5.1 Introduction to soil systems
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Soil composition
Made of air, water, organic matter (humus) and mineral particles (silt, clay, chalk, sand etc.)
Parent material
The general physical, chemical, and mineralogical composition of the unconsolidated material, mineral or organic, in which soil forms through erosion or other means of weathering.
Humus
Plant and animal matter in the process of decomposition
Translocation
The sorting of layers of soil due to the movement of water-carrying particles through the soil.
Salinization
The deposition of salts from freshwater due to constant watering
Leaching
When water flows down into the soil, dissolving minerals and transporting them downwards.
Humus
Plant and animal matter in the process of decomposition
Horizons
Horizontal layer of soil defined by distinctive physical features
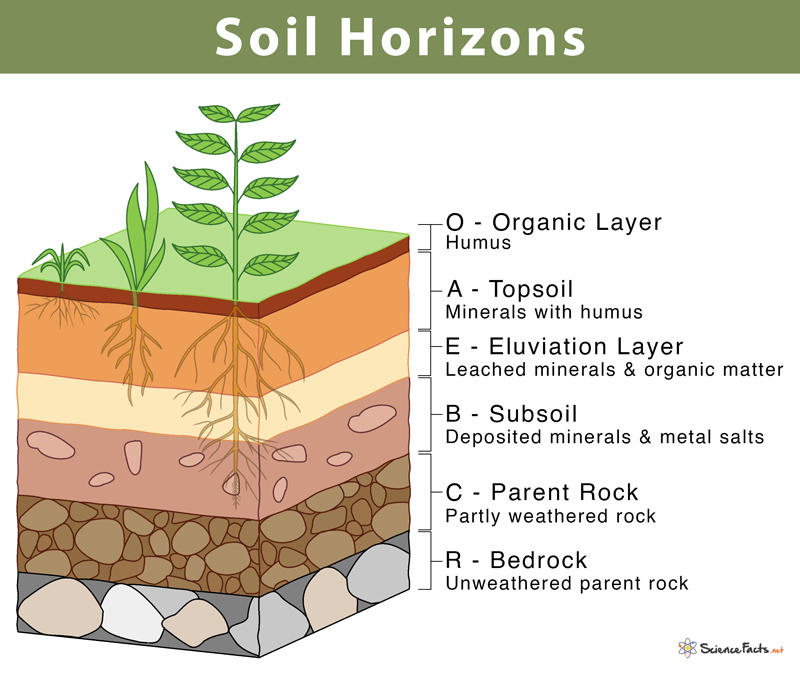
O horizon
Uppermost layer of soil conposed of newly added organic material with detrivores decomposing dead organic matter
A horizon
Below O horizon where humus is mainly formed and mixed with mineral layers. Can form peat soils in waterlogged conditions q
E horizon
Where leeching occurs of metals and organic matter
B horizon
Where minerals and organic matter gets deposited. Typically clay and salts.
C horizon
Weathered rock from which the soil forms
R horizon
No soil and made of parent material
Porosity
The amount of space between particles
Permeability
The ease with which gases and liquids can pass through the soil.
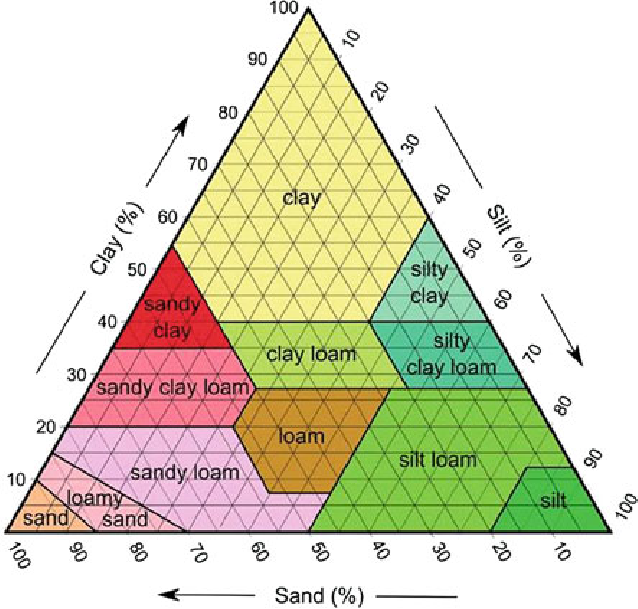
Sandy soil drain well while clay heavy soils retain water well due to particle sizes
Sand biggest, silt middle, clay smallest
Rate of soil formation
Takes a very long time at 1 ton per hectare a year.
Fertile soil is an extremely limited resource due to how long it takes to form
Various anthropocentric causes destroying microbes in soil, thus killing the soils fertility