SOC 100 (Exam 1)
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Social construction
idea/practice that a group of people agree exists; maintained by people taking its existence granted
ex: College life
Sociology
study of social life, change, causes, consequences of human behavior; investigation of group structures, organizations, societies, and human interaction within these contexts
Sociological eye
observation of social patterns, relationships, and structures around you; enabling you to understand society on a deeper level
Sociological imagination
understanding the connection between individual experiences and larger social, historical, structural forces
Social activism
collective effort to promote, guide, impede change (social, political, economical, environmental)
Fallacy of individualism
attributing human behavior/outcomes to individual traits, choices, actions
ex: Why did some students struggle during the pandemic?
Individualist: lack of motivation, poor time management, insufficient tech skills
Sociological: access to tech, support family, appropriate learning environmental
Theory
systematic framework that explains how and why certain phenomena occurs
Rational choice theory
individuals pursue self-interest
individuals act on rational evaluation costs/benefits
individuals seek to maximize personal advantage/utility
social structures emerge from combination of individual choices
critiques: overemphasizes rationality, assumes equal agency
Functionalism
interrelated parts, each serving necessary functions
social order + stability are desired, maintained through norms/values
change is gradual and often disruptive to the system
critiques: can’t explain social change nor account for dysfunctions in the system
Conflict theory
order is maintained by domination
the most powerful possess greatest resources/means of production
power and inequality are central to understanding social structures
social change = dominant group vs. subordinate group
critiques: overly focused on conflict, overly deterministic
Symbolic interactionism
microlevel interactions between individuals
symbols and language are core to human interactions
people actively shape their social environments
critiques: neglects larger social structures, power dynamics, historical contexts
Levels of analysis
Micro: day-to-day interactions
Meso: intermediate sized groups (larger than local community, smaller than nation)
Macro: entire nations, global forces, international trends
Nomothetic
study/discovery of general scientific laws
ex: gravity
Ideographic
study/discovery of particular scientific facts/processes
ex: case studies
Steps of research process
Define research problem
Review the literature
Make problem precise
Choose method
Carry out the research
Interpret results
Report the findings
Survey
ordered series of questions to gain information from respondents
Interview
one-on-one conversation between the researcher and the subject; participants not limited to predetermined choices
Focus group
group interview of people with similar traits/common experiences
Participant observation
observing people’s behavior in practice to uncover meanings behind social actions, qualitative
Ethnography
researcher immersed in natural setting of a social community to observe + experience their daily life/culture
Experiment
analyzing variables in a controlled, systematic way; either in an artificial situation or naturally occurring setting
hypothesis
independent variable
dependent variable
controls (doesn’t apply for field experiments)
random assignment
Tuskegee experiment
researchers observed low-income African Americans with syphilis but didn’t reveal purpose or offer treatment
Tearoom trade
researcher observed men who have sex with other men in public, obvious breach of privacy
Stanford prison experiment
male college students assigned role of guard or prisoner in prison simulation to observe the power of the situation
Respect for persons
ethical principle; individuals are autonomous and have free will, participation is voluntary and informed
Beneficence
ethical principle; maximize possible benefits without harming individuals
Justice
ethical principle; all individuals get same benefits/burdens from the research
Social media use
Benefits: community, information, self-expression
Harms: mental health, content, addiction
Culture: standards, global, communication
Culture
shared beliefs, values, norms, behaviors, artifacts that shape a group’s way of life and are passed down through generations
learned, not innate
Values
ideas about what is desirable, proper, good/bad; strongly influenced by culture
Norms
roles of conduct that specify appropriate behavior in a given social situation; prescribes/forbids behavior
can conflict with other people’s or society/s norms
Culture shock
doubt, confusion, anxiety arising from immersion in an unfamiliar culture
Code-switching
switching fluidly between two or more languages/sets of cultural norms to fit different cultural contexts
Cultural appropriation
when people of one cultural group borrow elements of another cultural group
ex: white people wearing Native American headdresses
Cultural relativism
accounting for the differences across cultures without judgement
ex: exchange of ideas, beliefs, lifestyles
Media
any format, platform, vehicle that carries, presents, communicates information
can reflect cultural change and shape cultural values/norms
Social media
technology that lets users produce, share, consume media in a variety of formats
Social media and authoritarianism
mis/disinformation and propaganda
surveillance tool
incites violence
algorithms amplify extremism
Socialization
becoming culturally competent in different social environments by internalizing beliefs, values, norms of the society
Families
primary agent of socialization; teaches importance of historical context and ideology, bidirectional
Schools
agent of socialization; pass down values, beliefs, attitudes important in American society (i.e. individualism, patriotism, meritocracy)
Peer groups
agent of socialization; friendship group comprised of individuals of similar age/social status
reinforce/contradict ideas, attitudes, beliefs that families promote
peer pressure
concern for the “wrong crowd”
Resocialization
when one’s sense of social values, beliefs, norms are reengineered (often deliberately) through an intense social process
Social status
position of prestige or privilege a person has in society/social group
Status set
all the statuses a person holds at once
ex: a daughter, a sister, a student
Ascribed status
status one is born into, involuntary
ex: assigned sex at birth
Achieved status
status one enters, voluntary
ex: earning a medical degree
Master status
status that stands out/overrides all others, can be ascribed or achieved
ex: being a mother
Roles
the duties and behaviors expected of someone who holds a particular status
Role strain
stress caused by the demands of a single role
ex: a student wants to get good grades and get scholarships = stress from studying + applications
Role conflict
stress caused when demands of multiple roles clash
ex: a grad student needs money for her next semester but also needs to provide for her child = stress from being a student + being a mother
Dramaturgical theory
social life is a theatrical performance where we are all actors on metaphorical stages with roles, scripts, costumes, props, sets
ex: SOC 100 lecture
role: student
script: be quiet and pay attention
costume: casual outfit suited for the weather
props: backpack, laptop
set: Lincoln Hall Theater
New consumerism
shift from middle-class comfort to luxury consumption
caused by:
workplace socialization
rising inequality
media and ads
rise of credit
Reference groups
we compare ourselves to these groups to understand our position in society
Social group
people with shared identity + regular interaction
ex: your friend group
Social aggregate
people in the same place, without interaction or shared identity
ex: students in a lecture hall
Social category
people with a common characteristic but no necessary interaction
ex: all college students
Primary group
small, strong emotional ties that are enduring
ex: family, close friends
Secondary group
larger, impersonal, goal oriented ties
ex: coworkers, classmates
Dyad
a group of 2
intimate but unstable
dependent on both members participating
ex: a married couple
Triad
a group of 3
more stable, allows for mediation
not dependent on any one member
ex: three college roommates
Social network
collection of people tied together by a specific configuration of connections
can be characterized by:
# of people involved
structures (who is connected to whom)
functions (purpose of connections)
Embeddedness
degree to which social relationships are reinforced through indirect ties (i.e. friends of friends)
Structural holes
gap between networks or two individuals who have complementary resources/information
an opportunity for someone to bridge the gap and connect the networks
Social capital
information, knowledge, connections that help individuals enter, gain power, or leverage social networks
ex: a blue-collar worker is friends with plumbers and mechanics, and thus never has to pay for repairs
Importance of social capital
strengthens norms of reciprocity
solve collective issues more easily
everyday transactions less costly
awareness of our shared fates
Capital
any asset, tangible or intangible, that can be used to produce an outcome
economic capital: wealth and assets
physical capital: tools, machines, equipment
human capital: education, training, job experience
cultural capital: tastes, manners, knowledge that signal social status
Bonding social capital
strong ties within a community, “horizontal”
ex: family members, close friends, neighbors
Bridging social capital
ties between different communities and across social boundaries, “vertical”
ex: career fairs/networking events
Decline of social capital in the U.S.
decreased membership in civic organizations (PTA, unions)
lower voter turnout and political engagement
decline in informal socializing (dinner/block parties)
Causes of decline in social capital in the U.S.
time and money pressure
suburban sprawl + commuting
electronic entertainment
generational change
Organization
social network defined by a common purpose and clear boundary between ingroup/outgroup
Utilitarian organization
org provides income or personal benefit
ex: business
Normative organization
org pursues moral goals, voluntary
ex: charities
Coercive organization
org membership is forced
ex: prisons, military drafts
Isomorphism
when organizations within a field become more similar in structures, practices, cultures due to pressures from regulation, imitation, professional norms
Coercive: legal, regulatory pressure (EPA regulations)
Mimetic: copying successful models (IT certifications)
Normative: professional norms (required degrees/certifications)
Deviance
any transgression of socially established norms, not necessarily illegal
ex: wearing a banana costume to class
Crime
violation of laws enacted by society, subject to social sanction, not necessarily deviant
ex: speeding
Social control
mechanisms that create normative compliance in individuals
formal social sanctions
informal social sanctions
Formal social sanction
mechanism of social control; rules or laws prohibit deviant criminal behavior
Informal social sanction
mechanism of social control, unspoken rules of social life
Social cohesion
social bonds, how well people relate to each other and get along on a daily basis
mechanical and organic solidarity
adaptive function
clarifies norms, increases conformity, strengthens reactions to deviance
can lead to positive social change
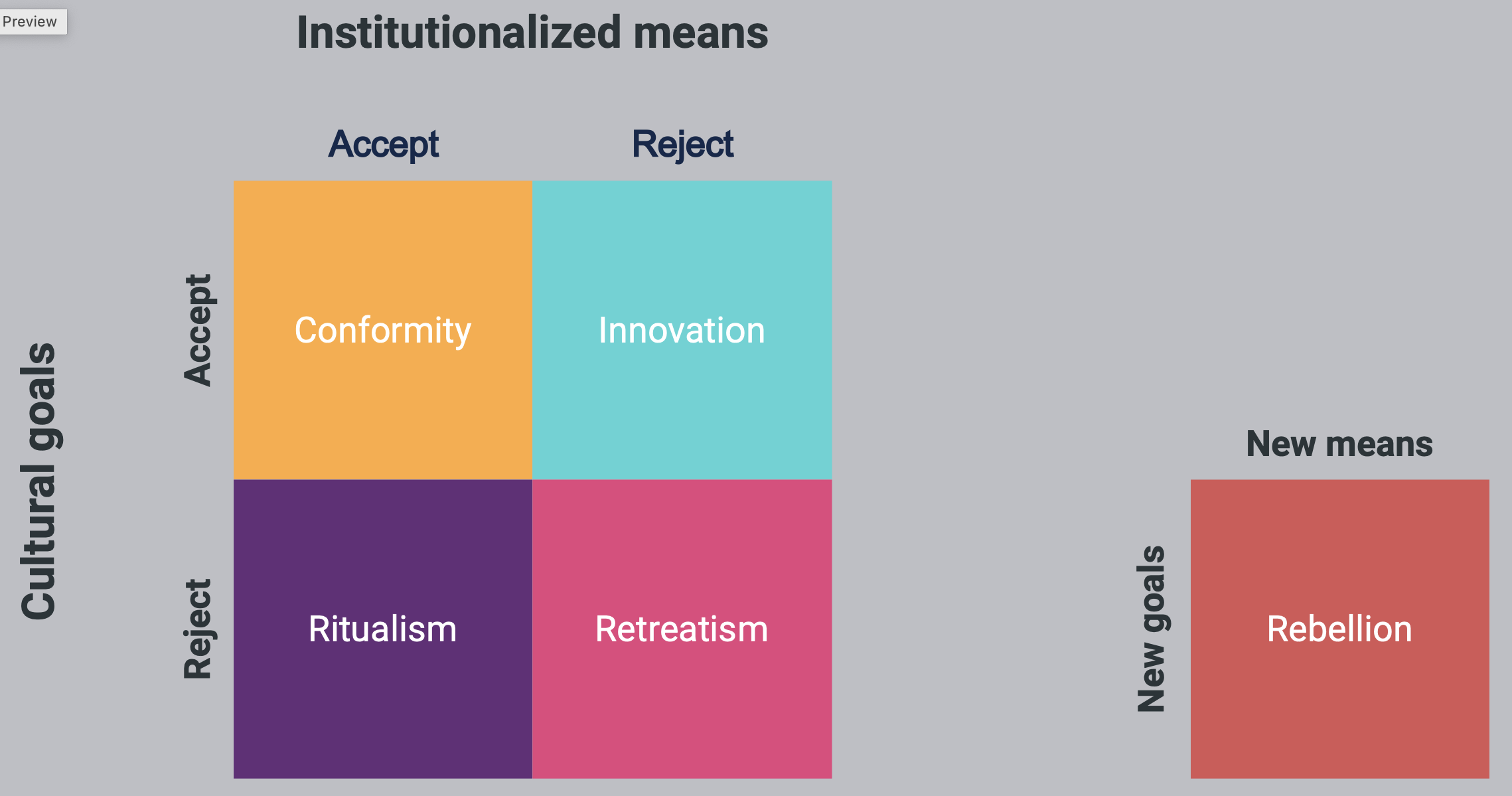
Merton’s deviance typology
Conformity
Innovation
Ritualism
Retreatism
Rebellion
Strain theory
pressure from social factors (i.e. lack of income/education) drives people to commit crime
ex: people below the poverty line commit crimes to reach the American Dream because they can’t achieve it through legal means
Labeling theory
individuals subconsciously notice how others view or label them and base their self-identity on those reactions
social groups can create deviance by settings rules for right/wrong
labels wrongdoers as outsiders; deviants are made, not born
Primary deviance
first act of rule breaking that leads to being labeled “deviant”, people think/act differently toward you
Secondary deviance
subsequent acts of rule breaking after primary deviance as a result of being labeled “deviant”
Broken windows
minor acts of deviance must be controlled to avoid a spiral of crime and social decay
any signs of disorder encourages more serious deviance
controversial policing strategy
Incarceration
legally imposed deprivation of personal liberty, typically in a facility designed for that purpose
Purposes of incarceration
retribution: punishment, offender should “pay” for their actions
deterrence: dissuade from committing crime
incapacitation: remove offenders from society
rehabilitation: educate to prevent future crime
Incarceration demographics
Bottom quintile of income
Men
African Americans
(often all three)
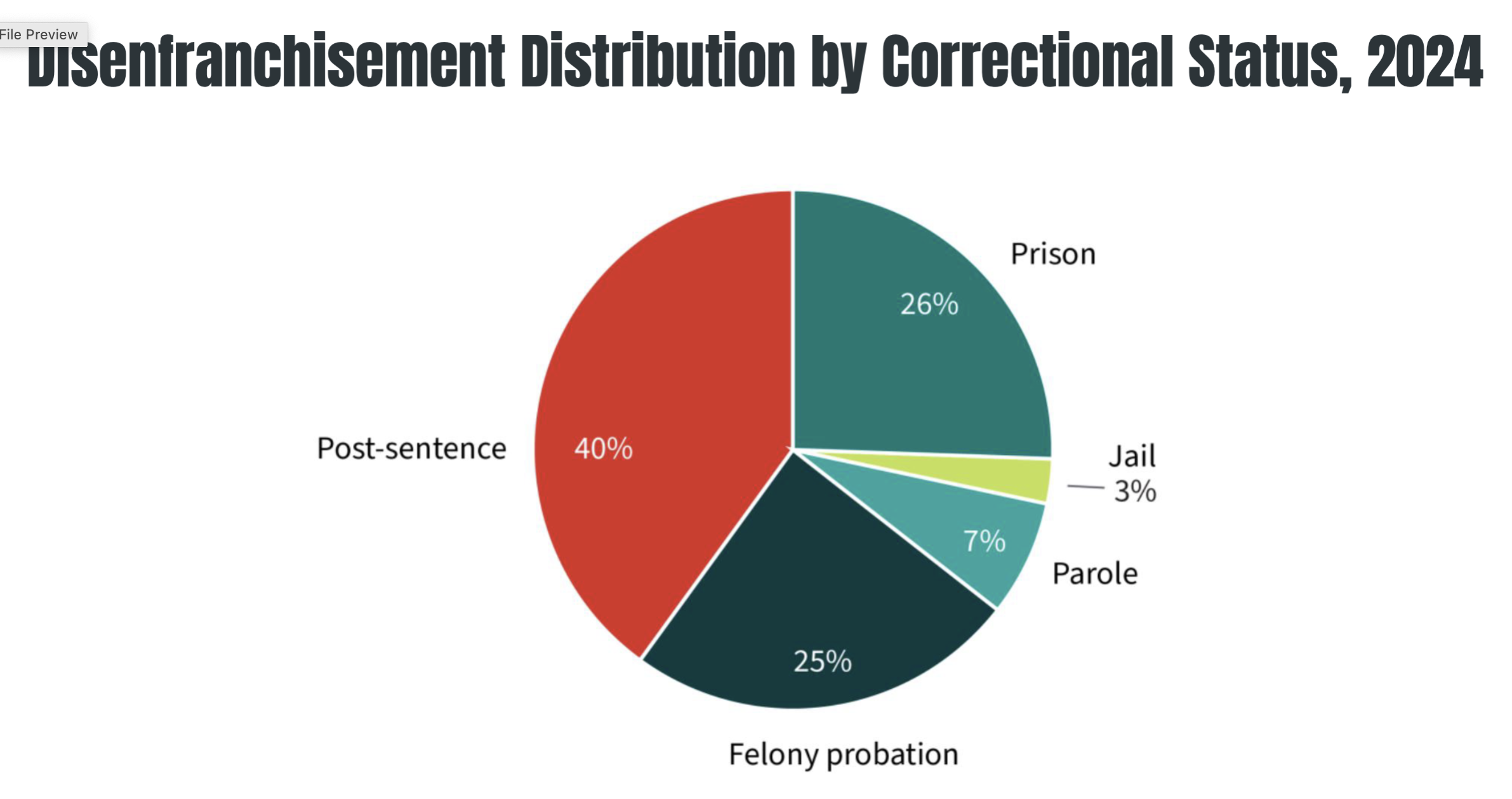
Felon disenfranchisement
restriction or denial of voting rights for individuals convicted of a felony, often persisting beyond incarceration
48/50 states
4 million Americans in 2024 or 1.7% of voting population
reduces representation of people whose preferences are aligned with disenfranchised felons (e.g. investing in poor communities)