Topic 3: Movement In & Out of Cells
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is diffusion?
The net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration down the concentration gradient, as a result of the particles random movement.
What is the source of energy that drives diffusion of molecules and ions?
The energy for diffusion comes from the kinetic energy of random movement of molecules and ions.
How do some substances move into and out of cells?
Some substances move into and out of cells by diffusion through the cell membrane.
What is the importance of diffusion of gases and solutes for living organisms?
Diffusion helps living organisms to obtain many of their requirements, get rid of many of their waste products, and carry out gas exchange for respiration.
What are the 4 factors that influence diffusion?
Surface Area, Temperature, Concentration Gradient, and Distance
How does surface area influence diffusion?
A larger surface area increases the rate of diffusion because there is more space available for molecules to pass through the cell membrane. This allows more particles to diffuse at the same time, making the process faster. The smaller its surface area to volume ratio is, slows down the rate at which substances can move across its surface.
How does temperature influence diffusion?
An increase in temperature increases the rate of diffusion because the molecules or ions gain more kinetic energy. This makes them move faster, causing particles to spread out and diffuse more quickly. A lower temperature slows down diffusion as particles have less kinetic energy. So, the higher the temperature, the faster molecules move as they have more energy.
How does concentration gradient influence diffusion?
The greater the difference in concentration on either side of the membrane, the faster movement across it will occur. This is because on the side with the higher concentration, more random collisions against the membrane will occur.
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
When there is a higher temperature, the particles move faster, making diffusion happen more quickly. While a cooler temperature makes the particles move slower, making diffusion slow down.
How does concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
By driving the movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. The greater the difference in concentration, the faster the diffusion occurs.
How does diffusion distance affect the rate of diffusion?
An increase in the distance particles have to travel slows down the rate of diffusion, because molecules take longer to move across a greater distance. A shorter diffusion distance allows substances to move in and out of cells more quickly. The smaller the distance molecules have to travel the faster transport will occur.
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential, down the water potential gradient, through a partially permeable cell surface membrane.
What is the role of water as a solvent in organisms, with reference to digestion, excretion, and transport?
During digestion, digested food molecules dissolve in water, allowing them to be absorbed and transported through the blood to cells across the body. In excretion, waste products such as urea and excess salts dissolve in water, enabling them to be removed efficiently from the body in urine. Water also acts as a transport medium in plants, where dissolved substances like minerals move in the xylem and sugars travel in the phloem.
What is the process by which water diffuses through a partially permeable membrane?
Water diffuses through partially permeable membranes by osmosis.
How does water move in and out of cells?
Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis through the cell membrane.
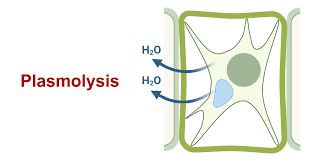
What is plasmolysis?
The process by which the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall as a result of water loss from the cell.
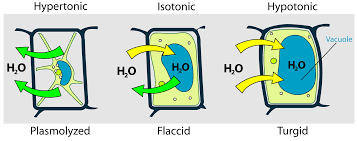
Describe a turgid plant cell.
Because of the water entering the cell because of osmosis, the plant cell increases in volume and pushes against the cell wall.
How does water inside plant cells helps support the plant?
Plants are supported by the pressure of water inside the cells pressing outwards on the cell wall, providing support and strength for the plant, and stopping too much water entering and preventing the cell from bursting.
What is a hypertonic solution?
A solution that has a high solute concentration or low water potential.
What is isotonic solution?
This is a solution that has the same solute concentration or same water potential as that of the cell.
What is hypotonic solution?
This is a solution that has a low solute concentration or a high water potential compared to the solution in a cell.
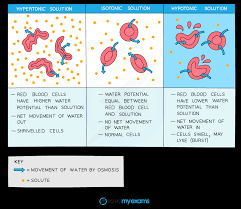
What happens when an animal cell is placed in hypertonic solution (low water potential) ?
The cell will lose water through osmosis and it will become flaccid (shrinks).
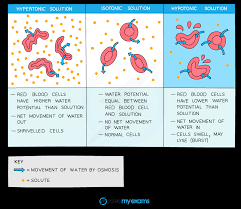
What happens when a animal cell is placed in isotonic solution?
There is no net movement of water in or out of the cell as the solution has the same water potential as the cell, so the cell remains the same size & shape.
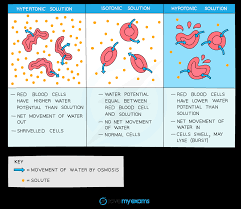
What happens when an animal cell is placed in hypotonic solution?
The cells swell and eventually burst as there is no cell wall.
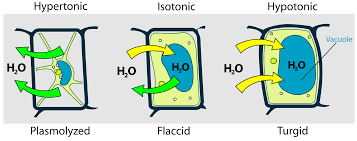
What happens when you put a plant cell in a hypotonic solution?
When plant cells are placed in a solution that has a higher water potential than inside the cells then water moves into the plant cells via osmosis. These water molecules push the cell membrane against the cell wall, increasing the turgor pressure in the cells which makes them turgid.
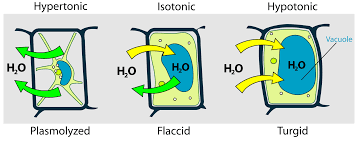
What happens when a plant cell is placed in isotonic solution?
There is no net movement of water and the cell becomes flaccid as the solution has the same water potential as the cell.
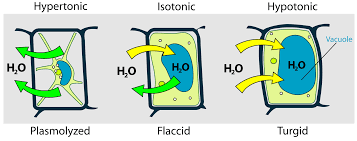
What happens when a plant cell is placed in hypertonic solution?
In a solution with a lower water potential (more concentrated than the cell’s cytoplasm), water leaves the cell by osmosis. The cytoplasm and cell membrane shrink away from the cell wall in a process called plasmolysis, making the cell flaccid or fully plasmolysed if water loss continues.
Why is water potential and osmosis in the uptake and loss of water in plants and animals important?
In plants, water enters root hair cells by osmosis because the cell sap has a lower water potential than the surrounding soil. This maintains turgor pressure, keeping the plant upright. If the soil has a much lower water potential, water leaves the cells, making them flaccid or plasmolysed, leading to wilting. In animals, osmosis controls water balance; too much water can cause cells to burst, while water loss makes them shrink. Maintaining proper water potential is essential for cell survival in both plants and animals.
What is active transport?
The movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, against the concentration gradient, uses energy from respiration.
What is the importance of active transport in plants and animals?
Its a vital process for the uptake of glucose by epithelial cells in the villi of the small intestine, by kidney tubules in the nephron, and the uptake of ions from soil water by root hair cells in plants.
What are the structures in the cell membrane that move molecules or ions during active transport?
Protein carriers move molecules or ions across a membrane during active transport.