Behavioural Ecology --- Study for Final
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
214 Terms
1. Causation (mechanism)
how is the trait produced?
3. Function (adaptation)
how does the behavior help fitness?
4. Evolutionary history (phylogeny)
how did the behavior evolve?
behavioral ecology
the study of the ecological and evolutionary adaptations for animal behavior
*optimal behavior will maximize fitness*
why is [behavioral ecology] important? (4 steps)
[behavior -> maximize fitness] -> population growth -> relevant conservation
definition of behaviour
the way an organism responds to its environment and to other species
environment includes...
- physical stuff (eg. food supply)
- conspecifics
- other species
Niko Tinbergen's 4 Questions
1. causation
2. development
3. adaptive function
4. evolutionary history
Ethology
the study of behavior in animals' natural environment
2. Development (ontogeny)
how does the behaviour change with age / what early experiences are needed to display the behaviour?
behaviors promote survival by...
-seek mates
-seek food
-seek shelter
-avoid predators
behavior is based on...
- sensory feedback (external trigger)
- coordination and control of animals physiology
**bridge between internal and external processes
Proximate
-HOW it works
-causation (mechanisms)
-ontogeny (development)
Ultimate
-WHY it happens
- adaptive significance
- evolutionary history
adaptation
changes brought about by selection that improve survival and/or reproductive success
for selection to occur...
-individuals must show variation in population
-some variation must be heritable
-competition is inevitable outcome
3 things to remember about genes in behavior
- molecular paths btwn genes + behavior are COMPLEX
- genes influence behavior AND behavior influences gene expression
- genes are NOT the only answer (genotype AND environment)
ethogram
a catalog of all of the behaviors an animal exhibits in its natural environment
- qualitative decr. --> quantitative data
1st step in methods of beh. eco.
Research question / Model system
2nd step
Test Hypotheses
(observations, experiments, comparisons, theoretical approach)
3rd step
Collect Data
4th, 5th, 6th step
4. analyze data
5. interpret results
6. communicate findings
Reproductive Success (RS)
the number of offspring an individual produces per year/breeding event; an individual's genetic contribution to the next generation
Lifetime Reproductive Success (LRS)
the number of offspring produced throughout the lifespan of an individual
can be difficult to measure in long-lived species
Fitness Proxies
indirect measures of fitness, may not be accurate alone
ex. body health, territory quality, social rank
optimality models
predict which decisions an animal should make in order to maximize its fitness in a specific environment
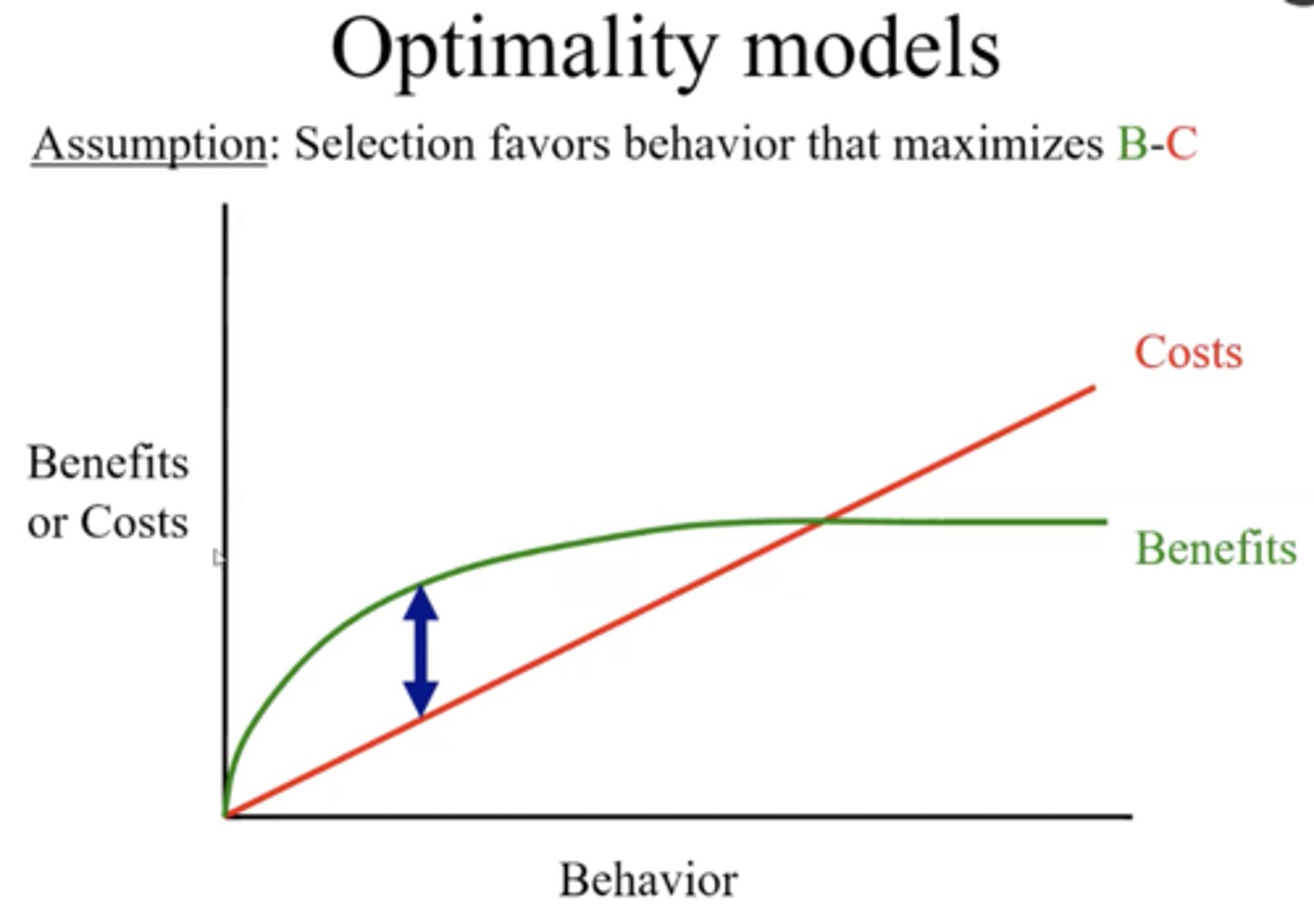
examples of optimality model uses
- carrying a load (parental investment)
- reproductive decisions (when dad stays/goes)
- prey choice (specialize/generalize?)
Charnov's Optimal Diet Model
predicts how a predator should choose between an array of prey types of different profitabilities
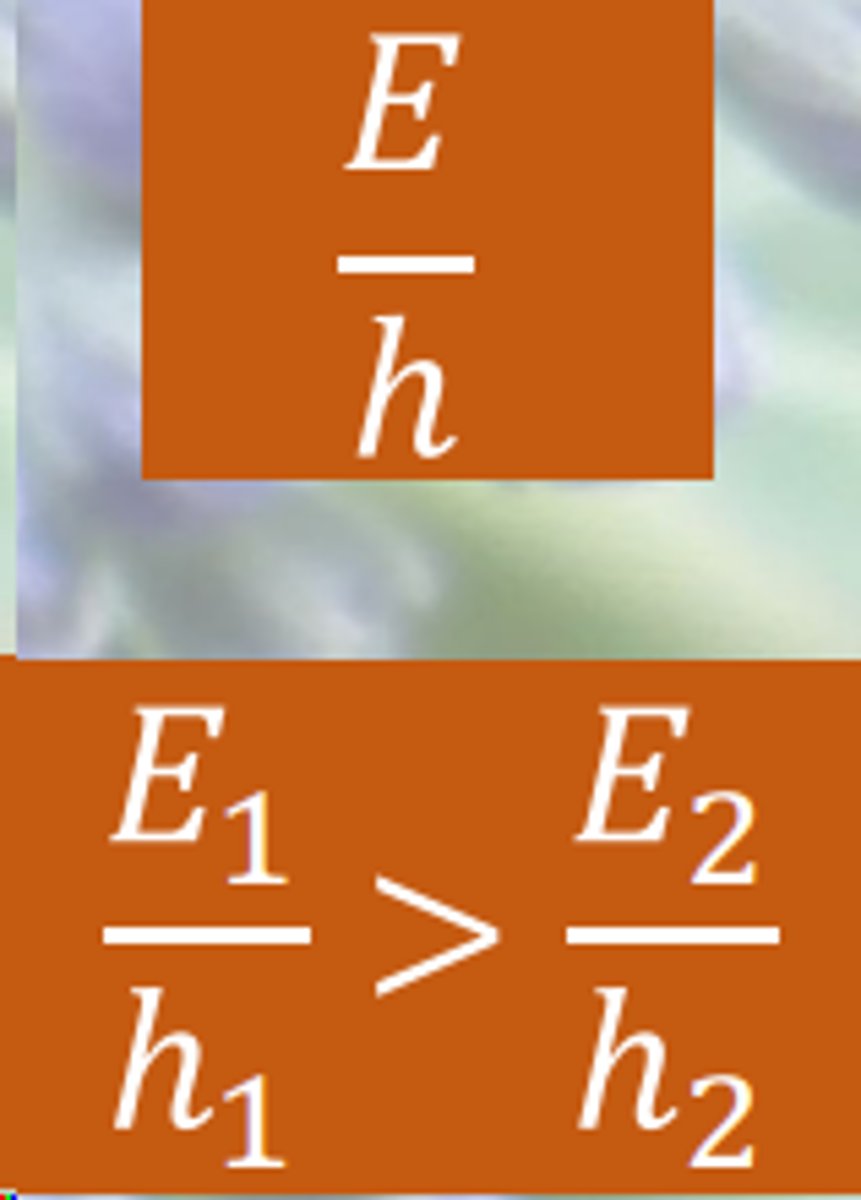
internal state matters
starvation = major currency
hungry animals take more risks
life history
schedule of an individual's life including all behavior and physical adaptations
darwinian demon
hypothetical ideal organism matures at birth, starts to reproduce immediately, is immortal and gives birth to infinitely many offspring
extrinsic factors (cause of life history variation)
imposed from outside (ecology and phylogeny)
intrinsic factors (cause life history variation)
tradeoffs among traits, phylogeny,
tradeoffs: current vs future reproduction
survival (future reproduction) vs fecundity (current reproduction)
semelparity
when organisms reproduce only once during their life
iteroparity
when organisms reproduce multiple times during their life
optimal clutch size
ideal number of offspring that yields the greatest fitness
general patterns in life history
1. variation in one trait = variation in another trait ("slow-fast continuum")
2. life history varies w/habitat/environment condition
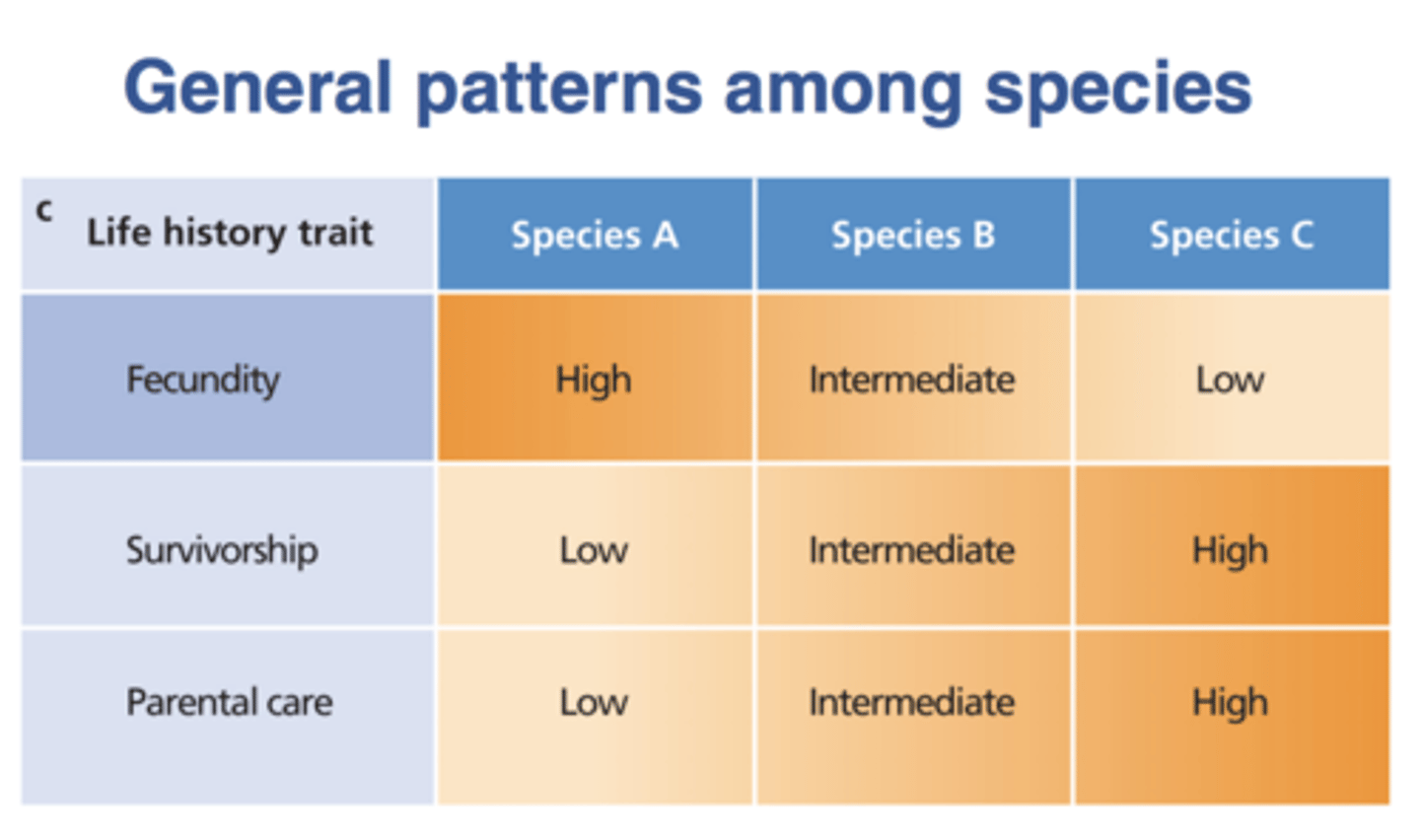
slow-fast continuum
variation in one trait correlates to variation in another trait

patterns w/ environmental conditions
-food supply: springtime vs wintertime
-large climate variation: winter mortality
Red Queen Evolution
Never-ending arms race where each organism has to keep evolving just to stay in the same relative place
Crypsis (prey tactic)
camouflage that makes prey difficult to see
apostatic selection (prey tactic)
negative frequency dependent selection
Mullerian mimicry
two or more unpalatable species resemble each other
Batesian mimicry
a harmless species mimics a harmful one
search image (predator tactic)
search for most common prey -> rarer morphs become more common -> evolution for prey polymorph
Apostatic selection (predator tactic)
-Predators focus on more common color morphs
-Promotes polymorphism because rarer morphs are more likely to survive
aposematism
warning colorations that advertise defenses
aggressive mimicry
angler fish, alligator snapping turtle
The cuckoo/host egg arms race
-no rejection -> egg rejection evolves -> egg mimicry evolves -> accept most cuckoo eggs
focal sampling
used to select a particular member who will be observed at any given time
scan sampling
at preselected times the observer rapidly scans each member of a group so that the entire group is observed within a relatively short period
Game Theory
-use of mathematical models to represent complex decision making
-the best strategy for given conditions
-depends on others' behaviour(s)
-moves and countermoves
co-evolutionary
how one's strategy co-evolves with other strategies within population, NOT among different species
Evolutionary Stable Strategy (ESS)
a strategy that, if adopted by a population, cannot be trumped by another strategy because it yields the highest fitness
Prisoner's Dilemma
a particular "game" between two captured prisoners that illustrates why cooperation is difficult to maintain even when it is mutually beneficial
ideal free habitat
individuals are free to make a choice and will distribute according to rewards per individual
Despotic Distribution
Holding a territory that comes with substantial benefits
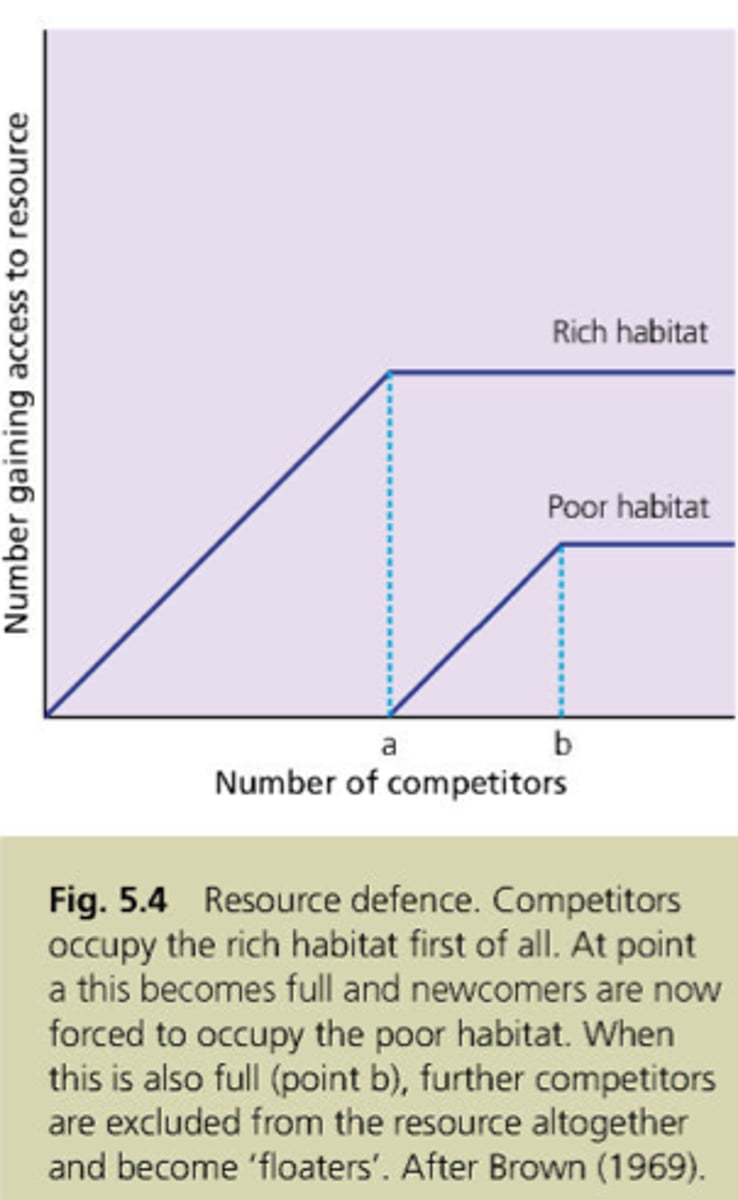
Economic Defendability Model
territorial behavior should be favored by selection when the benefits outweigh the costs
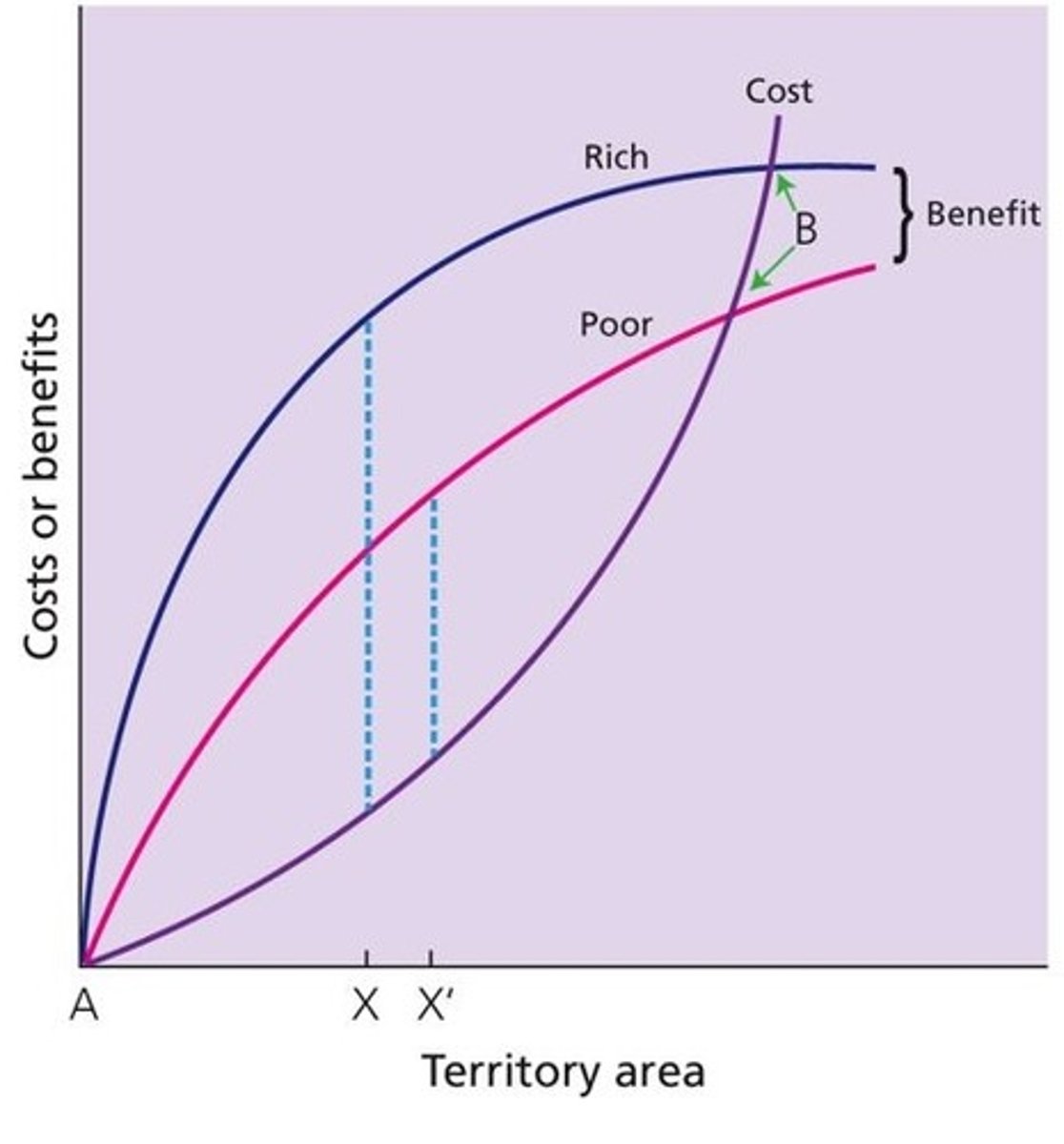
producer
An organism that can make its own food OR finds food independently
scrounger
uses information from others to find food
Personality
consistent differences among individuals
ex. "shy" indivs scrounge more often and spend less time foraging
alternative mating strategies
Different mating behaviors and morphologies that are maintained as a stable polymorphism by negative frequency-dependent selection.
morphological specialization
polymorphisms differing among males
ex. male dung beetles w/ horns vs without horns
endocrine system
a chemical communication network --> influences many aspects of animal behavior
ductless glands
produce hormones that they release into the blood or lymph
neurohormones
hormone secretion direct to blood via neurons
protein hormones
-small peptides or larger proteins
-water (blood) soluble
-can be stored
steroid hormones
-like testoterone + estrogen
-only fat soluble
-cannot be stored - releases immediately
transmission
elicitation of a behavioral response
dilution
safety in numbers
individual reduction in attack risk through grouping
predator swamping
an anti-predator strategy where there are so many individuals that preds have to limit their prey consumption
communal defense
Groups of prey actively defending themselves:
ex: Black-headed gulls will mob crows who come to eat eggs or chicks
vigilance
reduced as group size increases
optimal group size
the size that results in the largest relative benefit
sexual selection
when individuals select mates based on heritable traits
"result of differential mating success"
natural selection
heritable variation of fitness
Intra-sexual selection
competition between members of the same sex for access to mates of opposite sex
Inter-sexual selection
individuals of one sex CHARM indivs of opposite sex
"female choice"
Anisogamy
gamete dimorphism
-zygote survival depends on zygote size
-egg > sperm
why do males usually fight for females?
-anisogamy
-eggs larger w/ more resources, less #s, greater indiv RS
-sperm smaller w/less resources, more #s, less indiv RS
-ultimately, sperm are desperate for eggs
Polyandry
One female, several males.
evidence that sexual selection exists
-sexual size dimorphism: armaments
-female mate choice: ornaments
sexual conflict
-forced copulation
-mate guarding
-frequent copulation
-traumatic insemination
Chase-away sexual selection
evolution of a male character is neutralized by the evolution of a female character, which results in the in the evolution of an even more exaggerated male character.
parental investment
any behavioural/physiological contribution by a parent in an offspring that increases survival/fitness of offspring at a cost to the parent's ability to invest in other offspring
fitness-enhancing hypothesis
an initial benefit to offspring/parents when it was evolved
constraints hypothesis
moms forced to remain bc the embryo is internal
coefficient of relatedness
The fraction of genes that, on average, are shared by two individuals.
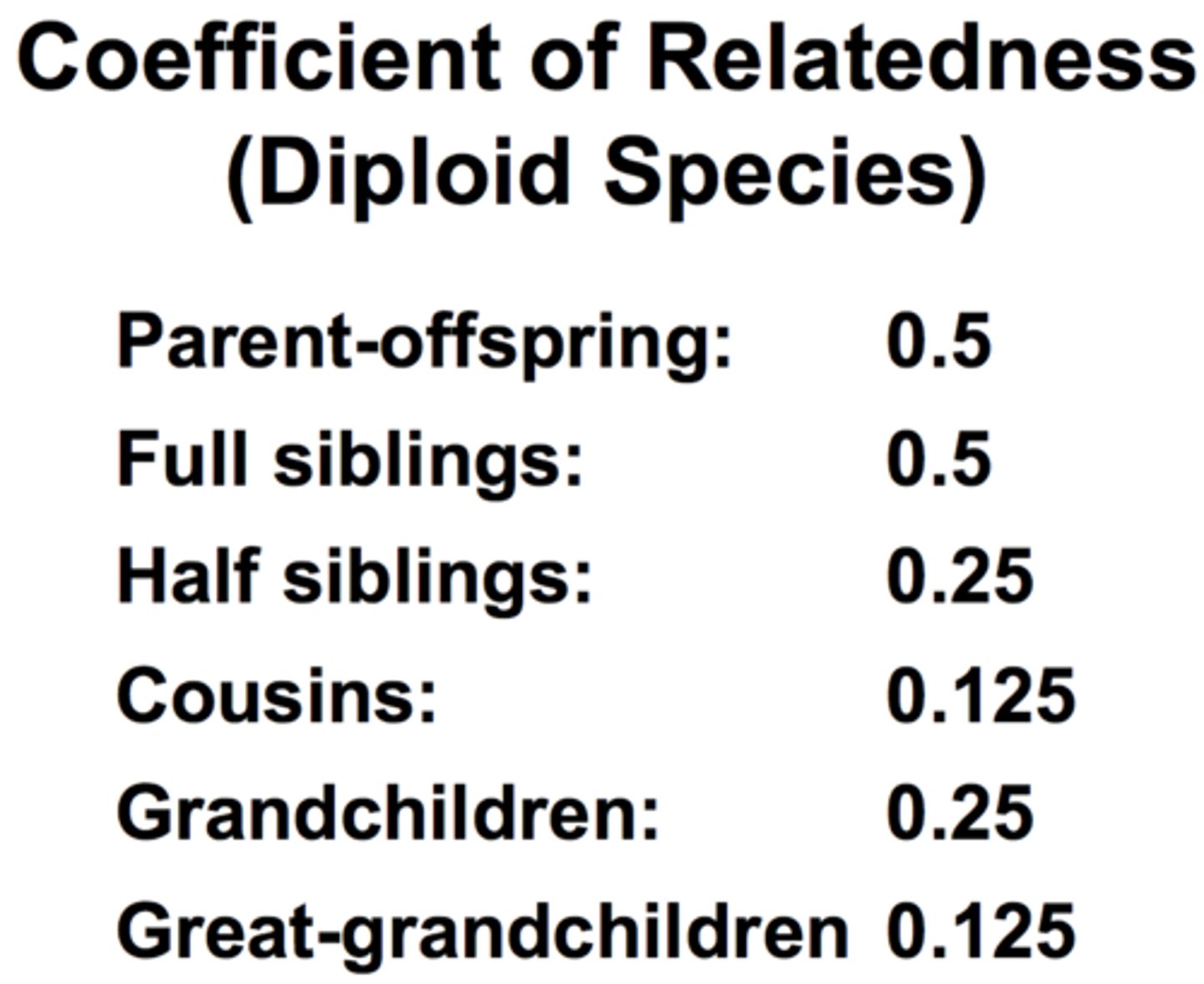
intra-brood conflict
offspring demands more than siblings bc its own r=1 (vs r=0.5 for siblings)
inter-brood conflict
current brood demands more than future brood
siblicide
killing your siblings so you don't have to compete with them
Facultative
only under certain circumstances
Obligate
a necessity
brood parasites
when a mama bird lays eggs in other species' nest so she doesn't have to raise them
mating system
how mates are acquired
monogamy
1 male, 1 female
permanent/sequential
polygyny
One male, several females

polyandry
1 female, several males
promiscuity
many males, many females
~free love~