Addiction and Substance Use Disorders: Definitions, Theories, and College Drinking Risks
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Addiction
Done regularly, habitually, or repeatedly; Compulsive (i.e., out of one's conscious control); Most common association = drugs; "Addiction" itself is not a diagnosis.
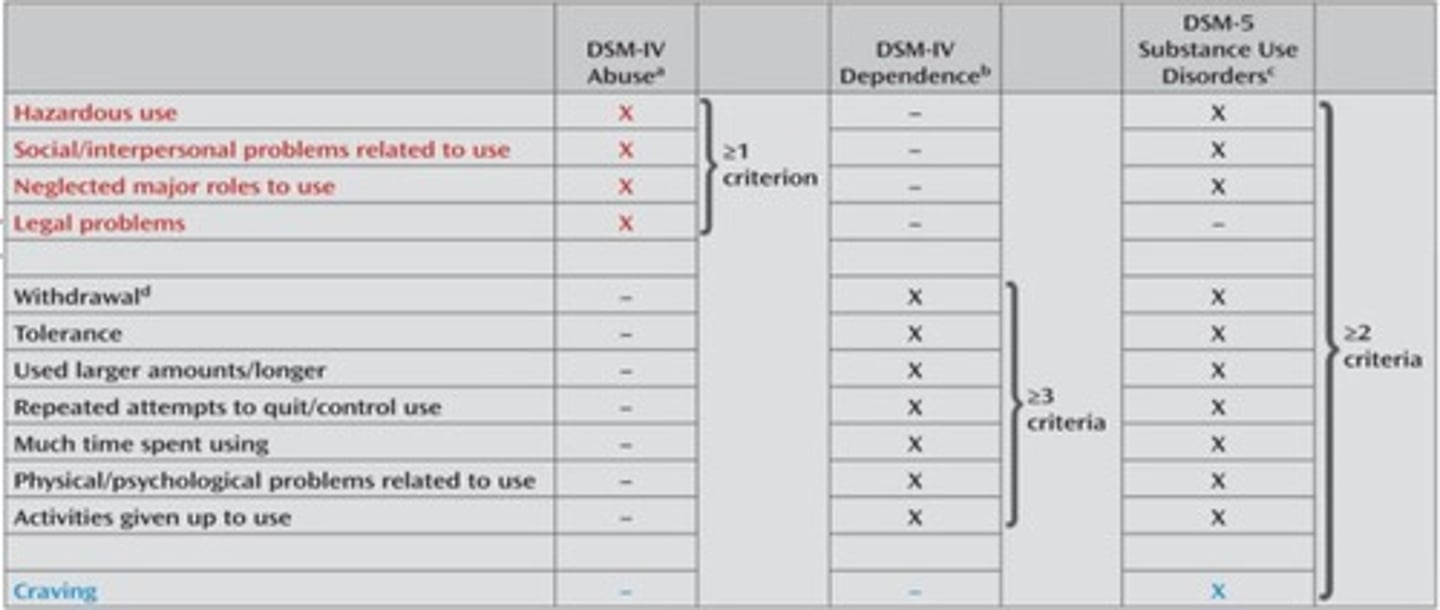
Substance Use Disorder (SUD)
Current DSM-V removed abuse/dependence distinction in favor of a single Substance Use Disorder diagnosis with severity levels.
Evolution from DSM-I to DSM-V
Changes in DSM conceptualizations progressed to separate abuse and dependence diagnoses.
Standard drink
Definition not provided in the note.
Heavy Alcohol Use
Men: >4 drinks any day or >14 drinks per week; Women: >3 drinks any day or >7 drinks per week.
Binge Drinking
5+ drinks (males) or 4+ drinks (females) at least once in 30 days.
12 oz regular beer
A standard serving size of beer.
8-9 oz malt liquor
A serving size of malt liquor.
5 oz wine
A standard serving size of wine.
1.5 oz 80-proof spirits
A standard serving size of distilled spirits.
Drinking Behaviors
Variations in substance use rates based on age, race/ethnicity, and gender.
Biological/Genetic Model
Genetic factors account for 35-70% of variance in vulnerability to substance use disorders.
Gateway Model
Proposes progression from nicotine/alcohol to marijuana to harder drugs.
Self-Awareness Model
Alcohol impairs information encoding and reduces self-relevance of environmental stimuli.
Externalizing Perspective
Conduct disorder and ADHD; behavioral disinhibition strongly predicts early-onset substance use.
Internalizing Perspective
People use substances to relieve psychological distress; mood and anxiety disorders related to substance use disorders.
Developmental Perspectives
By early adulthood, majority of people have experimented with substances; early initiation strongly predicts later substance use disorder risk.
Risk Factors for Adolescent Drinking
Environmental influences stronger in adolescence than adulthood; social and peer influences particularly important.
Alcohol Myopia Theory
Creates 'tunnel vision' where immediate aspects have disproportionate influence.
Expectancy Theory
Beliefs about what will happen when using substances; reliably differentiates heavy users from light/nonusers.
Impulsivity
Preference for immediate over delayed rewards; difficulty inhibiting behavioral responses predicts later substance abuse.
Social Learning Theory
We learn about drug use from observing the use of people around us; norms teach us when and where drug use is appropriate.
At-risk individuals
Children of people with substance use disorders develop expectations about the negative reinforcing benefits of drugs by watching parents.
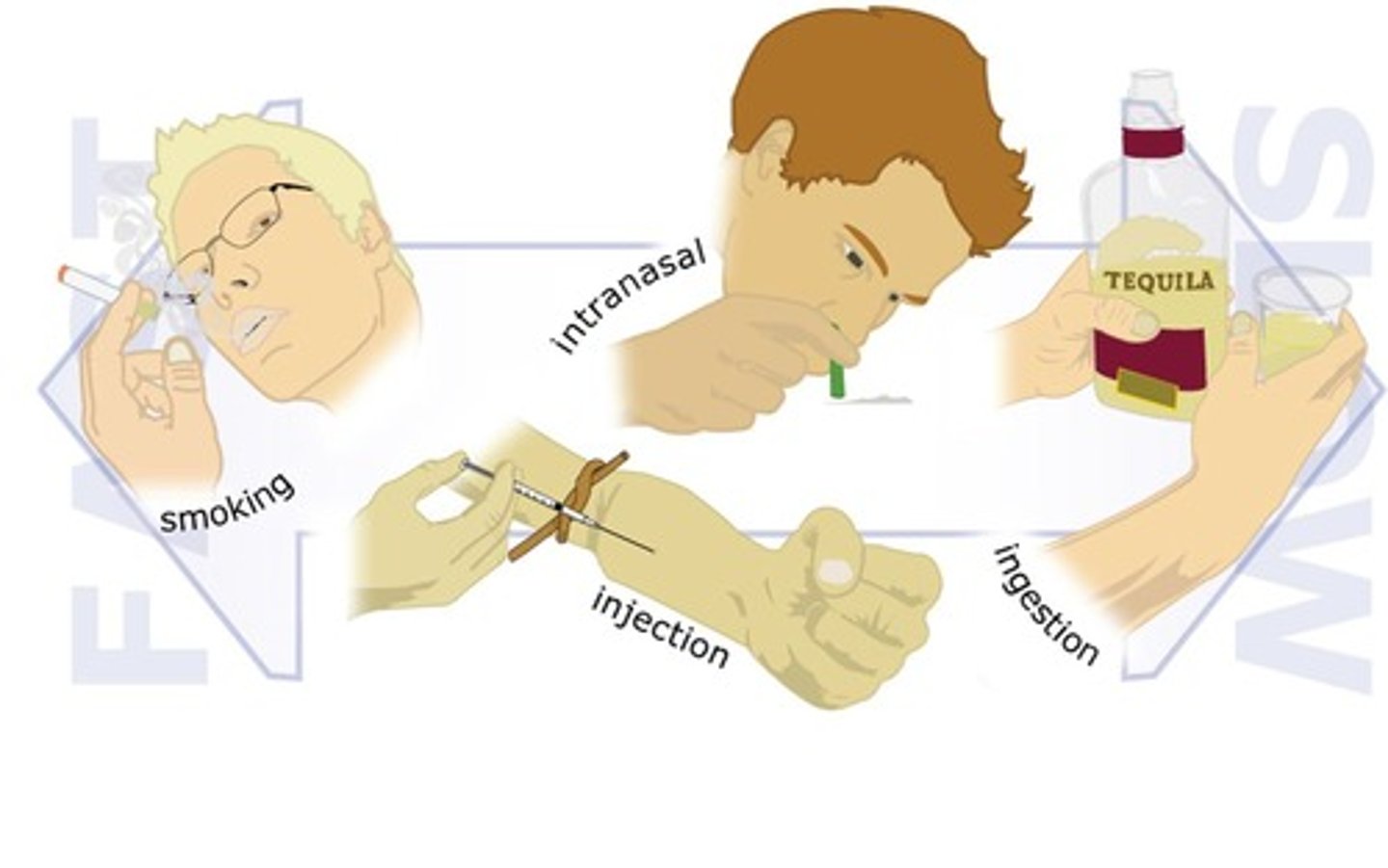
Routes of Administration
Different methods through which substances are consumed.
Definition of Addiction
Done regularly, habitually, or repeatedly
Compulsive Behavior
Out of one's conscious control
Most common association
Drugs
Addiction diagnosis
"Addiction" itself is not a diagnosis
Initial grouping of Addiction
Initially grouped with personality disorders
Evolution of DSM
From DSM-I (1950s) through DSM-V (2013)
Changes in DSM Conceptualizations
Progressed to separate abuse and dependence diagnoses
Current DSM-V diagnosis
Removed abuse/dependence distinction in favor of a single Substance Use Disorder diagnosis with severity levels
Risky Drinking
Men: >4 drinks any day or >14 drinks per week; Women: >3 drinks any day or >7 drinks per week
Substance Use Rates
Age differences show highest rates among young adults
Racial/ethnic differences
Show varying patterns of use
Gender differences
Men generally use more than women, except for prescription tranquilizers/sedatives
Biological/Genetic Factors
Alcohol impairs information encoding and reduces self-relevance of environmental stimuli
Vulnerability variance
Accounts for 35-70% of variance in vulnerability
Psychological Perspectives of Substance Use
Externalizing: Conduct disorder and ADHD; Internalizing: People use substances to relieve psychological distress
Developmental Perspectives of Substance Use
By early adulthood, majority of people have experimented with substances
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
Converts alcohol to acetaldehyde
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)
Breaks down acetaldehyde
Half-life
Time to reduce drug level by 50%
Two half-life periods
Eliminate 75%
Women metabolize alcohol differently than men
On average, compared to men, women have a greater percentage of body fat, less stomach ADH, and a less active form of liver ADH.
Antagonists
Blocks receptor
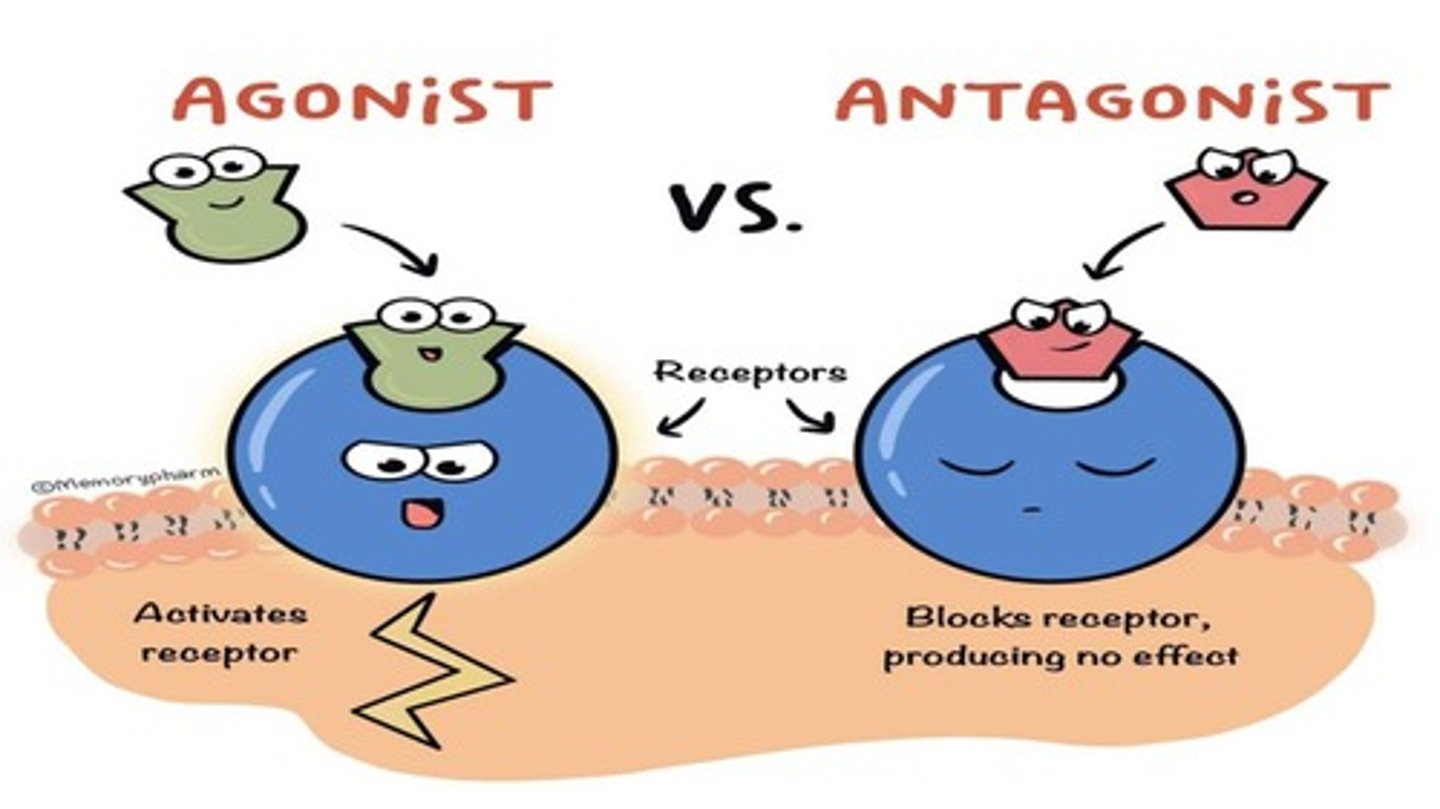
Agonists
Most drugs of abuse are agonists
Peaks
Sought after effects of intoxication
Valleys
Rebound period, usually opposite of peaks
Stimulants
Peak: Euphoria, sense of power; Valley: Anxiety, depression, fatigue
Sedatives
Peak: Reduced anxiety, mild euphoria; Valley: Agitation, anxiety, insomnia
Opiates
Peak: Euphoria, pain relief; Valley: Flu-like symptoms
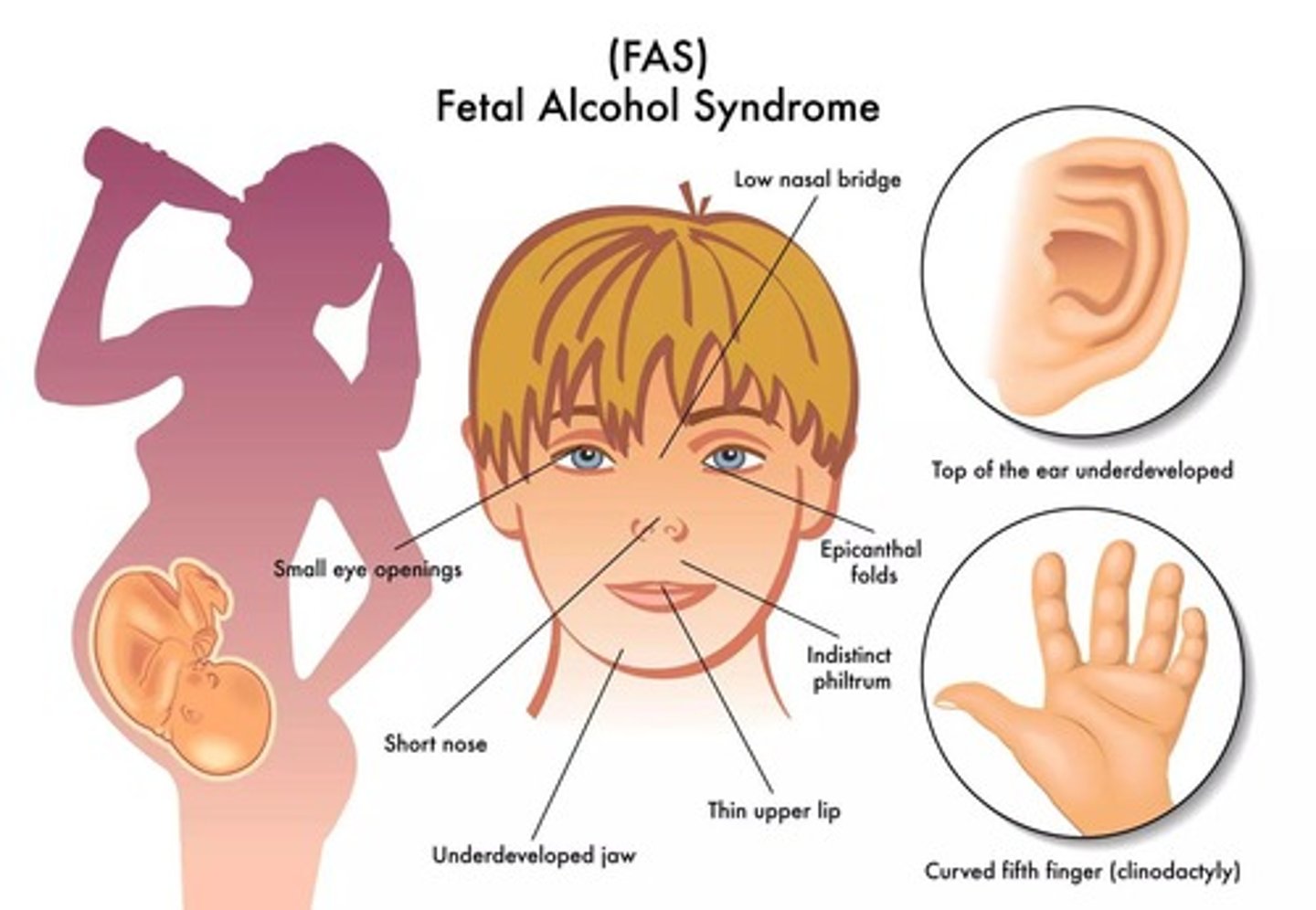
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Causes mental & growth retardation, birth defects of face and limbs, behavioral problems including ADHD, cognitive delays
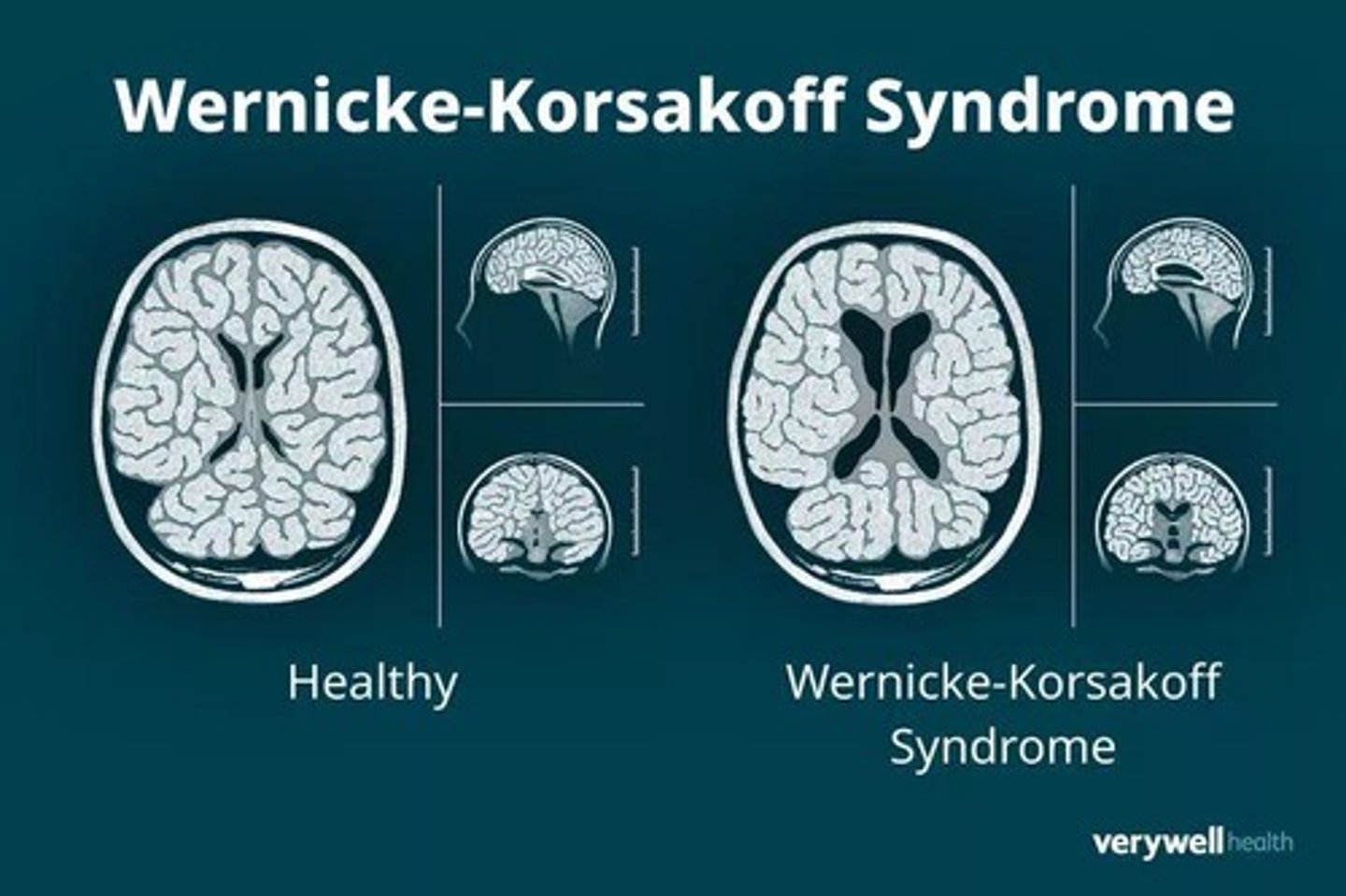
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
Caused by thiamine deficiency; Symptoms: Difficulty forming new memories, memory loss, confabulation, hallucinations
Cross Tolerance
Resistance to the effects of one substance because of exposure to another similar substance; Example: high tolerance of alcohol → high tolerance of other sedatives
Drug Interactions
Potentiation: Drugs in the same class amplify effects; Example: Alcohol + benzodiazepines = stronger than sum of parts; Can be lethal
Opioid Epidemic
Deadliest drug crisis in American history; More deaths in 2016 than entire Vietnam War; ~64,000 overdose deaths per year; Faster death rate than HIV epidemic at peak
Racial Demographics
Chart shows overdose deaths by race; Highest rates: White, Native American populations; Increasing rates among Black populations; Lower rates: Hispanic and Asian populations
US vs Other Countries
US consumes more opioids than any other country; Average days of opioid use per resident per year: US: 17.4 days, Canada: 12.6 days, Germany: 11.2 days; Other developed nations significantly lower
Carfentanil
Specific Opioid; Elephant tranquilizer; Extremely potent: few grains lethal; All US zoos need only 18g/year total
OxyContin
Absorbed through skin; FDA approved 1995 claiming reduced abuse potential; Hard to detect in toxicology; Actually had higher narcotic levels than Fentanyl
Fentanyl
Synthetic opioid made in 1960s; Could be snorted or injected; Medical uses: spray, patch, lollipop; Purdue Pharma knew about significant abuse by 1996; 2mg (salt shaker shake) can be lethal; Often mixed unknown into heroin
Pharmaceutical Companies
Purdue Pharma concealed abuse information; Continued marketing as safer option; Paid $600 million settlement
Doctors' Role
Pressured to treat pain more seriously; Limited time/resources led to quick pill solutions; Current US prescription rate still triple 1999 levels
Barriers to Reducing Prescriptions
Essential for legitimate medical needs; Sudden removal pushes people to illegal drugs; Still necessary for cancer/acute pain; Limited access to alternative treatments
Medical Assisted Treatment (MAT)
1. Methadone: Long-acting synthetic opioid; Prevents withdrawal; Requires careful supervision; Available through licensed programs

Buprenorphine
Partial agonist
Naltrexone
Opioid antagonist
Balloon Effect
When the supply of one drug is restricted, users shift to alternatives
Naloxone
Rapidly reverses overdose
College Drinking - General Patterns
79.2% drank in the past year
Moderate Drinkers
46% moderate drinkers (no binges in the past month)
Problem Drinkers
54% 'problem drinkers'
Super Bingers
7% 'super bingers' (>15 drinks)
Heavy Drinking
21% had at least 10-14 drinks once
Academic Performance
Declines with drinking
Victimization - Ethnic/Racial Harassment
6.4% reporting rate, 14.2% involved alcohol
Victimization - Physical Violence
4.0% reporting rate, 54.7% involved alcohol
Victimization - Theft with Force
1.7% reporting rate, 33.5% involved alcohol
Victimization - Sexual Assault
20-25% of women experience attempted or completed rape while in college
At-Risk Groups for Heavy Drinking/SUD
Inexperienced drinkers