ComputerArchitecture
5.0(3)Studied by 162 people
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Last updated 10:39 PM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
\
Networks
3
New cards
Networks is a hierarchical model and has 3 layers:
Access, Distribution, Core
4
New cards
What pulses into pits in physical layer (transmission media) of network?
Voltage, radio frequency or light
5
New cards
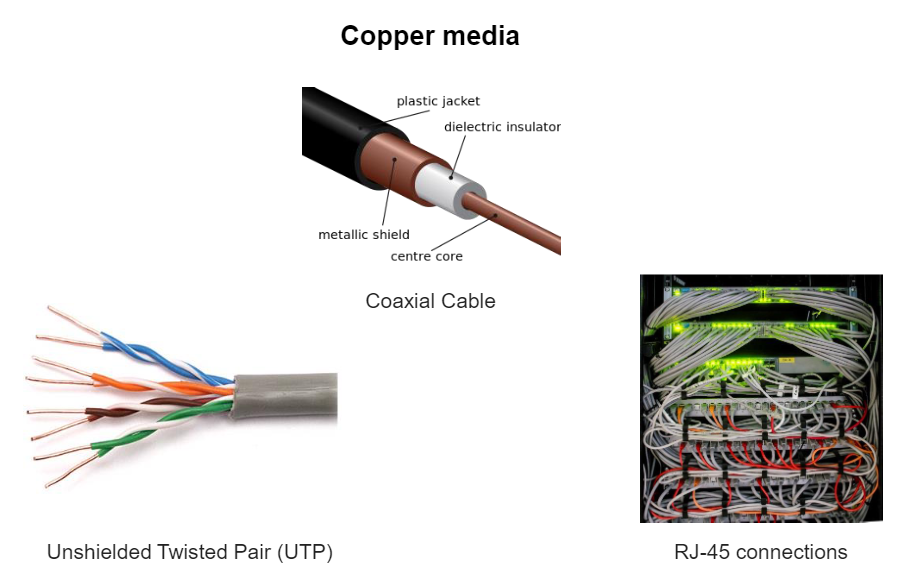
Types of wired physical layer
6
New cards
Network can get Interferences
from external signals such as:
from external signals such as:
\- Radio waves
\- Electric engines
\- Fluorescent tubes
\- Electric engines
\- Fluorescent tubes
7
New cards
Uses of unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
Ethernet networks, among many other uses (mainly indoor applications)
8
New cards
What advantages does unshielded twisted pair (UTP) have?
Twisted pairs cancel unwanted signals.
9
New cards
Describe physical aspect of unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
Four unshielded twisted pairs with different colours and plastic cover.
10
New cards
What type of performance does Cat (Category) 5e cable provide?
* 100MHz
* suitable for10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet), and 1000BASE-T (GigabitEthernet)
* suitable for10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet), and 1000BASE-T (GigabitEthernet)
11
New cards
What is Cat (Category) 5e cable?
Cable standard
12
New cards
What is crosstalk?
a signal transmitted on one channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel
13
New cards
Specifications of Cat 6 cable
* Backward compatible
* Specifications against crosstalk and noise
* performance of up to 250 MHz
* RJ-45 connectors when used as patch cable
* Specifications against crosstalk and noise
* performance of up to 250 MHz
* RJ-45 connectors when used as patch cable
14
New cards
Specifications of Cat 6a cable (augmented)
* Unshielded and Foiled
* defines the standard at frequencies up to 500 MHz
* rates up to 10 Gbps
* defines the standard at frequencies up to 500 MHz
* rates up to 10 Gbps
15
New cards
Specifications of Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
* Better transmission characteristics than UTP
* Shielding is applied to all pairs individually and an additional overall shielding is also added.
* Shielding is applied to all pairs individually and an additional overall shielding is also added.
16
New cards
Specifications of Cat 7 and 7A cables
* It allows 10 Gigabit Ethernet
* Up to 1000 MHz
* Up to 1000 MHz
17
New cards
Specifications of Cat 8 cables
* It allows 40 Gigabit Ethernet
* Up to 2000 MHz
* Up to 2000 MHz
18
New cards
Transmission problems - ATTENUATION
Attenuation is the gradual loss of signal intensity through a medium
19
New cards
Transmission problems - DELAY or LATENCY
* It depends on the operating frequency
* a measure of the time delay experienced by a system
* The delay of a network specifies how long it takes for a bit of data to travel acrossthe network from one node or endpoint to another.
* a measure of the time delay experienced by a system
* The delay of a network specifies how long it takes for a bit of data to travel acrossthe network from one node or endpoint to another.
20
New cards
Transmission problems - THERMAL NOISE– ELECTRONS (Thermal agitation)
* temperature-dependant
* it adds White noise to signal and can distort it
* it adds White noise to signal and can distort it
21
New cards
Transmission problems - INTERMODULTION NOISE– NONLINEAR SYSTEMS (Pink noise)
* Combined frequencies (f1+f2, f1-f2)
* Pink noise can interfere with the transmitted signal and degrade its quality.
* Pink noise can interfere with the transmitted signal and degrade its quality.
22
New cards
Transmission problems - PULSES
pulses problems are short time and
irregulars
irregulars
23
New cards
Describe Optical Fiber
* flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair
* used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications
* they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates)than electrical cables
* Signals travel along them with less loss
* Fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference
* used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications
* they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates)than electrical cables
* Signals travel along them with less loss
* Fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference
24
New cards
In optical fiber light is kept in
the core (by the phenomenon of total internal reflection)
25
New cards
Optical fibers typically include a core surrounded by
a transparent cladding material with a lower index of refraction. (so that light be kept inside of it)
26
New cards
\
To confine the optical signal in the core of optical fiber the refractive index of the core must be SMALLER/GREATER than that of the cladding.
To confine the optical signal in the core of optical fiber the refractive index of the core must be SMALLER/GREATER than that of the cladding.
Greater
27
New cards
Fibers that support a single mode are called single-mode fibers (SMF). While Fibers that support many propagation paths or transverse modes are called
multi-mode fibers
28
New cards
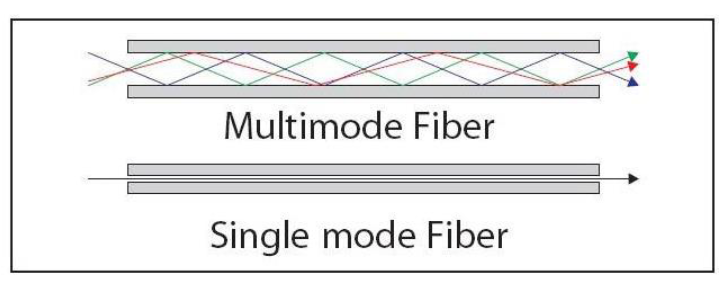
Multi-mode fibers generally have a WIDER/NARROWER core diameter and are used for LONG-DISTANCE/SHORT-DISTANCE communication links and for applications where high power must be transmitted.
Wider, Short distance
29
New cards
Single-mode fibers are used for most communication links longer than
1000 meters
30
New cards
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology for implementing
wired Ethernet local area networks (LANs) that enables the electrical current necessary for operating each device to be carried by Ethernet data cables instead of standard electrical power cords and wiring.
31
New cards
PoE (Power over Ethernet) specifics
* Powered via distributor
* Power and data is transmitted
* Standard IEEE 802.3af PoE
* Power and data is transmitted
* Standard IEEE 802.3af PoE
32
New cards
A collision domain is
a network segment connected by a shared medium or through repeaters where data packets may collide with one another while being sent. The collision domain applies particularly in wireless networks, but also affected early versions of Ethernet.
33
New cards
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is
a media access control method
34
New cards
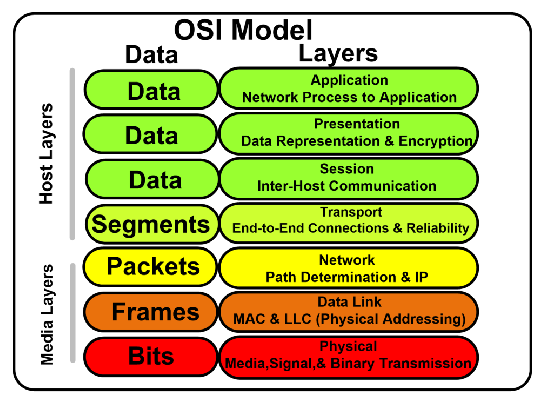
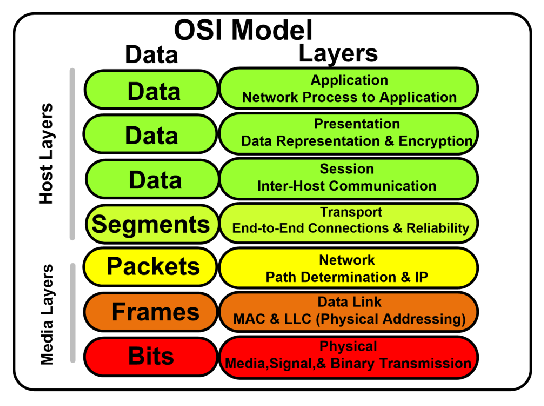
In OSI model Host Layers include
Data and segments
35
New cards
In OSI model Media Layers include
Packets, frames, bits
36
New cards
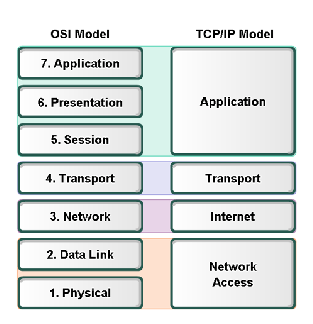
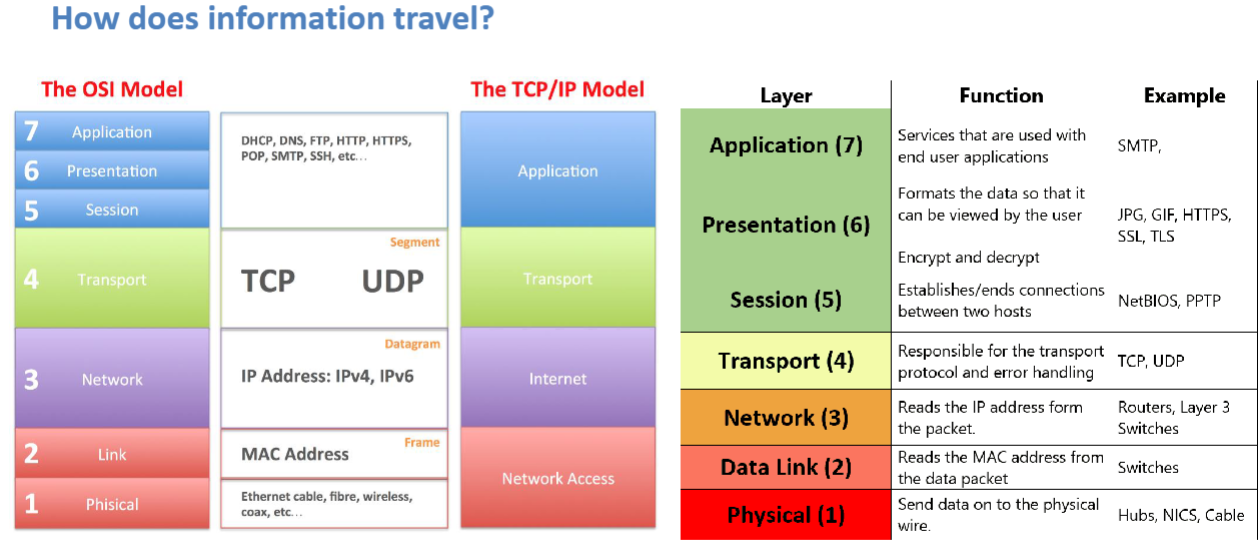
OSI vs TCP/IP diagram
37
New cards
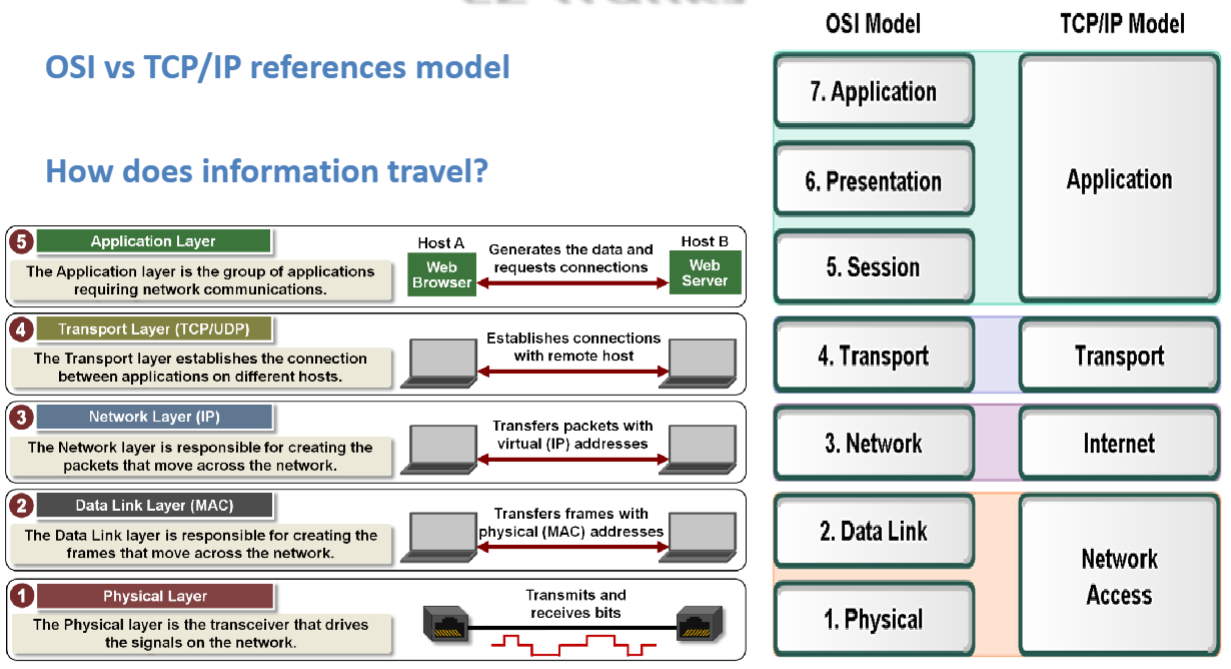
OSI vs TCP/IP diagram
38
New cards
A trunk port is
a port that is assigned to carry traffic for all the VLANs that areaccessible by a specific switch, a process known as trunking.
39
New cards
4 Basic processes in the network layer:
* Addressing
* Encapsulation
* Routing
* Decapsulation
* Encapsulation
* Routing
* Decapsulation
40
New cards
Networks can be grouped by:
* Geographic location
* Purpose
* Ownership
* Purpose
* Ownership
41
New cards
Why do we need to separate hosts in networks?
* avoid degradation in performance
* Security
* Addressing management
* Security
* Addressing management
42
New cards
VLAN is a
subnet, broadcast domain
(virtual local area network)
(virtual local area network)
43
New cards
\
VLANs are able to logically segment switched networks, based on
VLANs are able to logically segment switched networks, based on
* Physical location
* organizations
* organizations
44
New cards
Switches are level 2 devices which are able to understand (IP or MAC ) addresses
MAC
45
New cards
VLANs provide segmentation based on
broadcast domains
46
New cards
hosts in different subnets will be able to communicate with each other through
a Router
47
New cards
VLANs are assigned in the switch and are associated to the
hosts’ IP addresses
48
New cards
Ports assigned to the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain. TRUE/FALSE
TRUE
49
New cards
Members of static VLANs are known as
port based
50
New cards
Routable protocols VS Routing protocols
Routable protocols:- IP, IPX/SPX
Routing protocols:- RIP, EIGRP, OSPF
Routing protocols:- RIP, EIGRP, OSPF
51
New cards
Routable Protocols VS Routing protocols definitions
* Routable protocols:
A communications protocol that contains a network address as well as a device address. It allows packets to be forwarded from network to another.
* Routing protocols:
They specify how routers communicate with each other, distributinginformation that enables them to select routes between any two nodes ona computer network. Routing algorithms determine the specific choice ofroute.
A communications protocol that contains a network address as well as a device address. It allows packets to be forwarded from network to another.
* Routing protocols:
They specify how routers communicate with each other, distributinginformation that enables them to select routes between any two nodes ona computer network. Routing algorithms determine the specific choice ofroute.
52
New cards
By default, L3 switches don’t operate in layer 3. That’s why, first of all, to activate it X is required
\
IP routing
IP routing
53
New cards
To save the configuration backups we use
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
54
New cards
DNS is a
Domain Name System
55
New cards
Zone Authority is the part of a (X) on which a server is responsible
Name Space
56
New cards
What Name Server does?
* replies to all the client questions
* keeps the names assignment for all IP addresses of the area.
* keeps the names assignment for all IP addresses of the area.
57
New cards
What has static vs dynamic IP addresses?
* Static IP addresses
Servers, Switches, routers
* Dynamic IP addresses
Clients (end devices)
Servers, Switches, routers
* Dynamic IP addresses
Clients (end devices)
58
New cards
What does DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automate?
DHCP enables the network devices to obtain IP address automatically andsome additional information from a DHCP server. This software serviceautomates the IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways allocation
59
New cards
Wireless security types
* Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
* Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) best one now si WPA3 = improved WEP
* pre-shared key (PSK)
* TKIP - no longer considered secure
* AES-CCMP = encryption
protocol (better than WEP)
* Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) = authentication
framework
* Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) = networking protocol
* Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) best one now si WPA3 = improved WEP
* pre-shared key (PSK)
* TKIP - no longer considered secure
* AES-CCMP = encryption
protocol (better than WEP)
* Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) = authentication
framework
* Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) = networking protocol
60
New cards
Operating system is USER/KERNEL mode?
KERNEL
61
New cards
Driver is a
group of files that enable one or more hardware devices to communicate with the computer's operating system.
62
New cards
What resources does the operating system manage?
Processors● Memories● Timers● Disks● Mice● Network Interfaces
63
New cards
What is a system bus?
A bus is a subsystem that is used to connect computer components and transfer data between them.
64
New cards
System bus is made of 3 components
Control Bus, address bus, data bus
65
New cards
Types of operating systems:
Mainframes● Servers● Multiprocessors● Personal Computers● Handheld (Mobile)● Embedded● Sensor Node● Real Time● Smart Cards
66
New cards
What is a kernel?
It is the main layer between the OS and underlying computer hardware, and it helps with tasks such as process and memory management, file systems, device control and networking
67
New cards
What is the purpose of a Kernel?
1\. It provides the interfaces needed for users and applications to interact with the computer.
2\. It launches and manages applications.
3\. It manages the underlying system hardware devices
2\. It launches and manages applications.
3\. It manages the underlying system hardware devices
68
New cards
What is scheduling?
The process scheduling is the activity of the process manager that handles the removal of the running process from the CPU and the selection of another process on the basis of a particular strategy.
69
New cards
Goals of a scheduler:
* maximizing throughput
* minimizing wait time
* \
* minimizing wait time
* \
70
New cards
What is race conditions?
When two or more processes are reading or writing some shared data and the final result depends on who runs precisely when, are called race conditions.
71
New cards
What are critical regions?
It is the resource that is being shared between the processes.
72
New cards
How to solve problem with critical regions?
* No two processes may be simultaneously inside their critical regions.
* No assumptions may be made about speeds or the number of CPUs.
* No process running outside its critical region may block any process.
* No process should have to wait forever to enter its critical region.
* No assumptions may be made about speeds or the number of CPUs.
* No process running outside its critical region may block any process.
* No process should have to wait forever to enter its critical region.
73
New cards
What is memory management?
The task of subdividing the memory among different processes is called memory management.
74
New cards
Memory management algorithms:
* First fit (In the first fit, the first available free hole fulfills the requirement of the process allocated.)
* Best fit (In the best fit, allocate the smallest hole that is big enough to process requirements. For this, we search the entire list, unless the list is ordered by size.)
* Worst fit (Allocate the largest available hole to process. This method produces the largest
leftover hole.)
* Best fit (In the best fit, allocate the smallest hole that is big enough to process requirements. For this, we search the entire list, unless the list is ordered by size.)
* Worst fit (Allocate the largest available hole to process. This method produces the largest
leftover hole.)