Week 2- Effects of Radiation Exposure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Define Radiobiology
Studies the biological effects of ionizing radiation on living organisms
Direct vs Indirect Radiation
Direct = 1/3 of ionizing radiation
Indirect = 2/3 of ionizing radiation → MORE COMMON
What happens when biological material is irradiated?
DNA is damaged
Why is radiolysis of water the first step in the primary mechanism of biological damage to macromolecules? Indirect or direct?
Ionization causes particles in water to split causing free radicals such as those in hydroxyl and hydrogen
Indirect effect
Deterministic vs. Stochastic Effects of Radiation
Deterministic: manifest only after radiation exceeds a certain threshold
Stochastic: random, no threshold
Law of Bergonie and Tribondeau
The younger (stem) the cell the more radiosensitive, the older, the less radiosensitive
More proliferative = more radiosensitive
More metabolic activity = more radiosensitive
Tissues with High resistance to radiation vs tisues with low resistance to radiation
High resistance: optical lens, muscles and nerves
Low: Lymphoid, bone marrow, testes, Intestines, Mucous membranes
Radiation Early effects vs. Late effects
Early: occur right after irradiation, 3-4 months
Late: occur from 6 monthd-years
4 Stages of Acute Radiation Syndrome
Prodromal period: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea = earliest clinical symptoms
Latent: patient looks and feels ok
Manifest illness
Recovery or Death
Different dosages relating to syndromes
>200 -1000 rad = hematologic syndromes
>1000-5000 rad = gastrointestinal syndromes
>5000 = central nervous system syndromes
Therapeutic effects of radiation can cause other problems in the oral cavity, what are they (5)
Developmental
Acquired
Mucositis: death of basal cells causes focal hyperemia and edema
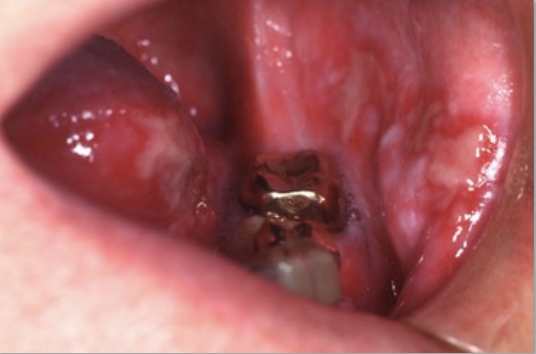
Candidiasis: fungal infection, decrease WBC count, causes loss of tissue
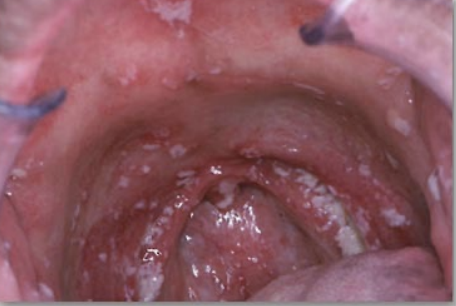
Xerostomia: salivary glands get affected by radiation (parotid most sensitive) which leads to reduced or thickening of saliva, causes dryness, burning, cracked lips, mouth, tongue change
Treat with artificial saliva and sialogues, control caries, avoid sugary and spicy foods
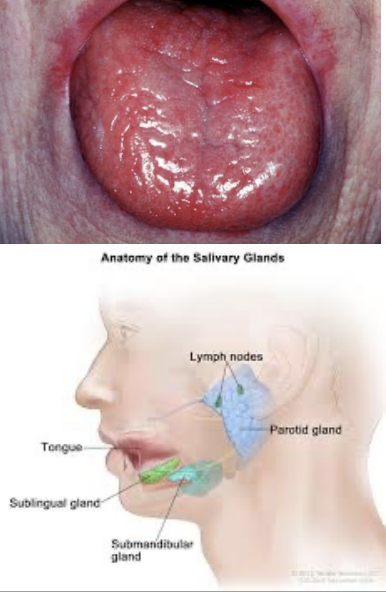
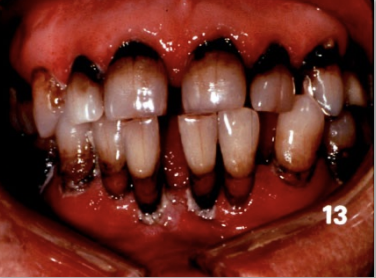
Radiation caries: Decrease in saliva and demineralization along with heavy plaque causes caries. Can also cause effects to fetus
Osteoradionecrosis: Bone becomes exposed after oral radiation
Stochastic effect: only appear when exposed to >50Gy
More common in mandible
3Hs: Hypovascularity, Hypocellularity, Hypoxia (local)
Pain, swelling, drainage
Radiation Effects on Embryo/Fetus
2 Weeks
3-8 Week
9 Weeks-birth
2 Weeks: embryonic death and miscarriage
3-8 Week: congenital malformations, miscarriage
9 Weeks-birth: mental retardation, microcephaly, stunting growth
What is the lowest level of radiation that can be lethal for young fetus?
What level of radiation will cause mental retardation at 8-15 weeks?
>0.1 grays (Gy) can be a lethal dose or damage threshold
0.5 grays (Gy)
Define teratogen
An agent that causes congenital birth defects
Can you take x-rays on pregnant women?
Yes, with proper precautionary measures