Cell Biology Biophysics Revision lecture
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Gibbs free energy
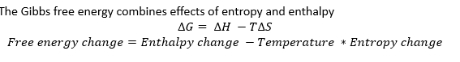
Free energy example

pH and buffers
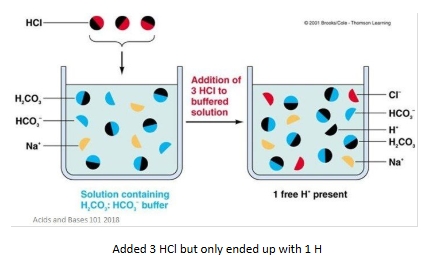
Calc buffer pH

Uses of henderson hasselbach
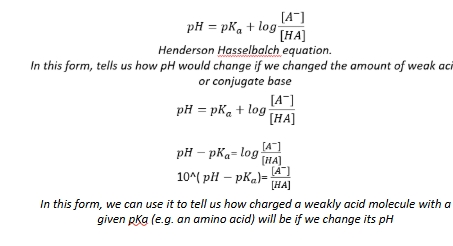
Importance of pH
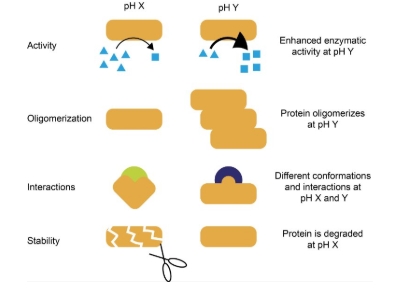
Amino acids and proteins affected by this
The Donnan problem and electroosmotic effects in cells
Macromolecules e.g. DNA, proteins contribute little to cellular osmolarity as despite their large size, they have relatively low copy number
However, due to their charge, they attract counter ions which do contribute to osmolarity.
The osmolarity of fluid outside the cell is mainly do to small inorganic ions.
These would leak slowly across the plasma membrane, attracted to theimpermeable macromolecules inside the cell
Eventually equilibrium would be reached with higher osmolarity inside the cell –the Donnan effect
’Because of the above factors, a cell that does nothing to control its osmolarity will havea higher concentration of solutes inside than outside. As a result, water will be higher inconcentration outside the cell than inside. This difference in water concentration acrossthe plasma membrane will cause water to move continuously into the cell by osmosis,causing it to rupture.Animal cells and bacteria control their intracellular osmolarity by actively pumping outinorganic ions, such as Na+, so that their cytoplasm contains a lower total concentrationof inorganic ions than the extracellular fluid, thereby compensating for their excess oforganic solutes
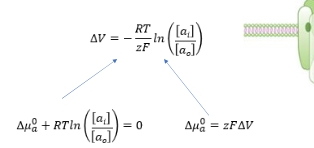
what does the Nernst equation give?
The Nernst equation tells us what the electricalpotential will be when ions have stopped flowingacross a membrane because the charge differencebalances out diffusion down a gradient

Electrical potential
Charges have an electric field around them which can generate a force – like other fields in physics e.g. magnetic, gravitational
Fields have potentials which for an electric field is just the energy,E, stored in the field divided by the charge moving in it

Nernst equation
Equation comes from 2 parts:
the electrical potential due to moving a charge in an electric field
Entropy change due to mixing