Soil and Plant Nutrition
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What does farmland productivity often suffer from?
Chemical contamination, mineral deficiencies, acidity, salinity, and poor drainage
How does healthy soil improve plant growth?
Enhancing plant nutrition
What do plants obtain from the soil?
Carbon dioxide, air, water, and minerals
Where do plants obtain their water (+ minerals)?
The upper layers of soil
How are soil particles classified by size?
From largest to smallest
What are the names of the classification of soil particles?
Sand, silt, and clay
Soil horizons
Soil stratified into layers
What is each layer of soil horizon classified as?
A, B, and C, horizon
Topsoil
Consists of mineral particles, living organisms, and humus
Humus
The decaying organic material
What happens to large spaces in the soil after a heavy rainfall?
Water drains from the larger spaces in the soil
What happens to smaller spaces of soil after a heavy rainfall?
Smaller spaces retain water
Why do smaller spaces in soil retain water?
Due to it’s attraction to clay and other particles
Loams
The most fertile topsoils
What do loams contain?
Equal amounts of sand, silt, and clay
What does a soil composition refer to?
It’s inorganic (mineral) and organic chemical components
Cations (K+, Ca2+, Mg2+)
Adhere to negatively charged soil particles
What does the adhering of cations prevent?
From leaching out of the soil through percolating groundwater
What occurs during cation exchange?
Cations are displaced from soil particles by other cations
What happens to the displaced cations?
They enter the soil solution and are taken up by plant roots
What do negatively charged ions do during cation exchange?
They do not bind with soil particles and are lost from soil by leaching
What type of soil does humus build?
A crumbly soil that retains water but is still porous
Why does the crumbly soil increase the soil’s capacity?
To exchange cations and serve as a reservoir of mineral nutrients
Detrivores
Organisms that help decompose organic material and mix the soil
What is the goal of sustainable agriculture?
Farming methods that are conservation-minded, environmentally safe, and profitable
Irrigation
A huge drain on water resources when used for farming in arid regions
Aquifers
The primary source of irrigation water known as underground water reserves
Subsidence
The settling or sinking of land that are a result of depleting aquifers
Salinization
The concentration of salts in soil as water evaporates
Fertilization
Replaced mineral nutrients that have been lost from soil
What are commercial fertilizers enriched in?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
How does soil pH affect cation exchange?
Cations are more available in slightly acidic soil
What does erosion of soil cause?
Loss of nutrients
What can erosion be reduced by?
Planting trees as windbreaks, terracing hillside crops, cultivating in a contour pattern, practicing no-till agriculture
How does soil compaction affect the soil?
Slows gas exchange, reduces root growth, and pore space between soil particles
What causes an area to be unfit for agriculture?
Contamination of soil or groundwater with toxic pollutants
Phytoremediation
A biological nondestructive technology that reclaims contaminated areas
Where do plants derive most of their organic mass from?
The CO2 of air
What are plants also dependent on besides CO2?
Soil nutrients such as water and minerals
Essential element
A chemical element required for a plant to complete its life cycle
Macronutrients
Essential elements that a plant requires in relatively large amounts
What are the macronutrients?
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, and magnesium
Micronutrients
Essential elements that a plant needs in very small amounts
What are the micronutrients?
Chlorine, iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, nickel, and molybdenum
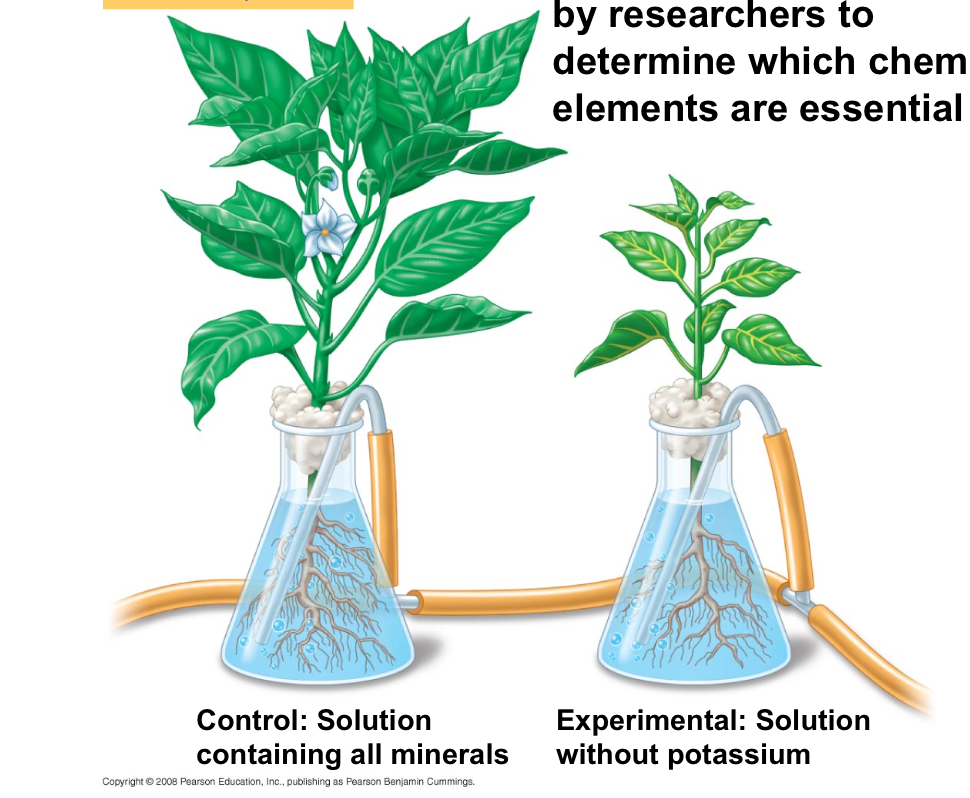
Hydroponic culture
Used by researchers to determine high chemical elements are essential
What do the symptoms of mineral deficiency depend on?
The nutrient’s function and mobility within the plant
How does deficiency affect a mobile nutrient?
By affecting older organs more than younger ones
How does deficiency affect a less mobile nutrient?
By usually affecting younger organs than older ones
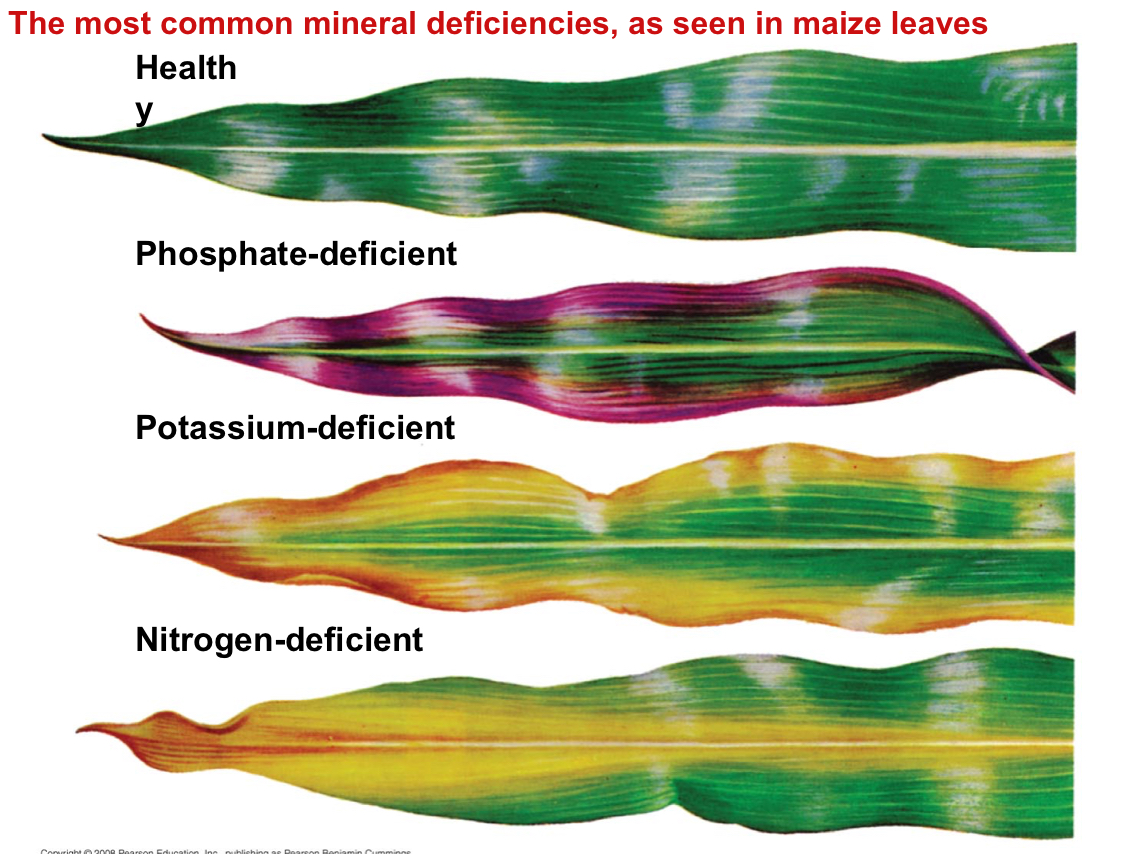
What are the most common deficiencies?
Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus
What can genetic engineering improve?
Plant nutrition and fertilizer usage
What are examples of genetic engineering?
Resistance to aluminum toxicity, flood tolerance, smart pants
How does aluminum affect acidic soils?
By damaging roots and greatly reducing crop yields
What can the introduction to bacterial genes in plant genomes cause?
Plants secreting acids that bind and tie up aluminum
How do waterlogged soils affect the plants?
It deprives the roots of oxygen and causes buildup of ethanol and toxins
Submergence 1A-1
A gene responsible for submergence tolerance in flood-resistance rice
What do “smart” plants do to prevent plant damage?
They inform the grower of a nutrient deficiency before damage has occurred
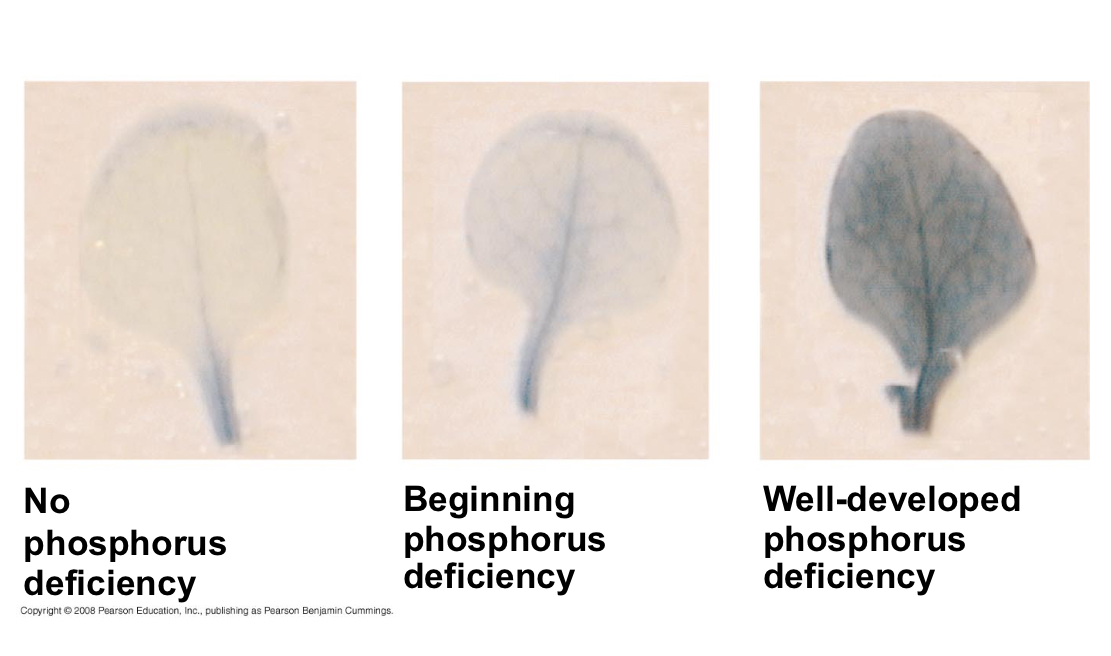
What does a blue tinge in a plant cell indicate?
It indicates when plants need phosphate-containing fertilizer
What type of relationship do plants and soil microbes have?
A mutualistic relationship
What do dead plants provide the soil microorganisms with?
Energy
What do secretions from living roots support?
A wide variety of microbes in the near-root environment
Rhizosphere
The layer of soil bound to the plant’s roots
What causes high microbial activity in the rhizosphere?
Sugars, amino acids, and organic acids secreted by roots
Where do free-living rhizobacteria thrive in?
In the rhizosphere or through entering roots
What kind of roles do Rhizobacteria play?
Producing hormones that stimulate plant growth, antibiotics that protect roots from disease, and absorbing toxic metals (making nutrients available to roots)
What is the purpose of the nitrogen cycle?
To transform nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds
Where does most soil nitrogen come from?
Actions of soil bacteria
In what way do plants absorb nitrogen?
As either NO3- or NH4+
How is Nitrification carried out?
By a bacteria that converts NH3 into NO3-
Nitrogen fixation
The conversion of nitrogen from N2 to NH3
What do symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing provide plant species?
A built-in source of fixed nitrogen
Where do key symbioses occur?
Between nitrogen-fixing bacteria and plants, including the legume family (peas, beans, and other similar plants)
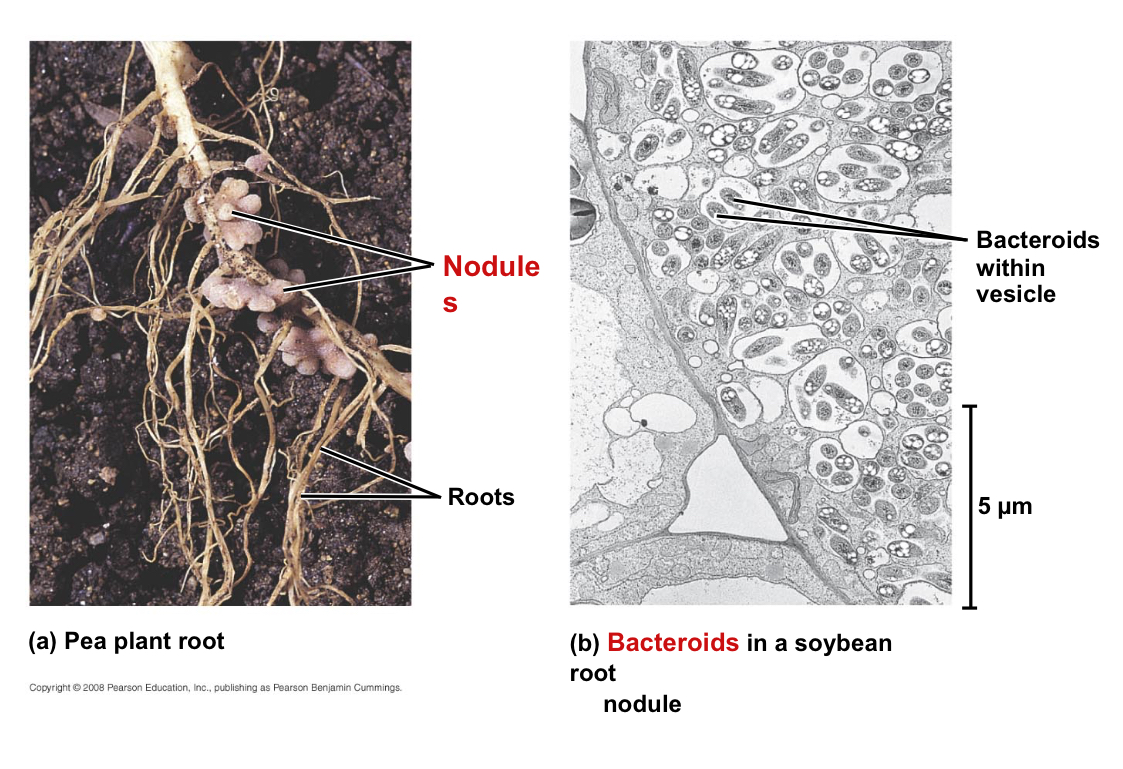
Nodules
Swellings found along a legume’s roots
What are nodules composed of?
Plants cells “infected” by nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium bacteria
Bacteroids
A form assumed by the Rhizobium bacteria inside of the root nodule
Where are bacteroids contained?
Within vesicles formed by the root cell
What is the mutualism between the bacteria of a root nodules and a plant?
The bacteria of a root nodule obtaining sugar and supplying the same plant with fixed nitrogen
What is each legume species associated with?
A particular strain of Rhizobium
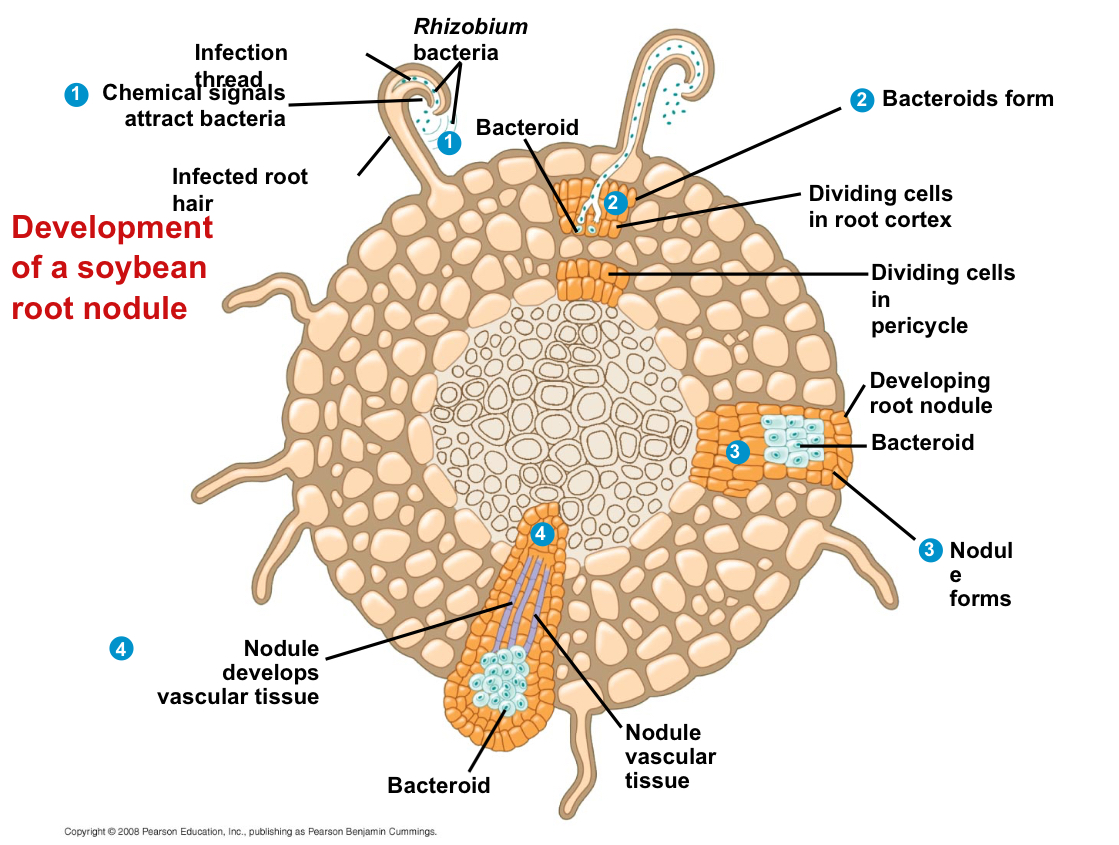
What does the development of a nitrogen-fixing root nodule depend on?
A chemical dialogue between Rhizobium bacteria and root cells of their plant hosts
What does crop rotation take advantage of?
The agricultural benefits of symbiotic nitrogen fixation
How is the concentration of fixed nitrogen restored in the soil?
A non-legume (maize) and a legume is planted every other year
Why is the legume crop plowed instead of harvested?
To decompose as “green manure” and reduce the need for manufactured fertilizer
Which types of non-legumes benefit from nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Alder trees, certain tropical grasses, and rice
Mycorrhizae
Mutualistic associations of fungi and roots
What does the fungus benefit from the host plant?
A steady supply of sugar
What does the host plant benefit from the fungus?
The increase of surface area for water uptake and mineral absorption
What is the importance of mycorrhizal relationships?
Their commonness and aid in plants first colonizing land
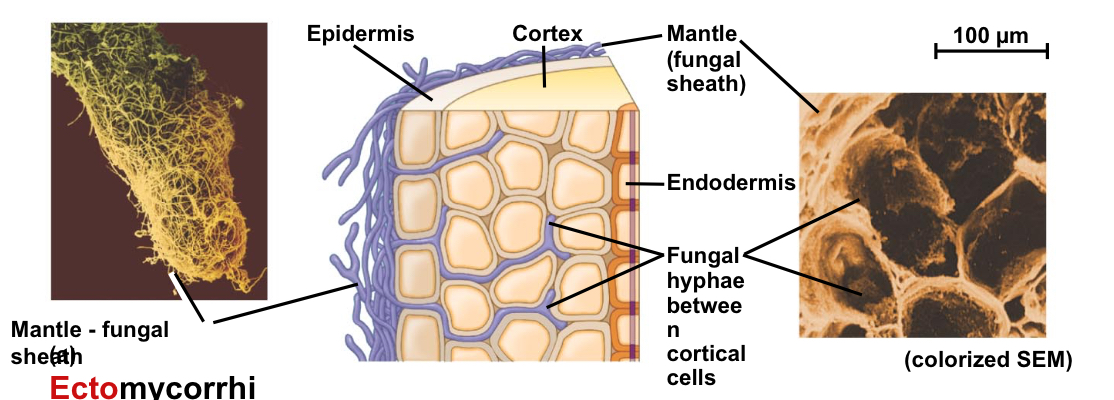
What occurs during ectomycorrhizae?
The mycelium of the fungus forms a dense sheath over the surface of the root
What do these hyphae form?
A network in the apoplast, which no longer penetrates the root cells
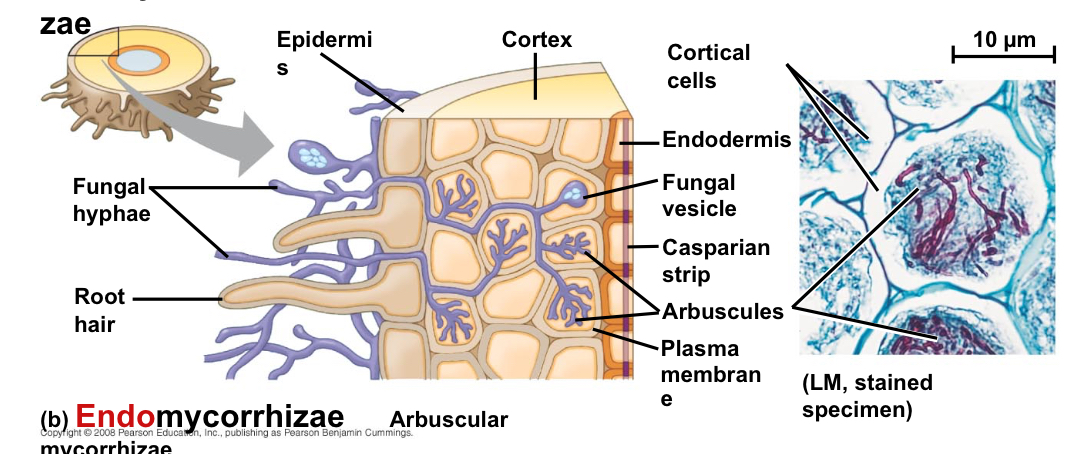
What occurs in endomycorrhizae?
Microscopic fungal hyphae extends into the root
What do these mycorrhizae form?
Branched arbuscules within root cells after penetrating the cell wall
How do farmers and foresters promote the formation of mycorrhizae?
Inoculating seeds with fungal seeds
How do invasive exotic plants affect plants and their mycorrhizal fungi?
By disrupting their interactions
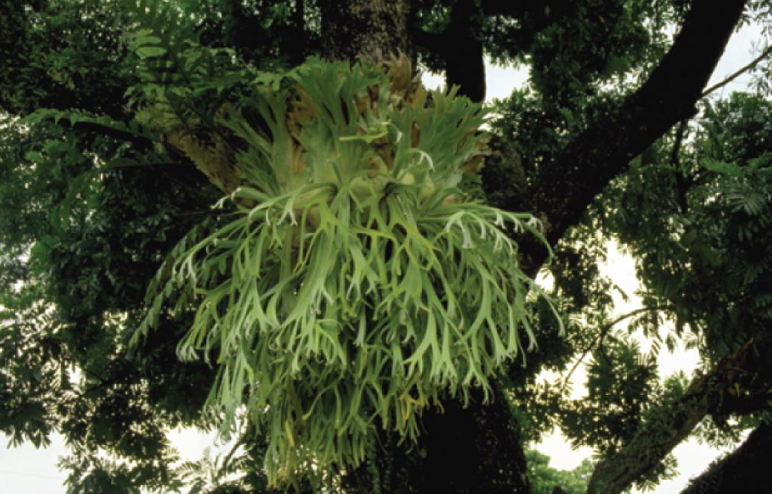

Epiphyte plants (non-mutualistic)
Grow on other plants and obtain water and minerals from rain
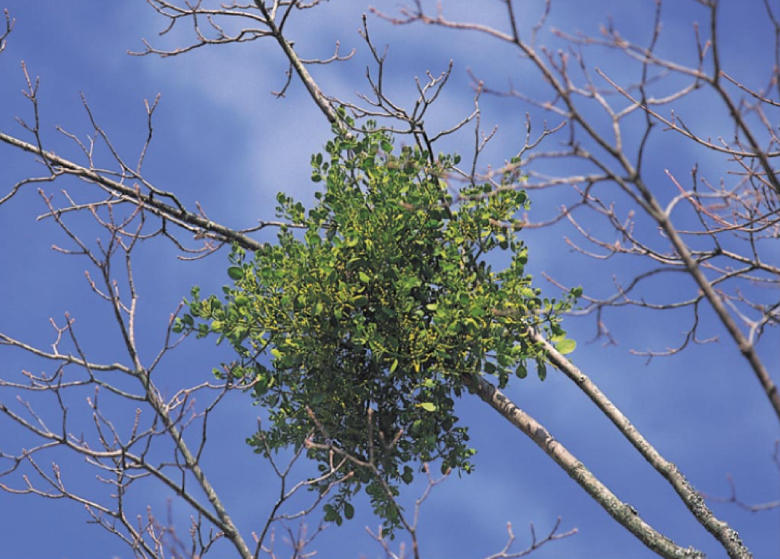

Parasitic plants (non-mutualistic)
Absorb sugars and minerals from their living host plants

Carnivorous plants
Photosynthetic but obtain nitrogen by killing and digesting mostly insects