Hemostasis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Vasospasm caused by
is part of primary hemostasis
sympathetic stimulation: norepinephrine
immediate release of endothelin from damaged endothelial cells
release of thromboxane a2, adp, serotonin from activated platelets
platelet plug formation
primary hemostasis
derived from bone marrow megakaryocytes (reach between cells and release fragments called platelets or thrombocytes
stimulated by hepatic and renal thrombopoietin
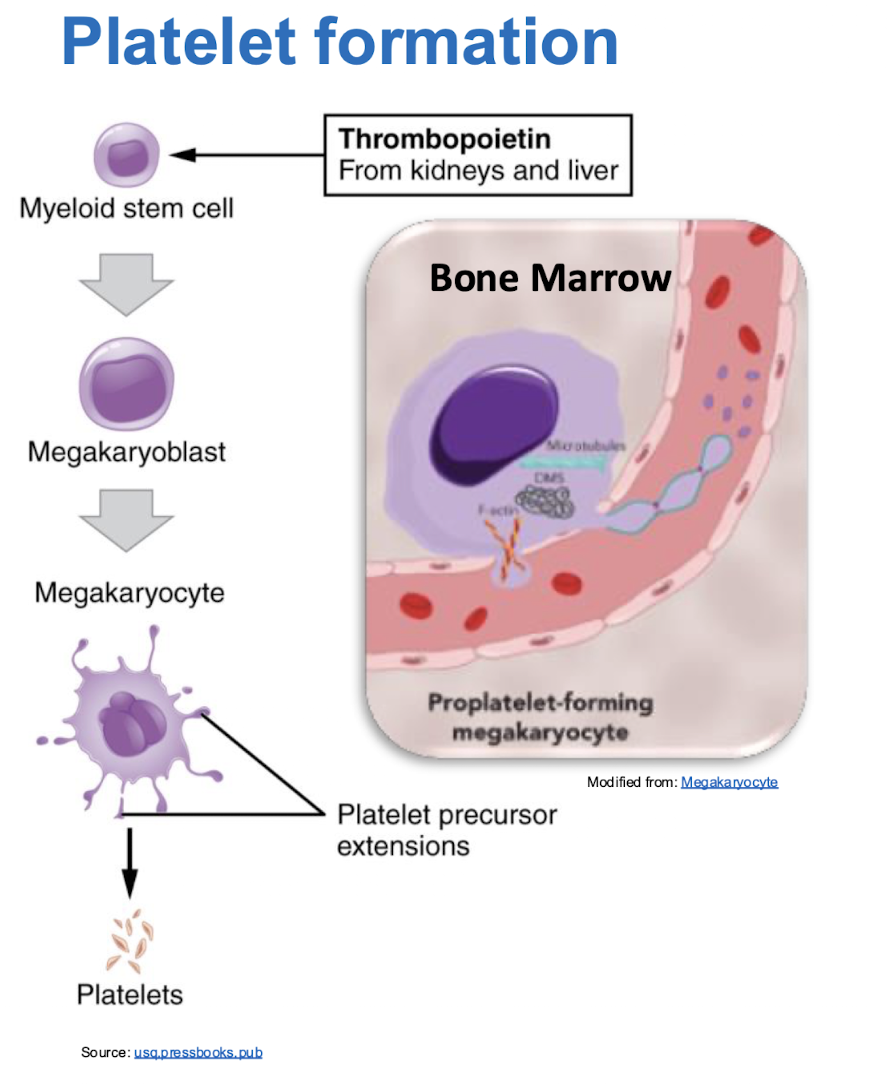
known as platelets in their resting state
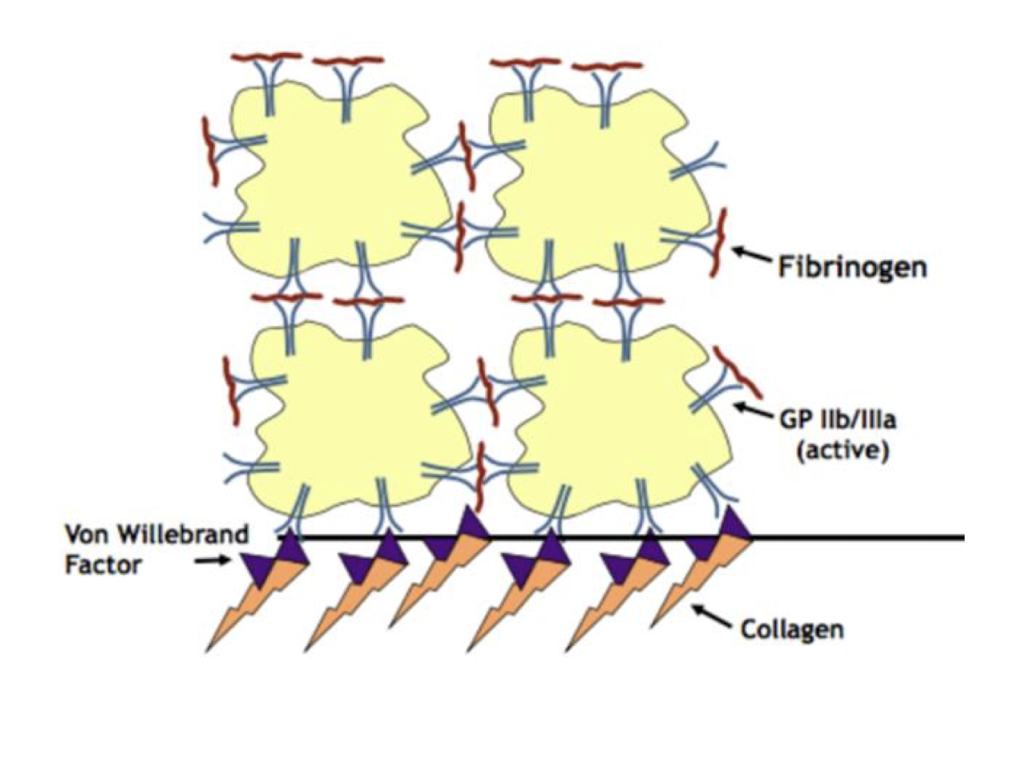
damaged endothelial cells release a glycoprotein known as von willebrand factor which bind to damaged cells and exposed collagen fibers
platelets then go through a confirmation change (along with degranulating) and exposes receptors for resting platelets → loose binding
then fibrinogen is used between platelets to make a more secure clot
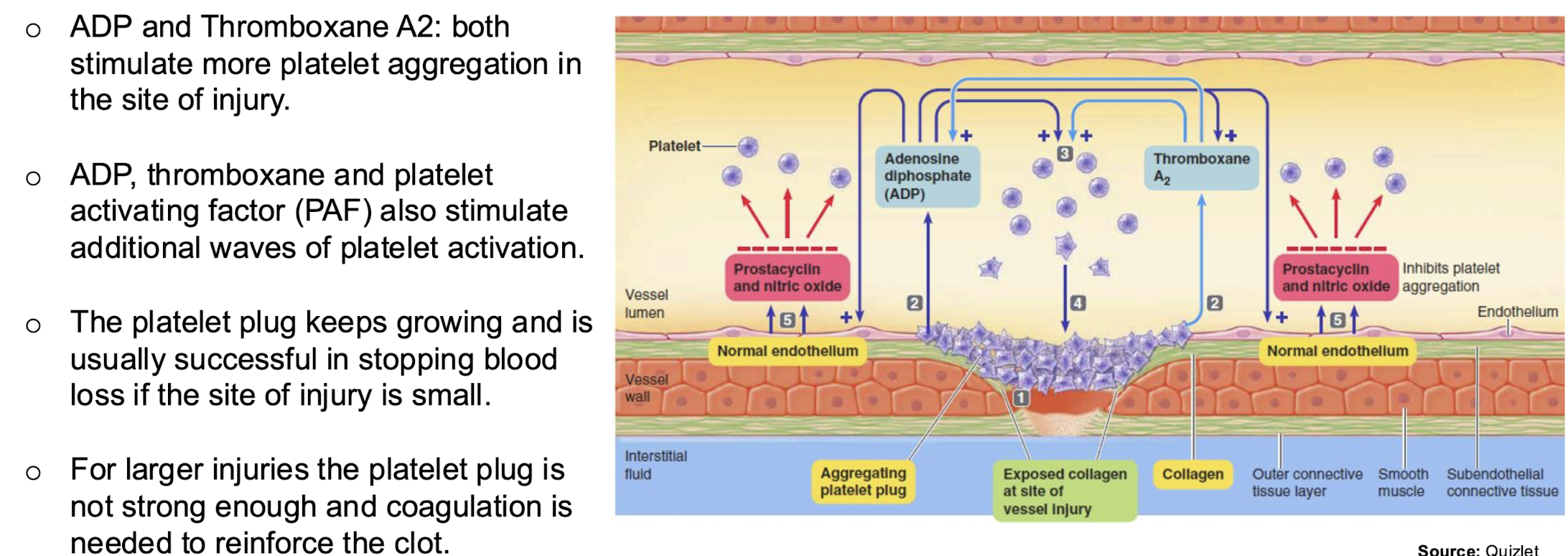
platelet degranulation releases
ADP, Platelet activating factor, thromboxane A2, coagulation factors and calcium in preparation for secondary hemostasis
what cellular process mainly associates primary and secondary hemostasis?
platelet degranulation
what molecules prevent platelets from binding to healthy endothelium
prostacyclin
Rickettsial disease
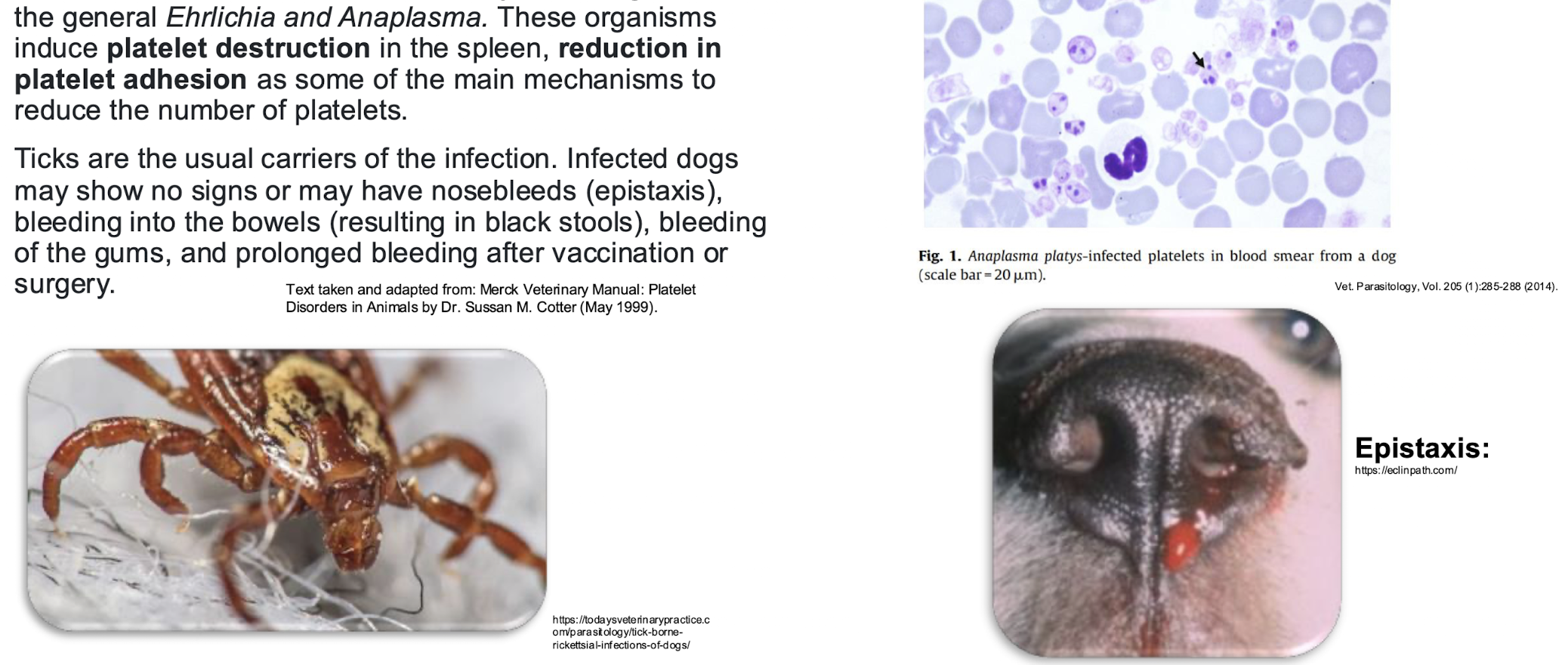
von willlebrand disease

Rodenticide poisoning
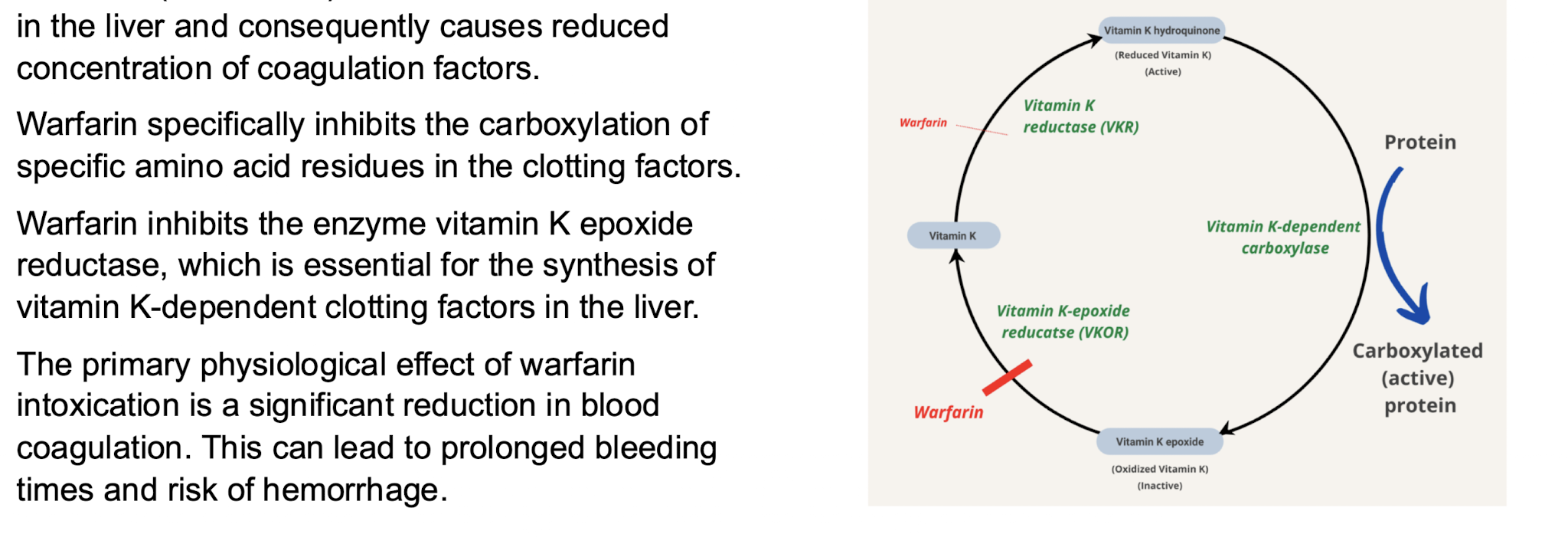
main goal of secondary hemostasis
also known as coagulation stage
form a well attached and strong seal of the vessel injury site to stop bleeding until healing of the vessel wall has occurred several days after the injury which is accomplished through a fibrin clot
stages of coagulation

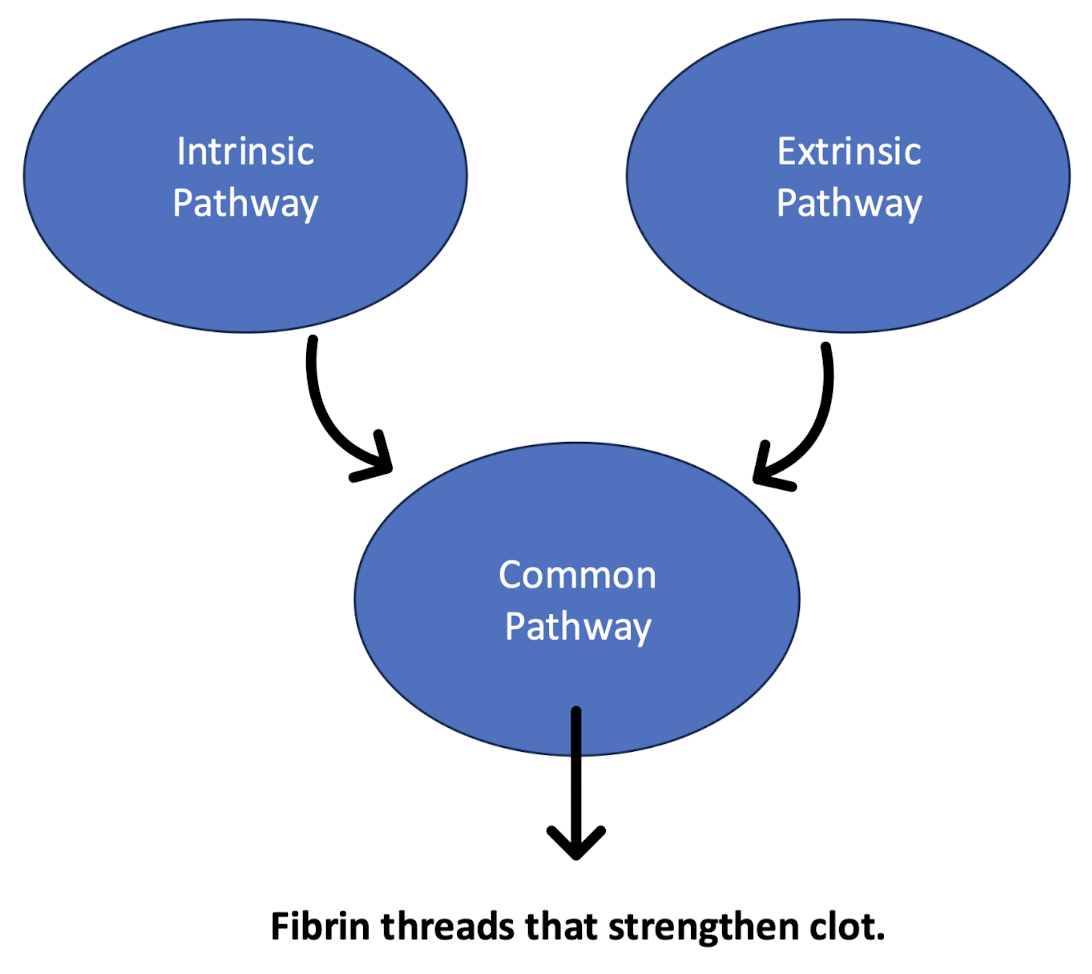
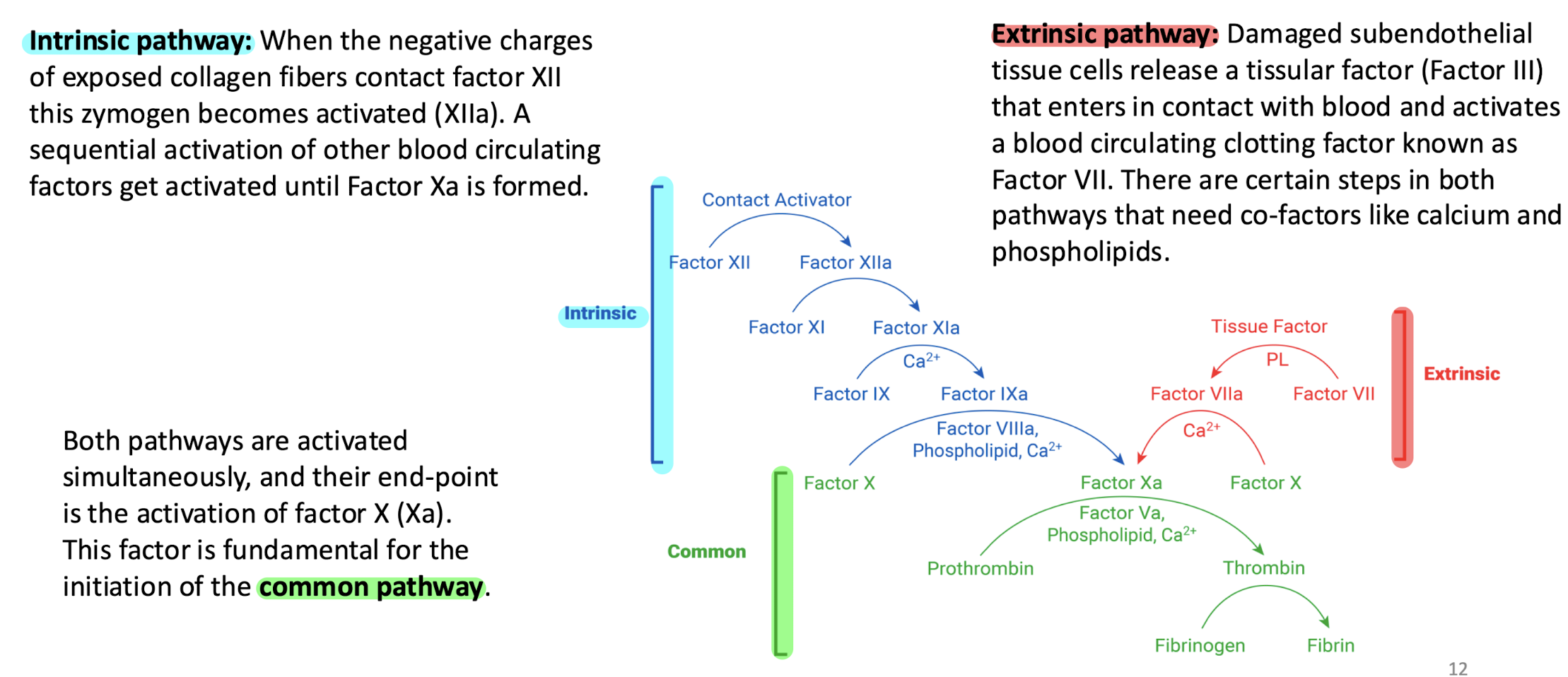
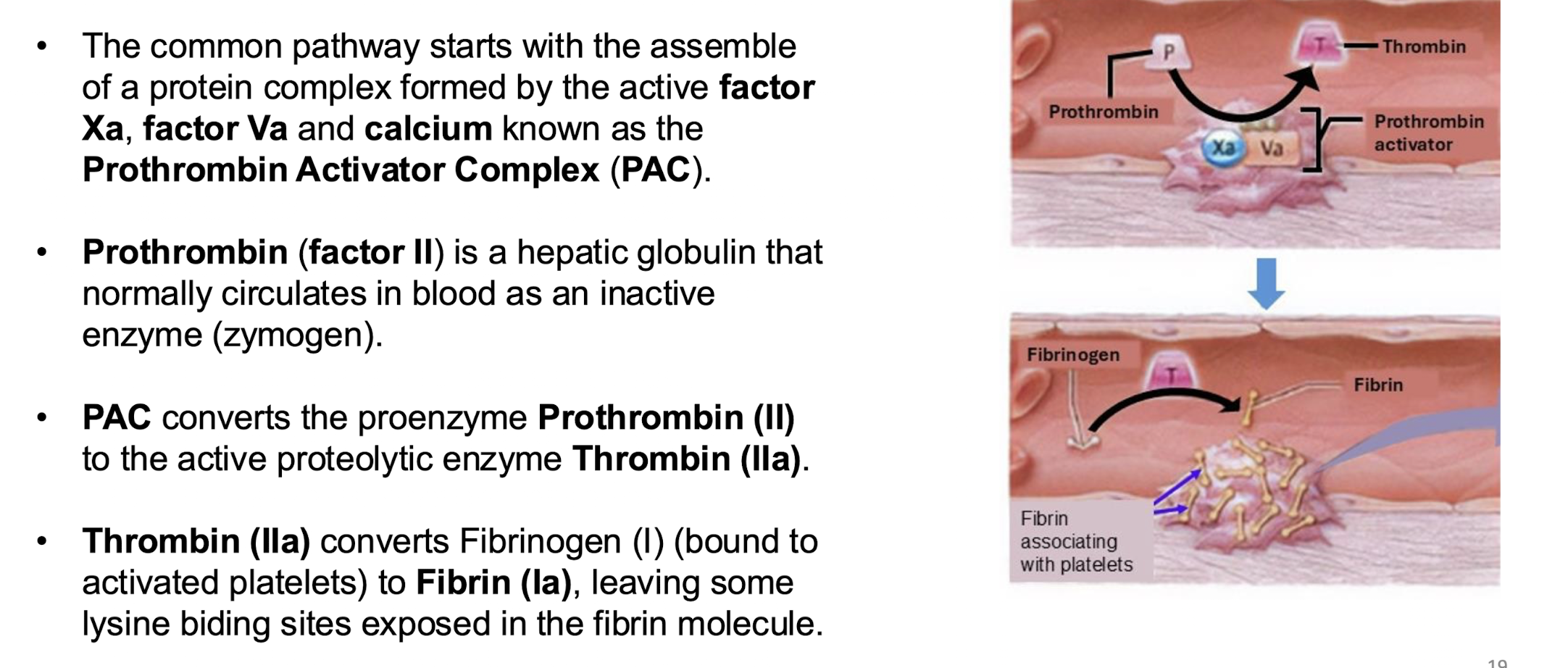
common pathway
coagulation factors and their half-lives
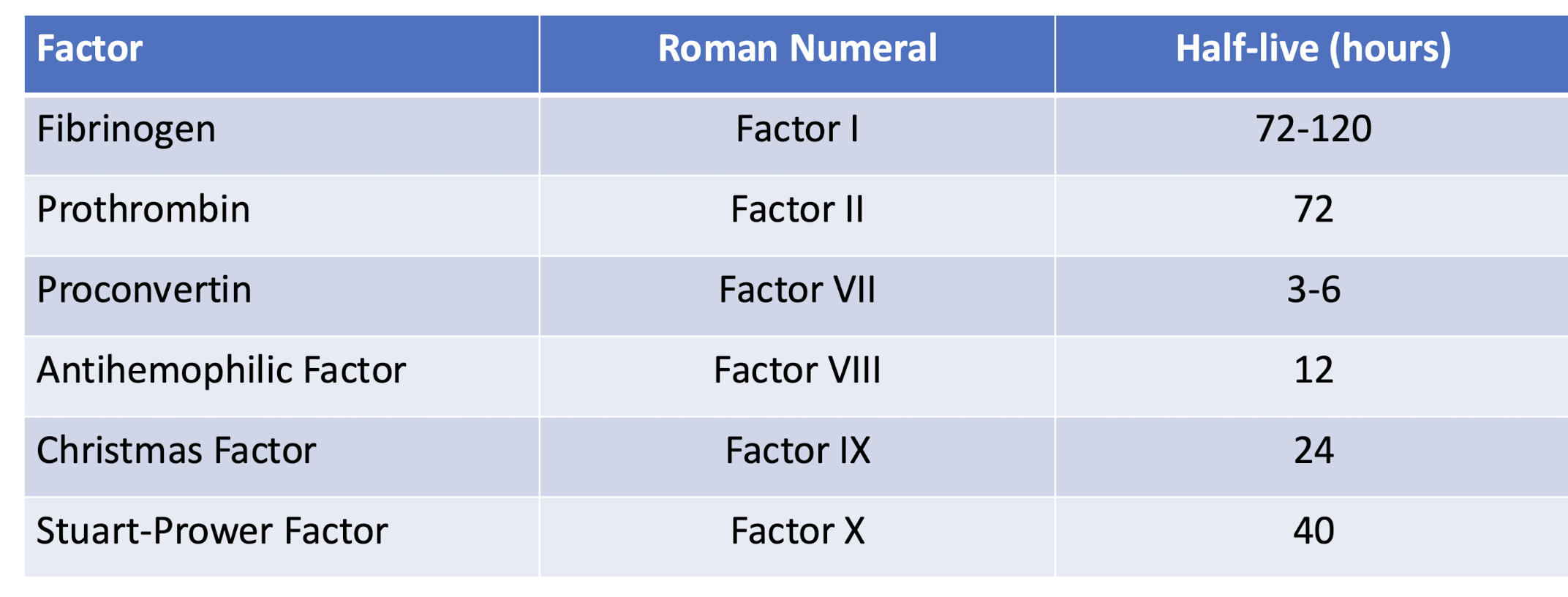
factor VII will disappear first after liver stops working
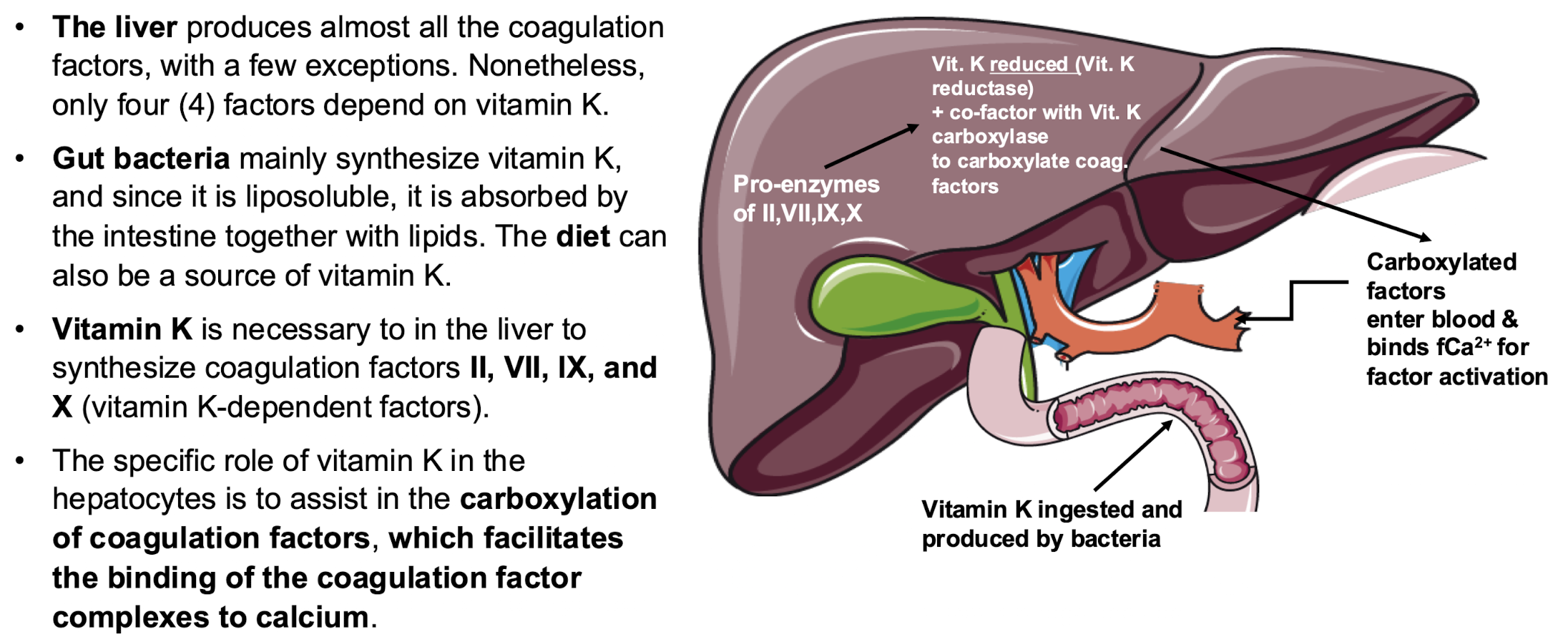
vitamin K dependent coagulation factors
1972
Tertiary hemostasis
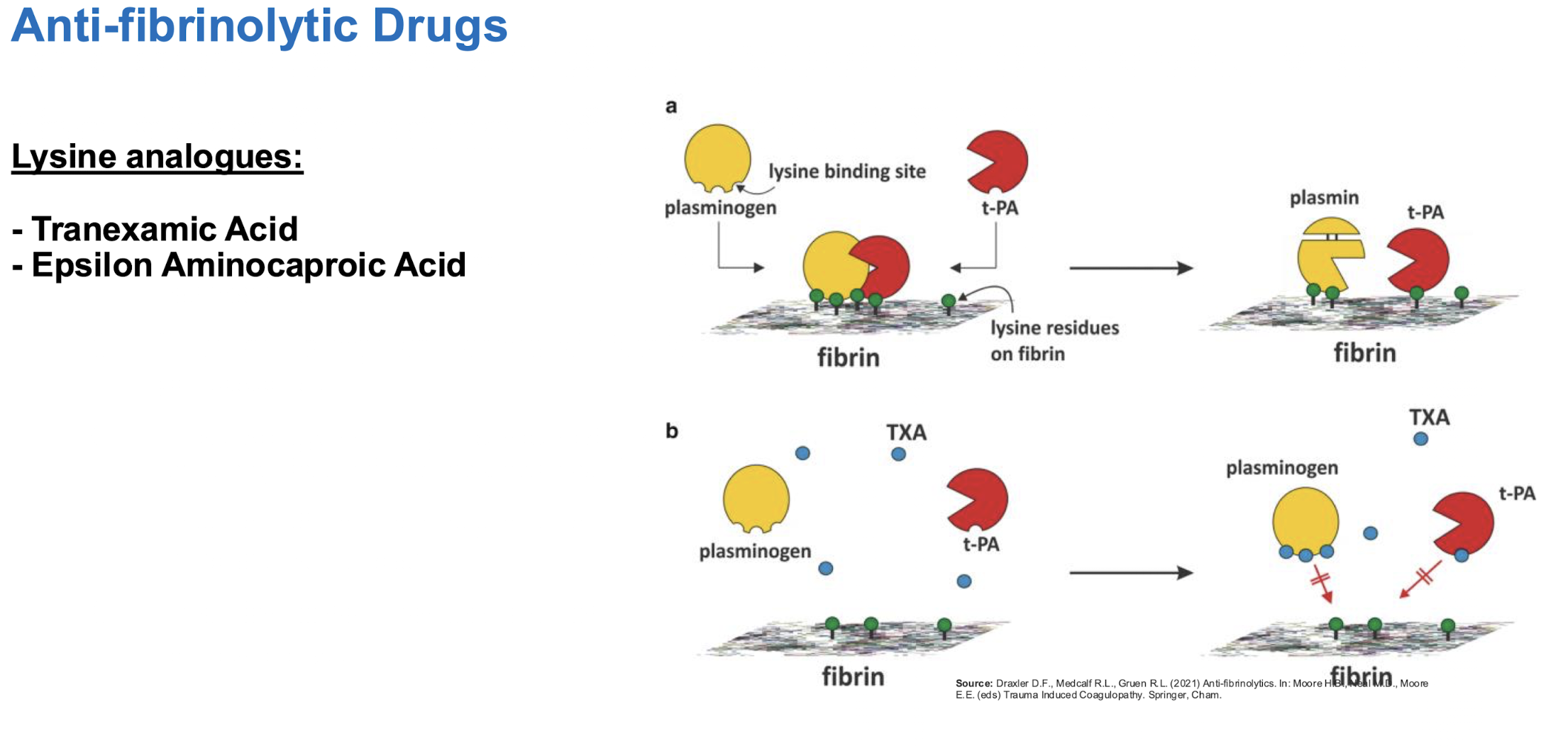
fibrinolysis
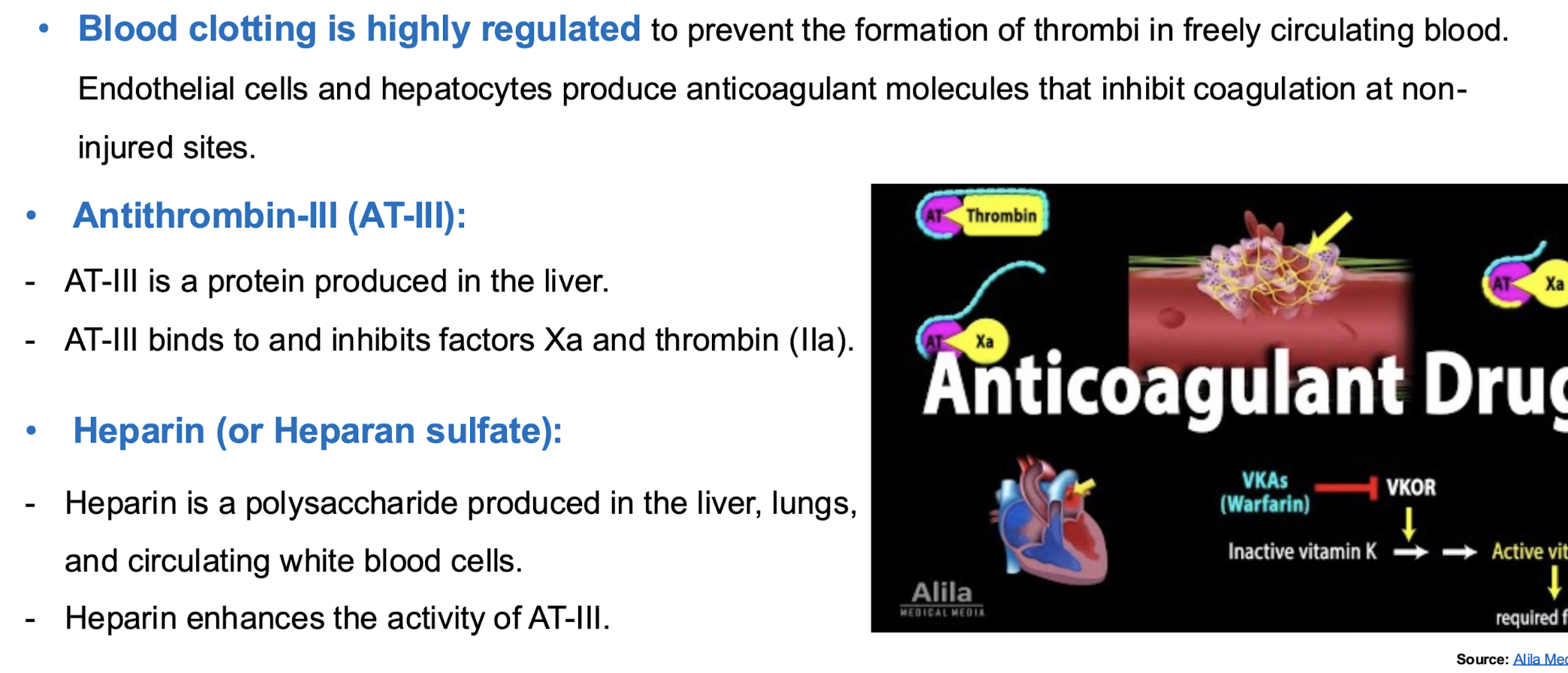
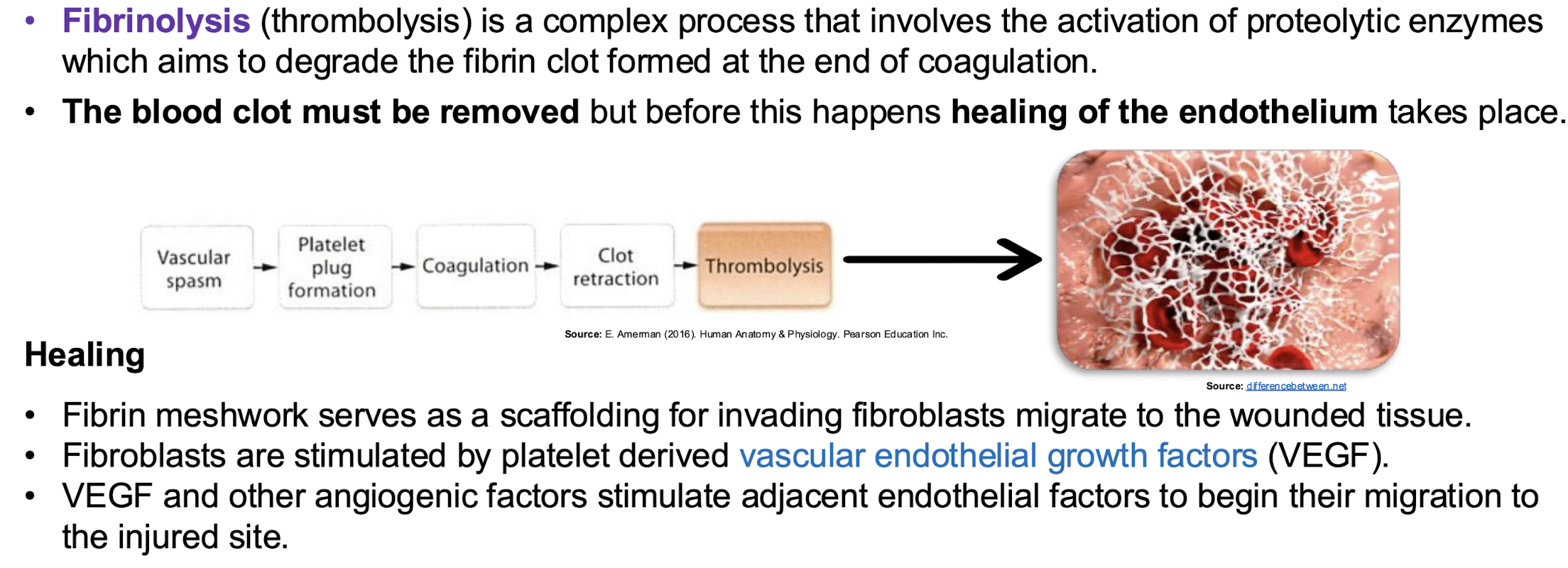
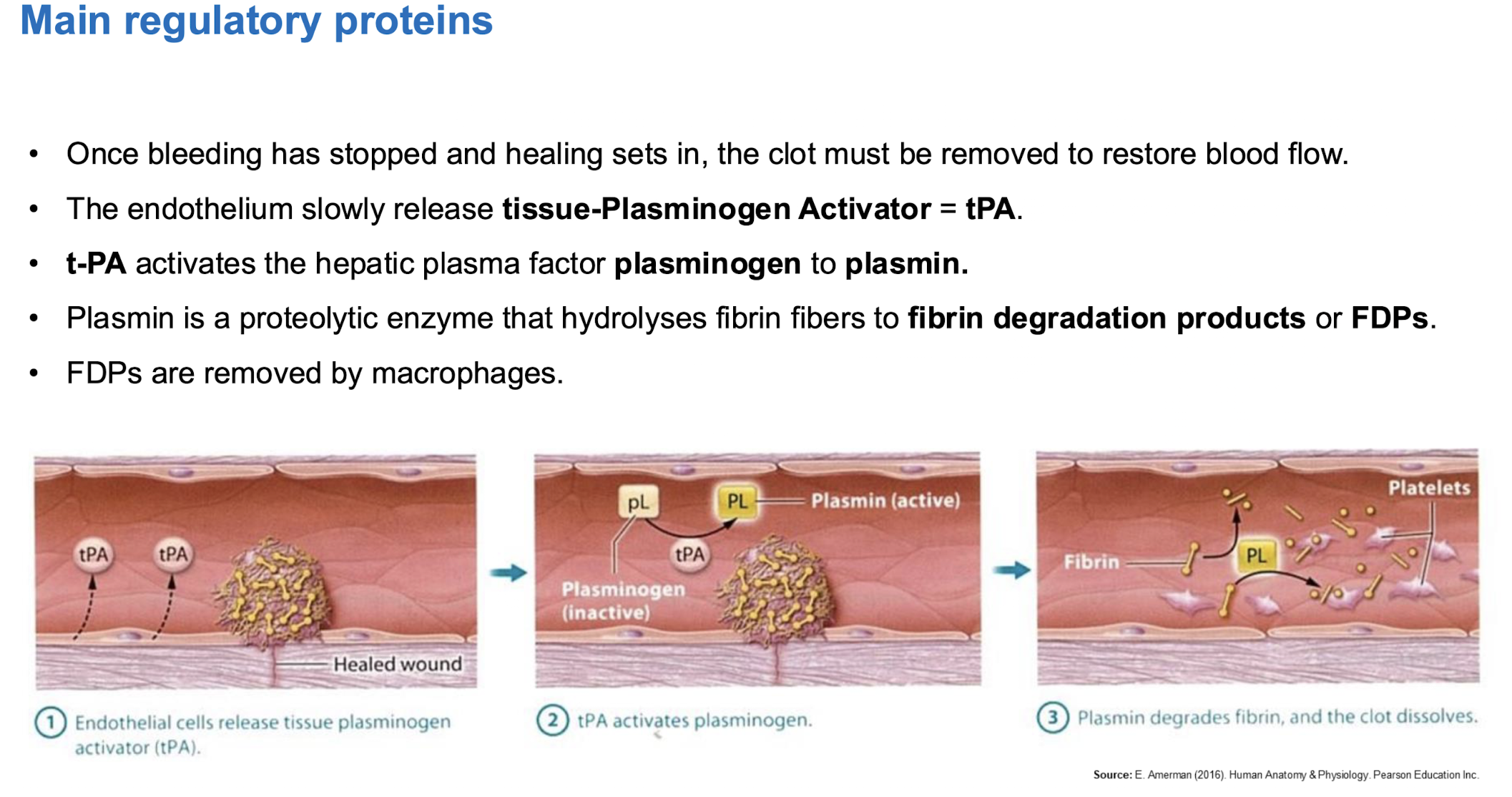
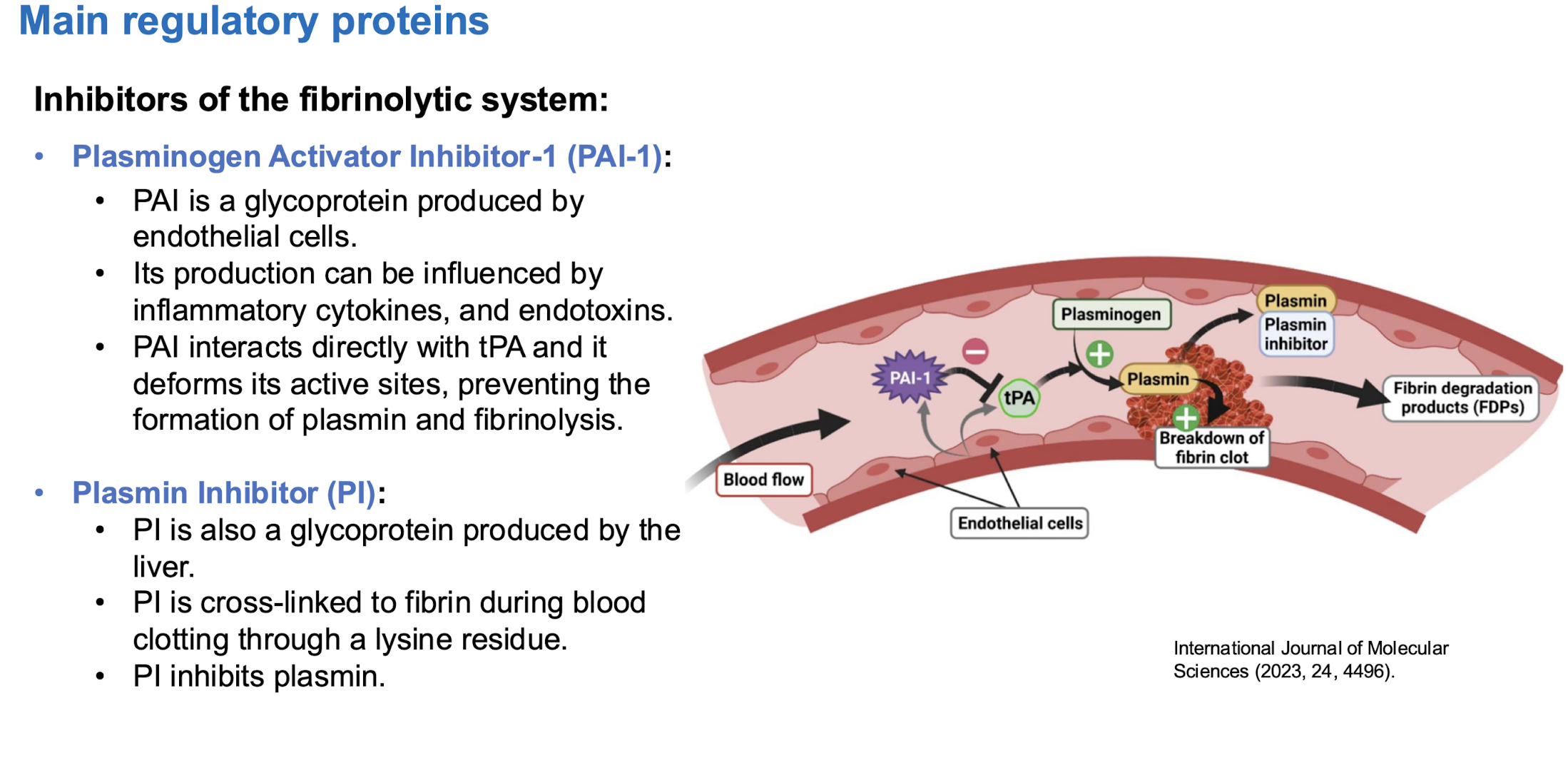
DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation)

greyhound bleeders
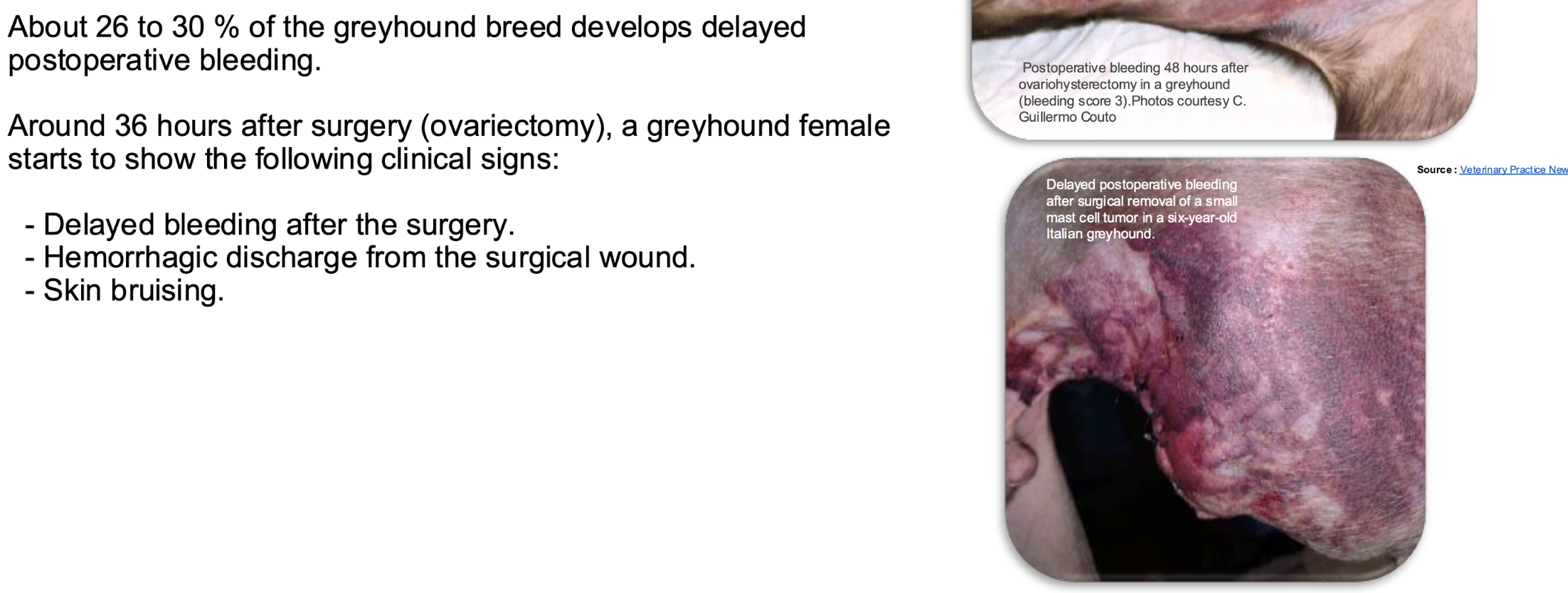
hyperfibrinolysis, significance of elevated FDPS= suggests the prsence of ongoing fibrinolysis and severity of DIC