Partitioning of Africa
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
Civil War
a war between two groups or two regions within the same country
Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.

Artificial Political Boundaries
boundaries created without regard to religion, ethnicity, or other native characteristics
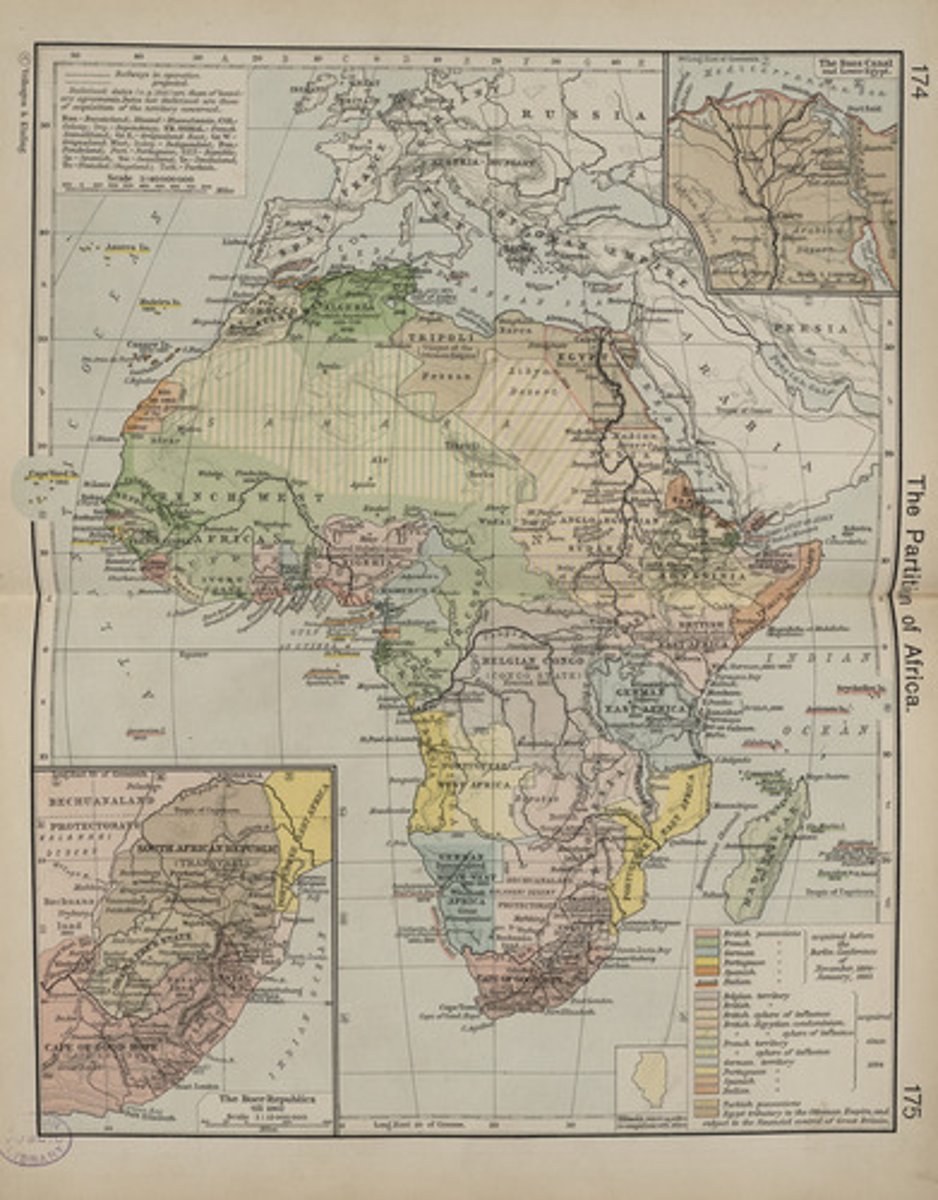
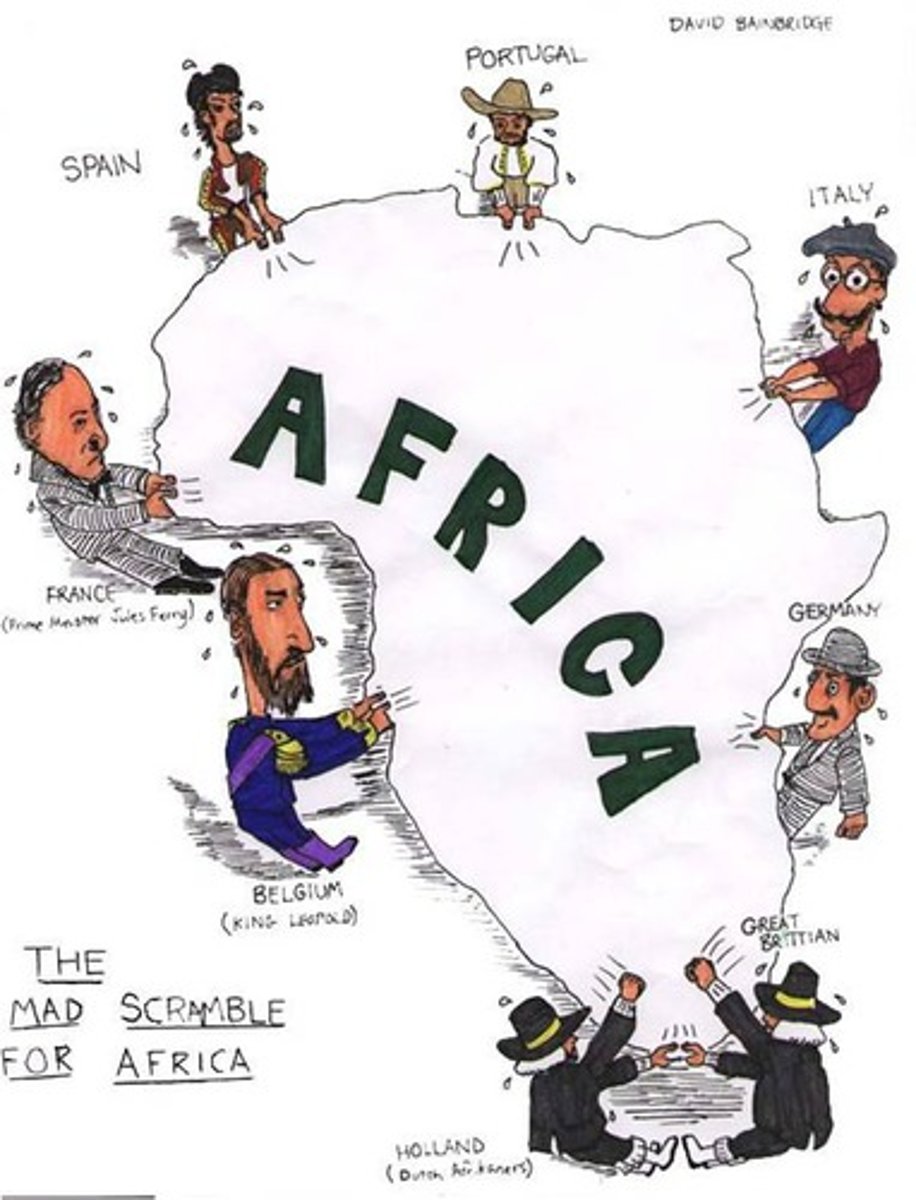
Scramble for Africa
Term given for the rapid invasion of Africa by the various European powers. This began imperialism in Africa.
Partitioning
to divide or separate into parts

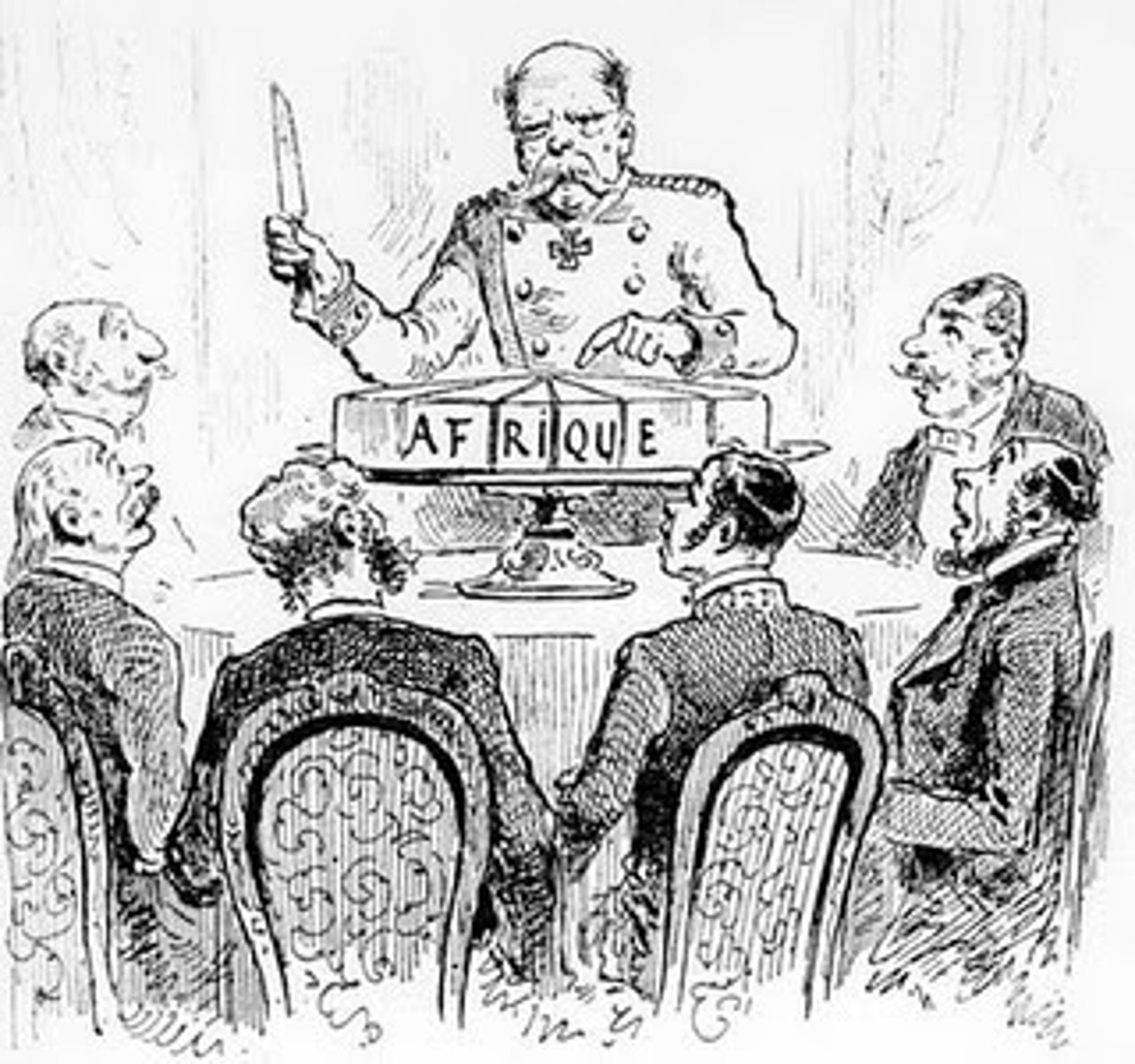
Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules colonization of Africa - there were not any Africans present at this meeting.

Nationalism
the idea that people love their country and are proud of it - a display of patriotism

Racism
Belief that one race is superior to another

Colonialism
An attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
Reasons for European Imperialism in Africa
Protect trade routes; Obtain raw materials / natural resources not in Europe (and then re-sell manufactured products in colonies); Spread Christianity & Western culture; Nationalism / competition between nations
How did partitioning lead to conflict in Africa?
The European nations disregarded the culture (ethnic groups) of the African people - they drew boundaries that benefited Europeans, often grouping enemies together or splitting groups that wanted to remain together. When they left the continent after independence, the nations of Africa did not have leaders with experience ruling a country.
independence
self-reliance and freedom from outside control
The Mau Mau
Revolutionary group in Kenya who used violent means to force out European settlers.
Jomo Kenyatta
Nationalist who helped lead Kenya to independence and first president of Kenya
After WWII
Many countries in Africa started to fight for independence from European countries
Pan-Africanism
the unity of all black Africans worldwide, to support countries with fighting for independence
Marcus Garvey
Pan-Africanist leader during the 1920s who founded the UNIA and advocated mass migration of African Americans back to Africa.
Nigeria gained independence through...
Peaceful and diplomatic means
Kenya gained indepence through...
violence and rebellion against the Europeans
Great Britain and France
The two nations claimed the most territory in Africa during the "Scramble for Africa".