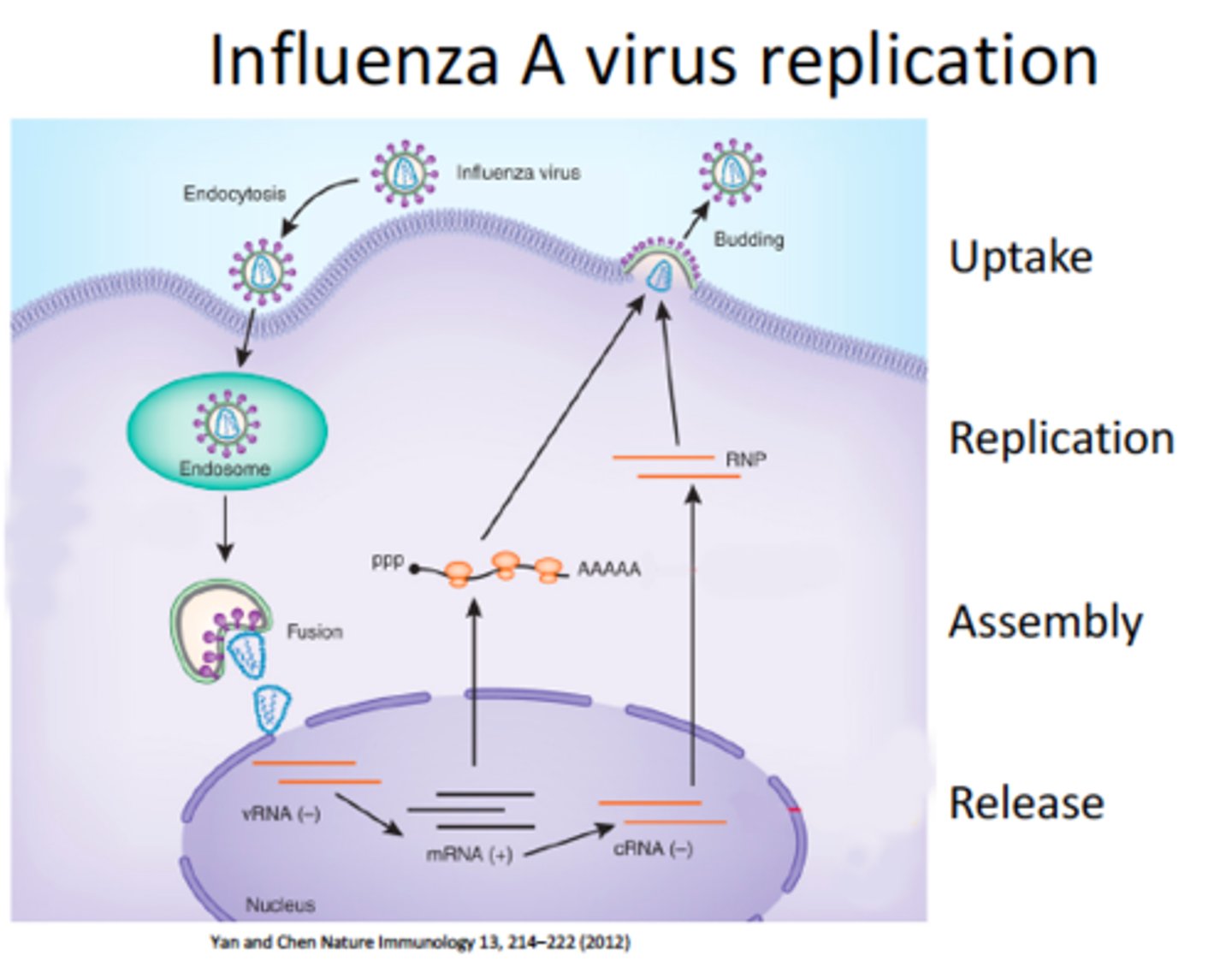
how does influenza replicate?
receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME)
- Endosome releases (-) strand
- segment goes to nucleus with RNA polymerase
- (+) strand is made, used to make more (-) strand and mRNAs
- genomes either return to nucleus or go for exocytosis to other cells
how does herpesvirus cause diseases in humans/animals?
- remains dormant for periods of time
- infection follows attachment of virions to specific cell receptors
- proteins inhibit macromolecular synthesis
--> turn linear DNA circular
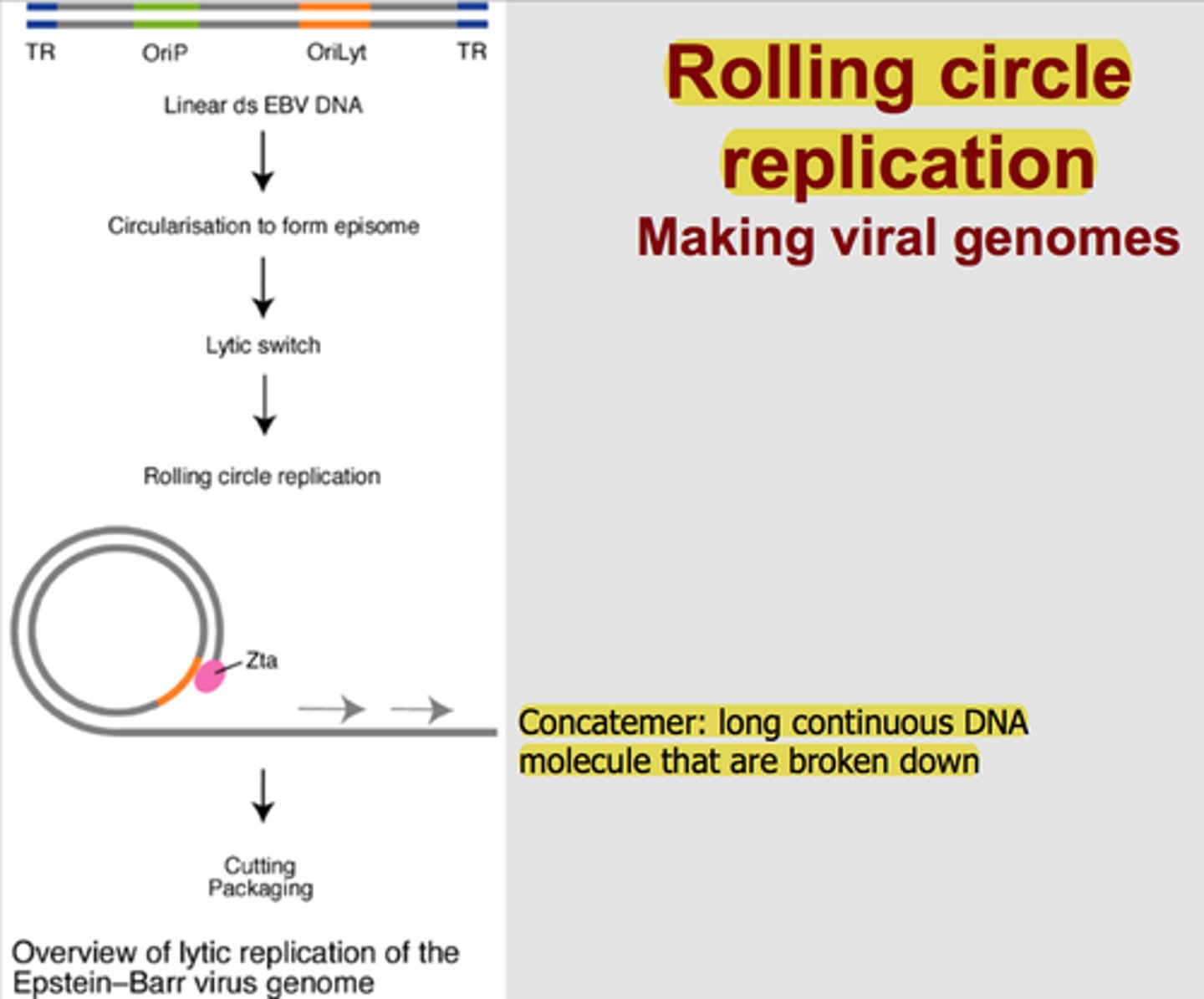
retrovirus
RNA virus that utilizes enveloped virions and reverse transcriptase to make a DNA copy of a genome
hepadnavirus
viral replication occurs through an RNA intermediate (uses reverse transcriptase)
tiny, only partially dsDNA, circular
what happens to extra DNA on the ends following reverse transcriptase?
serves as an artifact of the process
dsDNA gets inserted into host genome via integrase
can viral genomes get orphaned throughout evolution?
yes
- genes get passed on without being a virus (remain in DNA)
t/f: humans share more retroviral insertion sites with chimps than gorillas
true
epidemiology
the study of occurrence, distribution, and determinants of health and disease in a population
how do infectious and non-infectious disease rates compare in developed v. underdeveloped countries?
diseases (both types) cause significantly more deaths in underdeveloped countries
chronic infections
host and pathogen survive
well-adapted pathogen lives in balance with its host
acute infections
pathogen can be selective force
new natural pathogens sometimes emerge for which the host has no resistance
pandemic
widespread, usually worldwide
endemic
constantly present in a population, usually at low incidences
incidence
number of new cases of a particular disease in a given period of time
prevalence
total number of new and existing cases in a population in a given period of time
outbreak
occurs when a number of cases of a disease are reported in a short period of time
subclinical infections
diseased individuals with no/mild symptoms (carriers)
steps of disease progression
1. infection: organism invades host
2. incubation period: onset of symptoms
3. acute period: worst
4. decline period: symptoms subside
5. convalescent period: regain strength
reservoirs
sites in which infectious agents remain viable and from which infection of individuals can occur
zoonosis
any disease that primarily infects animals
occasionally transmitted to humans
how do epidemiologists follow transmission of a disease?
correlating geographic, climatic, social, and demographic data
how are pathogens classifed?
mechanism of transmission
steps in common: escape from host, travel, entry into host
2 modes of pathogen transmission
direct, indirect
direct host-to-host transmission
an infected individual transmits a disease directly to a host via an intermediate
indirect host-to-host transmission
transmission is facilitated by a living/non-living agent
vectors
living agents that spread disease
fomites
non-living agents that spread disease
why might the transmission of a virus peak in the summer?
a vector is required
west nile virus (mosquito)
why might the transmission of a virus peak in the winter?
a fomite is utilized
more people are indoors
common-source epidemic
result from common exposure to a single source of infection over a period of time
ex. poisoned water hole
host-to-host epidemic
the disease shows a slow, progressive rise and a gradual decline
ex. influenza, chicken pox
why is coevolution between a host and its parasite common?
parasites become less lethal overtime in order to survive
herd immunity
the resistance of a group to an attack by a disease to which a large proportion of the members of the group are immune
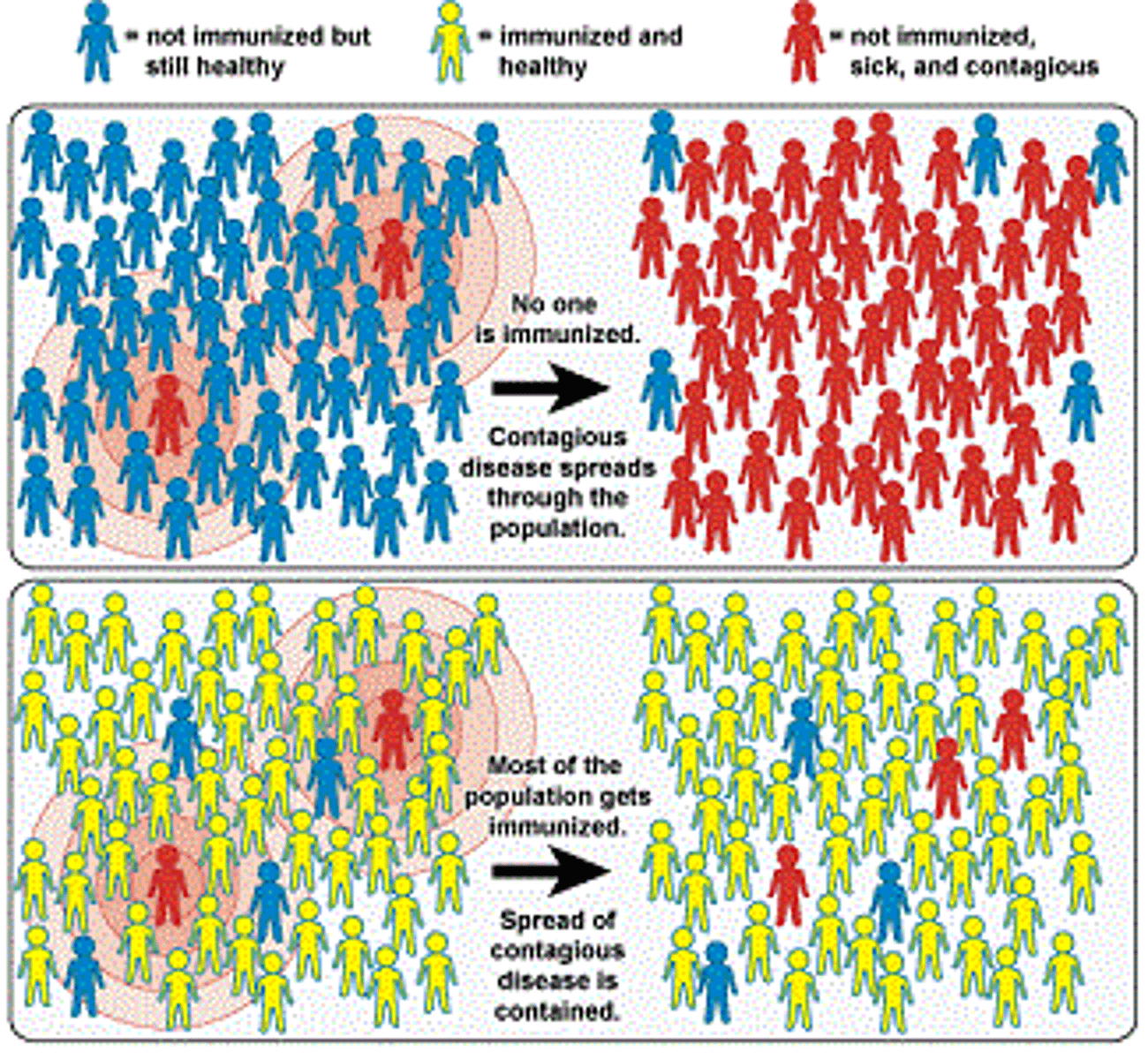
t/f: everyone in a population must be vaccinated to obtain herd immunity
false
the majority do (decreases ease of transmission)
how does AIDS spread?
bodily fluids
what is AIDS?
RNA retrovirus that attacks the immune system
opportunistic infections
infections that occur in individuals who do not have healthy immune systems
complicates epidemiology --> makes it difficult to determine cause of death
why is there no vaccine for RNA?
has an error rate of 10 during replication
--> quick evolution time
--> targets reverse transcriptase / RNA primer
healthcare-associated infections (HAIs)
infection acquired during admission to a healthcare facility
nosocomial infection
reasons for HAIs
- patients have low resistance
- overcrowding
- certain treatments increase risks
- use of antibiotics has selected / antibiotic-resistant organisms
controls for transmission of pathogen (4)
- immunization
- quarantine
- surveillance
- pathogen eradication
emergence factors
- human demographics/behavior
- techonology/industry
- economic development and land use
- international travel and commerce
- microbial adaptation and change
- breakdown of public health measures
- abnormal natural occurrences (climate change)
biological warfare and bioweapons
the use of biological agents to kill a military or civilian population
- easy to produce/deliver
- safe for use by offense
- able to kill in a consistent manner
why was B. anthracis used as a bioweapon?
endospores can be used as an aerosol
it is a very resilient microbe
3 forms of B. anthracis
- cutaneous (skin)
- gastrointestinal
- respiratory
how is B. anthracis treated?
ciprofloxacin
t/f: there is no prevention for anthrax infections
false; there are vaccines, however, they are only given to those at risk
unique features of archaea
- reverse gyrase of hyperthermophiles (maintains positive supercoils)
similarities of archaea and bacteria (3)
- circular genome
- gene size and density
- presence of operons
similarities of archaea and eukaryotes
- presence of intrones
- RNA polymerase
- histone homologs
t/f: archaeal phylogeny is poorly resolved
true
archaea were discovered fairly recently and live in extreme environments
t/f: archaeal metabolism is most similar to eukaryotes
false
most similar to bacteria EXCLUDING methanogenesis (unique to archaea)
euryarchaeota
- diverse archaea
- extremophiles
haloarchaea
- extremely halophilic
- REQUIRES high salt conc.
-found in salt lakes, salt evap. ponds, and saline habitats
how do archaea use light-absorbing pumps and sensors?
- use light energy to set up proton motive force to move substances
- halorhodopsin brings in chloride
how do halophiles maintain a water balance?
managing internal solutes
somtimes difficult in environments
methanogens
-archaea that produce CH4
- found in marshes
- energy yield is not great (little competition)
substrates for methanogens (3)
- CO2-type
- methyl
- acetotrophic
thermoplasmatales
- thermophilic and/or extremely acidophilic
- 3 genera (2 lack cell walls)
thermococcales and methanopyrus
- phylogenetically related genera of hyperthermophilic euryarchaeota
- branch near the root of the tree
- membrane contains degrees of unsaturation
archaeoglobales
- hyperthermophilic
- oxidize various compounds
nanoarchaeum and aciduliprofundum
- obligate symbiont of crenarchaeote
- small, contains smallest genomes
- depends on host for most cellular needs
crenarchaeota
- temperature extremes
- most cultured representatives are hyperthermophiles
- ocean is full of them
sulfobales
- order containing sulfolobus and acidianus
- from terrestrial volcanoes (convergent evolution)
sulfolobus
- grows in sulfur-rich acidic hot springs
- aerobic chemolithotrophs
- oxidize reduced sulfur/iron
acidianus
- grow in acidic sulfur hot springs
- use elemental sulfur both aerobically and anaerobically
thermoproteales
- inhabit neutral or slightly acidic hot springs or hydrothermal vents
nonthermophilic crenarchaeota
- abundant in deep ocean waters (cooler water)
- appear to be capable of nitrification (genes for it)