Lecture 17 | Fossil Fuels
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key Terms & Concepts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Peak Oil
when 1/2 of earth’s accessible oil has been exploited and price increases dramatically
After ____ production peaks, ____ continues to rise
oil, demand
Explain why the price of oil increases after Peak Oil and why demand continues to rise:
gap between supply and demand, overpopulation increases demand
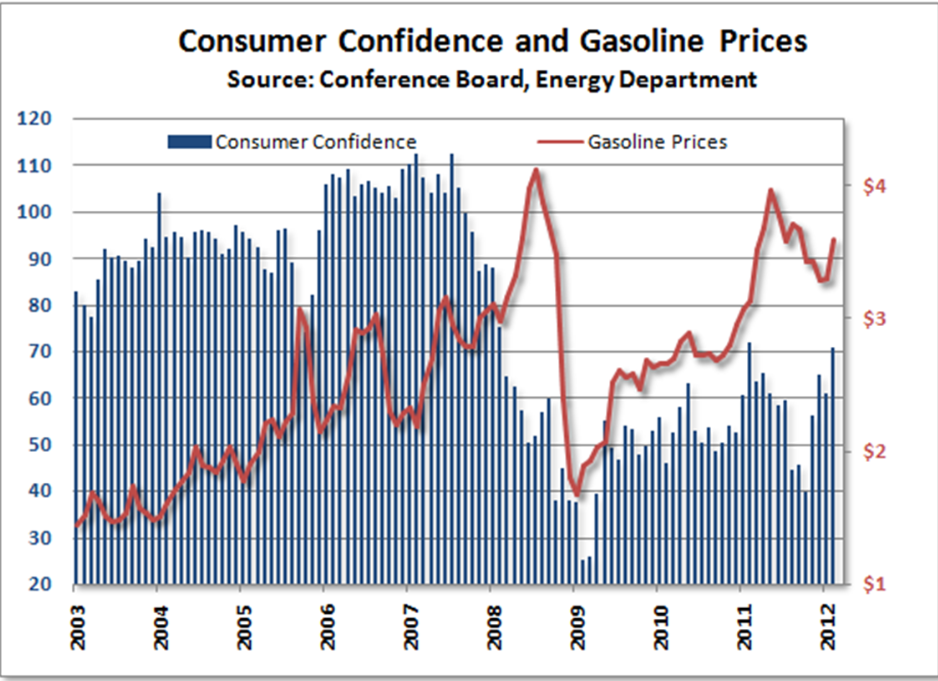
Why did the price of gas increase to nearly $5/gal in 2008?
industrializing china & india
To handle the rising demand for oil in 2008, OPEC increased oil supply, but not by much. Why didn’t they increase production more?
finite oil, didn’t want to reduce exporting for economy
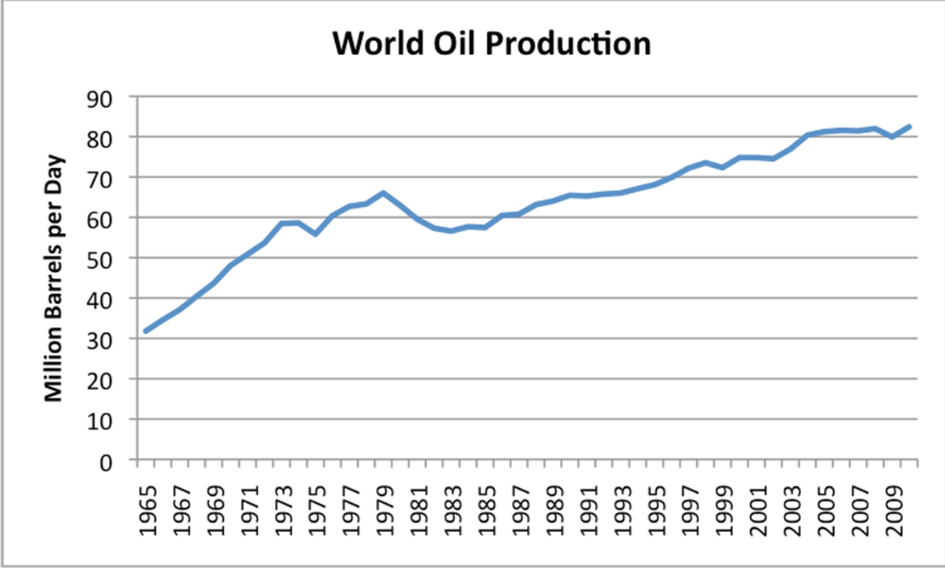
Why is it believed we’re close to hitting Peak Oil?
production at 30 bil barrels/year for long time
What is the smartest response to our approaching of Peak Oil?
find oil alternatives
When living things grow, they add _____, which is the _____ __ ______ ______
biomass, mass of some organism
A tree is able to grow from an acorn to a massive tree. Where does that biomass come from?
co2, water
Describe Photosynthesis
plants combine solar energy, co2, and h2o to form carbs
How do glucose molecules store energy?
chemical bonds
What are two ways we can break chemical bonds (that causes them to reform) so we can get the energy the plant stores?
eating plant, burning wood
The more ____ ____ we break, the more _____ we get
chemical bonds, energy
What are the two options for plant/animal biomass when they die?
decomposed or buried under sediment
Biomass gets _____ when buried and ____ ____ is conserved
compressed, chemical energy
_____ packs a lot of chemical bonds in a small package
compression
The ____ of biomass doesn’t change, only the _____ it occupies
amount, space
How old is the biomass that makes up the fossil fuels we use today?
500 mil
Most biomass comes from…
plants
What does the amount of compression for biomass depend on?
how deep it was buried
Describe the shallowest burying of biomass:
peat, moist, squishy
Describe the second most shallow burying of biomass:
lignite, brown coal, not dense, hard but light
Describe the second deepest burying of biomass:
bituminous coal, heavy, dense, burns well
Describe the deepest burying of biomass:
anthracite, gives most energy, most dense, most chemical bonds
What is the most common coal type?
bituminous
Peat Formation
low temp, low pressure
Anthracite/Coal Formation
low temp, high pressure
Natural Gas Formation
high temp, low pressure
Oil Formation
high temp, high pressure
Describe where low and high temperatures indicate for fossil fuel formation
low = continents, high = ocean near mantle
Under what natural structure will you find anthracite coal under? Why?
mountains, high pressure
Why do oil and natural gas try to find a way to the surface?
under pressure
Anticline
oil/gas trapped in soft, porous rock
Transform Fault
plates slide dense rock over oil/gas, traps it
What is the similarity between an anticline and transform fault?
oil & gas trapped
Primary Production
sinking a well into oil/gas formation, pumping out
Enhanced Recovery
injecting co2/n2 to build pressure and pump oil out
How much of an oil/gas deposit does primary production recover? Enhanced recovery? Why is enhanced recovery not used as much?
25%, 60%, costly
Where are the formations that contain oil?
60% in middle east
Which countries use the most oil?
europe, north america
Why was natural gas considered a byproduct of oil production?
not as much energy from burning
______ results in longer carbon chain molecules and more ______
higher compression, energy
List these natural gases in order of least to most energy: octane, methane, propane
methane, propane, octane
Why is natural gas considered cleaner despite still producing CO2?
fewer byproducts
Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
high pressure water to widen fractures, gas extraction
What is the danger of hydraulic fracking?
bursting new fractures, gas contaminates groundwater
Methane Clathrates (Hydrates)
gel-like methane ice, found on continental shelves
How do methane clathrates form? What two properties must be very specific?
ice freezes into hexagon, cage for methane, temp & pressure
What has more potential energy than all other oil & gas reserves?
methane clathrates
Why are methane clathrates so hard to extract?
very unstable, remove conditions and falls apart, chain reaction & methane bubble
What is the most commonly used fossil fuel?
coal
Why is coal considered the dirtiest fossil fuel?
sulfur and nitrogen oxides, mercury, particulate matter
What do sulfur and nitrogen oxides cause, which is a direct impact of coal burning?
acid rain
Where are the coal deposits in the US?
pa anthracite, lignite and bituminous
What are three ways we can make coal more environmentally friendly, in treating pollution?
bag houses remove particulate matter, catalytic reduction to convert no to n2 o2, flue gas desulfurization and traps mercury
What reduces particulate matter in coal production?
bag houses, high capacity filters
What reduces nitrogen oxides from coal production?
catalytic reduction
What reduces both sulfur oxides and mercury emissions?
limestone to gypsum conversion