Intro to Radiography & Projection Geometry
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Define Radiography
Conventional technique/process of using x-rays to produce a static, 2D imge of internal structures of the body (radiograph; plain or projection view)
Define Imaging Chain
Components that contribute to radiographic image formation and display
What are the components of an imaging chain?
X-ray source (produces x-rays), Image receptor (receives/detects x-rays), image display device (for digital imaging)
The entire volume of tissue between source and receptor image is
Projected onto a 2D image
What is radiograph formation?
The path of radiation (x-ray) beam, must include anatomy of interest and receptorIn
For the anatomy to be imaged, what must occur?
Beam must travel through the anatomy and then also hit the receptor
The radiographic image is essentially a map of beam
AttenuationDe
Define attenuation
Reduction in x-ray beam intensity as it travels through the anatomyThe
The thicker and denser the structure,
The more x-rays are absorbed and the more the beam is attenuated
What are some key features of x-ray beams?
Consist of many x-ray photos, x-rays travel in straight lines, x-ray beam is divergent
Incident beam is differentially attenuated by structures of different
Dentisty
What is the order of decreasing density?
Metal > enamel > dentin and cementum > bone > muscle > fat > air
What carries the attenuating information to the receptor?
Transmitted beam
What color would you see in radiolucency?
Black
What does black represent on x-ray images?
Less attenuating structures, more intense transmitted beam
What color would you see in radiopacity?
White
What does white represent on x-ray images?
More attenuating structures, less intense transmitted beam
Define radiodensity
Refers to an objects ability to attenuate or absorb x-rays
What are some characteristics of radiodensity?
They are dense and attenuate more x-rays, and appear radiopaque on the image
Define optical density
Degree of darkening or opacity of an exposed filmOp
Optical density depends on
The number of x-ray photons absorbed by the film
More x-ray photons (more intense transmitted beam) =
Greater film exposure = greater optical density = darker image
Define contrast
Range of densities on an image defined as difference in densities between light and dark regionsW
What does high contrast show?
Both light and dark areas with few shades of gray in-between
What does low contrast show?
Various light and dark shades of gray
What are some types of dental radiographs?
Intraoral and extraoral
What are some types of intraoral radiographs?
Periapical, bitewing, occlusal
What are some types of extraoral radiographs?
Panoramic, cephalometric and skull projectionswh
What is the fundamental difference between intraoral and extraoral dental radiography?
The location of the x-ray sensor
Define image quality
Reliability of an image in its representation of the true state of anatomy examinedWh
What are the parameters of radiographic image quality
Image sharpness
Spatial resolution
contrast resolution
Magnification
Distortion
Images should have
Minimal magnification and distortion and adequate contrast and spatial resolution for the diagnostic task
Define sharpness
Measures how well a boundary between two areas of differing radiodensity is revealed
Define spatial resoluation
Measures how well an image reveals small objects that are close together
What is image size distoration?
The different between object size on image and actual object sizeD
Define magnificaition
Increase in size of object on image compared to actual size of objectW
What causes magnification?
Divergent paths of x-ray photons in a beam
What id image shape distortion?
The difference in appearance of object shape on image compared to actual object shape
What does image shape distortion result in?
Unequal magnification of different parts of the same object
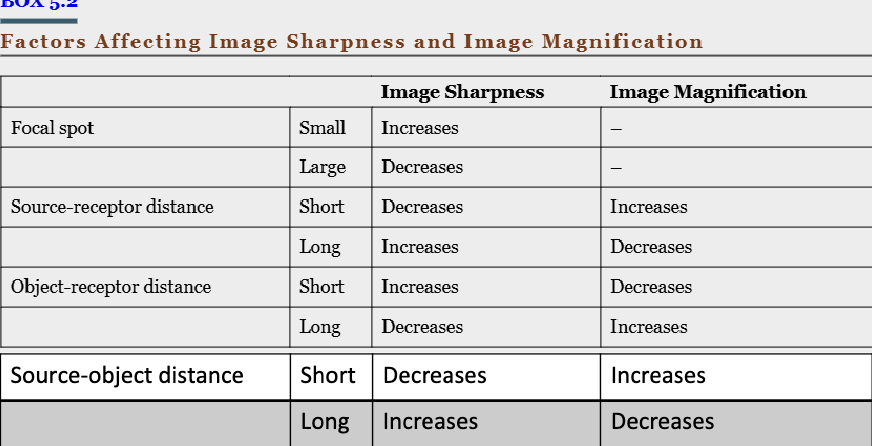
The focal spot should be
As small as possible
The source-receptor distance should be
As long as possible
The object-receptor distance should be
As small as possible
In which orientation should the receptor be to the long axis of the object?
Parallel
In which orientation should the central beam be to the object and receptor?
Perpendicular
Define focal spot
The area on the target of the x-ray tube where x-rays are producedW
Where do x-rays originate from?
All points within the area of the focal spot
What is the range of the focal spot size for dental, panoramic, and cone beam CT?
0.04-0.08 nm
A small focal point
Yields a sharper image
What is geometric unsharpness in radiography?
The blurring of object edges that occurs when x-rays projected at different points in the focal spot pass through the same point on an object but hit different spots on the receptor
What causes geometric unsharpness?
x-rays being projected from different points in the focal spot to the same point on an object, resulting in variations in where the x-rays hit the receptor
What are other terms for geometric unsharpness?
penumbra or adumbration
A larger focal spot creates
A wider zone of geometric unsharpness, which results in a loss of image sharpness
What happens if you increase the distance between the x-ray source and the object (move the x-ray tube further from the tooth)?
The x-ray beam spreads out less, the rays in the center of the beam are almost parallel which makes the image sharper, and the image has less blurriness and isn’t as magnified
Why is the x-ray tube recessed in the tube head housing?
To help increase distance and improve image quality
What happens when you decrease the object-to-receptor distance?
Reduce x-ray beam divergence, x-ray phons in the center travel nearly parallel, reduces geometric unsharpness (sharper image), and minimizes image magnification
How do you get a sharper and more accurate x-ray image?
Increase source-to-object distance
Decrease object to receptor distance
Object- tooth
Receptor- sensory
Source- x-ray tube
What is the magnification equation?
Image size / object size = source-receptor distance / source-object distance
What is the source to image distance (source-receptor distance)?
X-ray to sensor
What is the source to object distance?
X-ray tube to toothIn
Intraoral radiographic image magnification is
Usually less than 10%
How can magnification from a large object-to-receptor distance be reduced?
By increasing the source-to-object distance (e.g., from 8" to 12" to 16"), which reduces image magnification and improves sharpness.
What causes image shape distortion in dental x-rays?
Uneven source-object or object-receptor distances, which distort the shape of the image.
How can you minimize image shape distortion?
Align the object and receptor parallel
Aim the x-ray beam perpendicular to both
Why might some shape distortion be unavoidable?
Because the natural shape of teeth (like maxillary molar roots) makes perfect alignment impossible
What is foreshortening in a dental x-ray?
The image looks shorter than the real object because the tooth isn’t parallel to the receptor, and the x-ray beam is aimed at the receptor, not the tooth
What is elongation in a dental x-ray?
The image looks longer than the real object because the tooth isn’t parallel to the receptor, and the x-ray beam is aimed at the tooth, not the receptor
What causes both foreshortening and elongation in dental imaging?
When the tooth is not parallel to the receptor, and the central ray isn’t aimed correctly at both
What are three ways to maximize image sharpness in dental radiography?
Use a small focal spot
Increase source-to-object distance
Minimize object-to-receptor distance
Can the focal spot size be changed by the operator?
No, it’s determined by the x-ray unit manufacturer
Why does increasing the source-to-object distance improve image sharpness?
It reduces beam divergence and geometric unsharpness
Why does minimizing the object-to-receptor distance improve image sharpness?
It reduces magnification and keeps image detail more accurate.
Factors affecting image sharpness and image magnification