Non-Malignant Disorders of leukocytes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
leukocytosis
an increase in the total WBC
WBC > 10.6 × 10³ / uL or (10^9/L)
reference interval = 3.6 - 10.6 × 10³ / uL (10^9) (ASCP)
reactive to infection: - bacteria, viral, fungal, tubercular, and leukemia
physiologic leukocytosis - excessive exercise, hypoxia, stress
neutrophilic leukocytosis
Relative vs. absolute values:
– Absolute neutrophilia
• Absolute total neutrophils/ul is increased > 7.5x 103/ul
• % neutrophils x WBC count
• Percent neutrophils is increased
– > 70%
• Response to bacterial infection
• Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Neutrophilia - relative
Relative neutrophilia
– A relative increase in % of neutrophils >70%
– without a corresponding increase in total WBC
count
– Normal neut % = 50-70%
• Left shift:
– Increase in immature neutrophils
• (bands, metas, myelos, promyelo’s)
– With decreased % mature neutrophils
neutrophilia right shift
increased presence of mature neutrophils
> 65%
hyper segmented - in B12 and folic acid deficiencies
causes of neutrophilia
Infections:
– Bacterial, some viral
• Myeloproliferative disorders:
– Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
– Polycythemia
– Myelofibrosis
• Metabolic disorders:
– Uremia
– Diabetic ketoacidosis
– Eclampsia
• Inherited Disorders:
– Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
– Familial cold urticaria
– Hereditary neutrophilia
• Drugs such as steroids, lithium
• Smoking, Acute or Chronic blood loss, Myocardial Infarction,
Colitis, Vasculitis, Pancreatitis, Autoimmune Disease
• Stress, Exercise, Labor/Delivery, Surgery, Bur
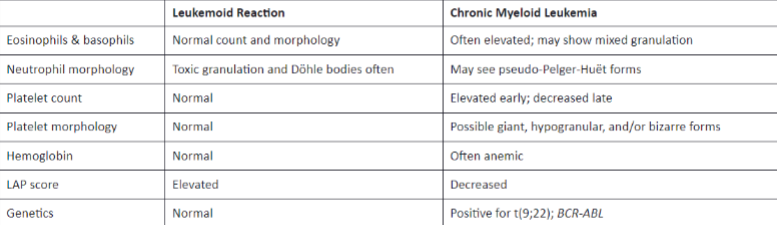
distinguishing features between leukemoid reaction and chronic myeloid leukemia
eosinophilia
increased number of eosinophils
> 0.400 × 10³ / uL or >3%
reference 1-3%
IL-3 and IL-5 stimulate release
causes of eosinophilia
Allergic Reactions
– Asthma, rhinitis
– Food and drug allergies
• Chronic dermatoses - dermatitis
herpetiformis
• Parasitic infections, especially helminths
– Trichinellosis, Stronglyoidiasis, Hookworm,
Filariasis, Shistosomiasis
• Hepatitis, HIV
• CML – eosinophilia with basophilia
• PDGRFB Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
– Platlet derived growth factor beta
• AML (previous M4 Eo)
• Leukemoid reactions
basophilia
Reference: 0-2%
• Absolute Count: 0.10 x 103/ul
• > 3%
• Leukemia
– CML be presenting sign
• Myeloproliferative disease
– Polycythemia vera
• Dermatitis
• Urticaria pigmentosa
• Mast cell disease
• Chicken pox, Small pox
necrobiotic changes in WBCs
necrotic nucleus
most often seen in infections
pyknotic cells
degradation or breakdown of WBC
ehrlichosis and anaplasmosis
morulae may be seen as WBC inclusions in the first week of infection
different than Dohle Bodies
Qualitative Disorders of Granulocytes
Neutrophilic Hypersegmentation
Pelger-Huet Anomaly (neutrophilic hyposegmentation)
Pseudo-Pelger Huet
Chediak Higashi Syndrome
Alder-Reilly Anomaly
May Hegglin Anomaly
Neutrophilic hyper segmentation
> 5 lobes
caused by interference with DNA synthesis
PA, b12 deficiency
folate deficiency
methotrexate chemotherapy
benign inherited disorder
Pelger-Huet anomaly
• Neutrophil hyposegmentation of nucleus
• Benign autosomal dominant inheritance
• “pince-nez” nuclei (spectacle appearance)
• Bi-lobed, non segmented, dense nuclei
• Neutrophils are functional
• Pseudo Pelger-Huet
– AML-Leukemia
– Myeloproliferative disorder
Toxic granulation
increase production of primary granules in neutrophils
reactive change caused by bacterial infections
small, dark staining granules in cytoplasm of neutrophils and monocytes
associated with leukemoid reactions and infections
not seen in CML
toxic vacuoles
as bacteria phagocytized and digested by neutrophils, vacuoles appear in cytoplasm
peripheral blood reveals “holes” in cytoplasm of neutrophils
may also be caused by prolonged contact with EDTA
associated with leukamoid reactions and infections
not seen in CML
Dohle bodies
cytoplasmic inclusions
associated with bacterial infections
causes neutrophils to mature faster than normal
hurried development causes residual RNA in cytoplasm
single or multiple, sky blue to gray blue inclusions
associated with reactive changes in leukemoid reactions and infectios
appear also with toxic granules and vacuoles
auer rods
aggregates of primary granule
seen in myeloblasts (primarily in these) and monoblasts
AML
cytoplasmic needle-shaped, red, rods
peroxidase positive
CML, AML, AMML
immune deficiency disorders
Inherited disorders resulting in disruption or
dysfunction of immune cells
• Primarily T, B & Natural Killer Cells
• Severe Combined Immune Deficiency
• Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
• 22q11 Syndromes
• Bruton-Tyrosine Kinase Deficiency
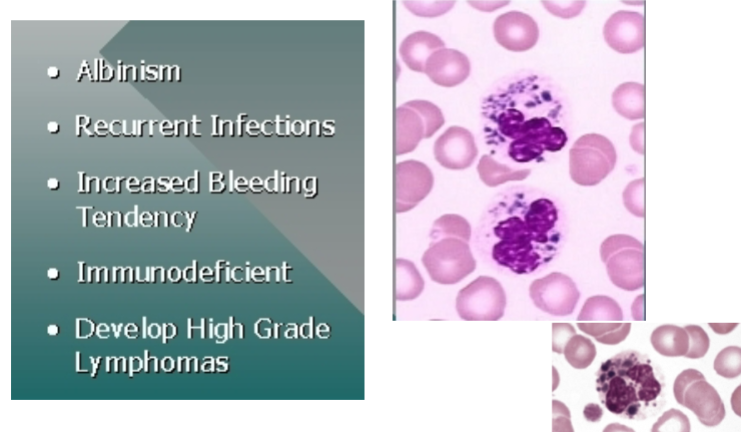
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
Autosomal recessive trait
– CHS1 LYST gene on chromosome 1q42.1-2 that encodes for a
protein that regulates the morphology and function of
lysosome-related organelles
• Large lysosomal inclusions that cannot release contents
during bacterial digestion
• Fusion of primary granules
• Large peroxidase positive granules in granulocytes and
lymphocytes
• Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
• Patients have ocular and cutaneous albinism
• Susceptible to pyogenic organisms
• Recurrent infections
• Decreased WBC count, Defective chemotaxis
Alder-Reilly Anomaly
Autosomal recessive
• Leukocyte function is not affected
• Gene prevents breakdown of mucopolysaccharides in
cytoplasm of neutrophils and monocytes
• Dense, Large, dark staining cytoplasmic granules in clusters
surrounded by vacuoles
• Mucopolysaccaridoses: Hunter’s and Hurler’s syndromes
• May be confused with toxic granulation
May-Hegglin Anomaly
Autosomal dominant
• Large (2-5 u), well defined pale blue cytoplasmic
inclusions in granulocytes
– Dohle body like inclusions
• Disordered production of myosin heavy chain type
IIA
– Thrombocytopenia with giant platelets
• Abnormal bleeding
• RNA derived from Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
• Characterized by mutations in the MYH9 gene
Nuclear appendages
• Drumstick appendage
• Seen in neutrophils
• Thought to be inactivated X chromosome.
• Abnormal numbers in Kleinfelter syndrome.
Lupus Erythematosus Cell (LE) cell phenomenon
neutrophil with phagocytized nuclear material
found in patients with systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE)
lymphocytosis
Increase in circulating lymphocytes
• >42-45%
• Reference: 18-42%; 1.2-3.2 x 103/ul
• 2 types: Absolute and relative
– Absolute
• 4.5 x 103/uL
– Relative
• Increase in % lymphs, < 4.5 x 103/uL absolute count
• Normal in blood of infants
– (reversed differential)
– Up to about 10 years of age
lymphocytosis - diseases and other affects
• Absolute lymphocytosis- with neutropenia:
– Viral infections (EBV & IM, CMV, Rubeola, Mumps, Rubella, Varicella, Herpes)
– Viral pneumonia, viral meningitis
• Aplastic anemia, pernicious anemia
• REACTIVE LYMPHOCYTOSIS:
– Proliferation during infections with Epstein Barr virus (EBV)
– infectious mononucleosis
– > 10% atypical lymphocytes
– Cytomegalo virus (CMV)
• Increase in atypical lymphocytes
• Leukemia
– ALL
– CLL
• Lymphoma
monocytosis
increase in the number of monocytes
Reference: 2-11 % and 0.1-1.3 x 103/ul
• >11%
• > 1.0 x 103/ul
• Causes:
– Infections (bacterial , viral, TB)
– Parasites
– Hodgkin’s disease
– Leukemia
• CML
• CMoL
leukopenia
decrease in total number of leukocytes
below 5.0 × 10³ / uL
most often coincides with neutropenia
increased risk for infection
neutrophenia
• Absolute decrease
– neutrophils < 2.3 x 103 /ul or 2.3 x 109/L
– <50%
• Causes:
– Decreased production by bone marrow
• Aplastic anemia, Fanconi’s anemia
– Viral Infections
– Increased Destruction
• Overwhelming infection, splenomegaly
– Alcoholics, chemicals, drugs
– Starvation, anorexia nervosa
– Chemotherapy
– Radiation (think Fukushima, Chernobyl, Three Mile Island, Hiroshima)
eosinopenia
decrease in number of eosinophils
below 0.15 × 10³ / uL
causes:
stress, shock, severe burns, blood loss, infections
hypoadrenalism (Cushing’s syndrome)
elevated ACTH
ACTH injections
lymphopenia
• Absolute count < 1.2 x 103/L (109/uL)
• <18%
• Neutrophilia (infections, leukemia)
• Immune deficiency disorders:
– Bruton’s B cell deficiency.
– SCID
– Thymic aplasia
• Aplastic anemia
• HIV
• Chemotherapy
atypical/reactive lymphocytes
• Occurrence
– Viral infections
– i.e. Infectious mononucleosis
– Epstein Barr Virus (EBV)
– Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
• General characteristics
– Pleomorphism
– Increase in nuclear and cytoplasmic size,
– Changes in cell size, shape of nucleus, chromatin pattern and
cytoplasm
– Changes in stain intensity
infectious monoculeosis
• An acute, benign, self-limiting disease caused
by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
• IM like illness - Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
– proliferation of atypical/reactive lymphocytes
– high titer of mononucleosis antibodies
– Presence of EBV antibodies
• Virus infects B lymphs
• Reactive lymphs are T lymphocytes reacting to
infected B cells
• Clinical findings:
– Occurrence: most frequent in children and young adults
– Virus lives in B lymphs and epithelial cells of oropharynx
– Transmitted primarily by oropharyngeal secretions , blood,
and transplacental
side effects of infectious mononucleosis
• May be severe with high fever and systemic manifestations
suggestive of septicemia or leukemia
• Most often mild and undiagnosed
• ½ population is exposed before 5 years old, ages 15 to 24 -
90% have antibodies
• Splenomegaly- 50% of patients
• Common symptoms: sore throat, headache, generalized
aching, loss of appetite, malaise, lymphadenopathy
• Incubation- 10 to 50 days; lasts 1- 4 weeks
laboratory evaluation of infectious mononucleosis
• Laboratory evaluation:
– Lymphocytosis
– leukocyte count increases as disease progresses
– Absolute lymphocyte count is >4.5 x 103/ul
– Relative lymphocytosis 60-90 %
– with > 10% reactive lymphocytes
– Plasmacytoid lymphocytes
– Heterophile Antibodies
– Monotest or Monospot: positive after 1 week
– CMV titre : negative
cytomegalovirus (CMV)
• Absolute lymph count > 4.5
• Blood – reactive lymphs > 10%
• Heterophile abs – negative
• EBV antibodies- negative
• CMV antibodies- positive- IgG, IgM
leukemoid reaction
• Non-leukemic leukocytosis
• WBC > 30,000/ul
• Peripheral blood change resembling leukemia, but
due to other cause
• Lack of myeloblast in Peripheral Blood
• Shift to the left
• LAP increased
• Cause: infections, pneumonia, meningitis,
tuberculosis, inflammation, metastatic cancer
general characteristics:
aka leukoerythroblastotoic reaction
increase in total number of leukocytes (50,000 - 100,000) as well as presence of immature and pathological forms in peripheral blood
presence of nucleated RBCs in blood
leukemoid reactions fall in the following categories
• Neutrophilic leukemoid reaction
– infections: bacterial, viral, parasitic, TB
– causes similar to leukocytosis
– trauma: electrical, chemical, ischemia, bleeding
– collagen vascular diseases: SLE, RA
– neoplasm- metastisis in bone marrow
• Hematologic causes
– myeloproliferative disorders
– hemolytic anemias: transfusion reactions
– folic acid therapy of megaloblastic anemia of pregnancy
– recovery of drug induced agranulocytosis
• Splenectomy
• Gram negative bacilli endotoxins
• Exercise, convulsions, post surgery, uremia, diabetes,
gout, genetic and idiopathic
differentiating between leukemoid rxn and CML

lab evaluation of leukemoid rxn
• WBC count
• Detailed differential
• LAP count (leukocyte alkaline phosphatase)
– differentiates CML and leukemoid rxn
– > in leukemoid rxn, > 100
– < in CML, < 10
• Check for Philadelphia chromosome +