Macromolecules and Organelles
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cell membrane
Protects cell contents, allows for transport, delineates bounds of the cell, cell-cell communication
Endomembrane system
series of interconnected membranes that allows for transport throughout the eukaryotic cell
part of the endomembrane system
nuclear envelop, rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, and cell membrane
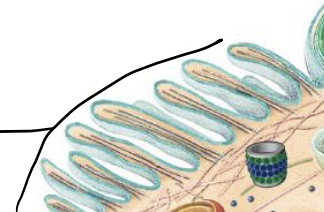
Endoplasmic reticulum
Network of flattened membranes
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes, assists with protein folding, making proteins, lipids, and carbs
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes, assists with making some lipids, detoxifies drugs
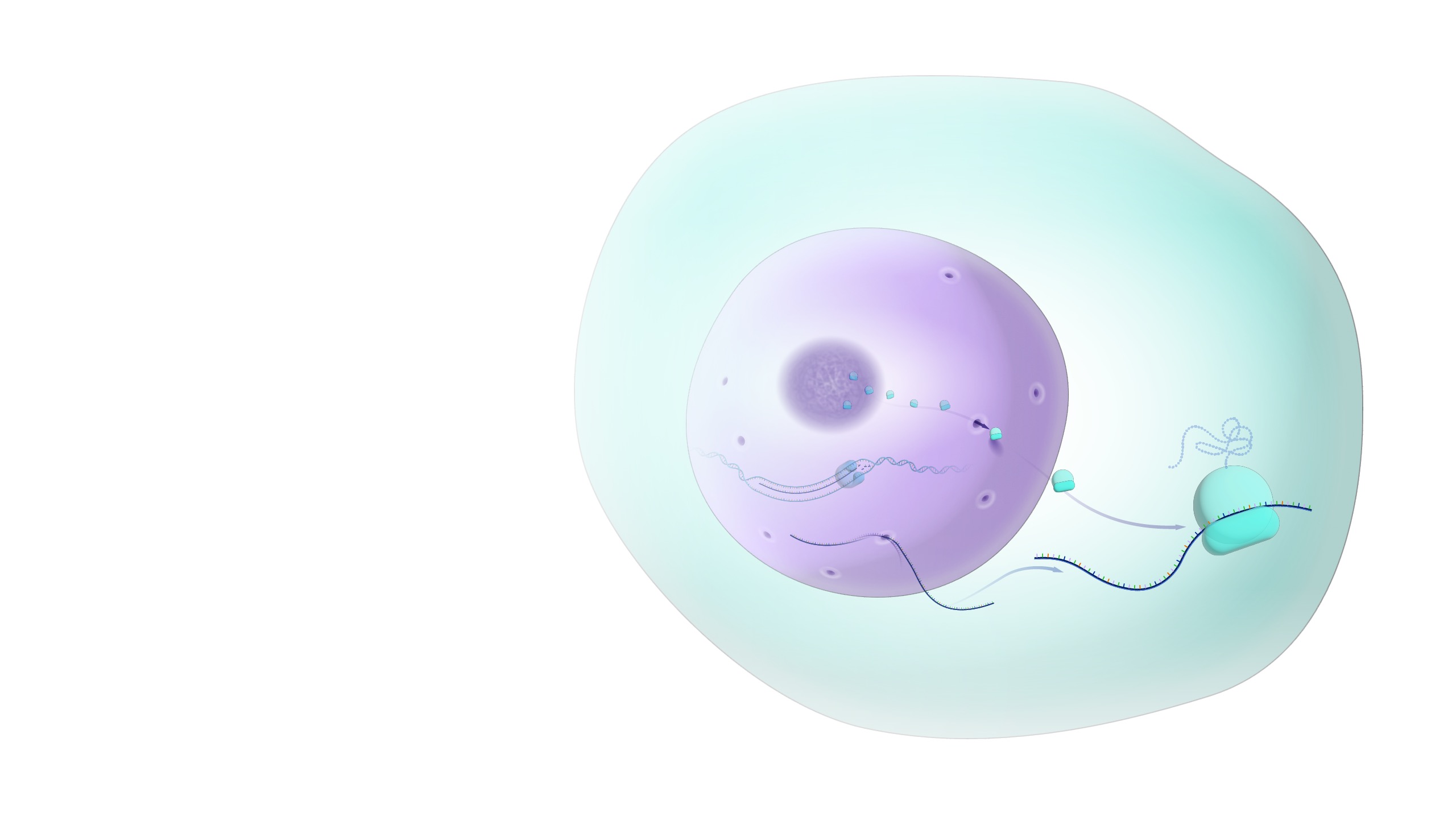
Nucleus
houses DNA, consists of it’s own nuclear membrane and nuclear pores (small openings), also houses nucleolus (which makes ribosomes)
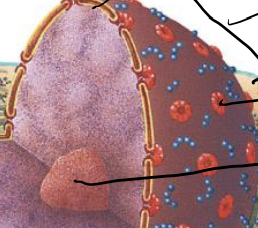
Nuclear pores and envelope
membrane and porous openings of nucleus, membrane made of phospholipid bilayer
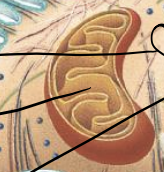
Mitochondria
“powerhouse of cell”, location of aerobic respiration
nucleolus
Inside nucleus, makes ribosomes
Cilia
small hair-like projections around cell, short in length, present in large numbers, part of cytoskeleton
Flagellum
long hair-like projections from cytoskeleton, present as single, double, or triple numbers, long, help with movement
Cytoplasm
inside region of the cell, location of all organelles

centrosome
makes mitotic spindle during mitosis (cell division), component of cytoskeleton

lysosome
membrane sack of digestive enzymes, helps cell digest and recycle structures
peroxisome
membrane sack of detoxifying enzymes
Ribosome
made in nucleolus, housed in nucleus, “workbench of cell”, makes proteins
Cytoskeleton
“skeleton” of cell, structures that support cells, provide structure and shape, and help with transport around the cell, made of different filaments
Golgi
flattened sacks of membranes, help with shipping newly made molecules to where they need to go around the cell
Monosaccharides (ring structure)
Monomer Structure Name of Carbohydrates
Disaccharides (2 rings) and Polysaccharides (strand of monosaccharides)
Polymer Structure Name of Carbohydrate
Stores energy, Provides structure, Fuel for metabolism
3 Functions of Carbohydrates
Glycosidic Linkage
Carbohydrate Bond Name
Glucose: in cells, plants, animals, simple sugar for metabolism
Starch: energy storage molecule in plants
Glycogen: energy storage in animals
Carbohydrate Examples
Fatty acid and structure: Long chain of hydrocarbons
Monomer Structure Name of Lipids
Triglyceride Structure: 3 fatty acid chains bonded to glycerol, fat storage molecule
Polymer Structure Name of Lipids
Energy storage, Temperature insulation, Protects organs
3 Functions of Lipids
Ester Bond
Lipid Bond Name
Steroids: All cells, communication
Phospholipids: All cells, makes membranes
Waxes: Plants, helps stop water movement
Lipid Examples
Amino Acid structure: Same in every Amino Acid
Monomer Structure Name of Proteins
Polypeptide (strand of amino acids)
Polymer Structure Name of Proteins
Structure
Communication
Enzymes
3 Functions of Proteins
Peptide Bond
Protein Bond Name
Any enzyme: All cells, enable metabolic reaction
Structural proteins like keratin in hair
Insulin, controls blood sugar
Protein Examples
Nucleotide: Contains nitrogenous bases which code A,T,G, and C
Monomer Structure Name of Nucleic Acids
Polynucleotide (strand of nucleotides)
Polymer Structure Name of Nucleic Acids
Carry genetic information
Pass along information
ATP: energy molecule
3 Functions of Nucleic Acid
Phosphodiester bond
Bond Name of Nucleic Acid
DNA – All cells, makes the genome
RNA – All cells, carries and translates genetic info
ATP – All cells, carries energy
Nucleic Acid Examples