Neuro: Reward, Reinforcement, and Addiction
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What happens when the action is followed by a reinforcer?
It is acquired and increases in frequency.
What happens when an acquired behavior is no longer followed by a reinforcer?
The behavior extinguishes and decreases in frequency.
Reward-Related Learning
A target behavior is gradually molded by rewarding increasingly accurate approximations of the behavior. (ex. lever pressing)
Which striatum is associated with Parkinson’s?
Motor striatum pathway
Where do most dopamine neurons originate?
Two areas of the midbrain, the VTA and SN.
What two major pathways does the VTA give rise to?
Two major dopamine pathways. One projecting to the frontal cortex (mesocortical pathway) and the other to the nucleus accumbens (mesolimbic pathway).
Medial Forebrain bundle (MFB)
A neural pathway containing fibers from the forebrain and brainstem. Including the ventral tegmentum area (VTA). Simulation here has positive effects on mood. When simulated on rats/mice to press lever, rats/mice will press the lever with greater vigor to get the simulation.
What happens when rats are trained to lever press with VTA stimulation, but the next day is put under the influence of a dopamine antagonist drug?
Begin to lever press at a normal rate and soon give up as if the drug blocked the reward value. (reinforces hypothesis that dopamine is necessary for brain stimulation to reinforce behavior).
What happens to dopamine neuron firing when there is a positive signal?
(activation) when an appetitive even is better than predicted (positive prediction error) (ex. instead of candy for volunteering you get money) AKA increased firing.
What happens to dopamine neuron firing when there is a negative signal?
(decreased activity) when a appetitive event is worse than predicted (negative prediction error) (ex. when you expect money when volunteering but instead get nothing). AKA decreased firing.
What happens to dopamine neuron firing when there is no signal?
(no change in activity) when a neutral stimulus occurs without reward (ex. no reward at all). AKA no change.
What is activated when subjects expect monetary gain?
The nucleus accumbens is activated. When expecting large gain, the accumbens activity increases. When the expecting large loss, the accumbens activity is not activated.
When is the nucleus accumbens most strongly activated?
When subjects sees signal that large reward is coming.
Cortical Sensory Inputs release?
glutamate to activate striatal neurons that correspond with a specific action (e.g., lever press).
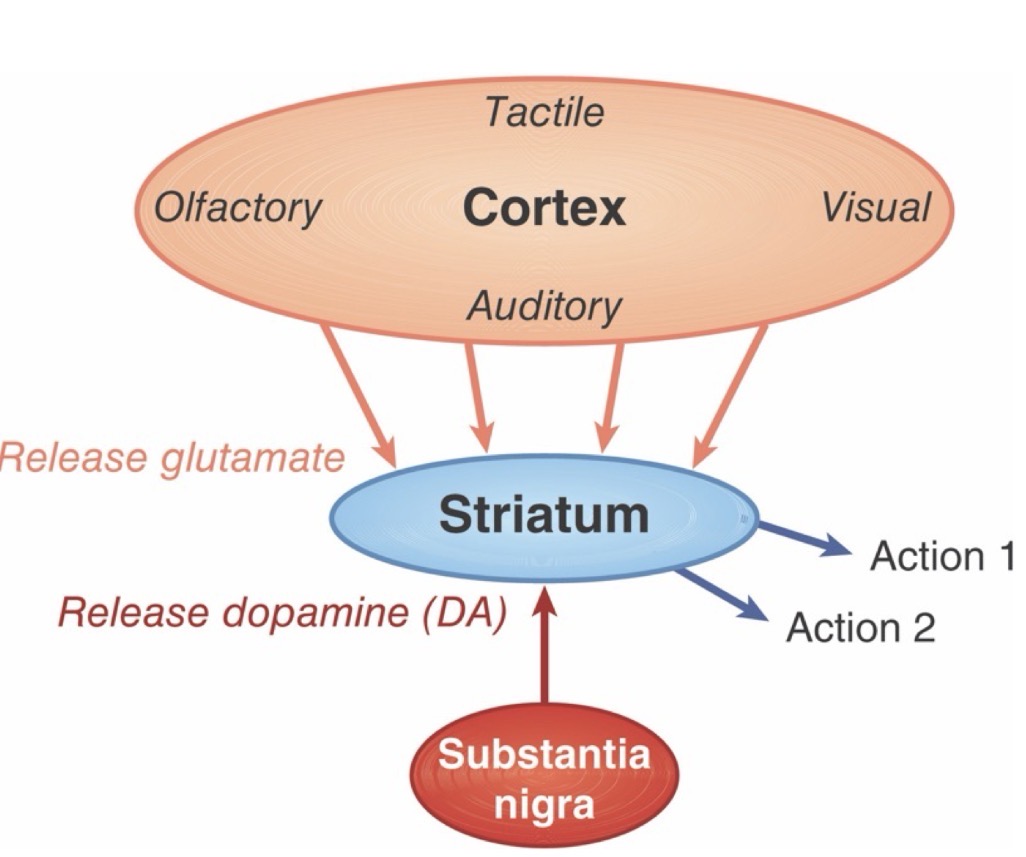
Substantial nigra neurons release?
dopamine to the striatum in response to unexpected reward to action.
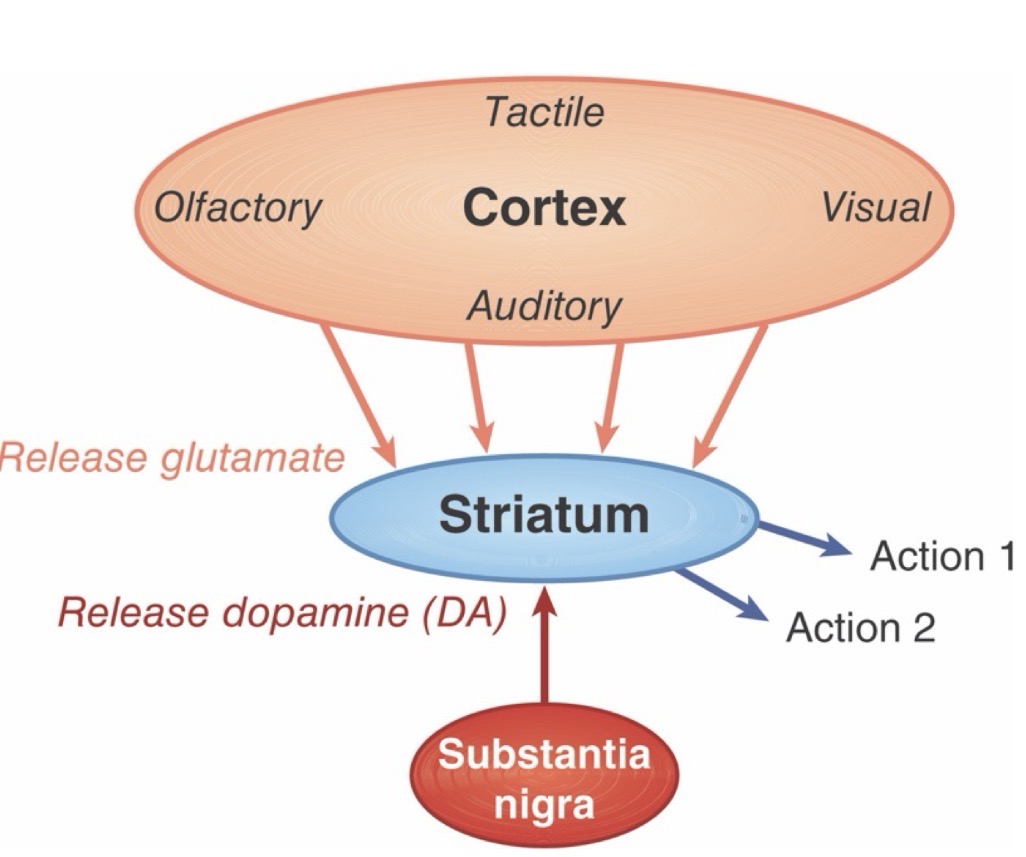
What does dopamine strengthen?
The connection between the most recently active cortical and striatal neuron.
What does an increase in glutamate receptors at the synapse increase?
Likelihood animal will press lever in future
What enlarges after glutamate and dopamine bind to receptors on an activated striatal neuron?
Small dendritic spine of a striatal neuron enlarges. Appears within 2 minutes and is long lasting.
What does cocaine block?
Dopamine reuptake so it is an agonist. Allowing dopamine to accumulate in the synapse.
How does cocaine effect behavior?
When rat receives low dose when press lever, it presses the lever frequently. When the dose is lower, rats press it at a higher rate to increase dopamine level. But if dose very low, the rate may give up pressing the lever.
What is nicotine?
Like cocaine and amphetamine, it is a stimulant drug. It binds to the nicotinic type of acetyloline receptor and that is found in various areas of the brain like VTA. When it binds to the receptors the neurons increase their dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex.
What are enkephalins and endorphins?
They are endogenous opioids (naturally produced by the body), activate opioid receptors. Enkephalins are natural analgesics (reduce pain). Endorphins are released during intense physical activity aka runners high.
What about heroin, morphine, and oxycodone that are opioid drugs?
They activate the same opioid receptors normally activated by endogenous opioids. When binded, it elevates dopamine release in nucleus accumbens which is associated with drug high.
How does alcohol effect the brain?
It produces a number of common neuroadaptations, including DA hypoactivity. The addition is etched in midbrain and frontal structures that reinforce alcohol use by dominating attention and decision-making.
What can reduce alcohol assumption in people with alcohol dependence?
Opioid antagonist naltrexone
What can years of chronic alcohol abuse lead to?
Korsokoff syndrome
Korsakoff syndrome
Memory disorder results from vitamins B1 deficiency. It damages nerve cells and supporting cells in the CNS and impacts memory acquiring and establishing new memories and in retrieving previous memories.
What happens when you show more alcohol advertisements?
The ads elicited activation in orbitofrontal cortex and ventral striatum (regions of the reward system). More self-reported binge drinking correlated with the amount of activation in orbitofrontal cortex.
Drug tolerance
a drug’s reduced effectiveness in producing physiological and/or behavioral effects when used repeatedly.
Because of this, the user needs to increase the amount of drug consumed in order to achieve the desired effect.
Forms of drug tolerance
Metabolic tolerance, functional tolerance, conditioned drug tolerance
Metabolic tolerance
occurs when the body becomes better able to rid itself of the drug. As a result, a reduced amount of drug reaches its target regions of the brain.
Functional tolerance
is the reduced sensitivity of target sites to the drug (e.g., a reduction in the number of opioid receptors on neurons in the VTA or nucleus accumbens give heroin fewer sites upon which to act).
Conditioned drug tolerance
occurs when an individual becomes tolerant to a drug only in the environment in which they took the drug in the past.
What happens when an addict abstains from the drug?
Withdrawal symptoms happen from days to months. An increase in stress hormones accompanies withdrawal. Drugs preventing increase in stress can reduce anxiety associated with drug withdrawal.
Inhibitory control allows?
to inhibit impulses when they get in the way of our carrying out desired tasks. (it takes addicts a lot of inhibitory control to refrain from taking the drug).
What does inhibitory control depend on?
The activity within the prefrontal cortex.
What is associated with prefrontal cortical impairment?
Major drugs of abuse and this can cause impairments in the brain circuits that are necessary to avoid taking those drugs.
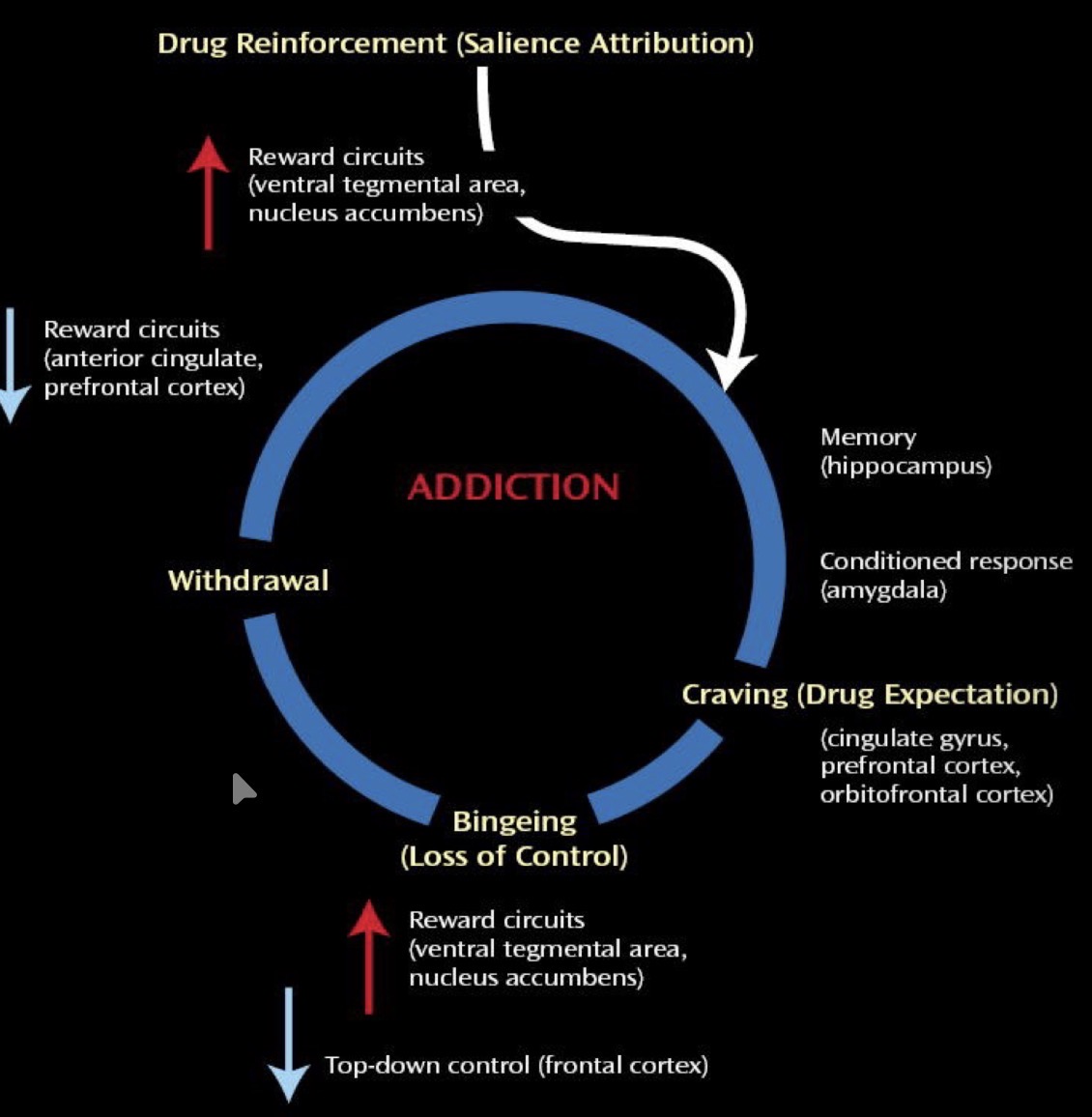
Cycle of Addiction