Science 8: Mix and Flow of Matter MF2
MF 2.1: What is density and how do we calculate it?
What is MATTER? Matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume.
What is MASS? Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It is measured in g or kg.
What is VOLUME? Volume is the amount of space something takes up. It is measured in cm3, mL, or L.
What is DENSITY? Density is the amount of particles in a given space, or the mass in a certain volume. Density is Mass/Volume. It is measured in g/cm3 or g/mL.
MF 2.2: What is buoyancy, and how does it relate to density?
What is BUOYANCY? Buoyancy is the upwards force of a fluid acting on an object. The force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced (pushed away). Buoyant force is the upwards force exerted on objects submerged in or floating on a fluid.
What is a HYDROMETER? A hydrometer is an instrument designed to measure the density of a liquid. The lower it sinks, the less dense the liquid is.
If a ship is made of steel, which is much more dense than water, what allows it to float? The ship can float because its average density is less than the density of water.
How do fish and submarines change their average density?
Fish can change their average density by expanding and contracting their swim bladder. Depending on how much gas in inside, it changes the buoyancy of the fish.
Submarines can change their average density by allowing water in and out of their ballast tanks to make the submarine sink and rise. They push water in and out using compressed air.
What is ARCHIMEDES’ PRINCIPLE? Archimedes’ Principle says that the buoyant force acting on an object equals the weight (force of gravity) of the fluid displaced by the object. 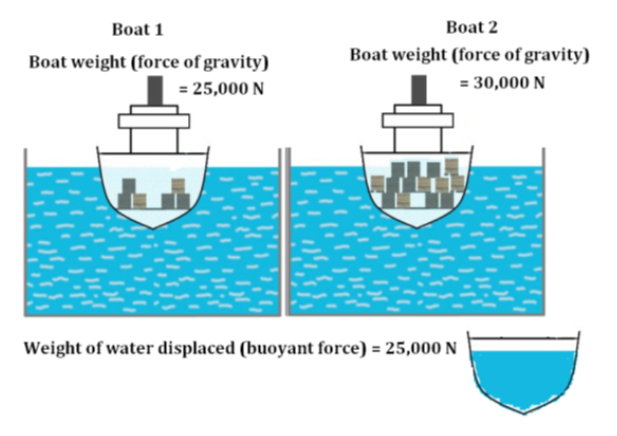
If the force of gravity equals the buoyant force, we call this neutral buoyancy.
How is density and buoyancy related to each other?
A dense object can float as long as the average density is less than the density of the fluid it floats in.
Example: a ship made of metal, wood, and air can have an average density less than water it floats!
Salt water is more dense than freshwater, so it produces a greater buoyant force. Therefore, a ship will float higher in salt water than freshwater.
MF 2.3: What is viccosity and flow rate, and how are they related?
What is VISCOSITY? Viscosity is the measure of how fast a fluid will flow; the “thickness'‘ or “thinness” of a fluid. A slow moving fluid is more viscous than a fast moving fluid, and a thin fluid is less viscous than a thick fluid. 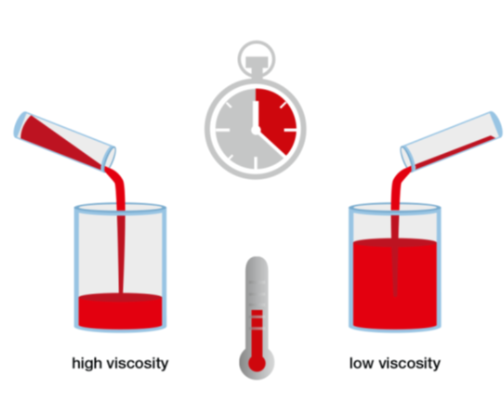
What is FLOW RATE? Flow rate is a measure of the distance traveled by a certain volume of fluid in a given amount of time. It is a measure of speed and is usually recorded in the units cm/s. Flow rate is Distance (cm)/Time(s).
What is INTERNAL FRICTION? Internal friction is when particles bump into each other, and the motion-resisting forces between the surfaces of the particles of a substance. The more bumping into each other, the slower they move because they have more internal friction. The speed they move is the flow rate. The more internal friction between particles, the slower the flow rate. The higher the internal friction, the higher the viscosity.
Factors that affect internal friction?:
Particle size: The larger the particles are, the more they bump into each other, and the slower they will flow.
Particle shape: Some particles are more prone to sticking than others. These fluids flow more slowly.
Particle temperature: The colder the particles, the slower they flow. The warmer the particles, the faster they flow.
MF 2.4: What is pressure, how do we calculate it, and what kinds of materials can be compressed when pressure is applied to them?
What is FORCE? Force is measured in Newtons. The force of gravity refers to how much gravity pushes on objects. On Earth. 10 Newtons (10N) of force is applied to every 1 kilogram (1kg) of mass, due to gravity.
What is PRESSURE? Pressure is how much force is applied over a certain area. It is measured in Pascals (1 Pascal= 1 N/m2). Pressure is Force/Area. Increasing ONLY FORCE will increase prsesure, and decreasing ONLY AREA will increase pressure.
Snowshoes have less pressure than high heels because it has a bigger surface area, which means you would not sink in the snow.
A larger force or a smaller area can increase the pressure of a system. The tip of a pin has a smaller area, so a large pressure can be created using only a small force. A car crusher provides a large force over a large area to produce a large amount of pressure.
Pressure also affects gasses. The air surrounding us provides pressure on our bodies all the time. We don’t feel it much because the pressure within our bodies balances the pressure outside our bodies. Fluids will move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
Examples of air pressure changes?:
When you fly on a plane, ride in an elevator, or drive high into the mountains, your ears pop because the air pressure outside the car or plane becomes lower than the air pressure inside your ears (The pressure inside your ears is higher).
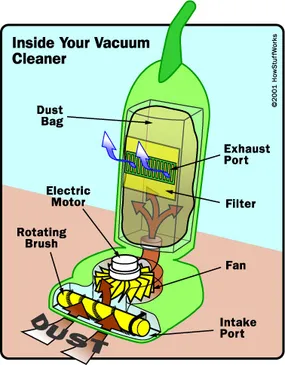
Vacuum cleaners also work because of pressure differences. A vacuum creates a low pressure environment inside the dust canister which causes the higher pressure air outside to rush in, bringing dirt with it.
Juice boxes also experience this phenomenon. When you suck out all the juice and air, you reduce the pressure inside until the container collapses due to the difference between the internal and external pressure.
What is COMPRESSION? Compressibililty is the ability to be squeezed into a smaller volume. If something is compressible, it means that there is space between the particles that are large enough to pushed together into a small space.
What types of matter can be compressed?:
Gasses are compressible, due to the large spaces in between the particles.
Liquids are not significantly compressible because the particles are too small to squeeze together.
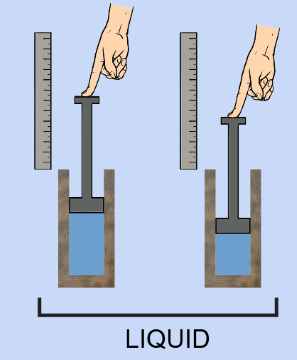
Solids are not compressible because there is even less spaces between the particles than in liquids.
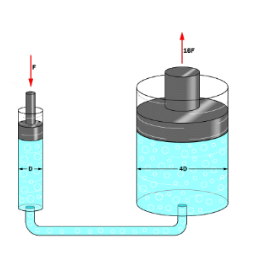
A syringe of air can be squeezed and compressed, while a syringe of water cannot be squeezed and compressed. This can be useful though, as pressure on a fluid transfers the force throughout the liquid equally (hydraulics).
Hydraulics are devices that transmit an applied force through a liquid in a closed system to move something else by means of pressure. Liquids are used in hydraulics because they are incompressible.
Important measurements and units:
Force: measured in Newtons (N)
Volume: measured in mL or cm3
Density: measured in g/cm3 or mL/cm3
Mass: measured in g or Kg (1 kg = 10 N)
Area: measured in cm2 or m2
Flow rate: measured in cm/s
Pressure: measured in Pascals (Pa) or N/cm2 or N/m2