musculoskeletal
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
what are stronger than bones until puberty?
ligaments and tendons
2
New cards
what is the most common area for a child to break a bone?
distal forearm
3
New cards

plastic deformation
4
New cards
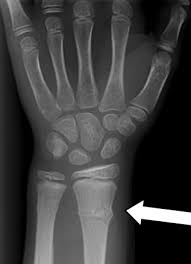
buckle/torus break
5
New cards
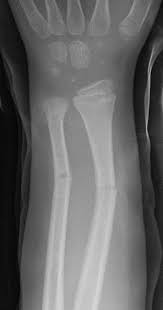
greenstick fracture
6
New cards
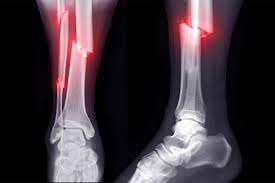
complete fracture
7
New cards
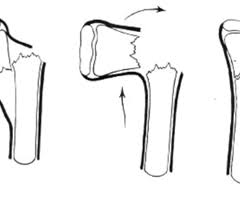
complete break with periosteal hinge
8
New cards
a child who had a cast placed complains of pain and tightness - what do you suspect?
compartment syndrome
9
New cards
a group of conditions that cause the femoral head and the acetabulum are improperly aligned
developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
10
New cards
what is a common causative factor DDH?
breech position
11
New cards
an infant’s one knee is lower than the other when their legs are flex, this is known as -
Galeazzi sign
12
New cards
what maneuvers can be done by a physician to check for HHD?
Ortolani and Barlow
13
New cards
when do minor cases of DDH normally resolve?
4 months
14
New cards
what is the treatment for DDH if the infant is less than 6 months old?
bracing (23 hours a day)
15
New cards
what is the treatment of DDH if the child is older than 6 months?
closed reduction with spica casting
16
New cards
plantar flexion of the foot, inversion of the heel, and medial deviation of the forefoot are all parts of -
clubfoot
17
New cards
what is the treatment of choice for clubfoot?
serial casting (Ponseti method)
18
New cards
what are options of serial casting is not working to repair clubfoot?
tenectomy or surgical repair
19
New cards
medical adduction of the toes and forefoot are referred to as -
metatarsus adductus
20
New cards
what normally causes metatarsus adductus?
positioning in utero
21
New cards
what are the common treatments for metatarsus adductus?
usually stretching, can be surgical
22
New cards
inherited connective tissue disorder where the production of collagen is effected, resulting in fragile bones -
osteogenesis imperfecta
23
New cards
what is the most severe form of osteogenesis imperfecta?
type 2
24
New cards
what is the most common type of osteogenesis imperfecta?
type 1
25
New cards
what dietary changes should be suggested for a child with osteogenesis imperfecta?
high vitamin D and calcium intake
26
New cards
a self-limited condition of avascular necrosis of the femoral head as a result of an interruption in blood supply
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
27
New cards
what is a hallmark sign of Legg-Calve’-Perthes disease?
limp with mild to severe pain
28
New cards
condition where the femoral head is displaced from the femoral neck
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
29
New cards
what is a common predisposing factor for slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
obesity
30
New cards
what is the hallmark sign of slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
pain and a limp
31
New cards
a lateral curvature of the spine that is associated with a rotational deformity?
scoliosis
32
New cards
dose a child with scoliosis experience pain?
rarely
33
New cards
how often should a child with a brace wear it within the day?
23 hours
34
New cards
how should a brace be worn for scoliosis?
over a shirt; not directly on the skin
35
New cards
where is osteomyelitis more common?
lower extremities
36
New cards
what is the most common cause of osteomyelitis?
bacterial infection
37
New cards
what is the most common bacteria that causes osteomyelitis?
staph aureus
38
New cards
what are the expected laboratory findings associated with osteomyelitis?
elevated WBCs, elevated ESR, and elevated CRP
39
New cards
what is the treatment for osteomyelitis?
broad spectrum antibiotics (vancomycin and clindamycin)
40
New cards
what are common side effects of vancomycin use?
hearing and kidney problems