Chap 13 Emotions attachment + social relationships
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
First emotions
Izard and collegues theorize that basic emotions are biologically based, develop early in life, play critical roles in motivating and organising behaviour
Distinct emotions that emerge in first 6 months of life
eg, at birth babies show contentment and distress, at 6 months, contentment → joy, interest → surprise, distress → anger, disgust, fear, sadness
at 18 months, self conscious emotions emerge, requires awareness → embarrassment, guilt, shame, pride
Emotion regulation
at 9 months infants use social referencing → monitor companions emotional reactions and use it to decide how to behave/feel
12 months → move away from distressing events
18-24 months → attempt to control whatever is upsetting them
When does jealousy develop? Alternative explanations to jealousy?
Displayed earliest at 9 months
preferences, temperament and hatred towards new stimuli can all be alt explanations to jealousy
Emotional competence
Patterns of emotional expression, greater understanding of emotion and better emotion regulation skills
they also learn display rules for emotion, which r cultural rules specifying what emotions should be expressed in what circumstance
Why do adolescents experience mildly negative moods more than children?
Experience more negative life events developmentally
Not as good at regulating emotions compared to adults
may choose to savour negative/mixed emotions at times
Do older adults experience more negative emotions?
No, emotions r not any less important to them, they experience similar level of emotional intensity as young adults, actually seem to live more positive emotional lives
Emotions and aging in older adults
Overall emotional wellbeing increases with age
Older adults experience longer lasting positive emotions, fleeting negative emotions, fewer emotional ups and downs per day
Socioemotional selectivity theory
Perception that one has little time
left to live
Prompts more emphasis on the goal
of fulfilling current emotional needs
Leads to the positivity effect in older adults
They tend to place more emphasis on positive information
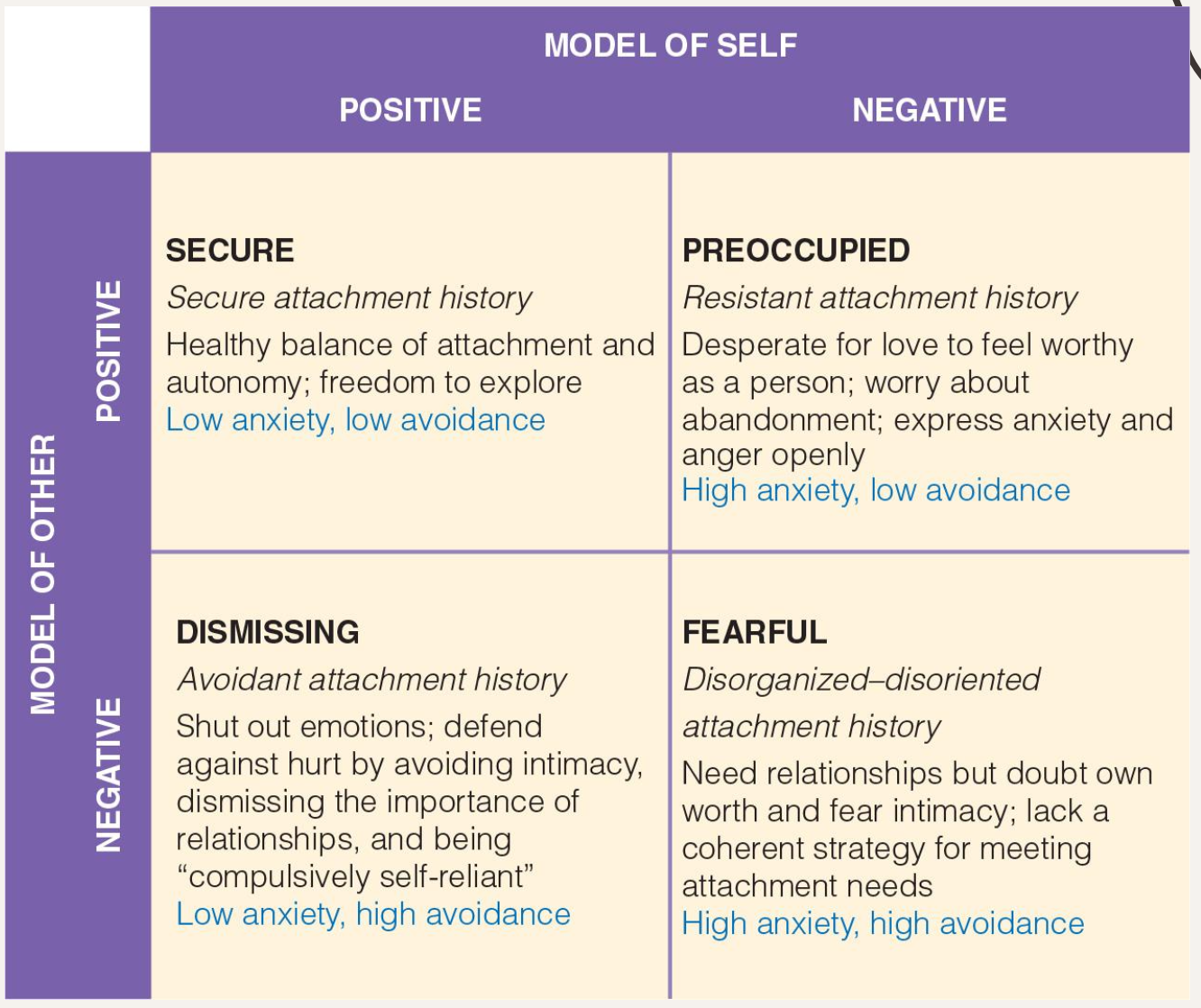
Attachment theory
Based on ethology
Investigates how attachment helped our ancestors adapt to env
Attachment is a strong emotional tie that binds a person to an intimate companion
Babies make sure adults tend to their needs by sucking cooing smiling crying
Adults are hormonally prepared for caregiving (oxytocin)
Cognitive aspect of attachment theory
Infants construct expectations of relationships through internal working models
Cognitive representations of themselves and other people like a network of schemas
Guides processing of social info and their behaviour in relationships
Securely attached infants will develop secure internal working models that they are loveable
Insecurely attached infants develop models that they are difficult to love
Peer relationships and how they assist development
Children learn peers are their social equals, relationships r reciprocal and forces them to hone their perspective taking skills, contributing to moral + cognitive development
Chumships → Close childhood relationships teach children how to
participate in emotionally intimate relationships
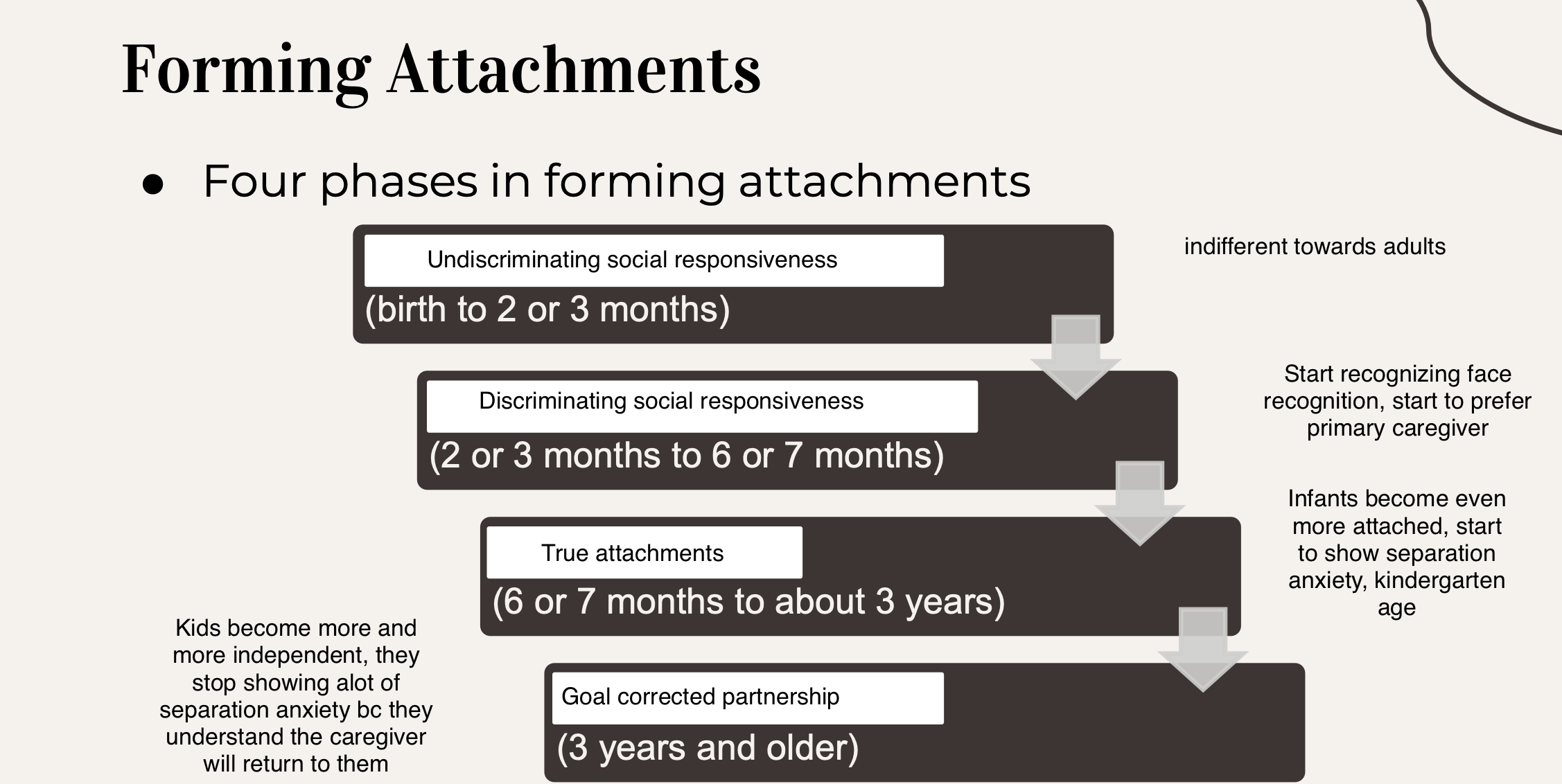
The Infant
Attachment formed between caregiver and infant
Bonding at birth is neither necessary nor sufficient for a strong parent– infant attachment to form
over the weeks they develop synchronised routines
4 phases of forming attachments
Attachment related fears
Separation anxiety → Wary/fretful when separated from parent, peaks at 14 - 18 months
Stranger anxiety → Wary or fretful reaction to the approach of an unfamiliar person
Peaks around 1 year of age
Attachment figure serves a secure base for exploration + safe haven, when infants experience these fears they may not do these things
What did the Strange Situation by Ainsworth et al (1978) find?
4 types of attachment styles
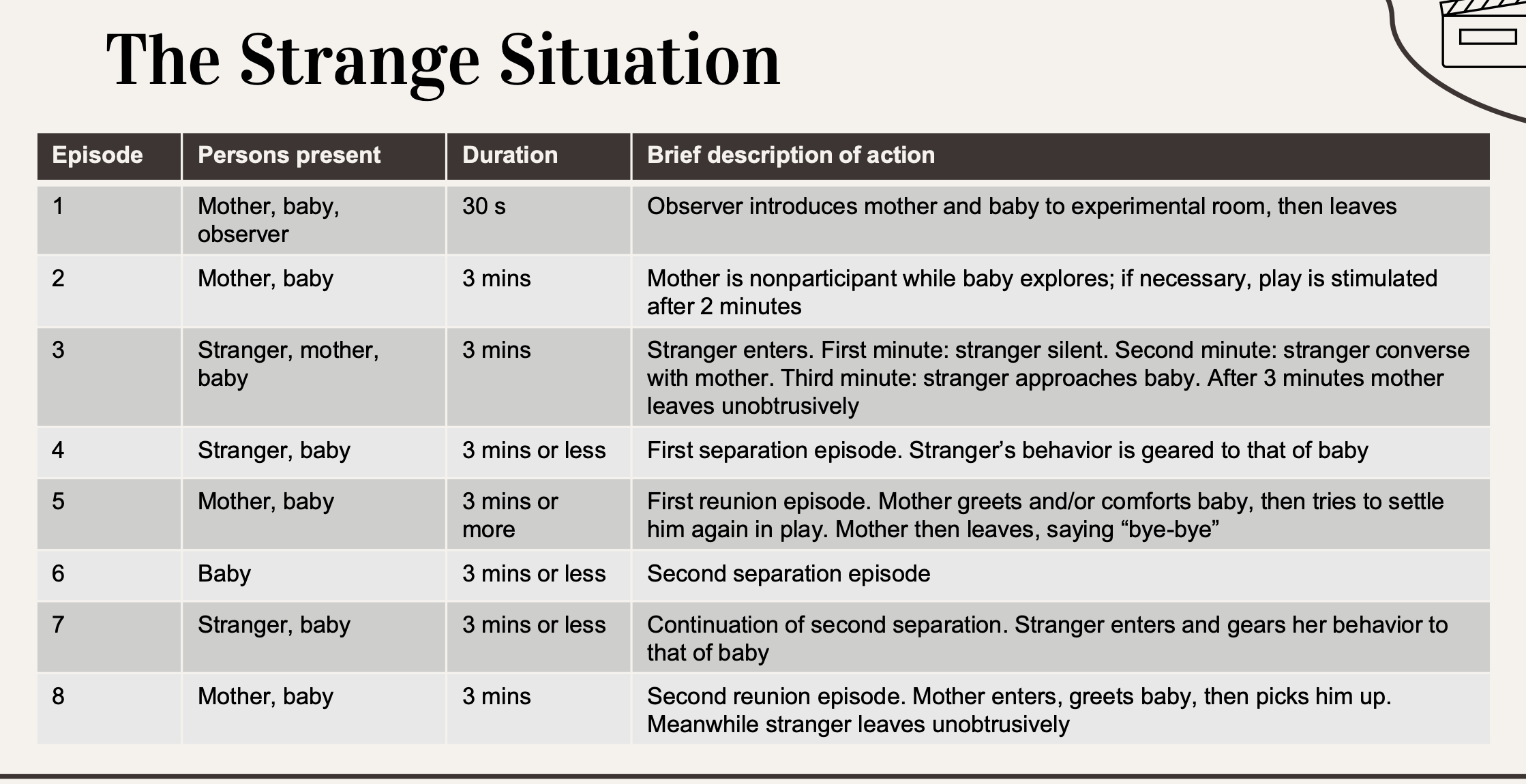
What makes quality attachment?
Contact comfort promotes human attachment, parents who r sensitive and responsive to baby needs signals secure attachments
Its more abt the parent’s efforts, not the infant, relationship btw infant temperament and attachment is pretty weak, but caregivers who are responsive to temperamental changes are more able to establish secure attachment
Cultural & Social contexts related to attachment
Alloparenting distributes care across multiple caregivers
Individualistic cultures
■ want babies to take interest in objects, interact face-to-face
with their parents, and explore independently
Collectivist cultures
■ keep their babies in physical contact all day and train them to
stay close and do as they are told
What happens if an infant never has an opportunity to form an attachment?
Infants who spent their first several months or more in deprived orphanages experience:
■ Poor growth
■ Medical problems
■ Delays and differences in physical, cognitive, and social- emotional development
After being adopted 90% grow attached to adoptive parents, saw parents as comforting AND threatening
Separation in infants
They go thru a grieving process
Search frantically for loved ones, become sad after giving up, sometimes ignore after caregiver comes back, but will gradulaly warm up
In military families:
Sometimes infants still develop emotional and behavioural problems whether sensitive care is provided by a family member
Is day care bad for infant attachment?
No, infants experiencing routine care by someone not their parent does not develop much differently, quality of parenting is the stronger influence on later development
What is secure attachment linked to in later development?
Intellectual competence
Social competence
Emotional regulation
Good peer relations
Parent child attachment
At age 3 kids grow more independent from their parents
Wants separations to be predictable
and controllable
Still seek attention from parents, look to peers for social support
Peer networks in children
10% of social interactions in toddlerhood (tf is this word) are with peers
30% in middle childhood are w peers
Children and Play
Types of play (Ages 1-5)
locomotor play
object play
social play
pretend play -> use object pretend its smt else
Unoccupied play
Solitary play
Onlooker play
From infancy to age 5, play becomes more social and imaginative
Why is play important?
Allows children to develop many skills
Associated with the development of motor, cognitive,
language, social, and emotional skills
May contribute to healthy emotional development
Types of peer acceptance (sociometric scale)
Accepted (or popular): Well liked by most and rarely disliked
Rejected: Rarely liked and often disliked
Neglected: Neither liked nor disliked; these children seem to
be invisible to their classmates.
Controversial: Liked by many but also disliked by many
Average: In the middle on both the liked and disliked scales
Does peer acceptance mean friendship?
Peer acceptance not equal to friendship
in 7-8 yr olds, 39% of rejected kids had at least 1 mutual friendship
31% of popular children lacked such friendship
Having at least one friend
increases the odds that a child will
be happy and socially competent
Parent - adolescent attachment
Need independence but also security of parents to explore
Adolescents with secure parent−child attachments
■ Stronger sense of identity
■ Higher self-esteem
■ Greater social competence
■ Better emotional adjustment
■ Fewer behavioral problems
What are adolescent friendships based on?
enjoyment of common activities
mutual loyalty
intimacy and self disclosure
physical and psychological qualities
all of this changes qualitatively, not fixed
How are adolescent friendships evaluated?
Sociometric popularity
○ peer acceptance
○ being liked by many peers
Perceived popularity
○ being viewed as someone who has status, power, and visibility in the peer group
Dexter Dunphy’s theory about social networks
How peer-group structures change during adolescence may explain how peer relations lay the foundation for romantic attachments
late childhood → same sex cliques
boy + girl cliques begin interacting
11, 12yrs boy and girl cliques mix
Crowds then form
Late high school → crowds lessen bc of couple formation
Adolescent dating
4 phases: initiation , status, affection, bonding
Dating has more positive than
negative effects on development
Adult attachment
We all have social convoy → social networks that support us throughout life
Trend towards smaller social networks as we age
Adult attachment styles r related to quality of their romantic relationships + wellbeing + physical health
quality of their own child - parent attachment predicts their adult attachment + romantic relationship quality
They have a confident (wife/husband) which improves life satisfaction, physical health, cognitive functioning,
and longevity
Adult romance
Greatest influence on mate selection is homogamy (similarities)
Ppl might also look for complementarity (diffs that make up their weaknesses)
Universally men prefer youth and attractiveness
Women prefer older + financial resources
Kindness intelligence and health r universally preferred
Sternberg’s triangular theory of love
Passion
■ Sexual attraction, romantic feelings,
and a sense of excitement
Intimacy
■ Feelings of warmth, caring, closeness,
trust, and respect
Commitment
■ first deciding that one loves the other
person and then committing to a
long-term relationship
Adult attachment style chart