Anatomage Week 10 - combined
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
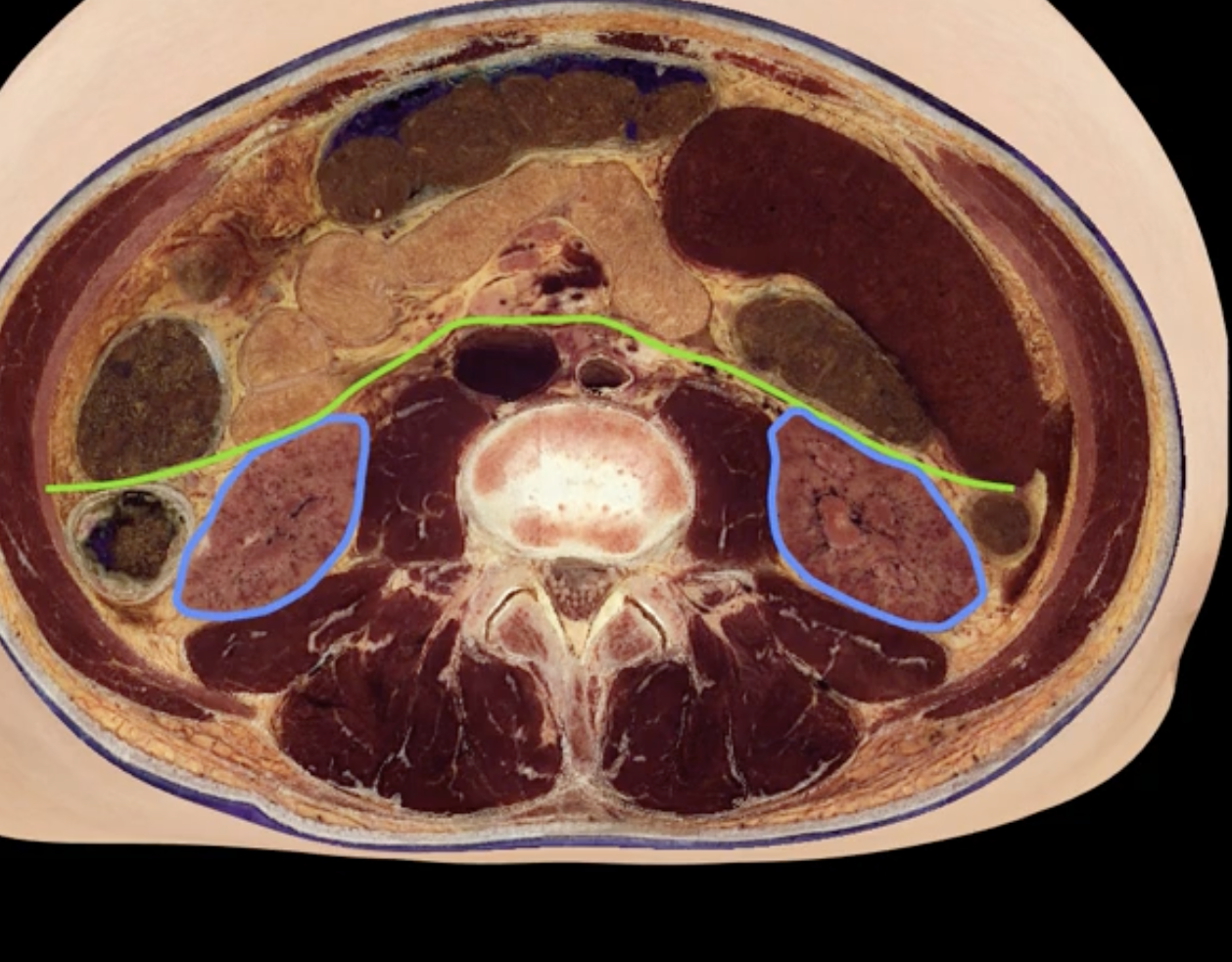
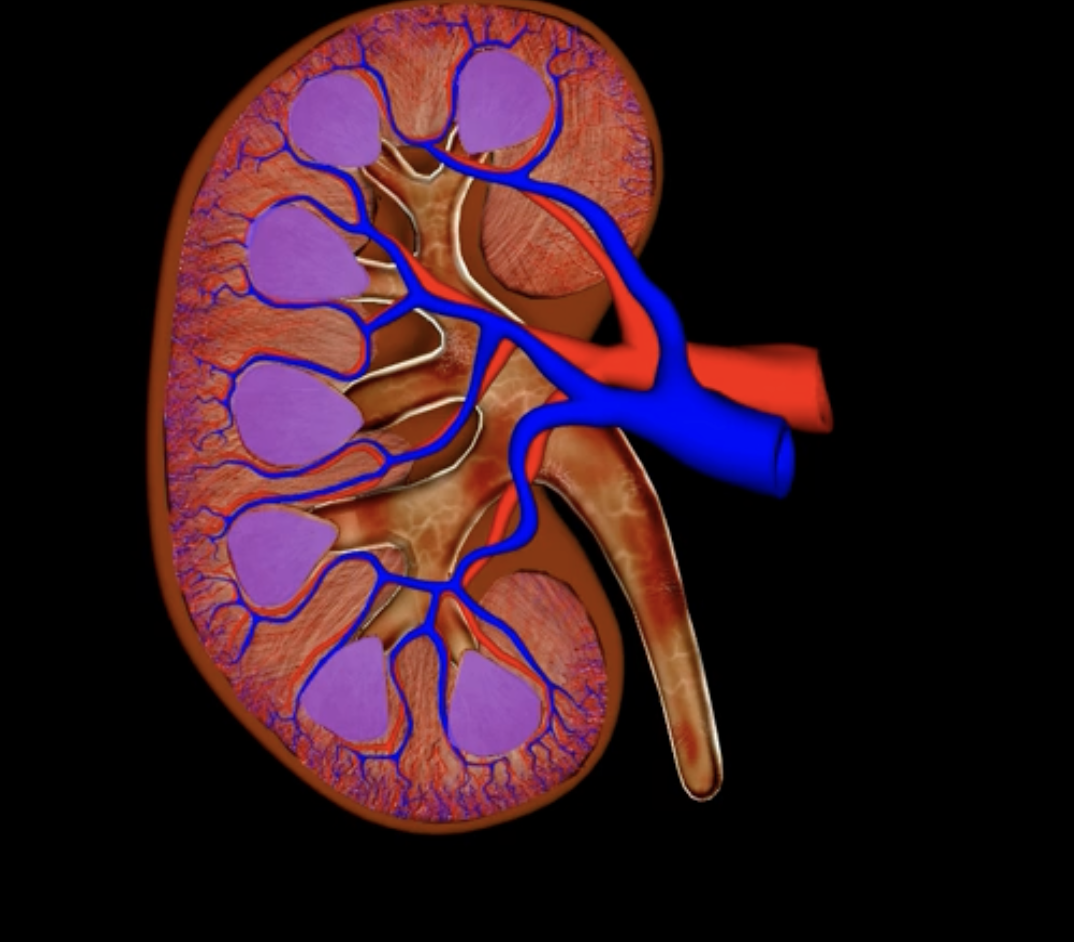
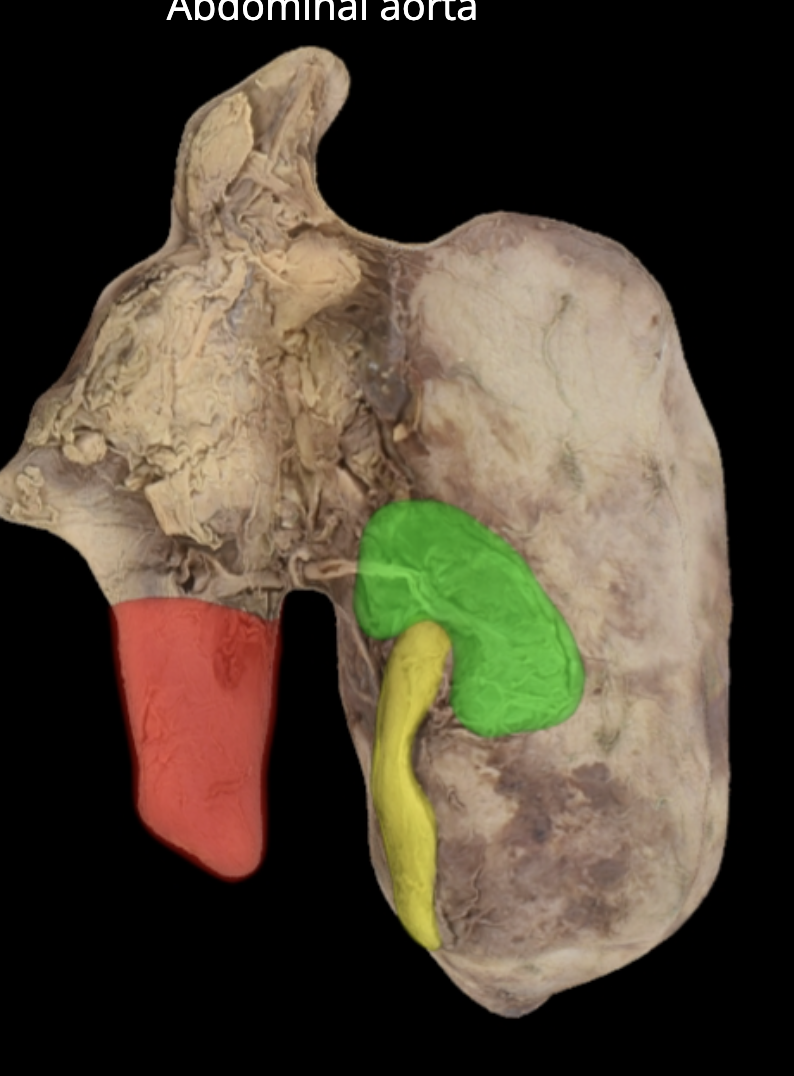
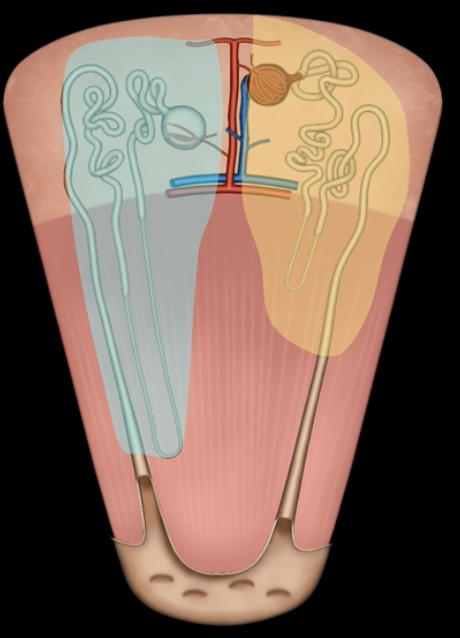
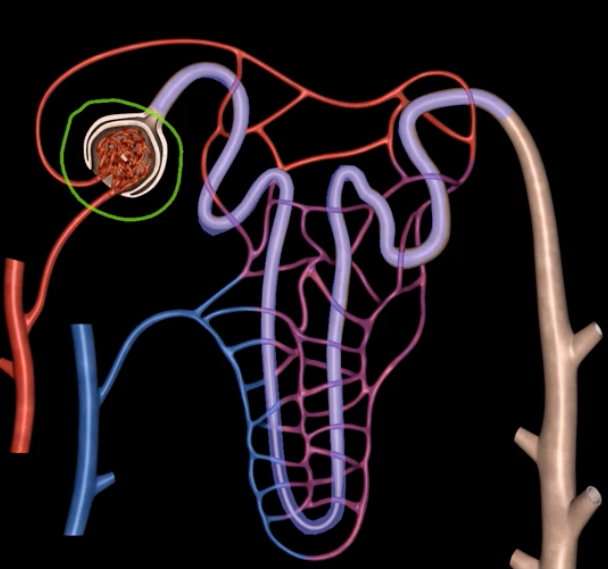
green: peritoneum
blue: kidneys
green and blue are showing that the kidneys are retroperitoneal
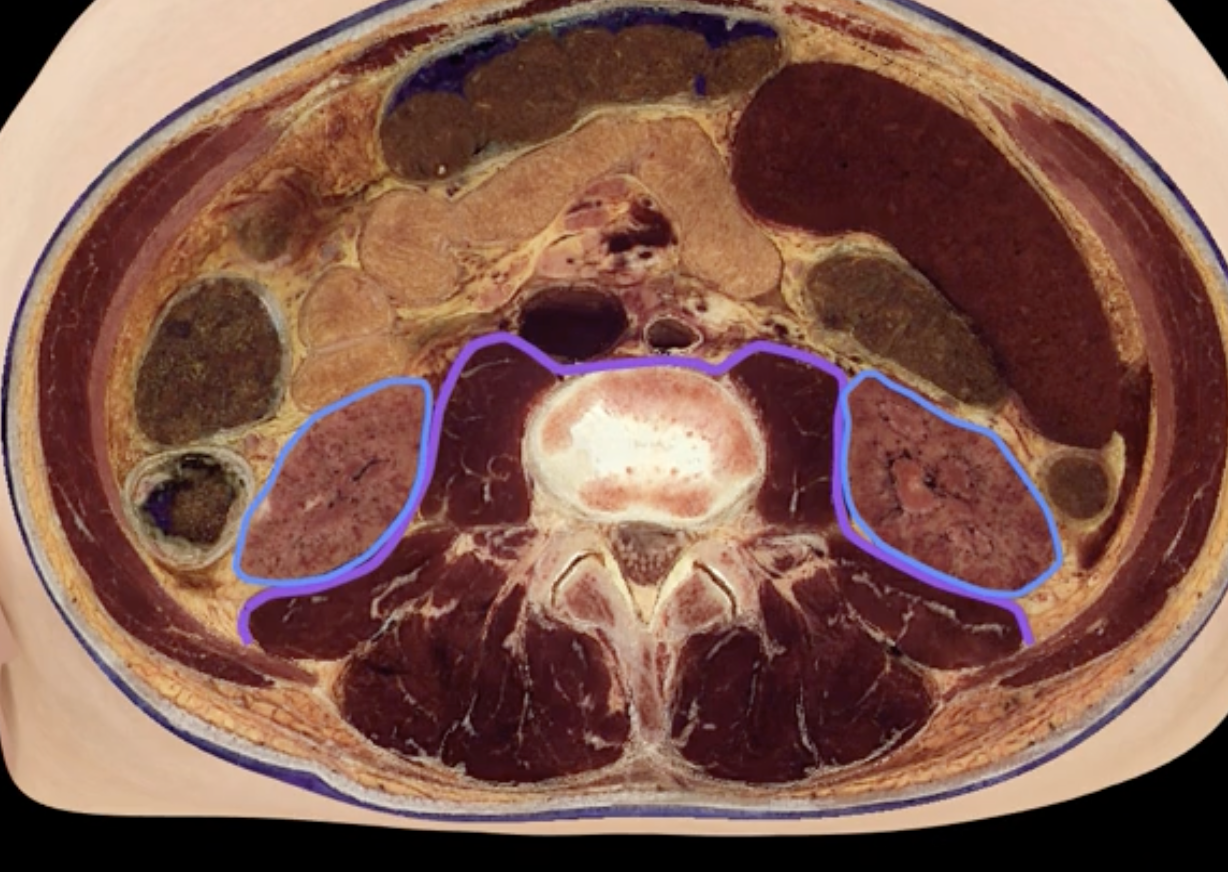
posterior abdominal wall
purple
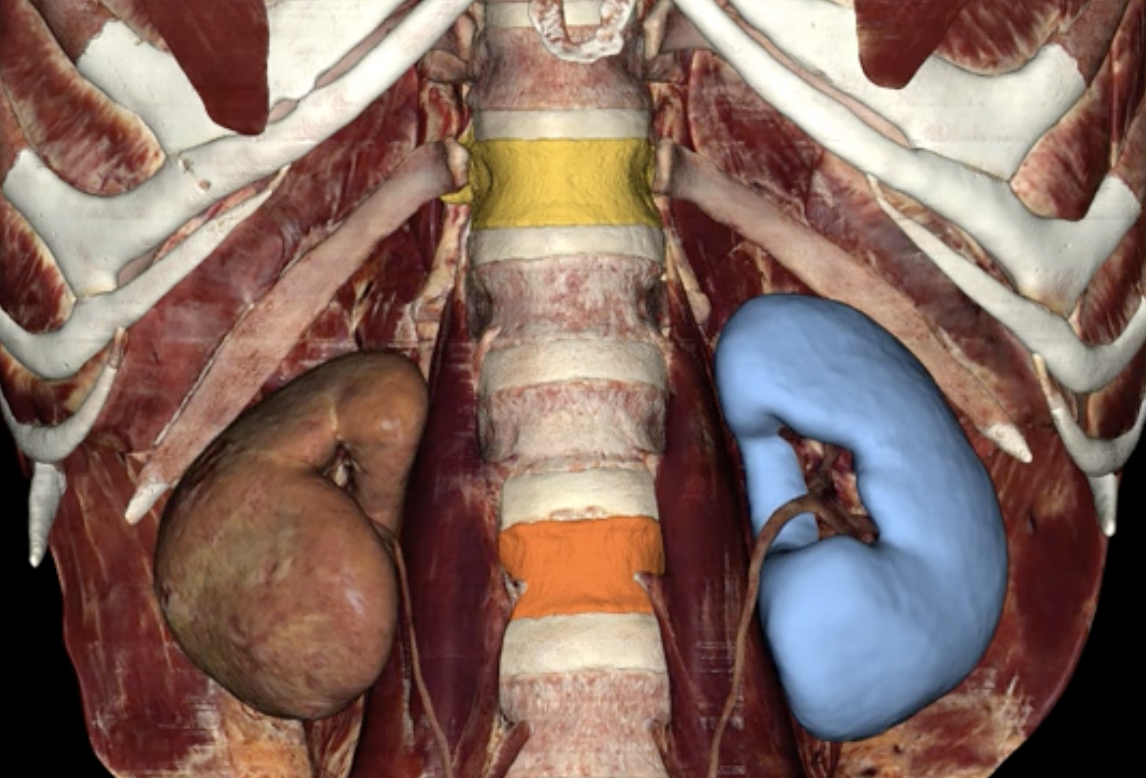
blue: left kidney
yellow: T12
orange: L3
blue, yellow,orange
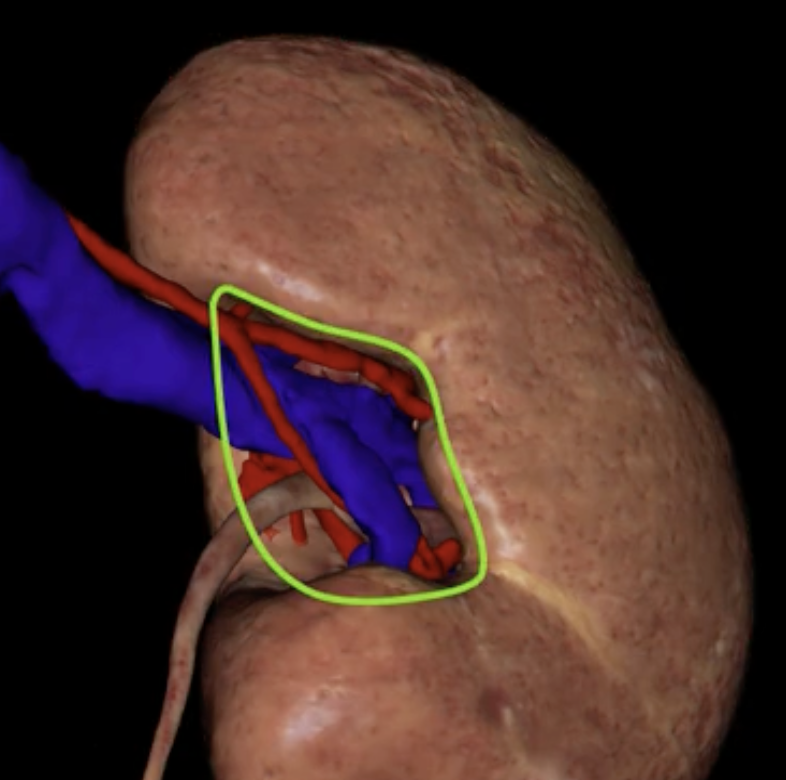
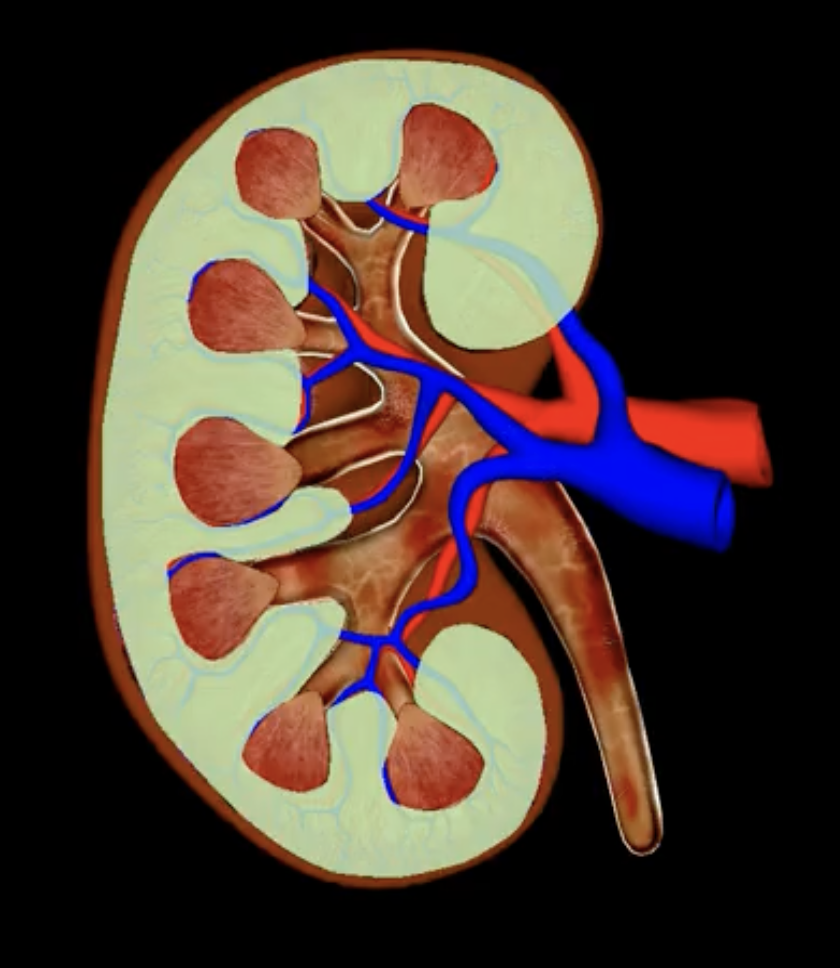
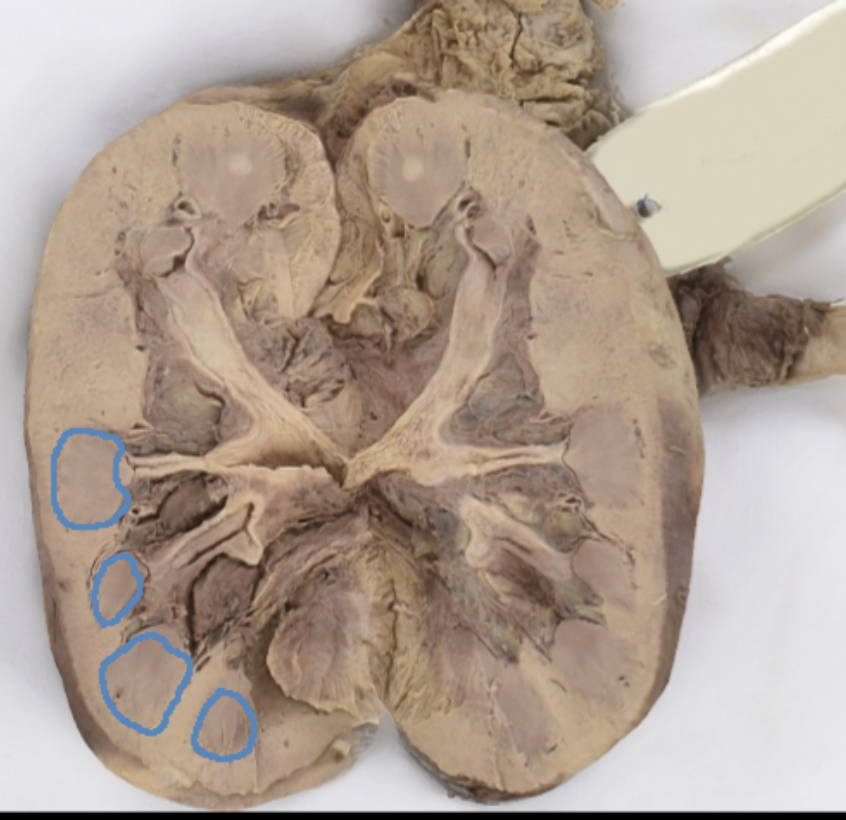
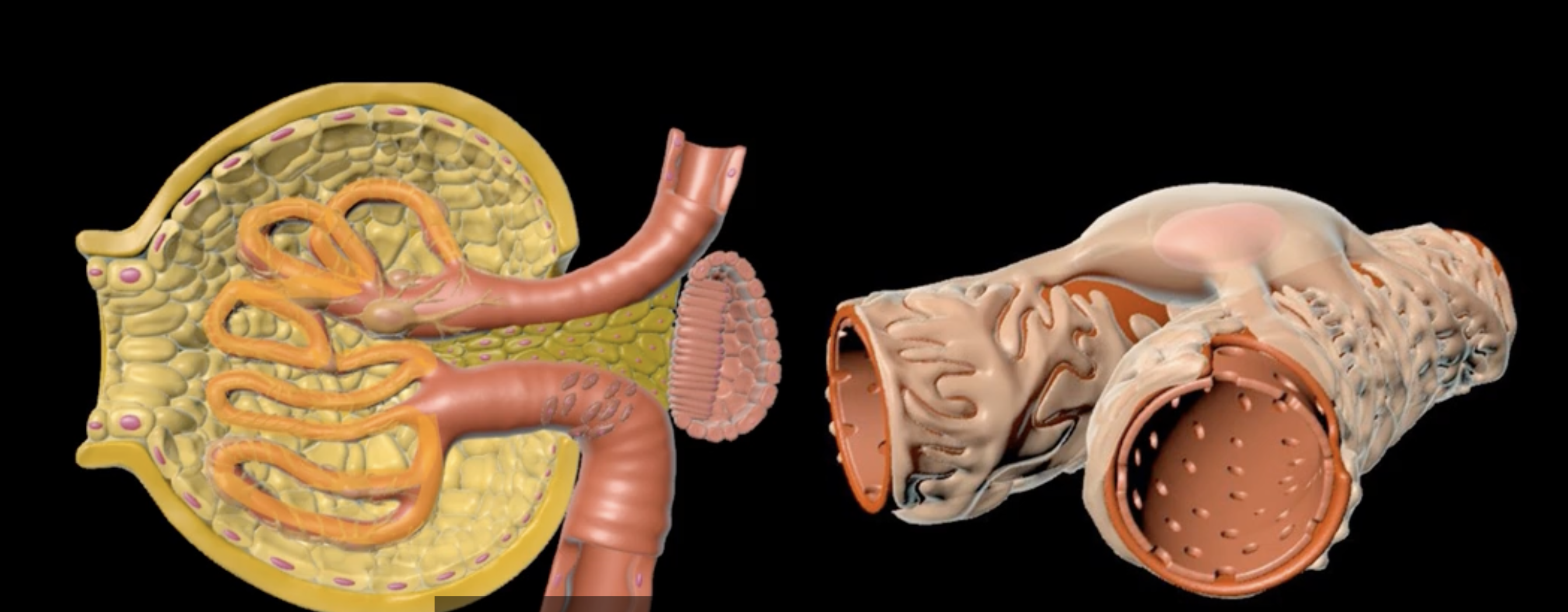
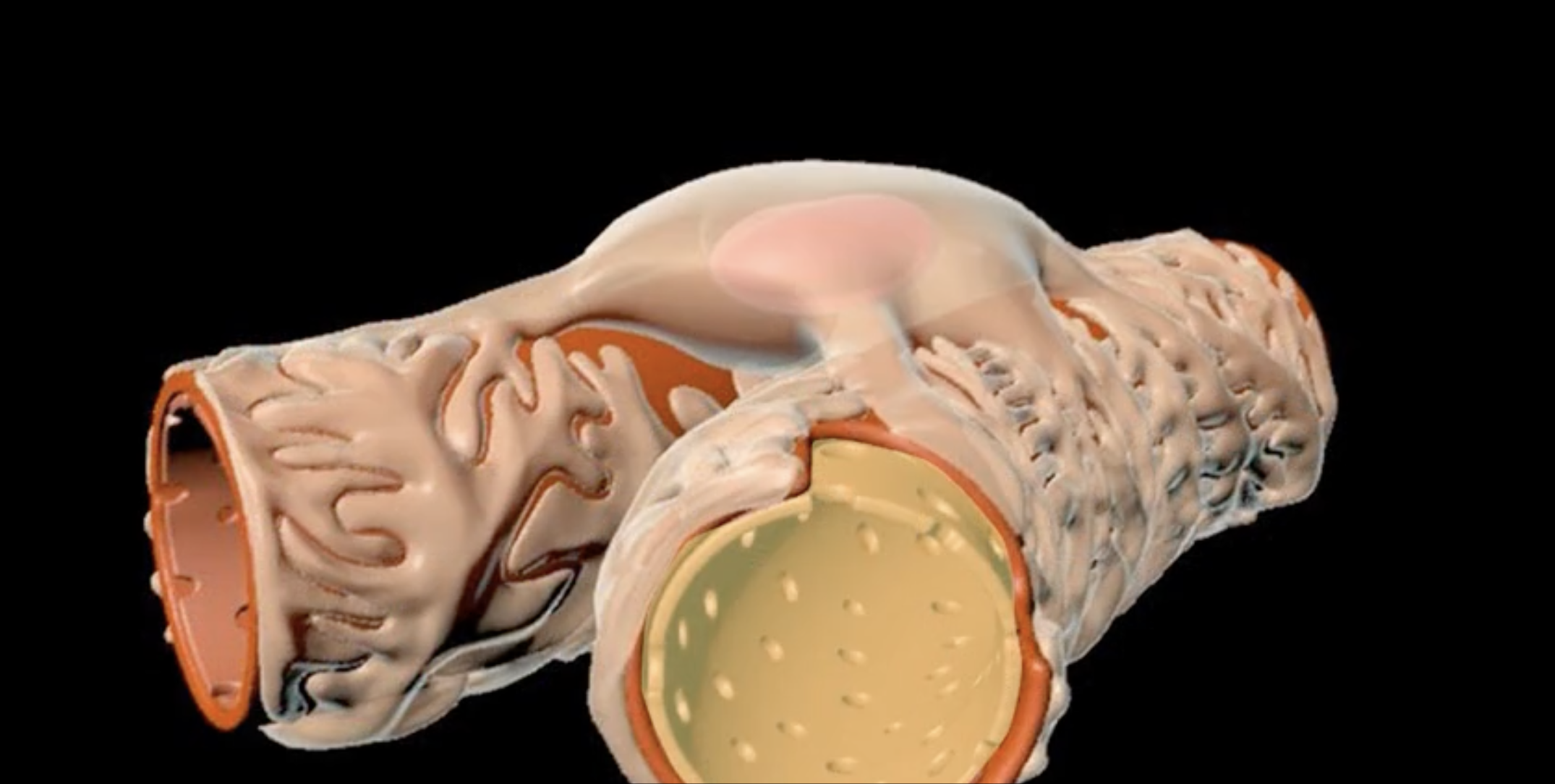
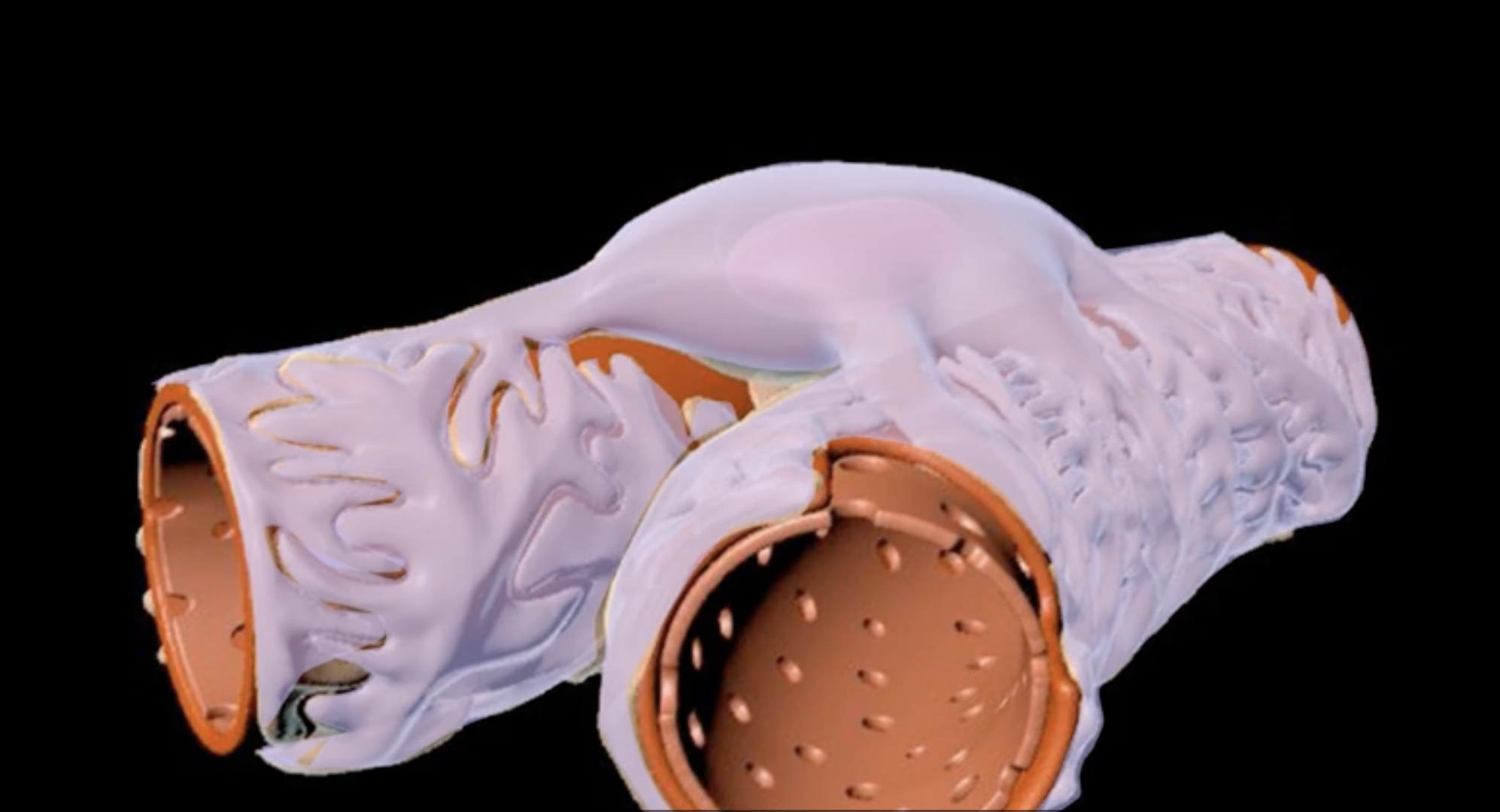
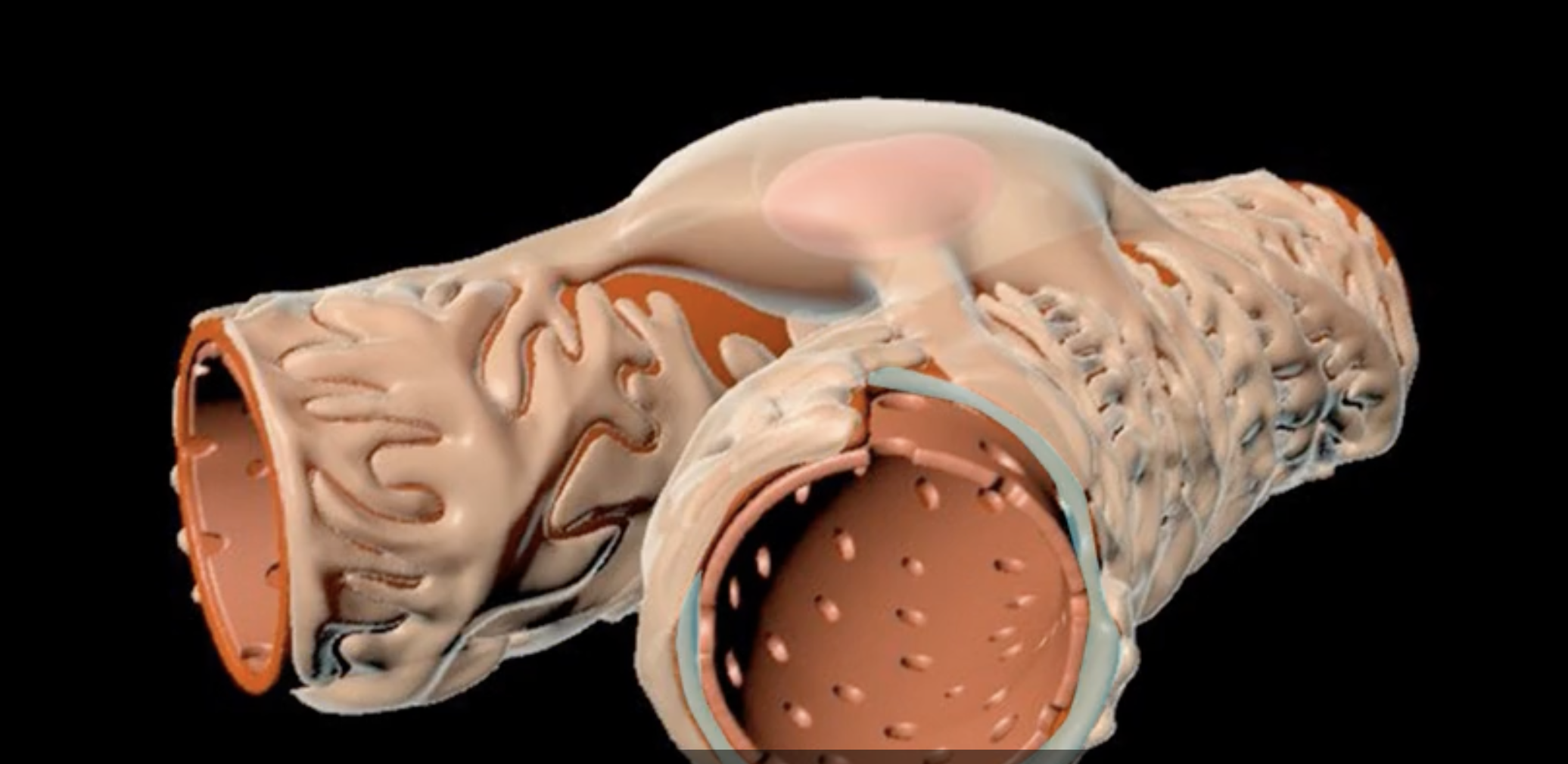
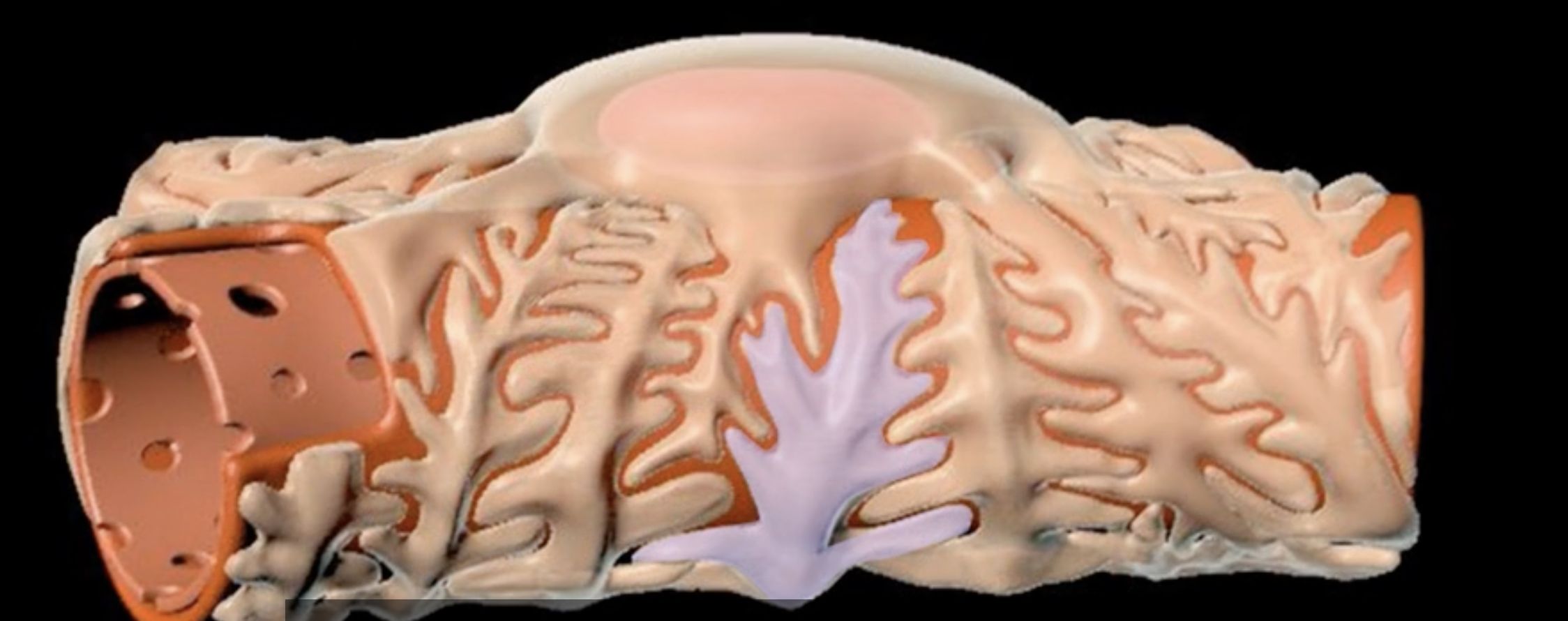
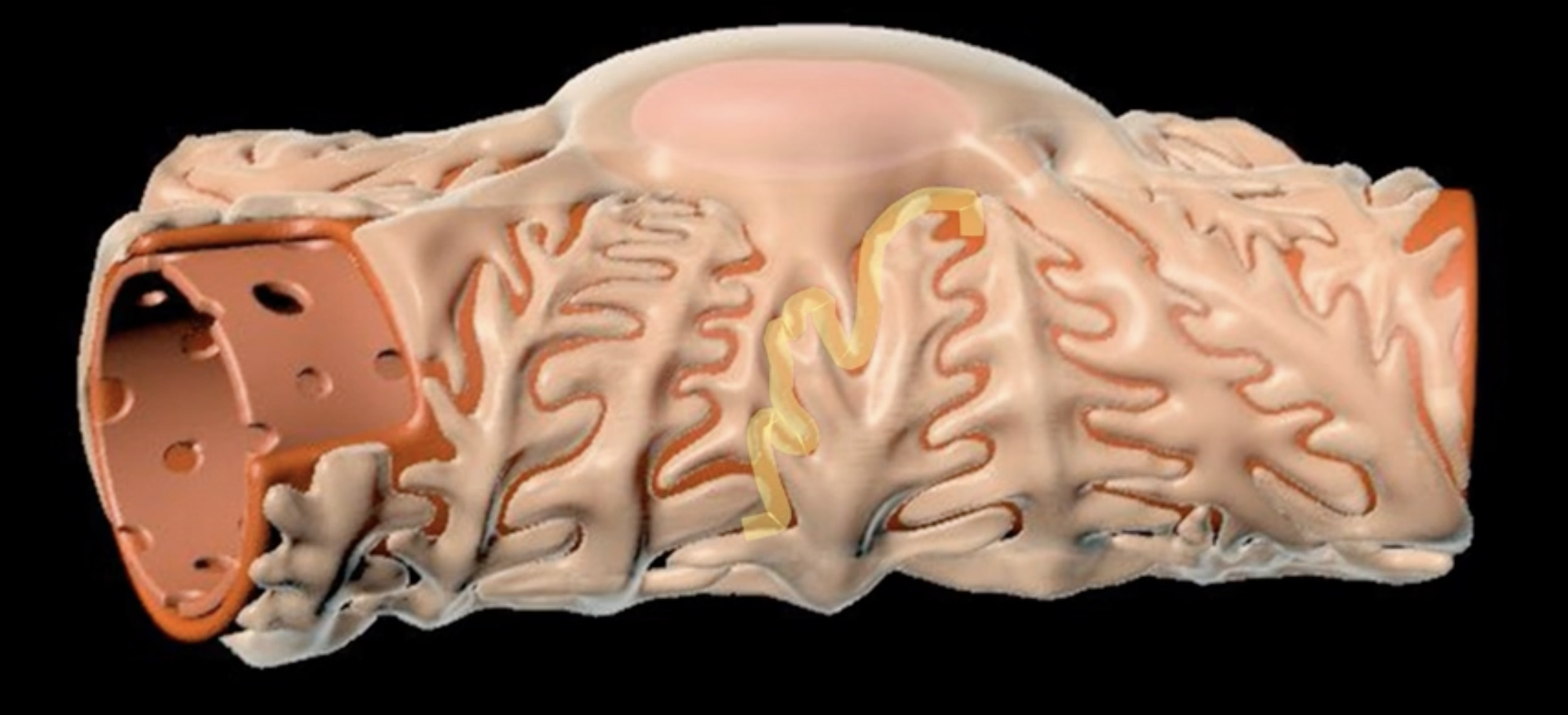
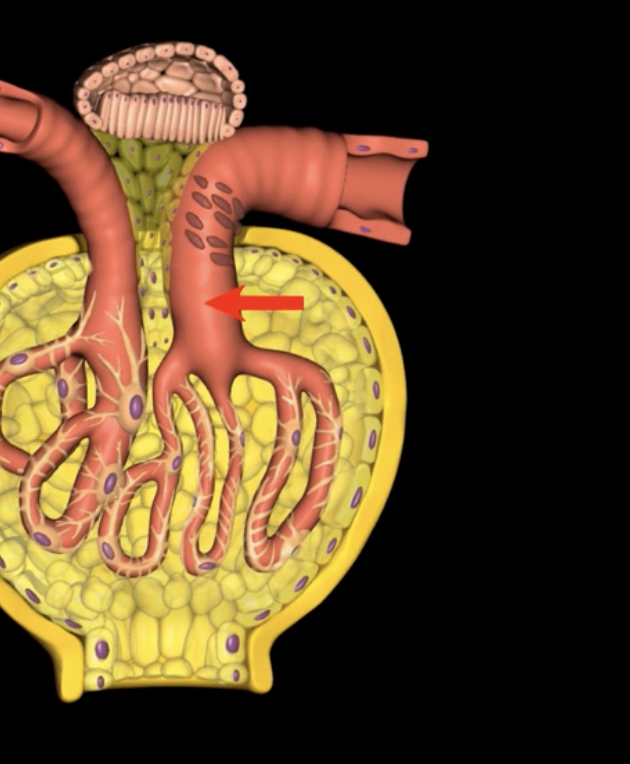
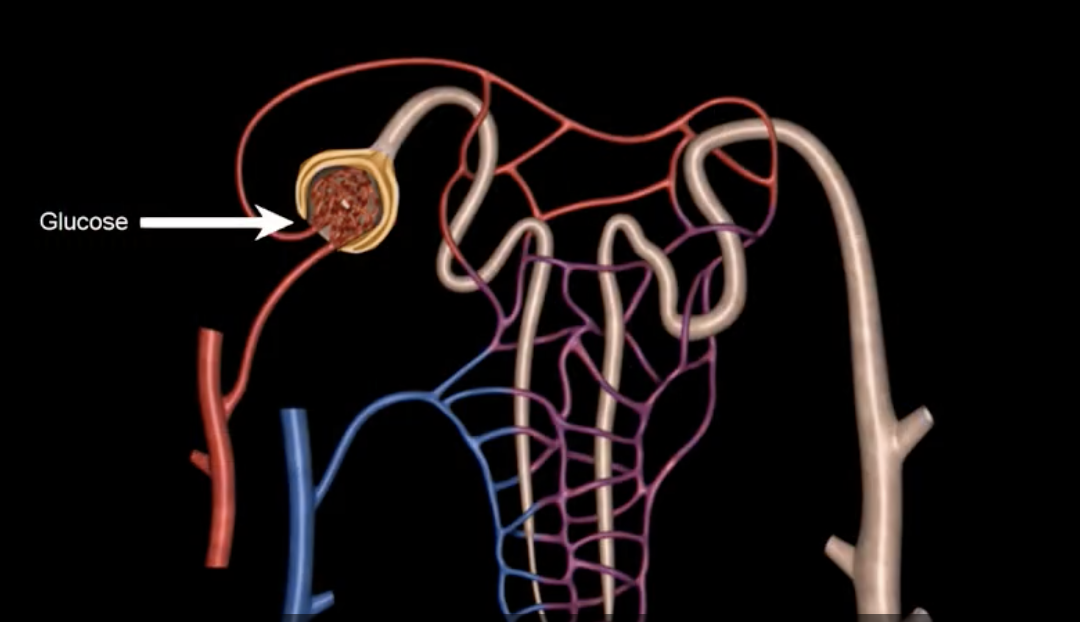
hilum
green
green: fibrous renal capsule
blue: perirenal fat
green and blue surrounding each kidney
orange: renal fascia
purple: pararenal fat
orange and purple
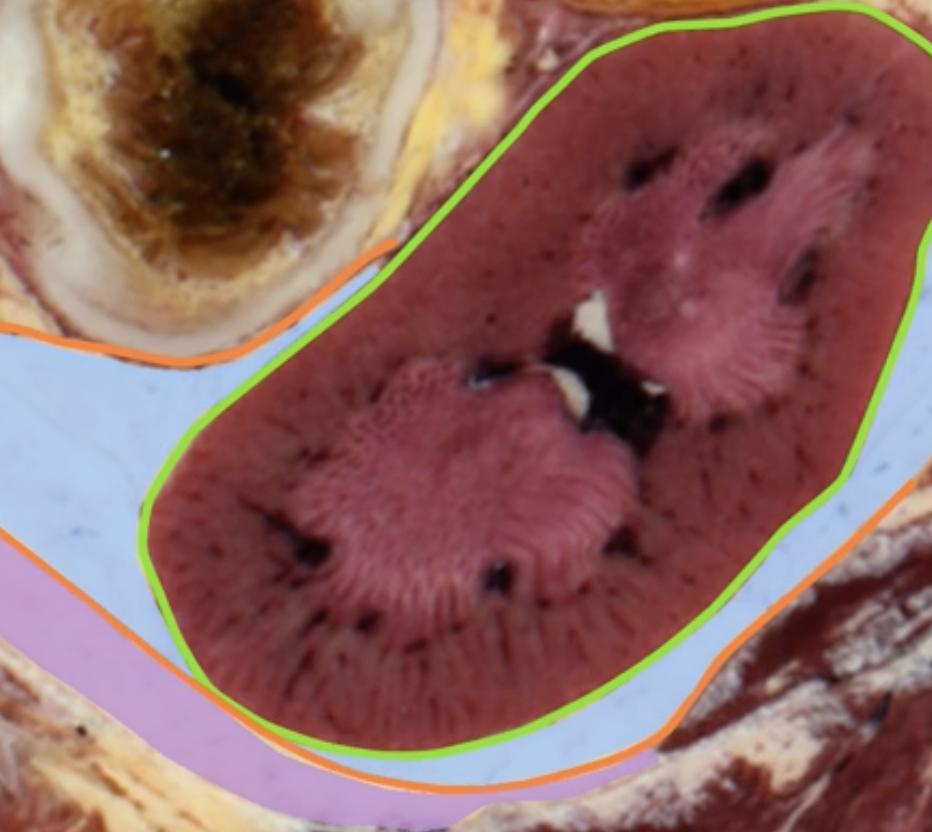

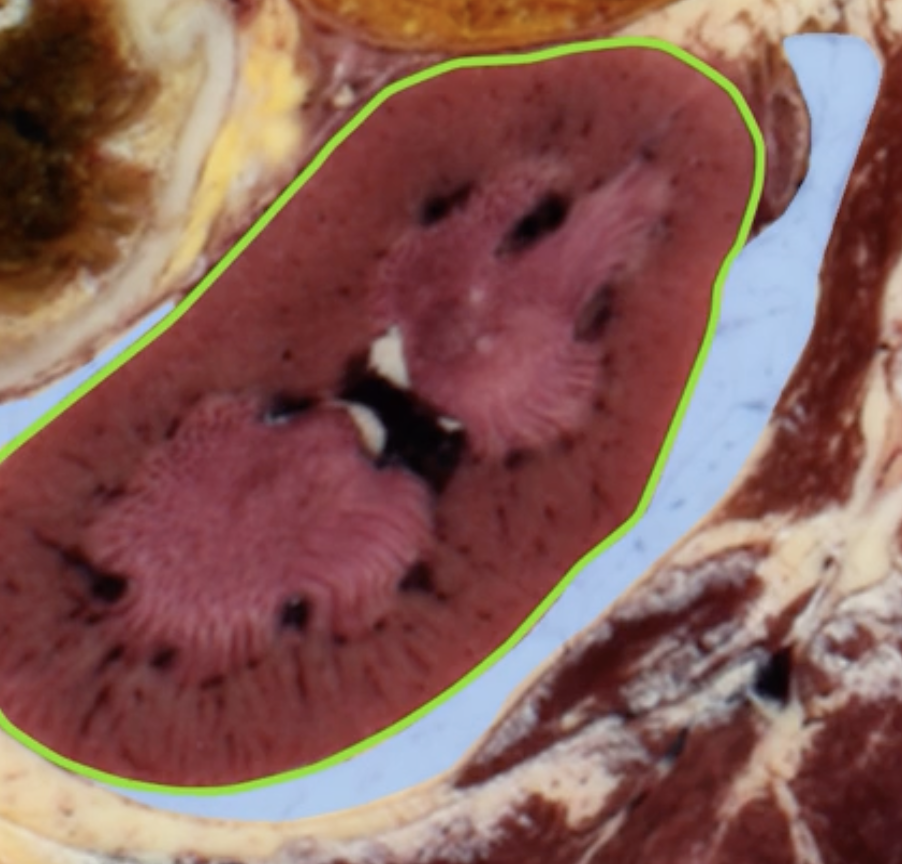
renal cortex
green
renal medulla
blue
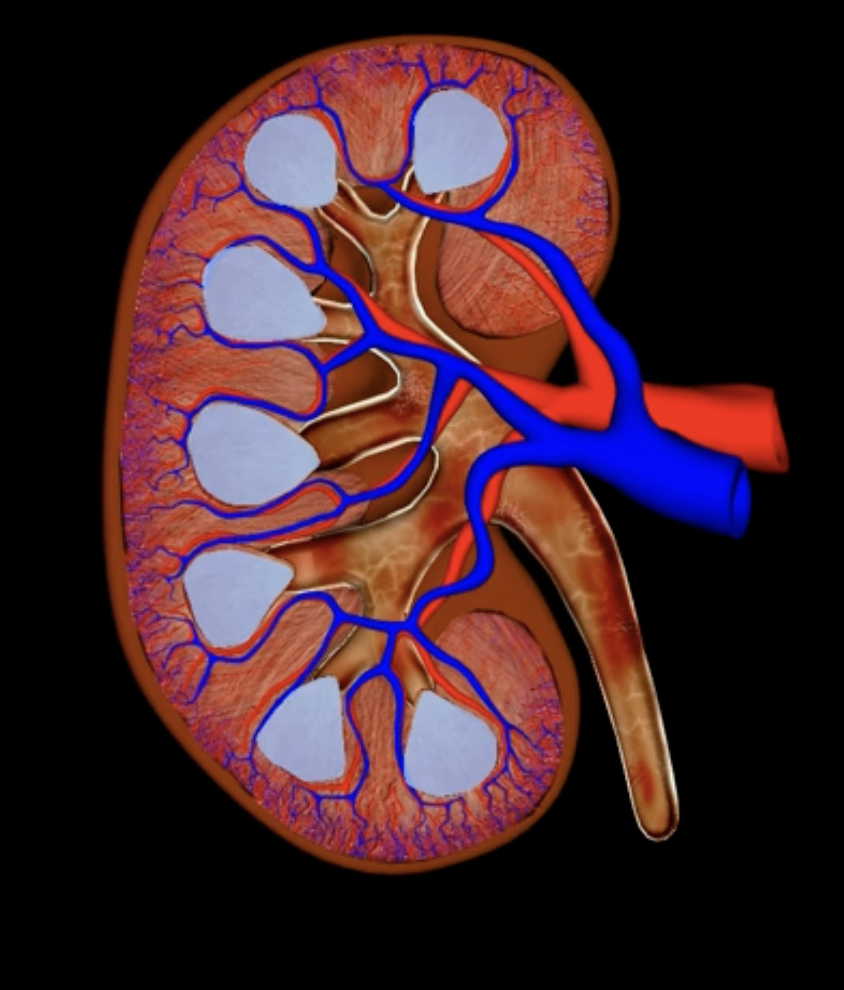
renal columns
yellow
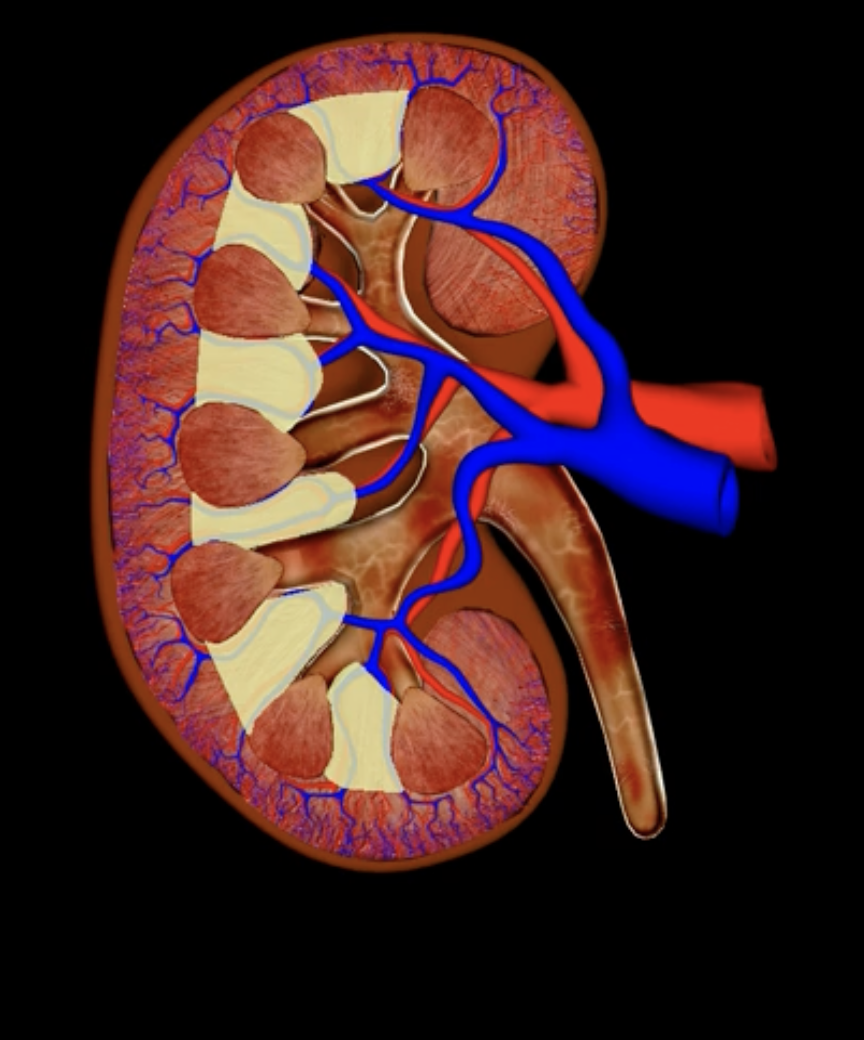
renal pyramids
purple
renal lobe
orange
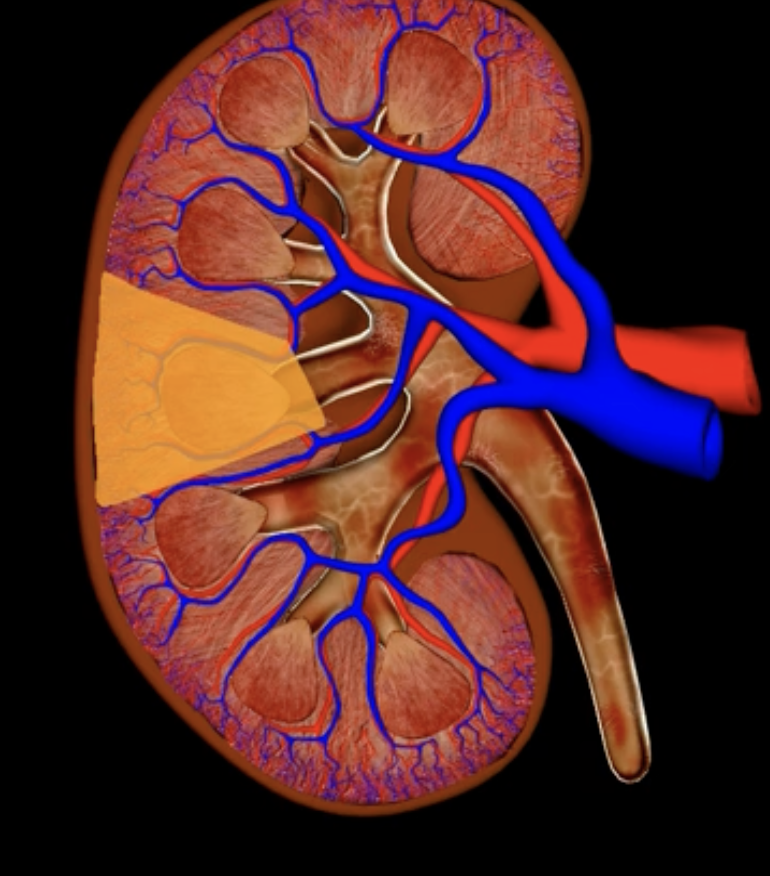
renal papilla
green
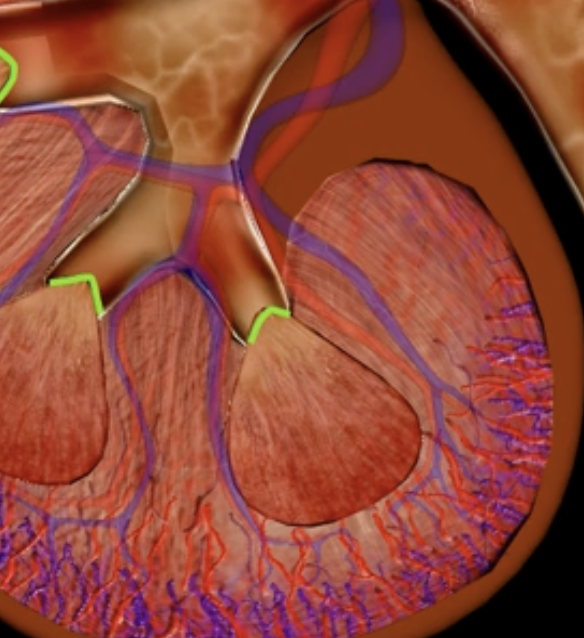
minor calyx
teal
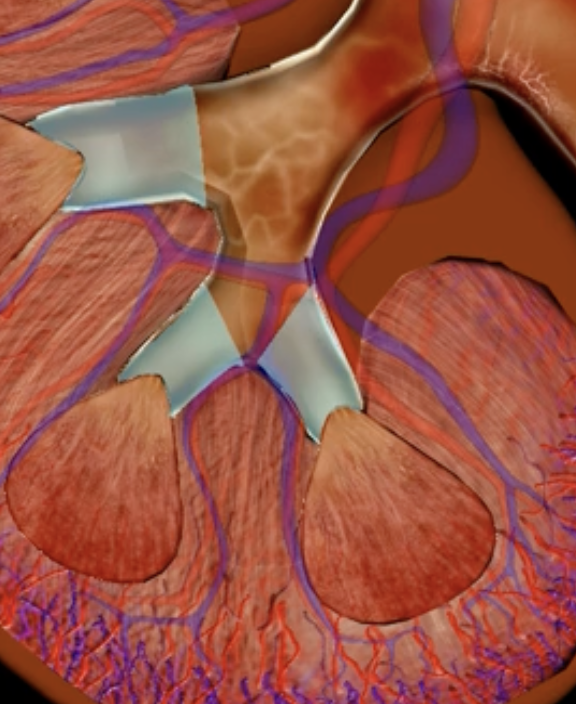
major calyces
blue
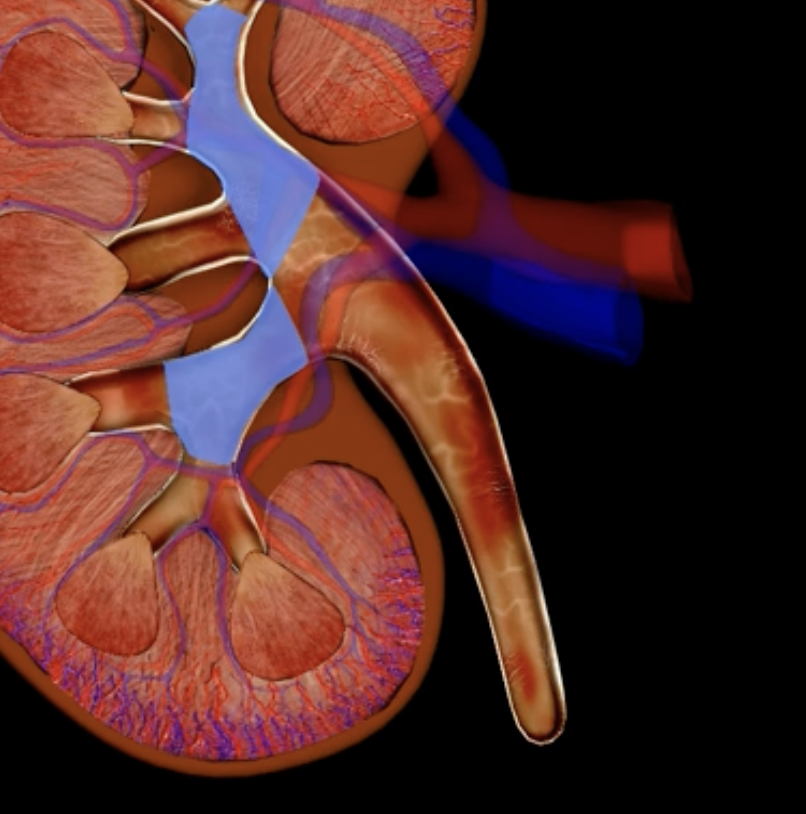
renal pelvis
teal
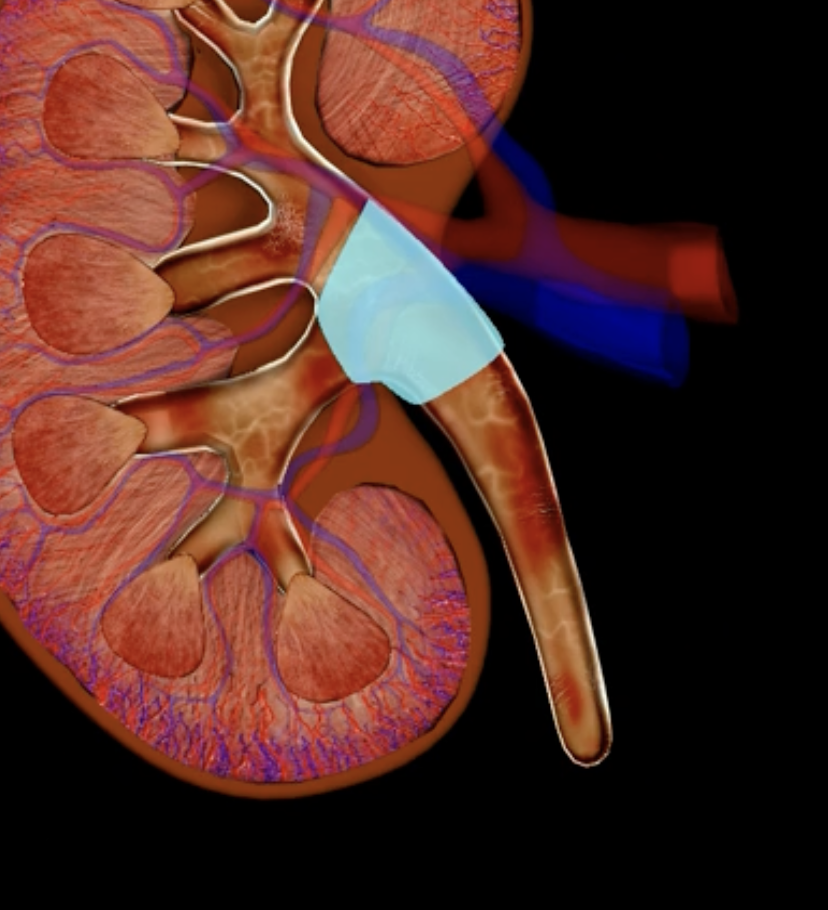
minor and major calyces
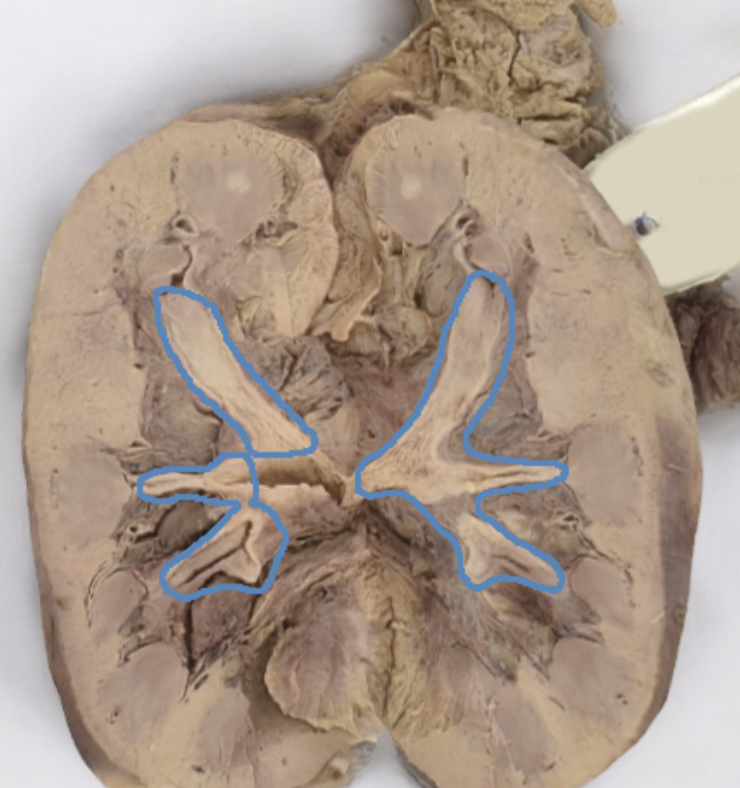
renal medulla
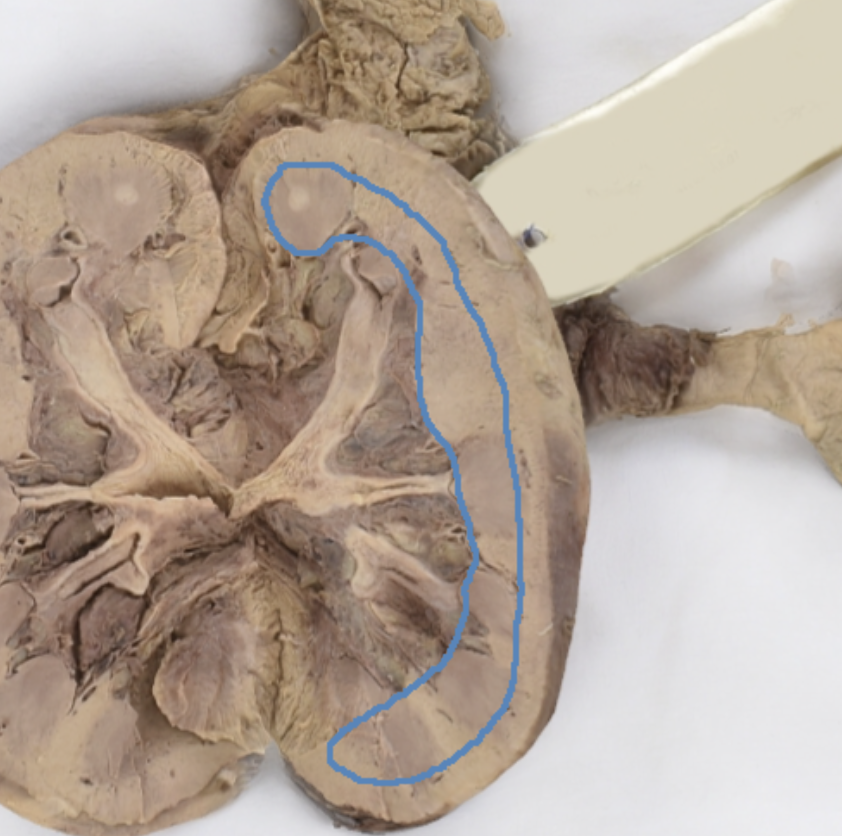
renal pyramids
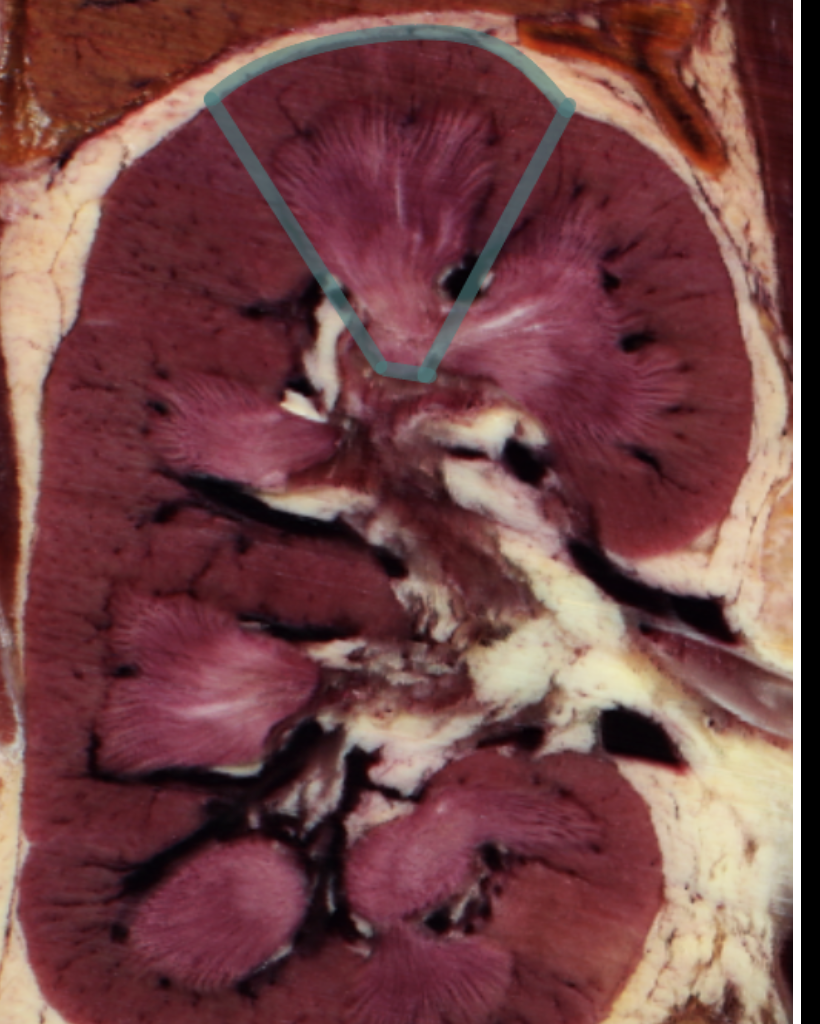
renal lobe
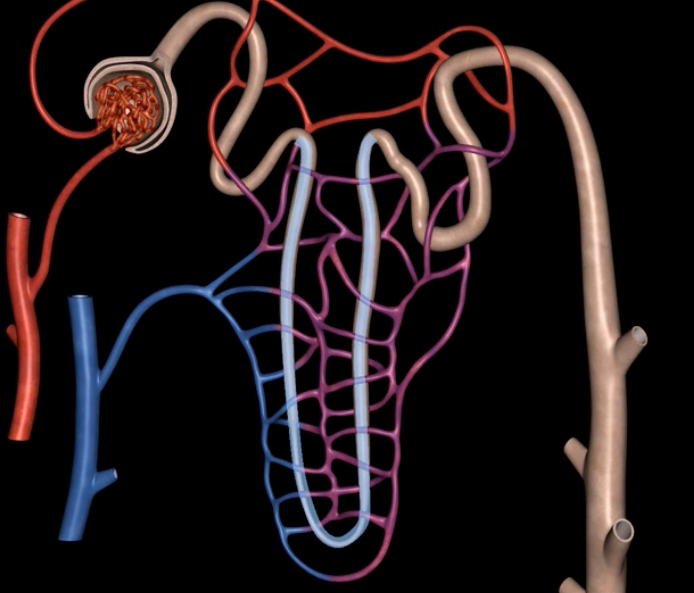
afferent arteriole
yellow
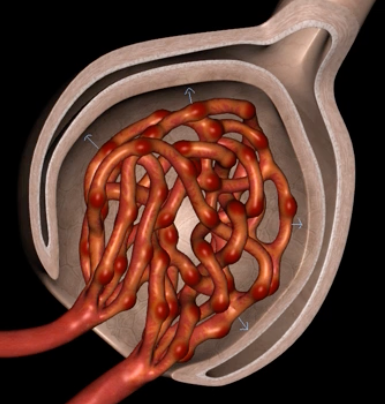
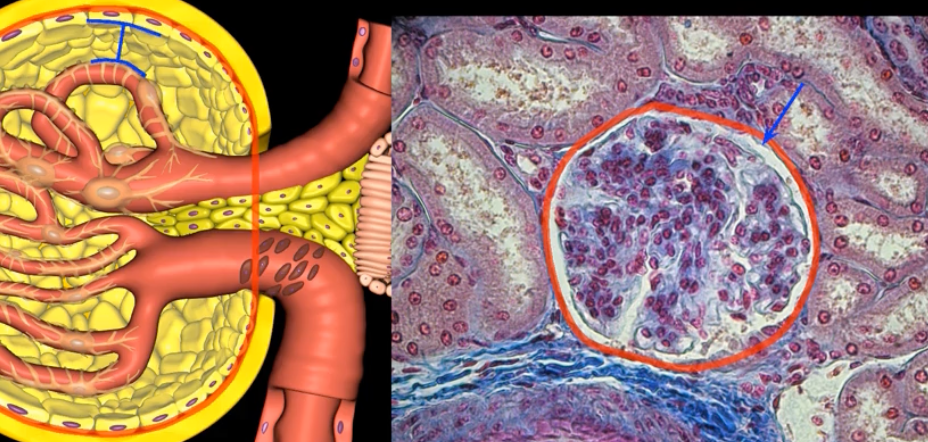
glomerulus
green
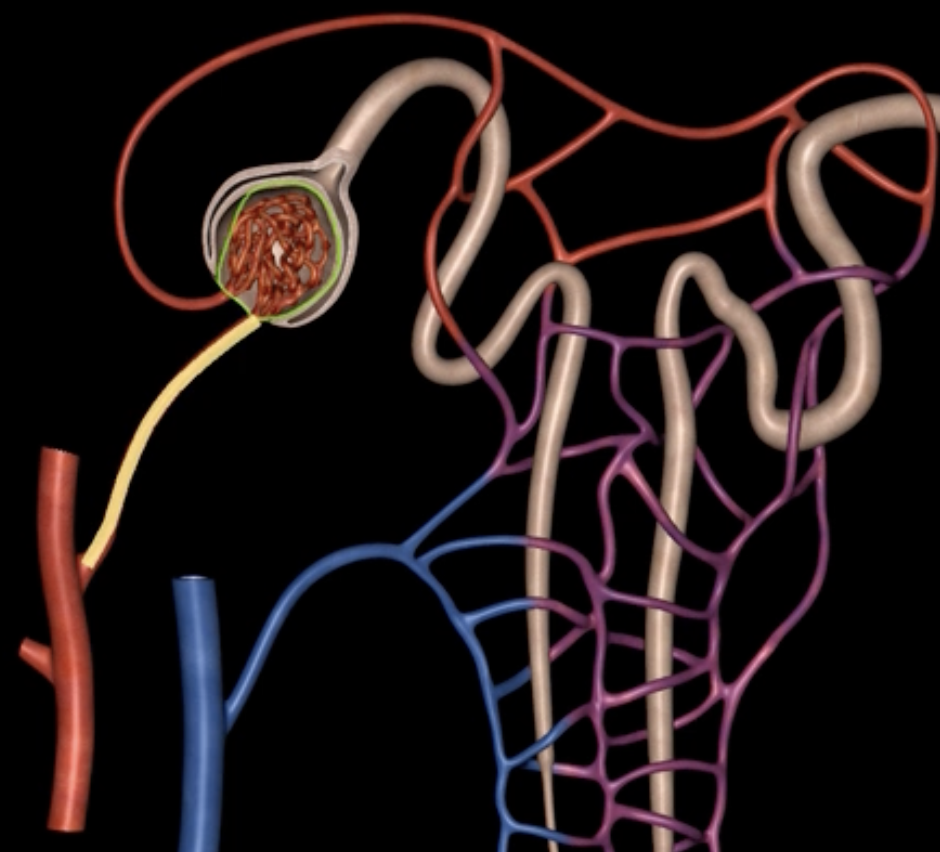
efferent arteriole
purple
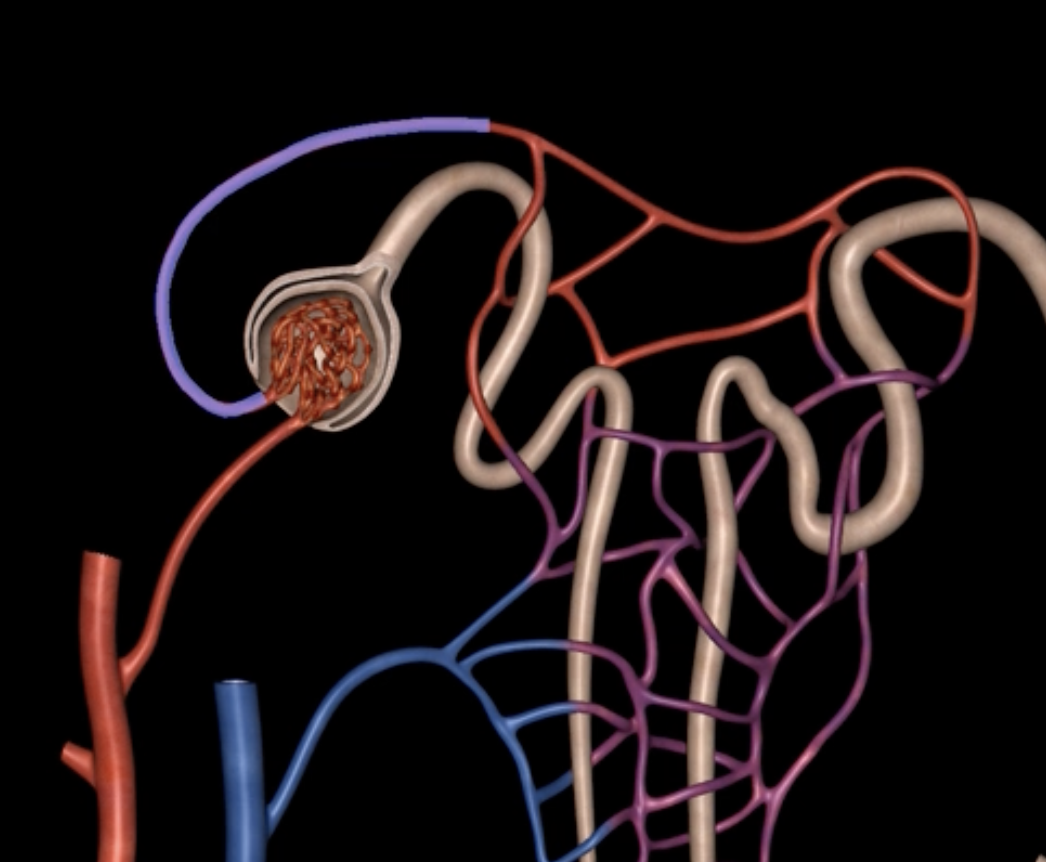
orange: peritubular capillaries
green: vasa recta
efferent arteriole give rise to orange and green
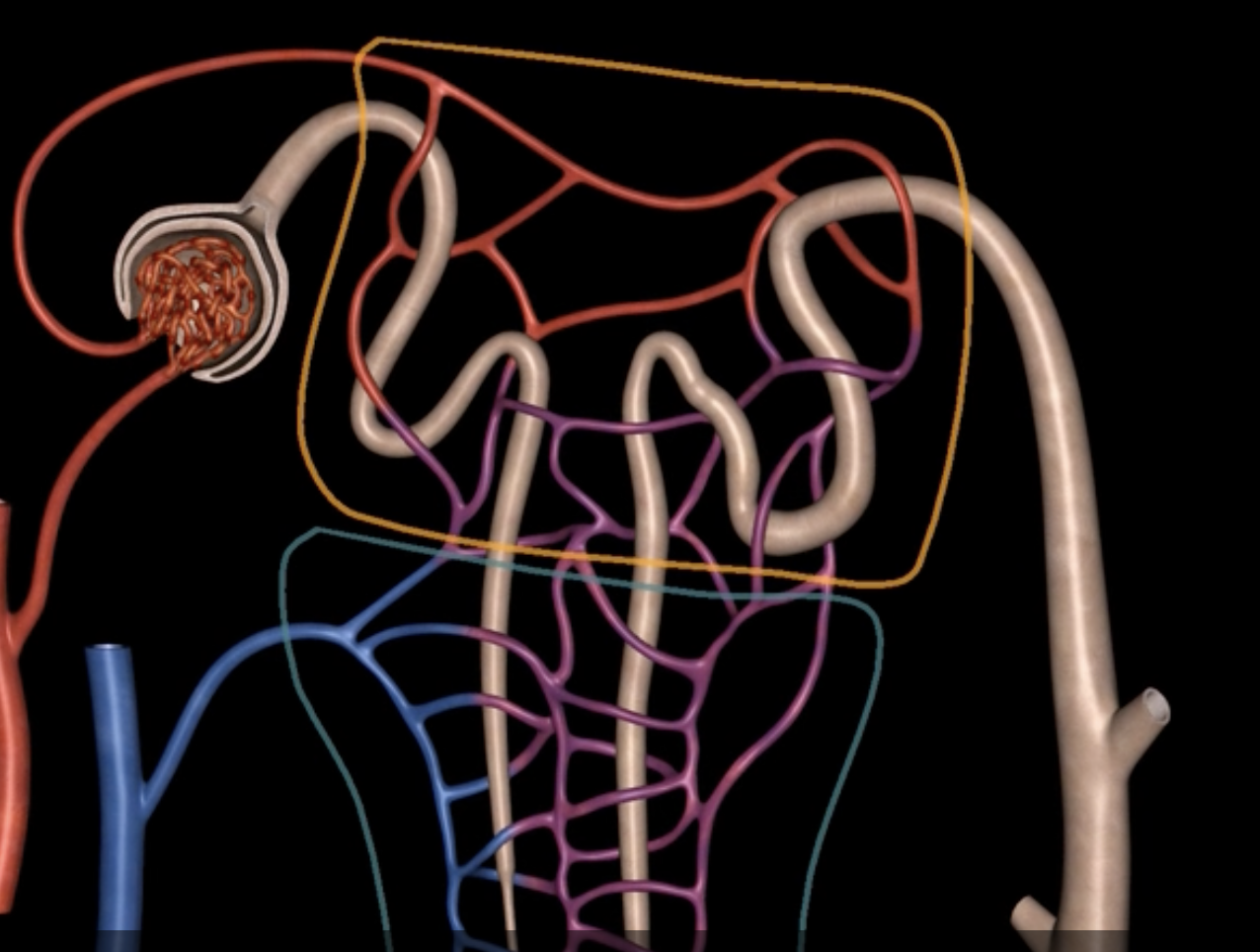
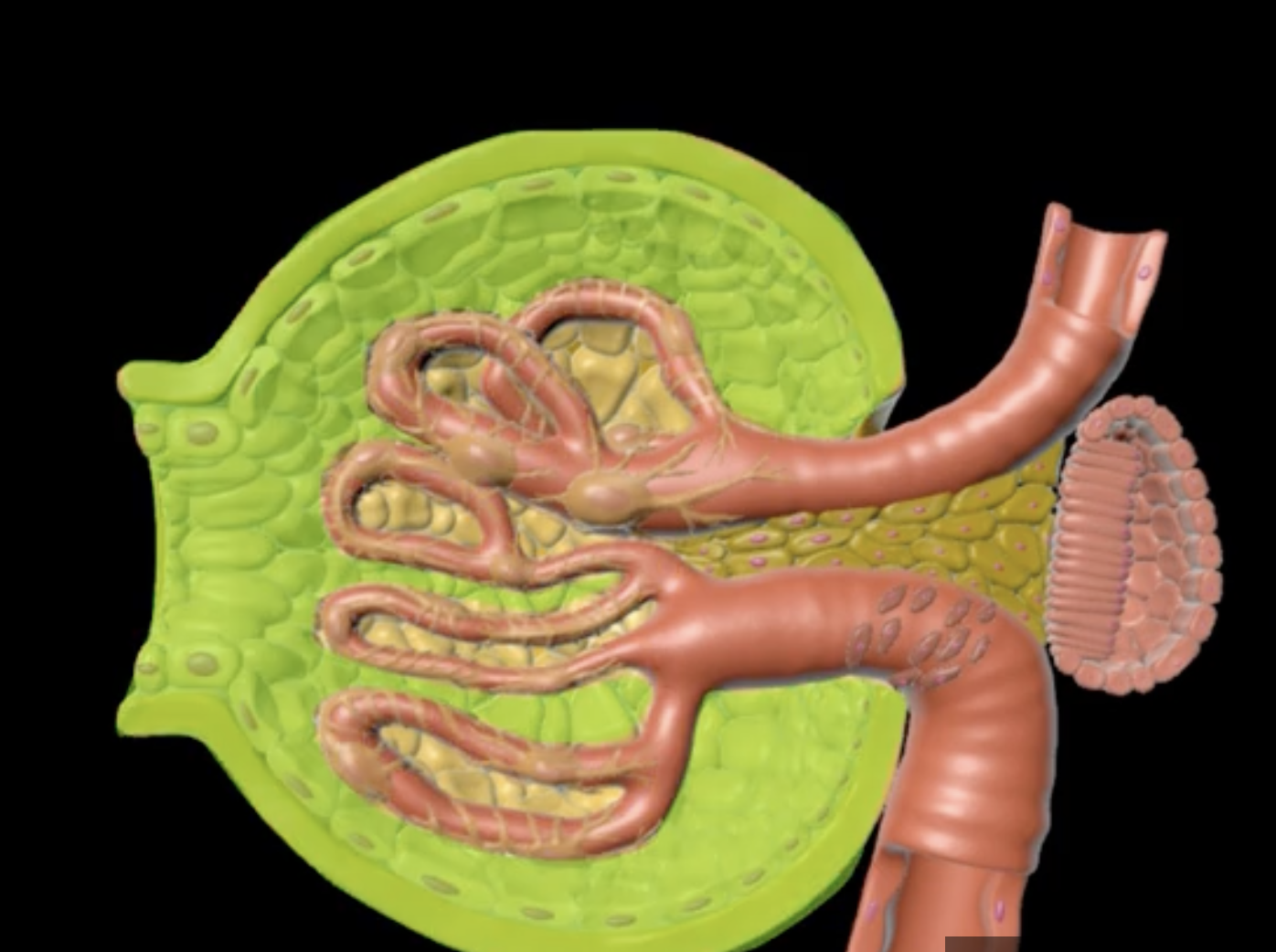
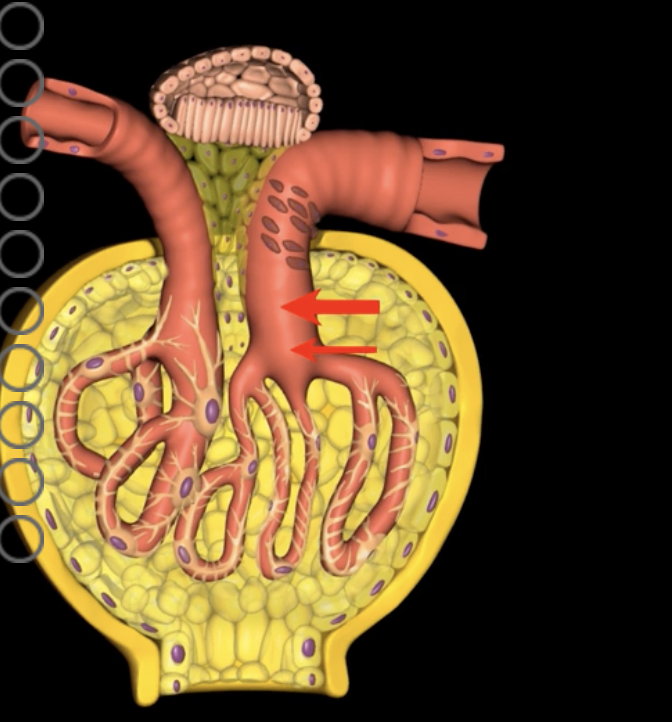
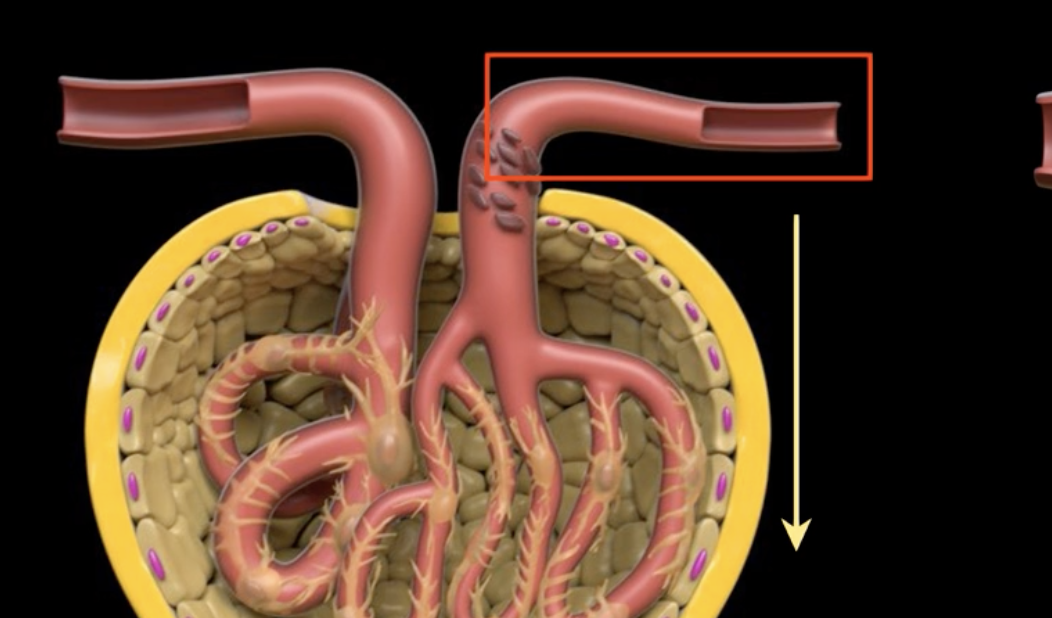
green: renal hilum
yellow: ureter
red: abdominal aorta
green yellow and red
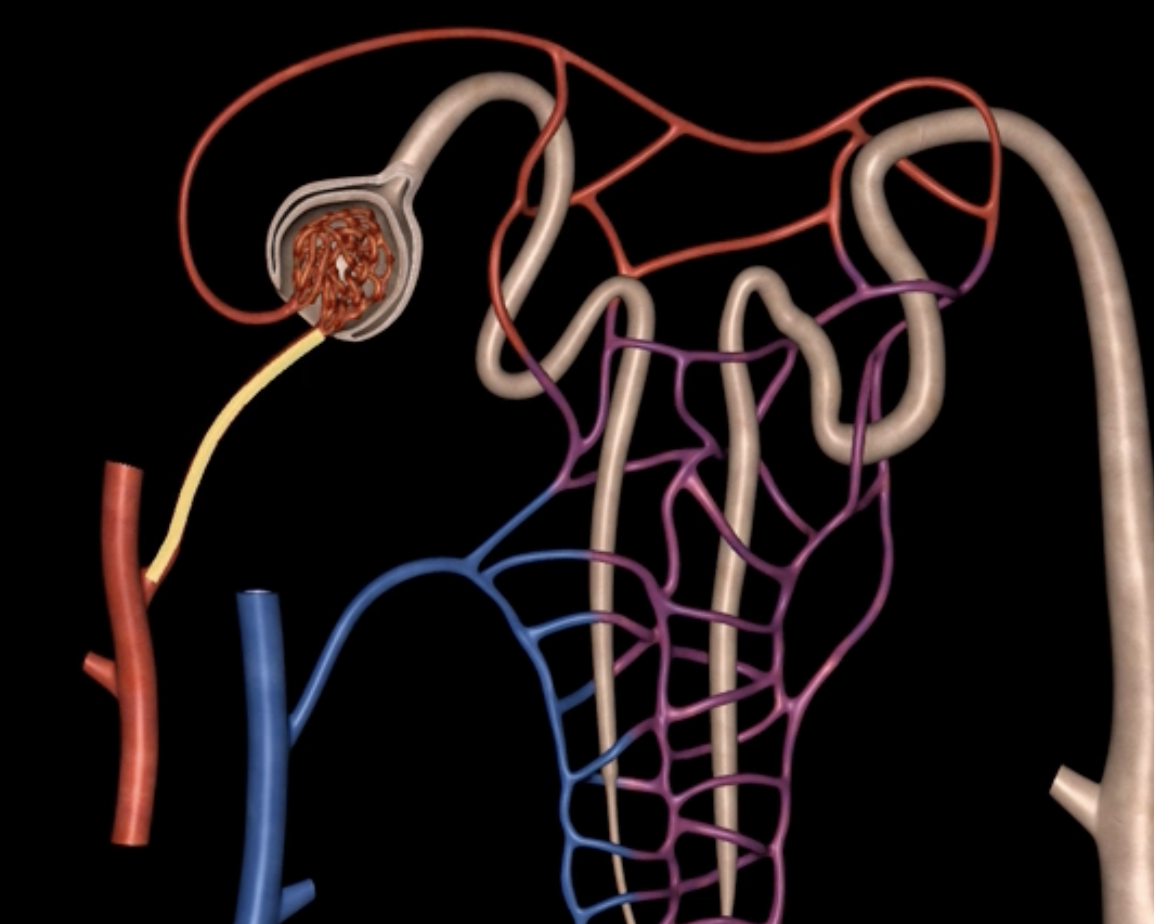
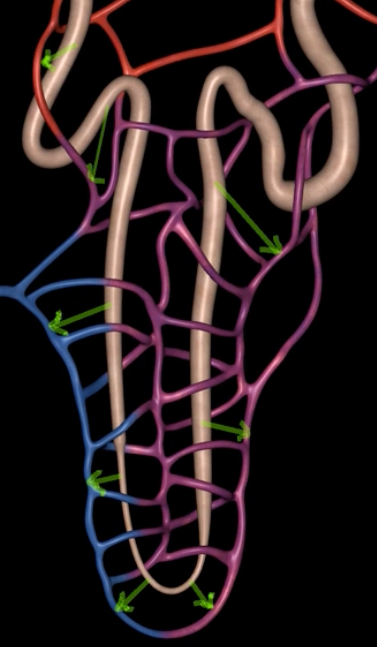
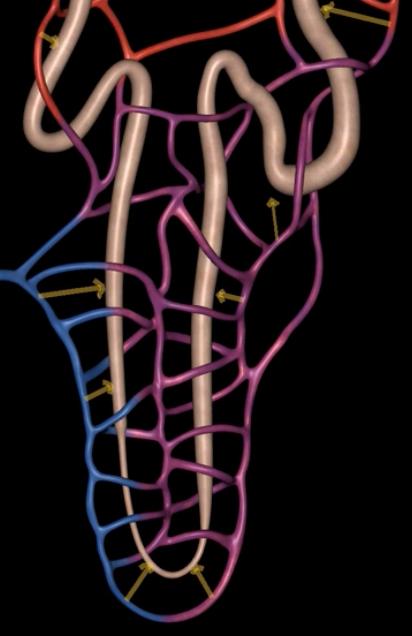
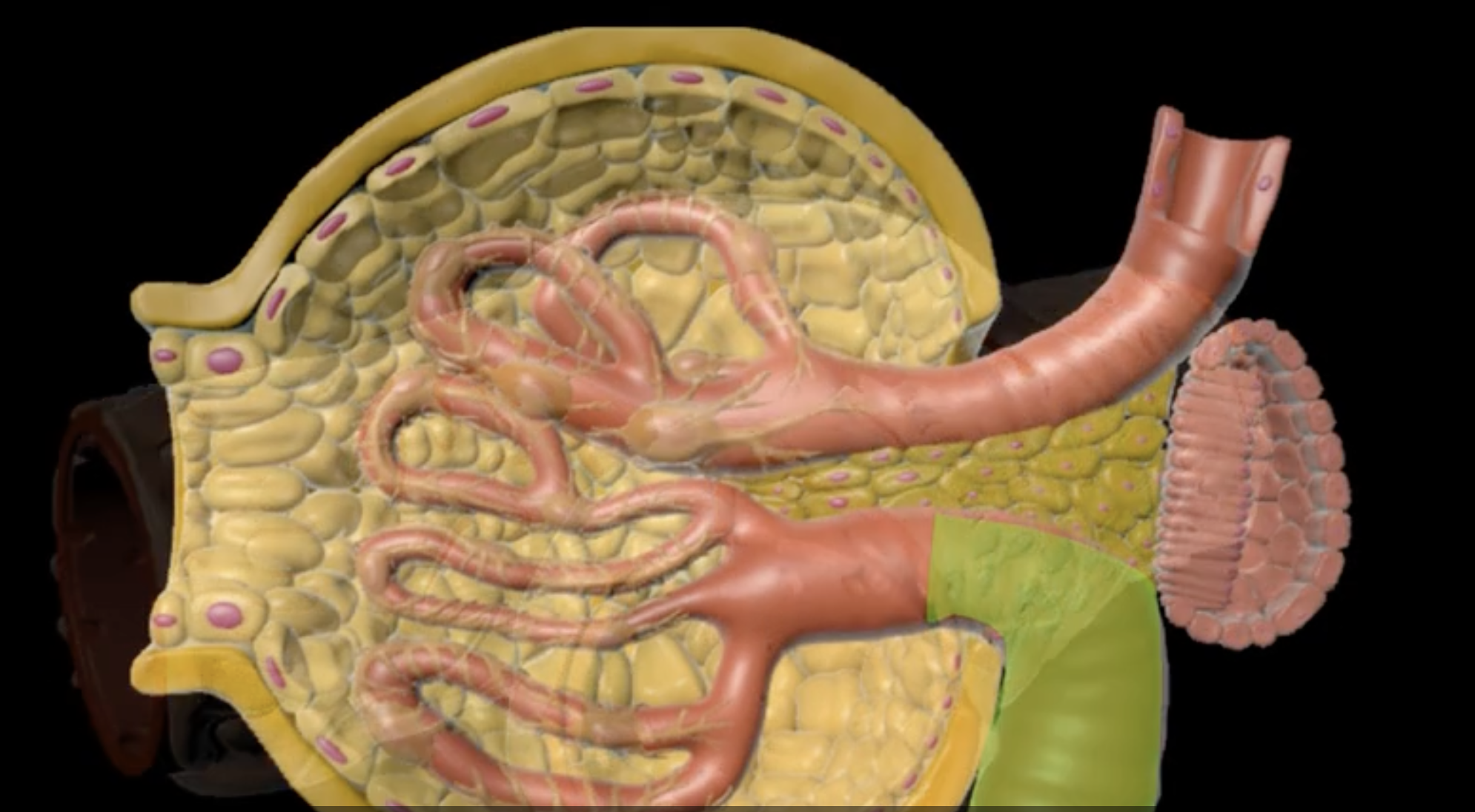
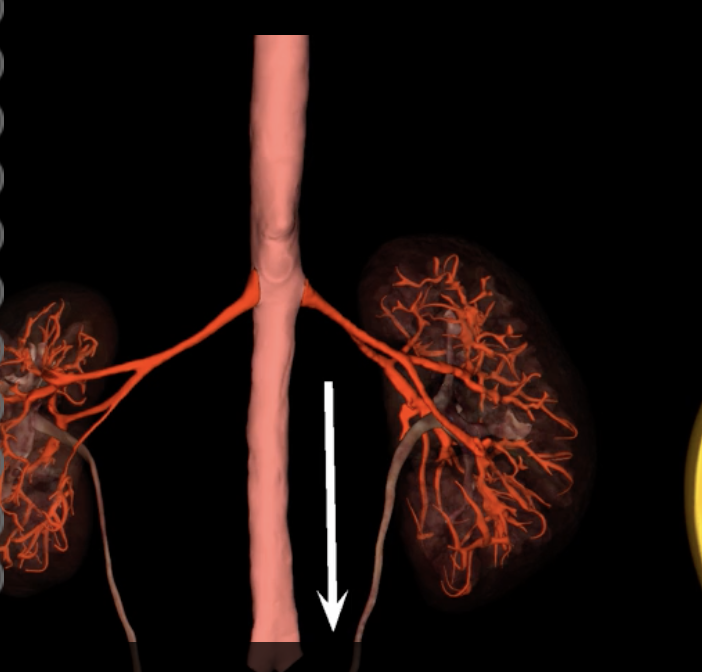
interlobular vein
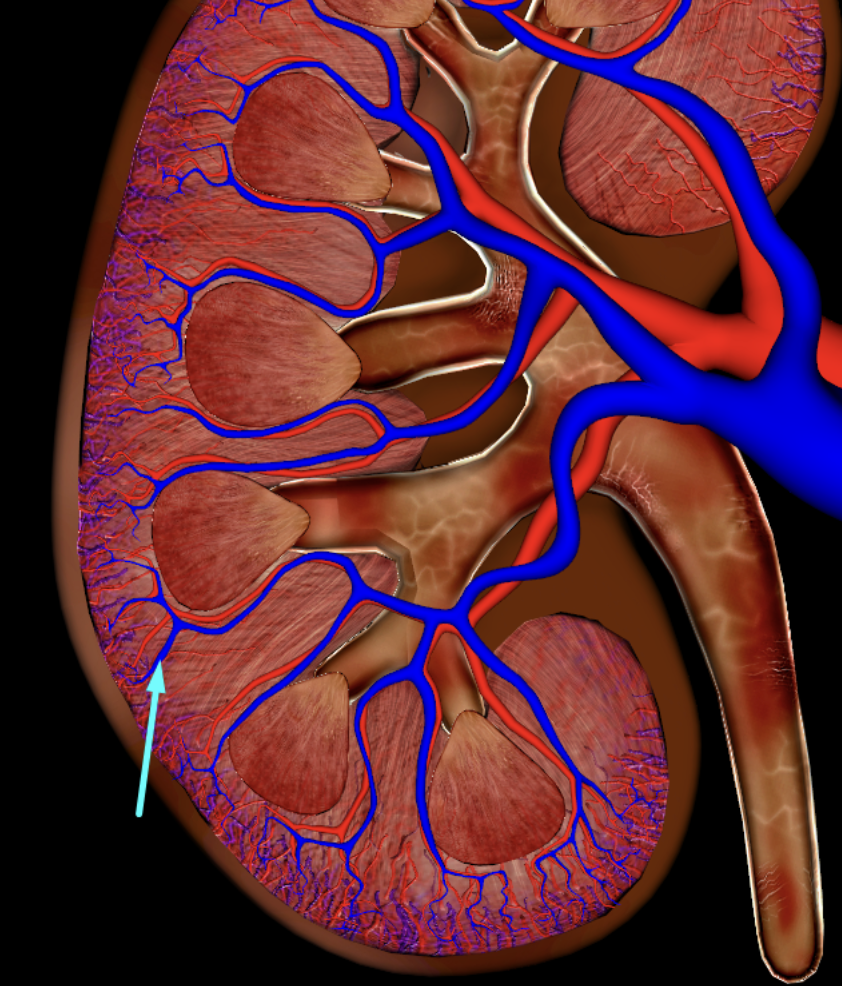
segmental artery
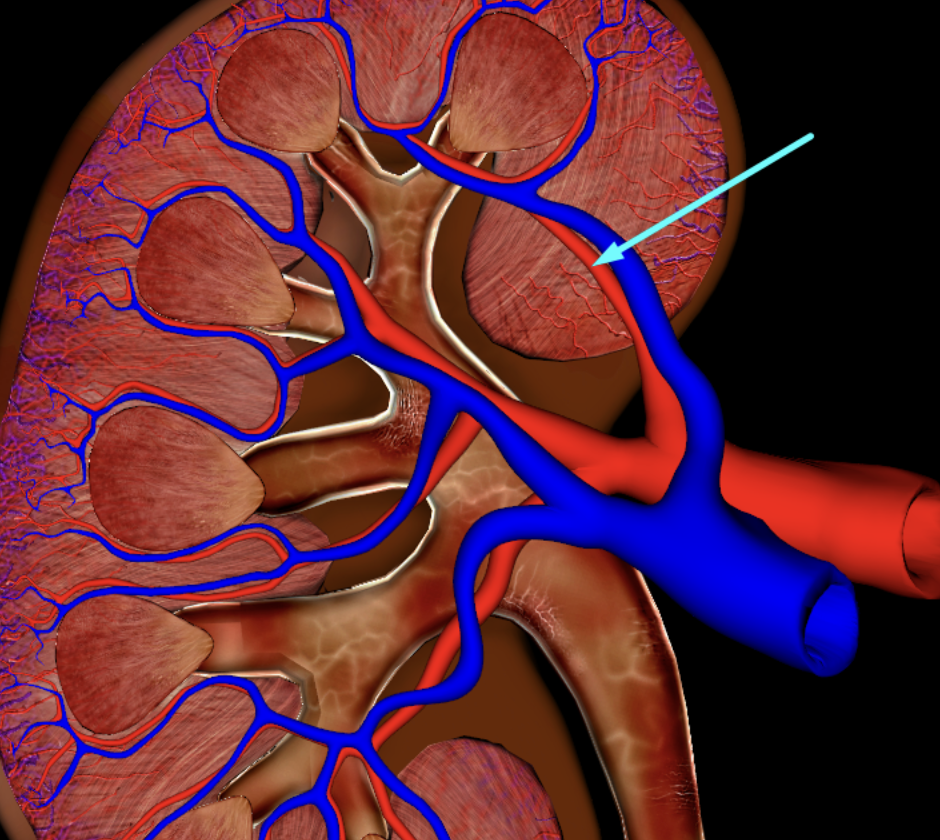
interlobar vein
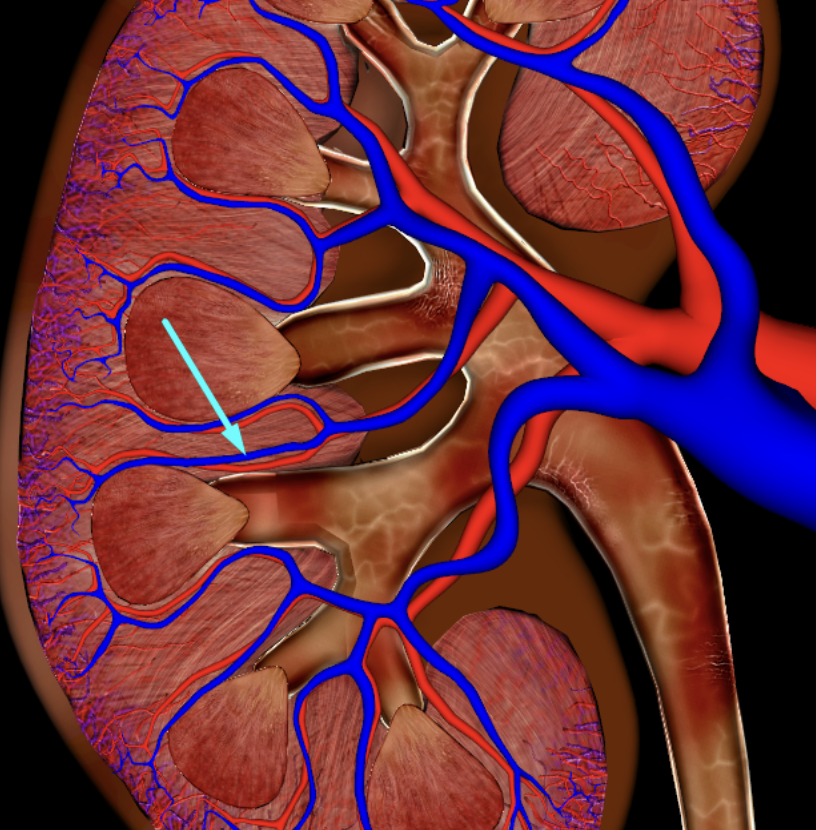
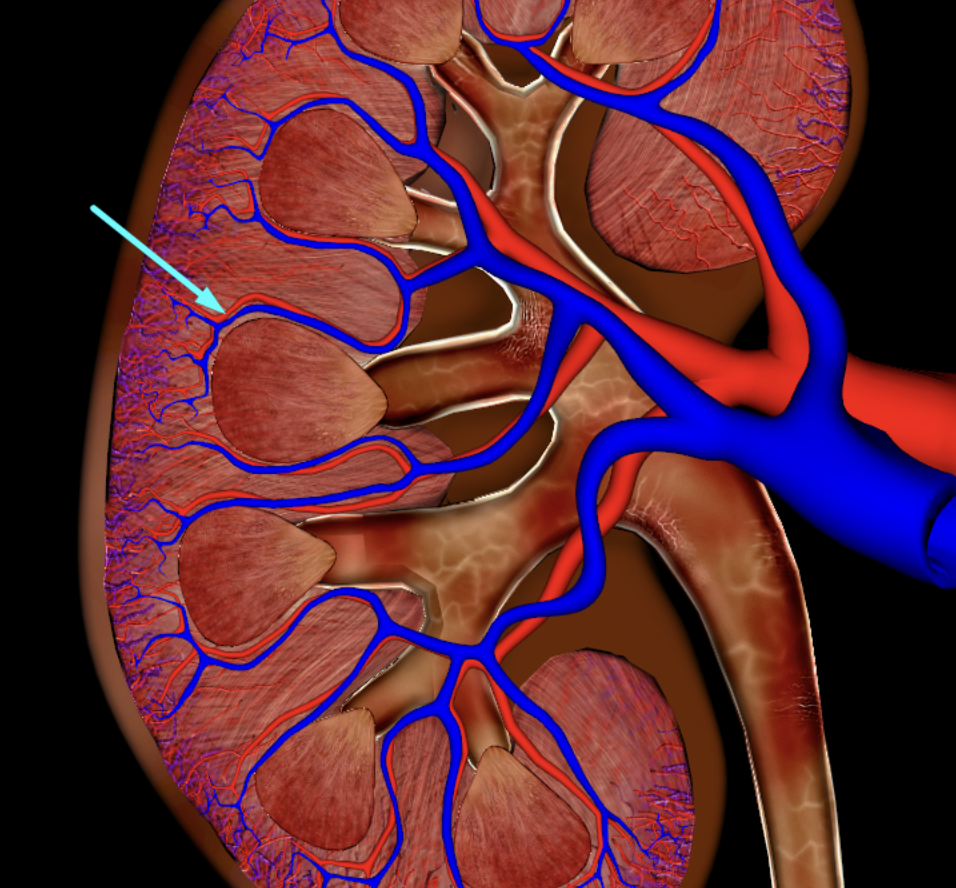
arcuate artery
renal plexus
the kidneys are innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system via
sympathetic nerve fibers from T10-T12/ splanchnic nerves
role in blood pressure regulation
yellow
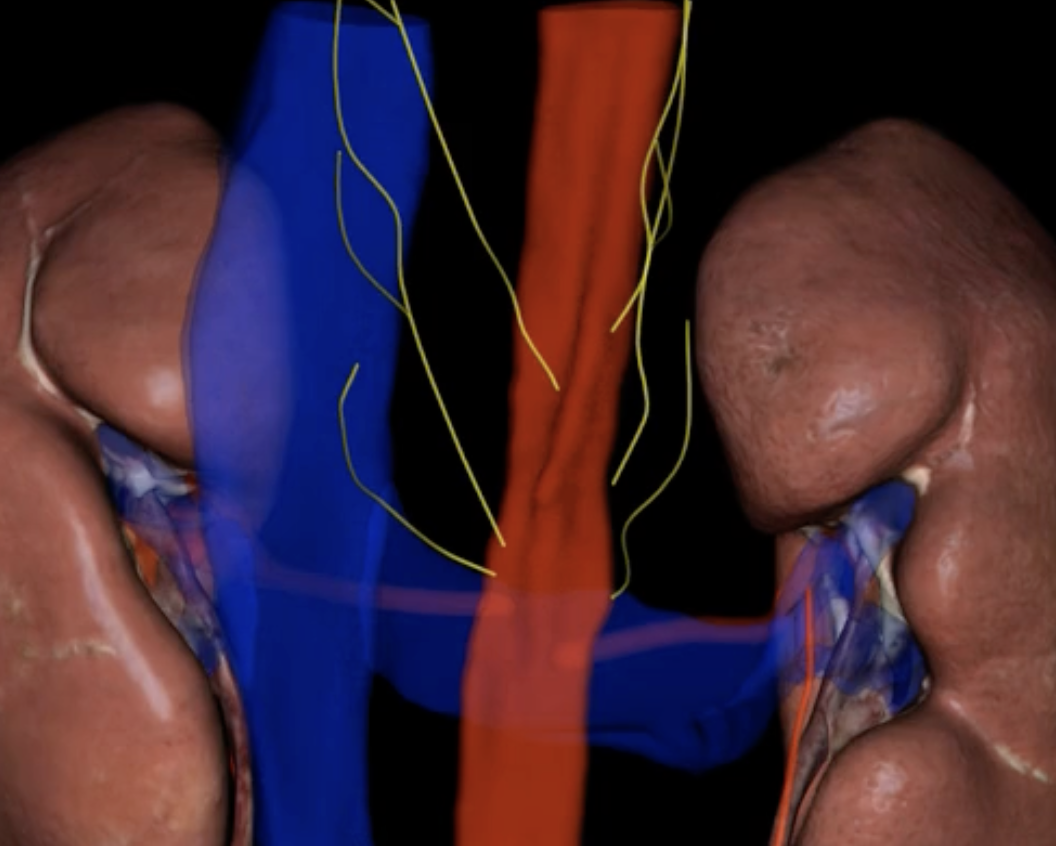
Vagus nerve
the parasympathetic innervation occurs thru the
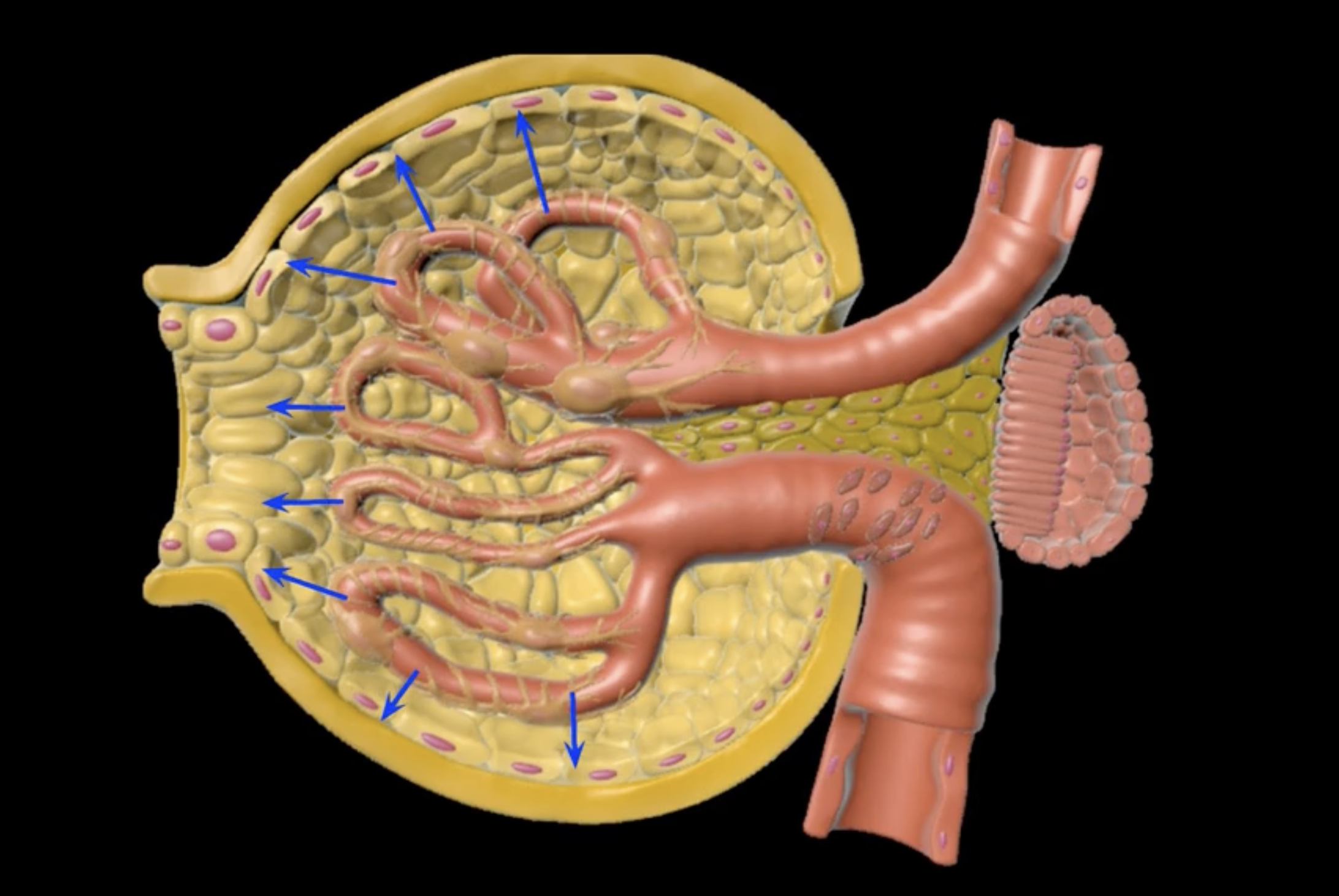
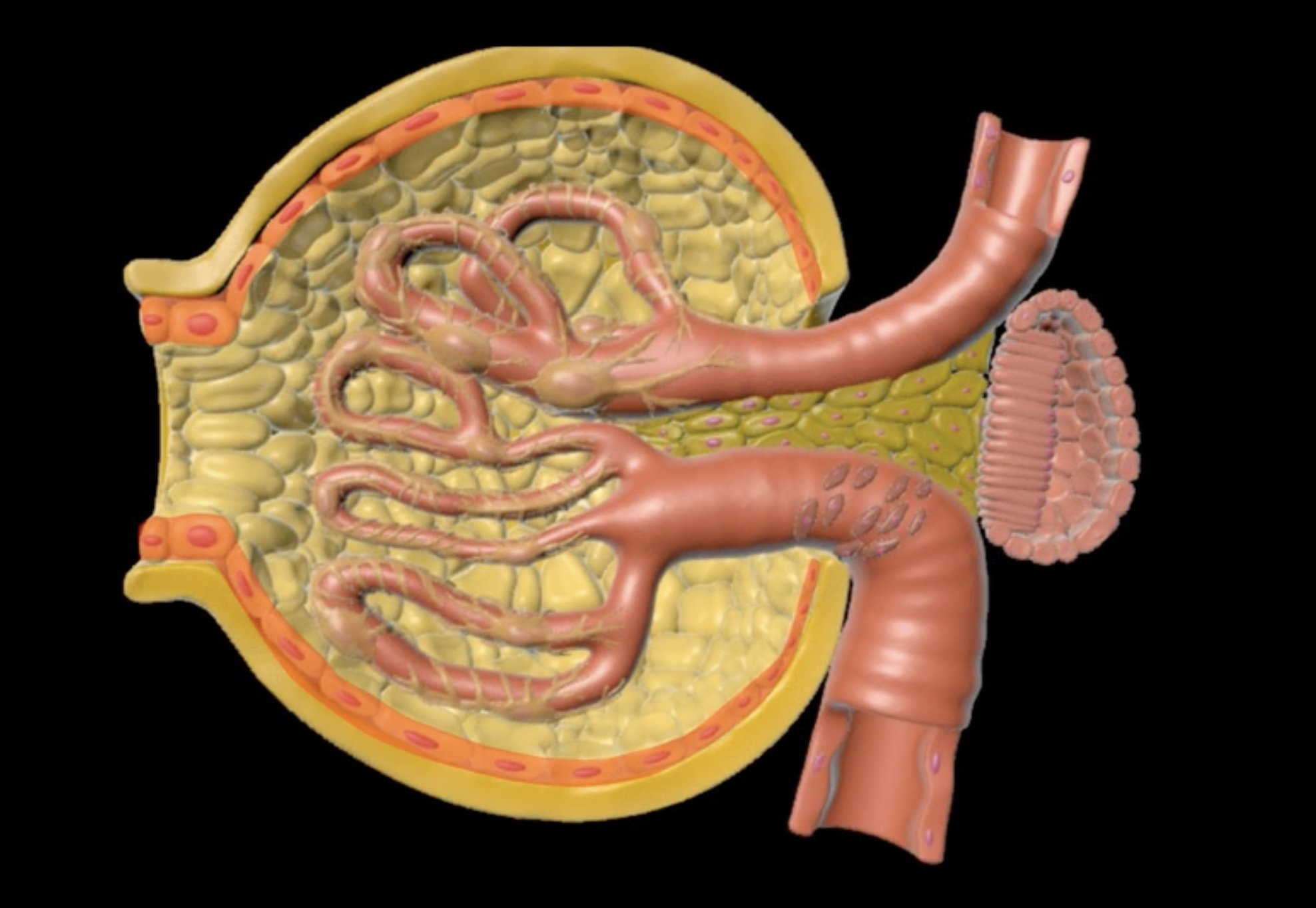
yellow: cortical nephron
blue: juxtamedullary nephron
yellow:
blue:
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
3 processes of urine formation
golmerular filtration
pressure driven movement of fluid and small solutes out of blood to form filtrate (ions, glucose, amino acids, nitrogenous wastes)
tubular reabsorption
process by which substances are moved via diffusion or active transport from filtrate back into blood
tubular secretion
active transport of solutes from the blood into the tubular fluid. allows for excretion of substances that were not initially apart of the filtrate
urine= filtration - reabsorption + secretion
urine= [ ] - [ ] + [ ]
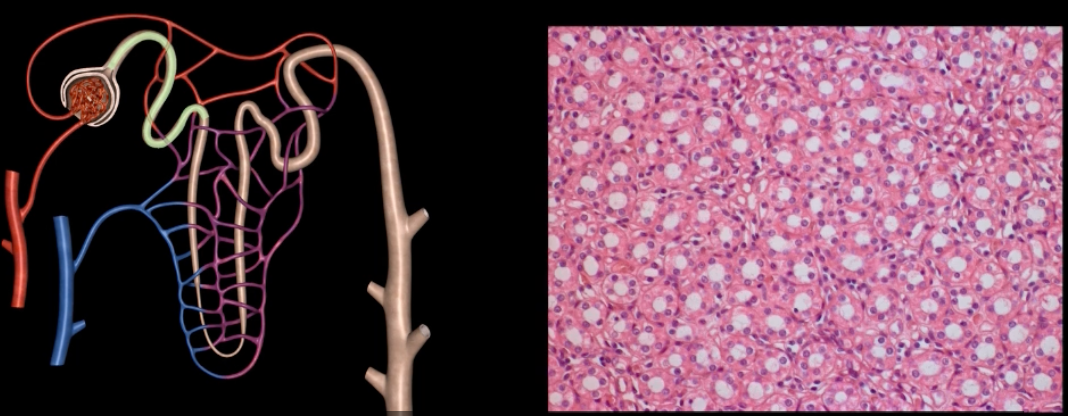
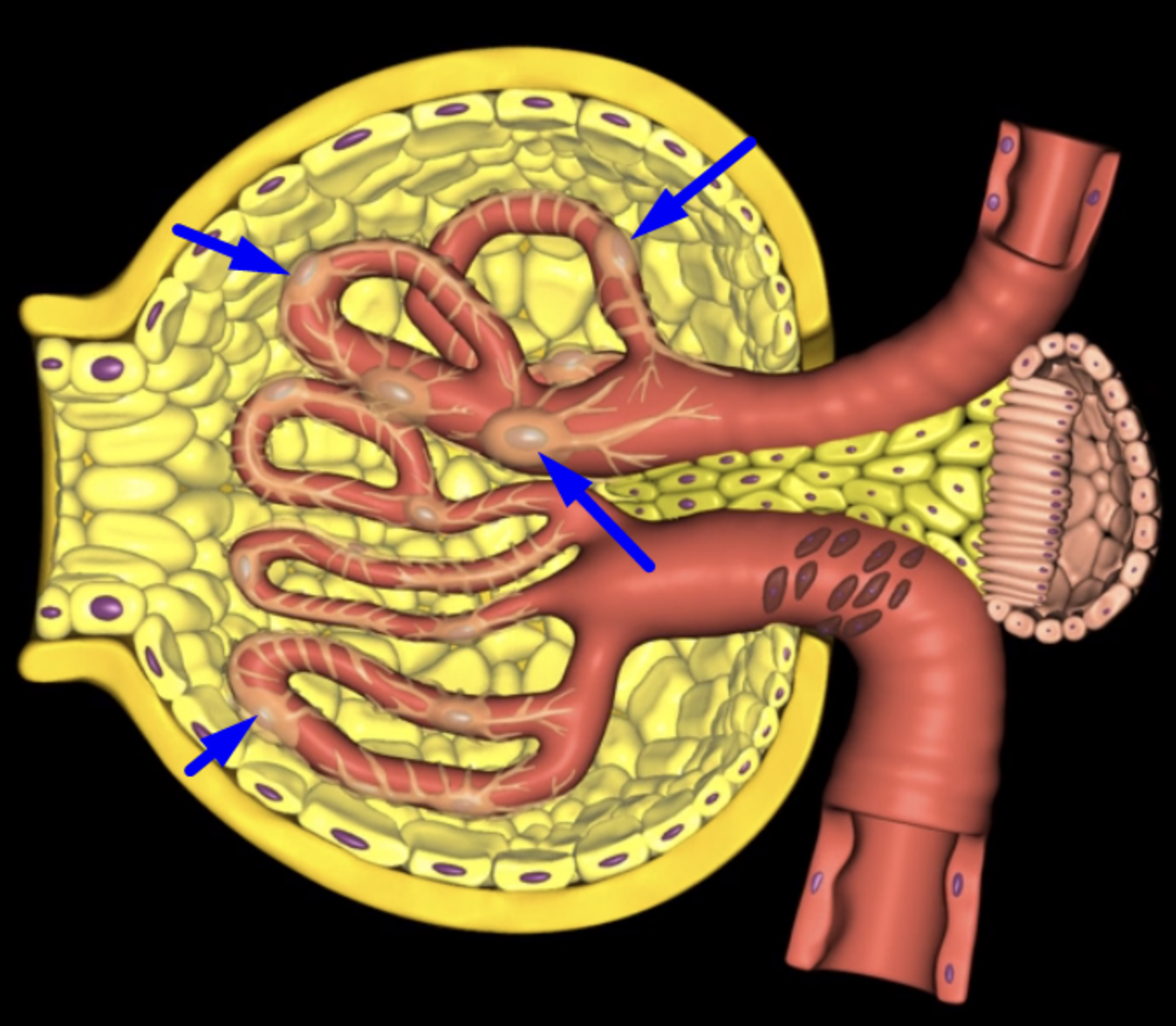
nephron
functional unit of the kidney
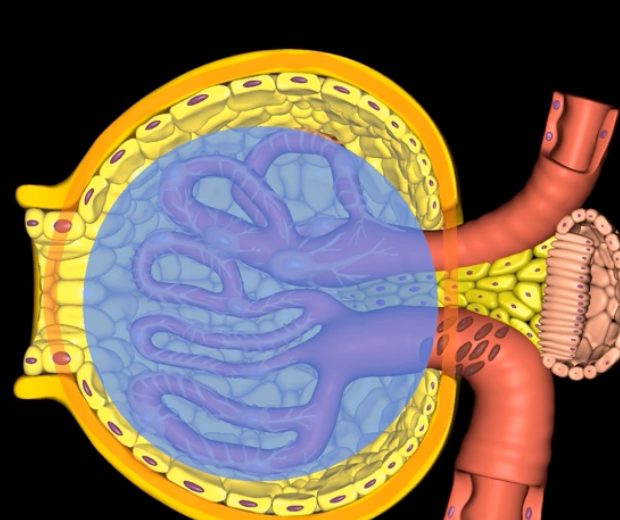
green: renal corpuscle
purple: renal tubule
green:
purple:
blue: glomerulus
orange: Bowman’s capsule
blue:
orange:
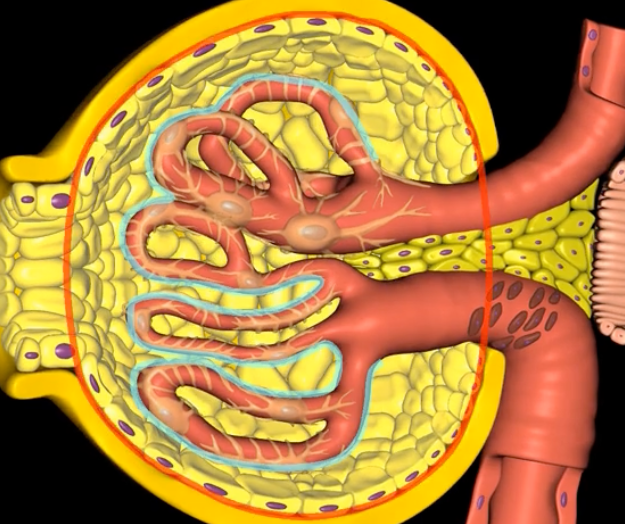
blue: visceral layer
red: parietal layer
blue:
red:
simple squamous
the parietal layer consists of [ ] epithelium that surrounds the glomerulus
![<p>the parietal layer consists of [ ] epithelium that surrounds the glomerulus </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/20330763-6a93-400d-997e-309761252254.png)
capsular space
pink: podocyte
purple: pedicels
pink:
purple:
filtration slit
filtration membrane
fenestrated capillaries + podocytes = [ ]
0.8-2 L
avg urine output per day
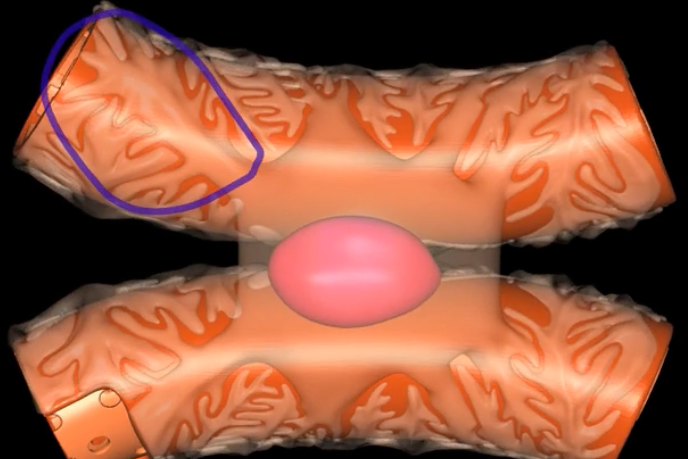
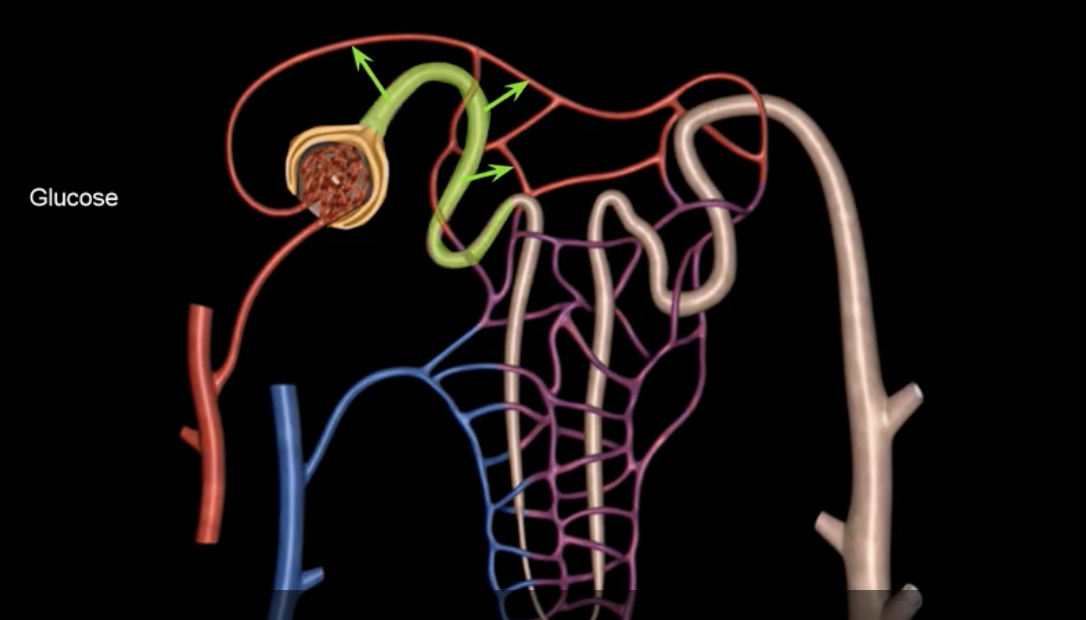
name: proximal convoluted tubule
function: tubular reabsorption
lining: simple cuboidal epithelium w/ microvilli for increased surface area
name:
function:
lining:
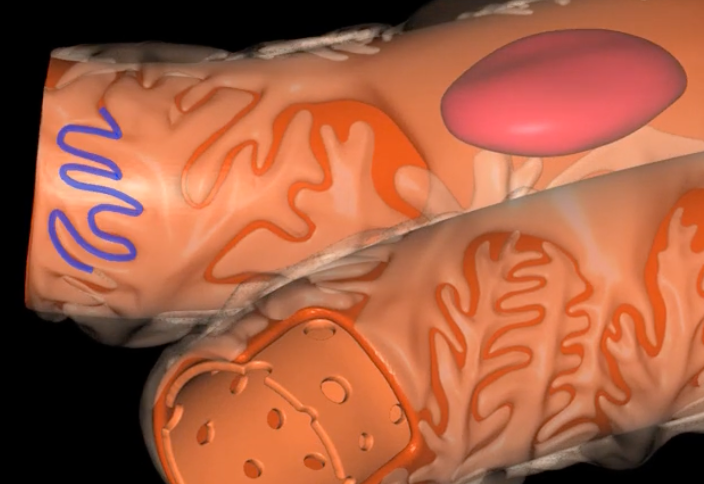
loop of Henle
red: descending limb
blue: ascending limb
red:
blue:
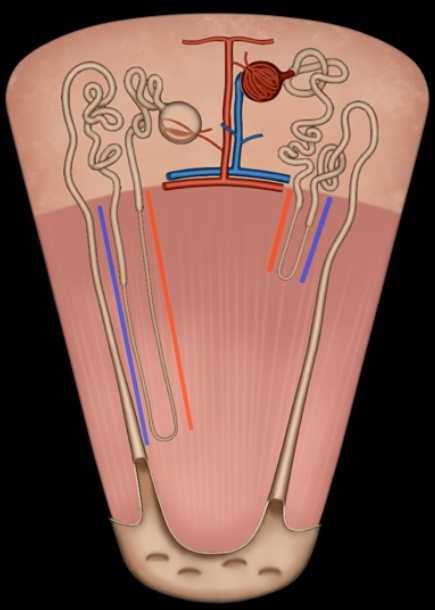
reabsorb ions
blue’s function
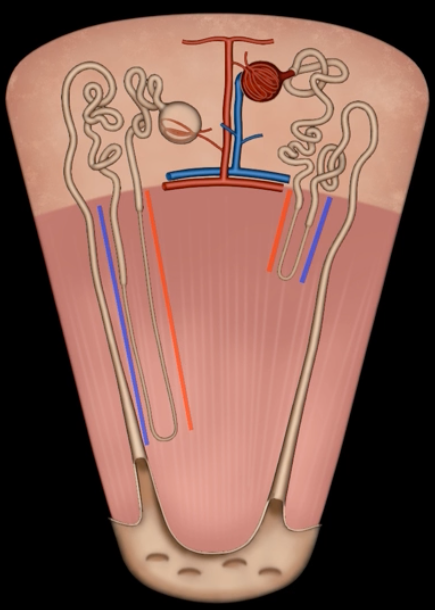
reabsorb water
red’s function
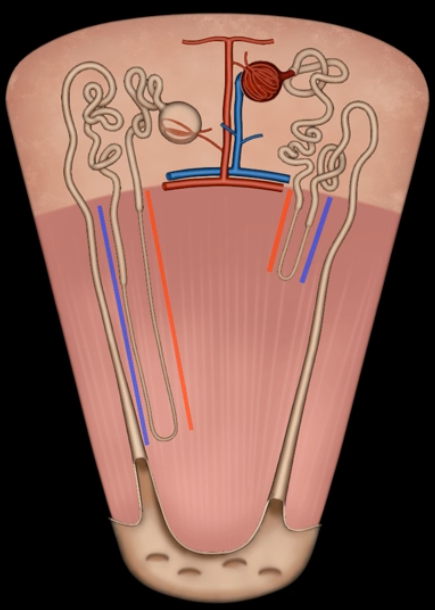
green: thick segment lined with simple cuboidal
purple: thin segment lined with simple squamous
green:
purple:
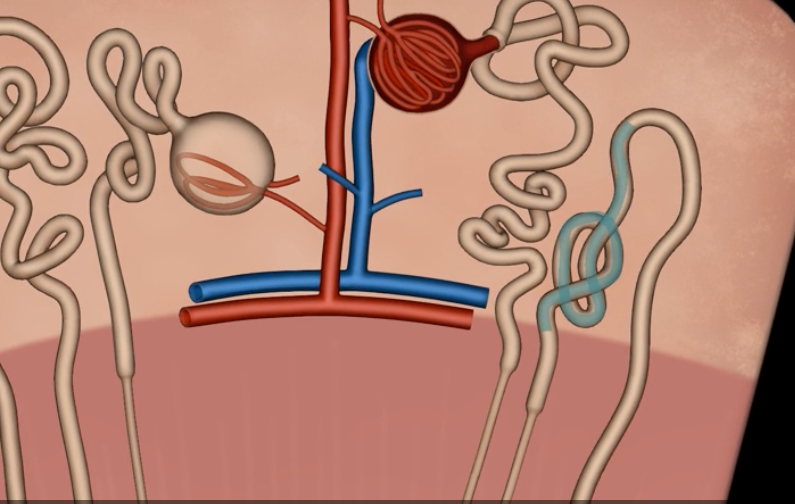
name: distal convoluted tubule
function: secretion of H+ and K+ ions
lining: simple cuboidal, sparse microvilli
name:
function:
lining:
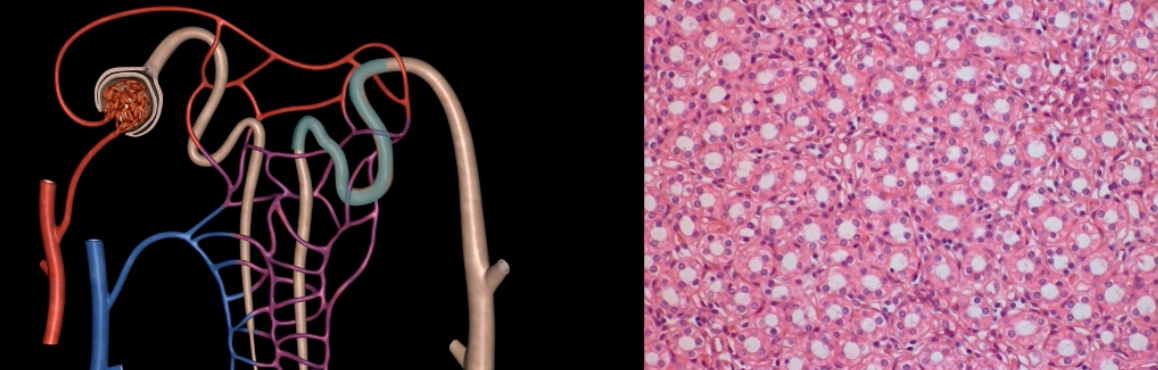
ADH stimulates DCT to reabsorb additional water
increased blood solute concentration leads to what in the DCT
aldosterone stimulates the DCT to have additional reabsorption of Na+ and secretion of K+
decreased blood volume or increase in blood potassium leads to what in the DCT
PTH stimulates the DCT to reabsorb Ca2+ resulting in less Ca2+ excretion
decreased blood calcium levels leads to what in the DCT
name: collecting duct
function: last structure to modify fluid, but only under the influence of only ADH and aldosterone
lining: simple cuboidal epithelium
name:
function:
lining:
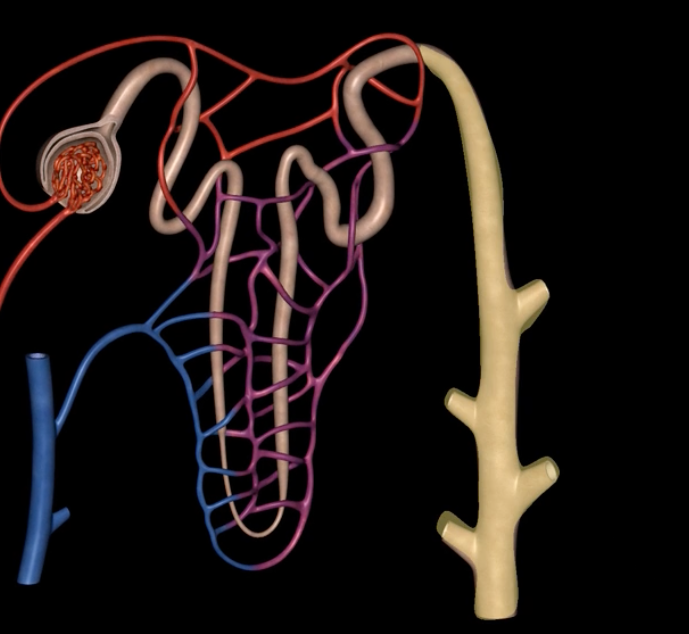
papillary ducts
collecting ducts form [ ], which empty into the minor calyx
![<p>collecting ducts form [ ], which empty into the minor calyx </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f6a9ab44-51cd-4666-8187-93d644ff2989.png)
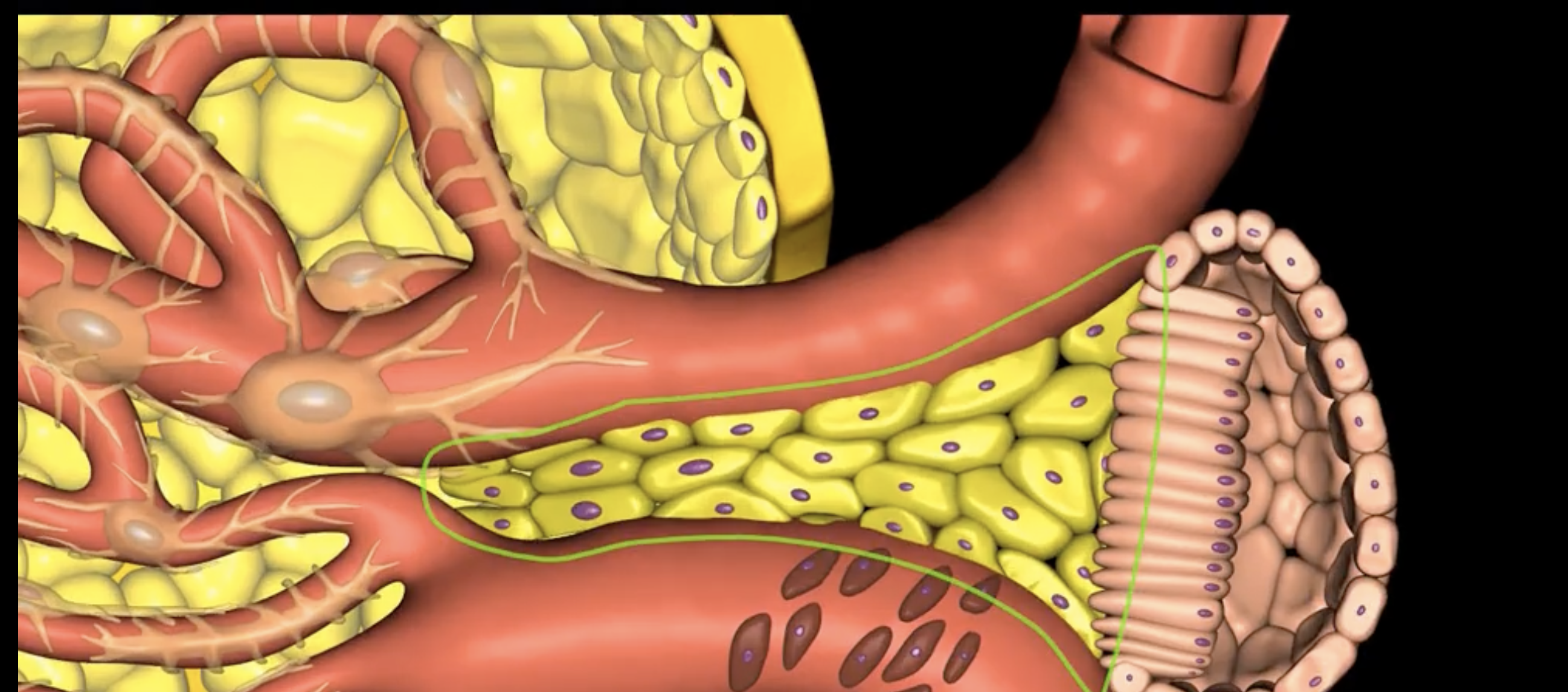
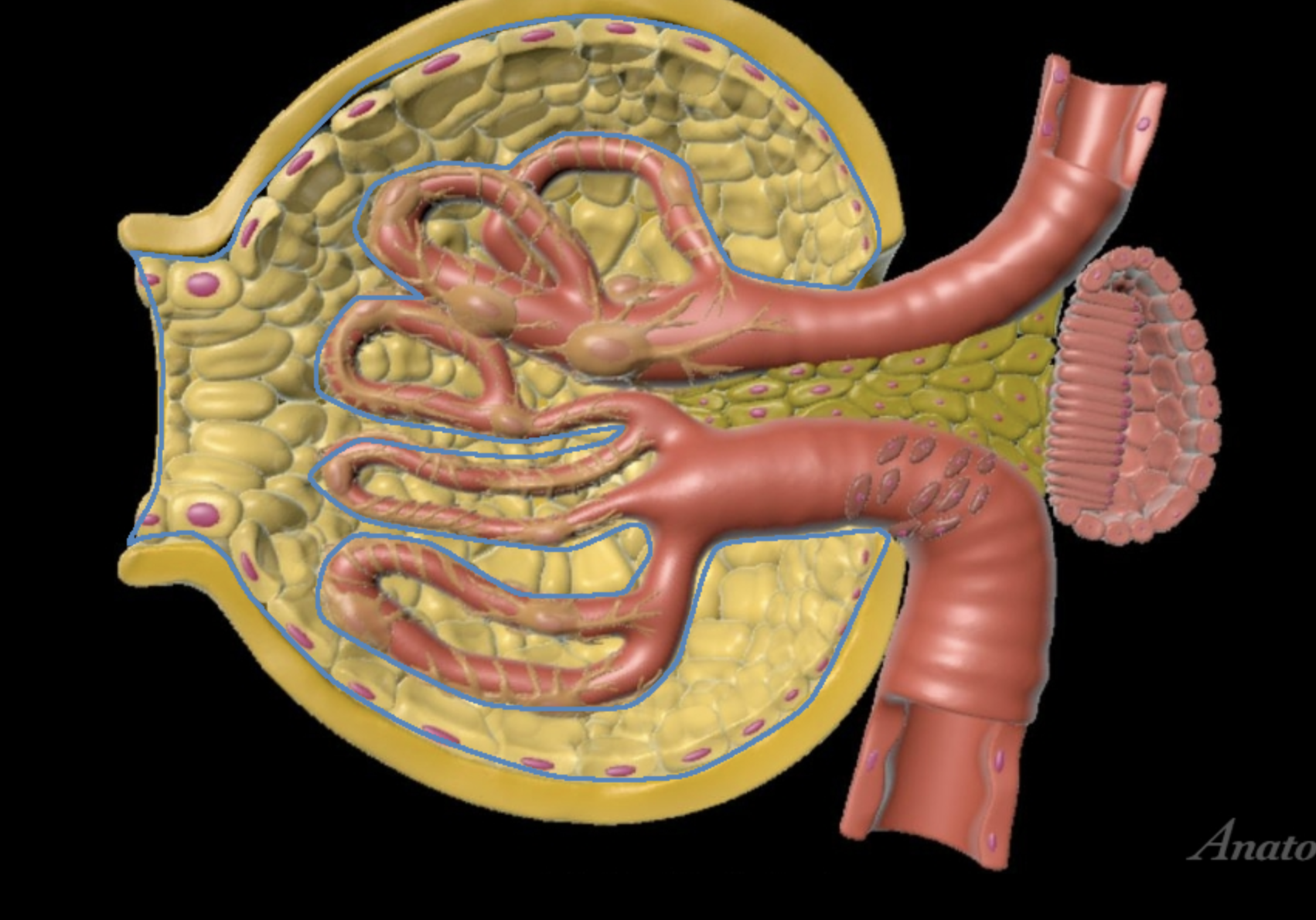
juxtaglomerular structure
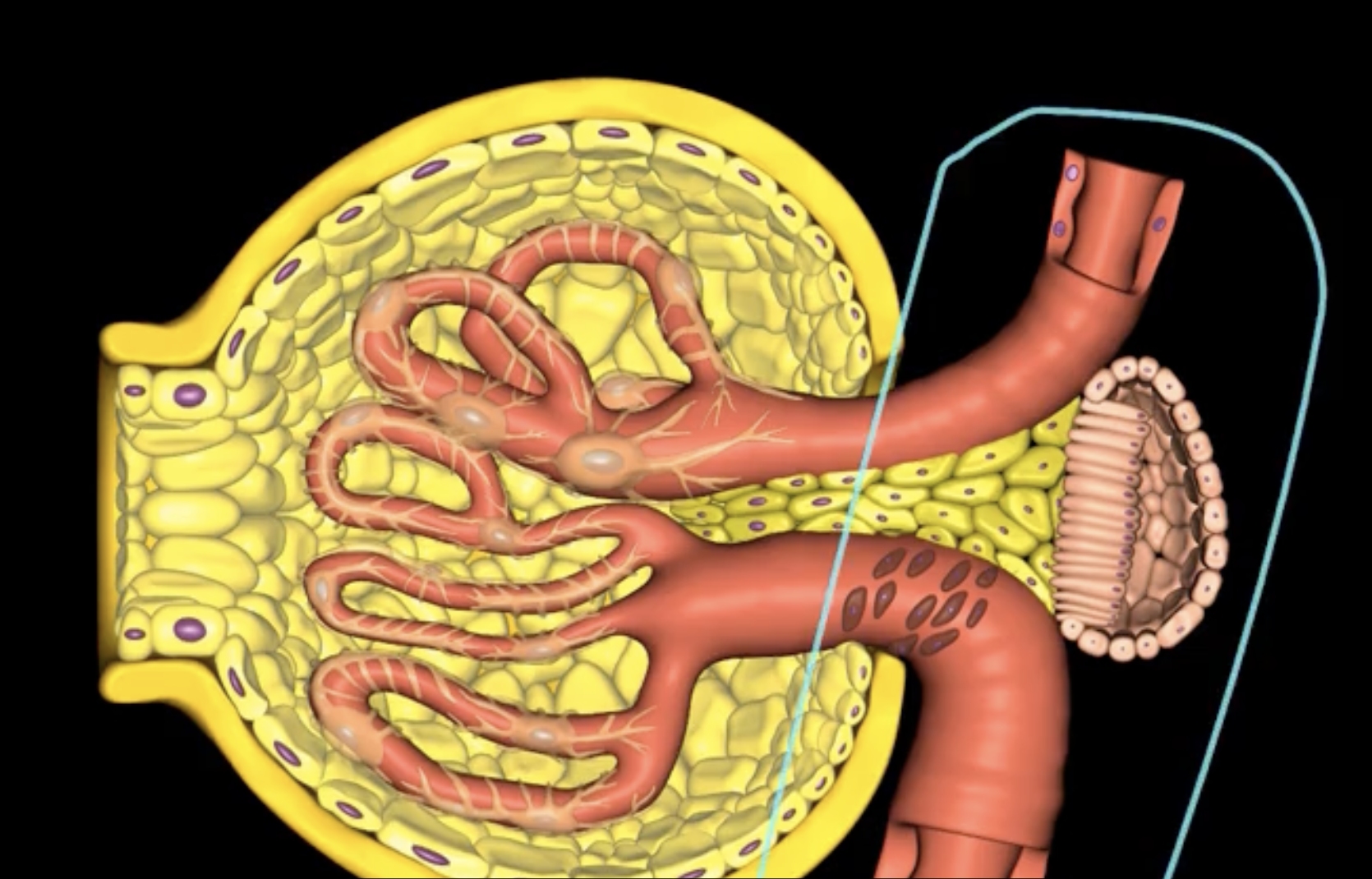
juxtaglomerular (granular) cells, modified smooth muscle cells, release renin in response to signals from macula densa
yellow arrow
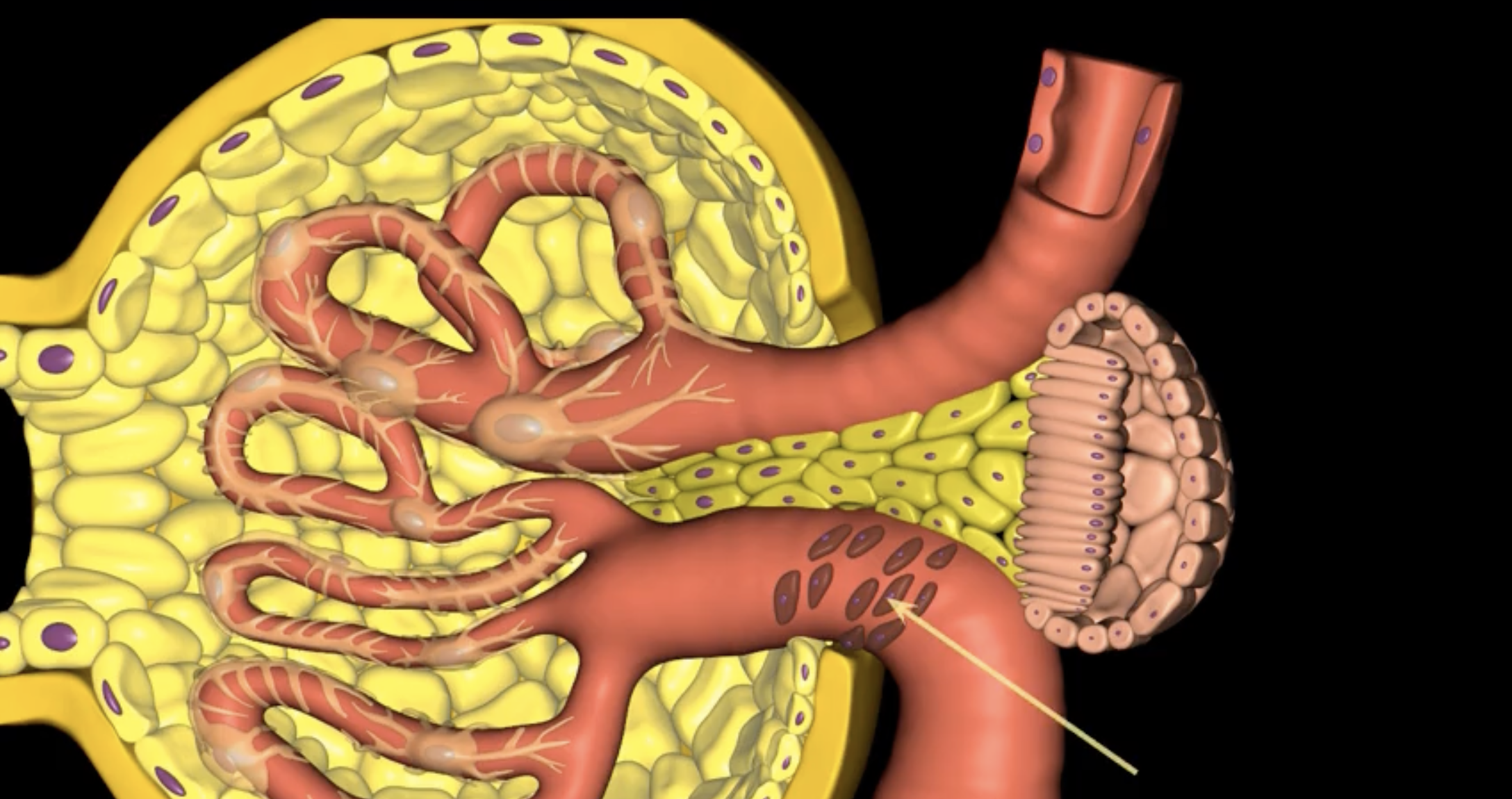
macula densa
blue arrow
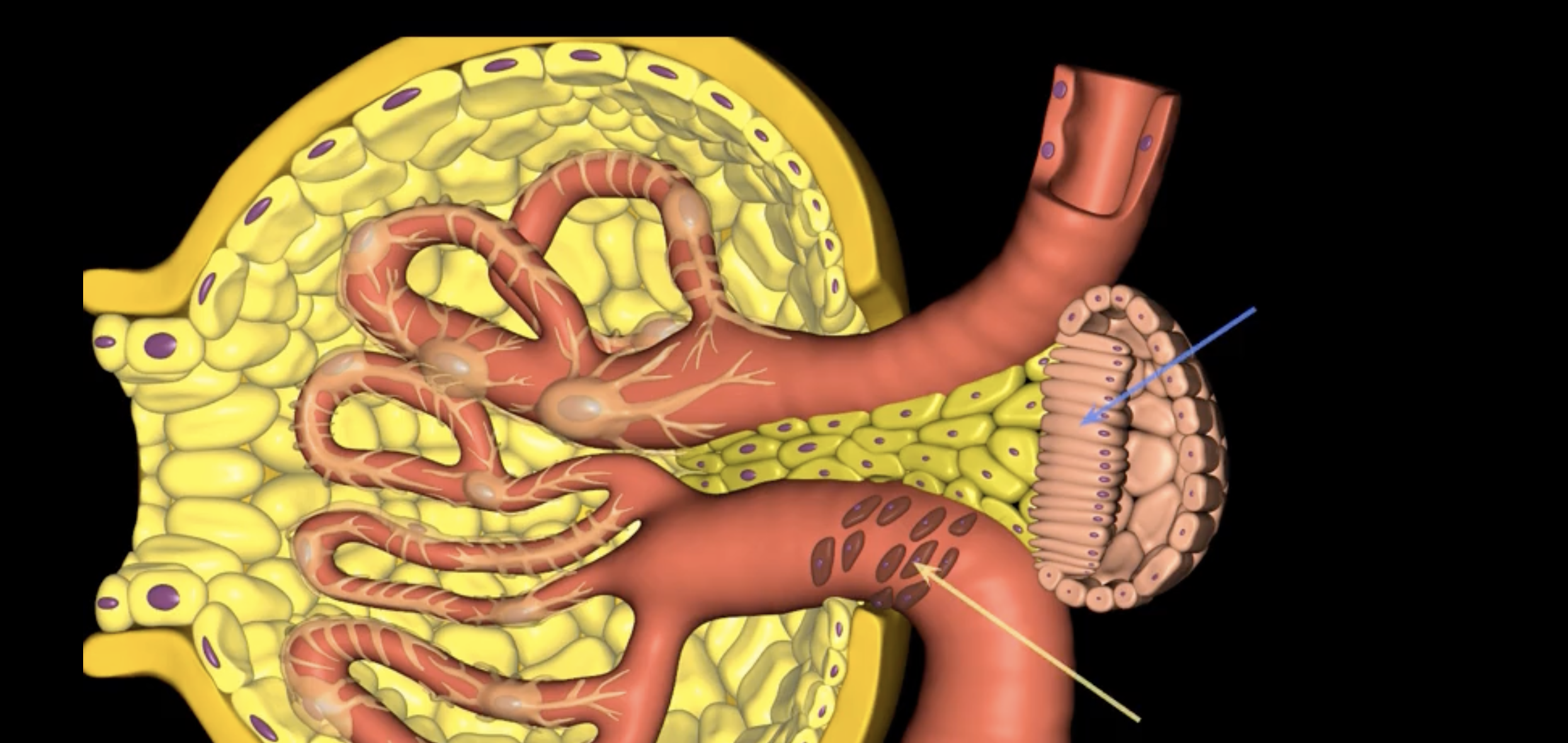
extraglomerular mesangial cells
green arrow
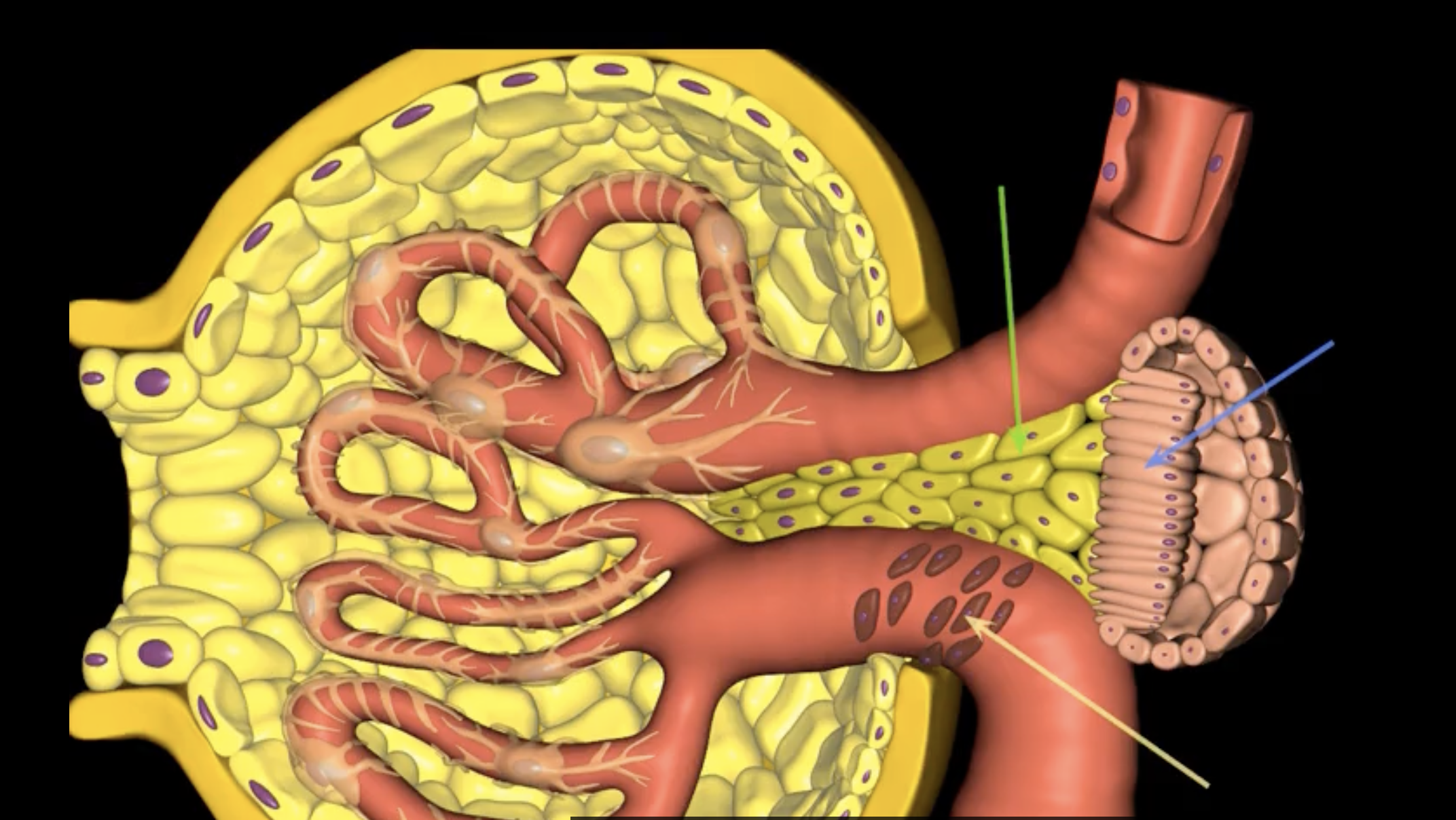
macula densa, modified columnar epithelium
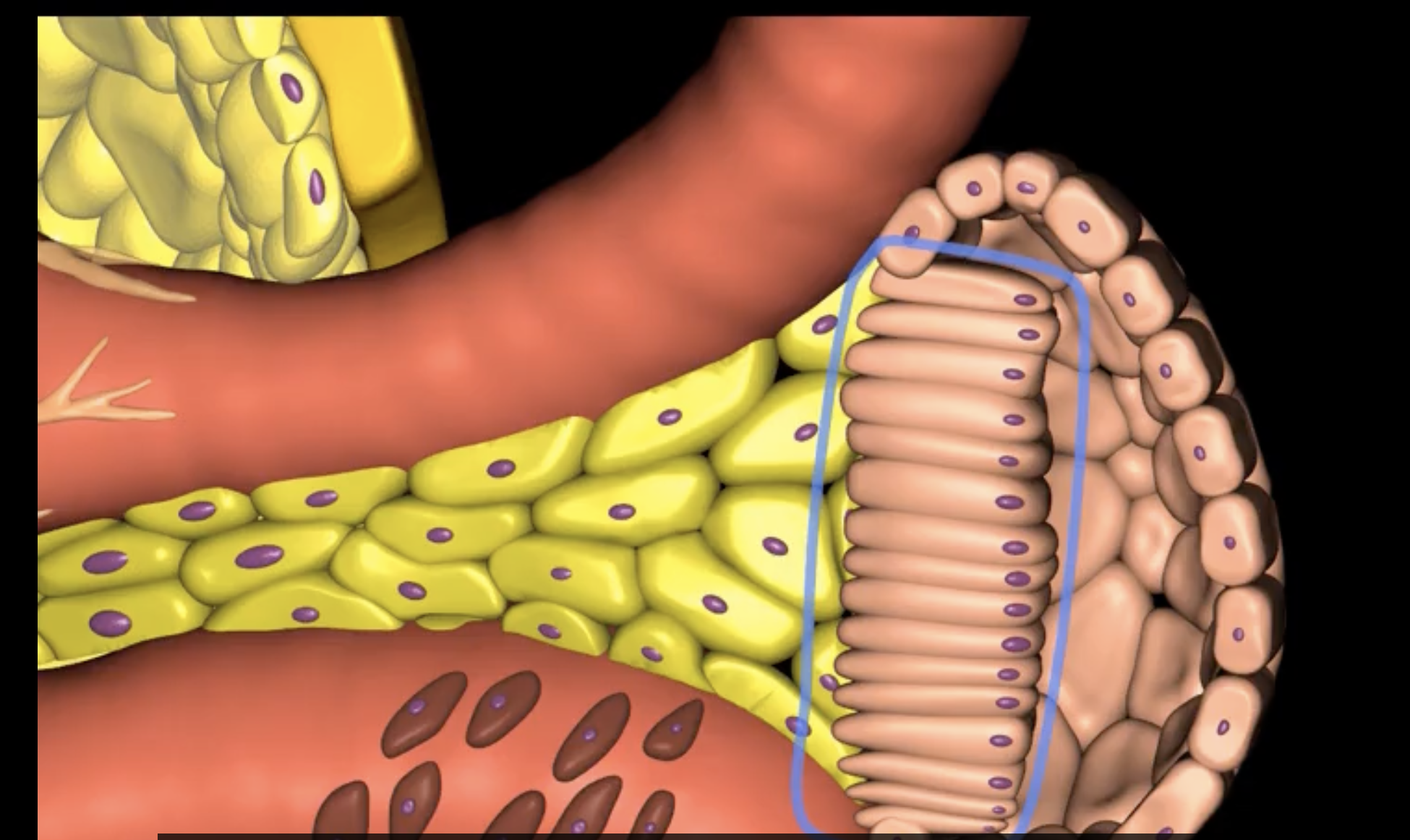
juxtaglomerular cells
If macula densa detect a decrease in ion concentration, then they stimulate _____ cells to release renin which actives RAAS
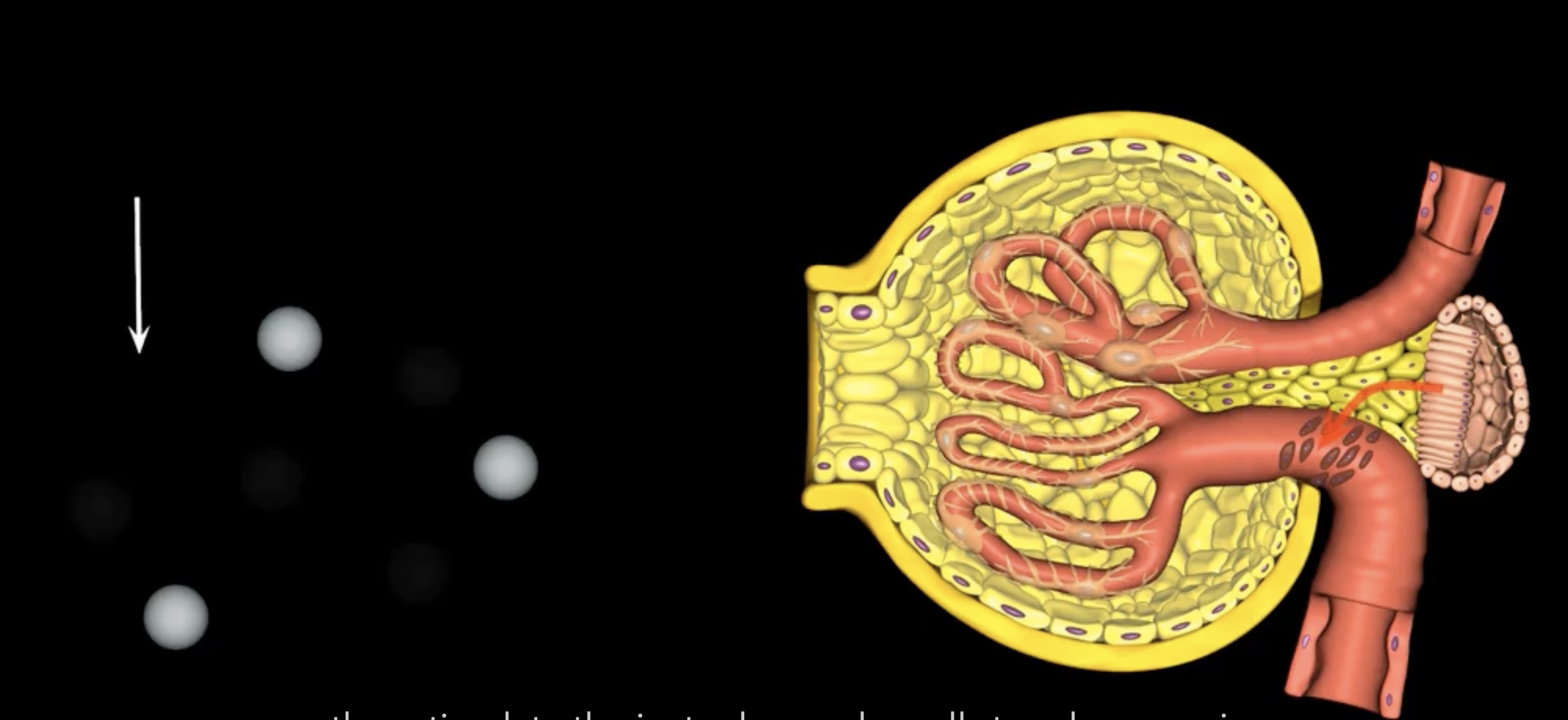

extraglomerular mesangial cells
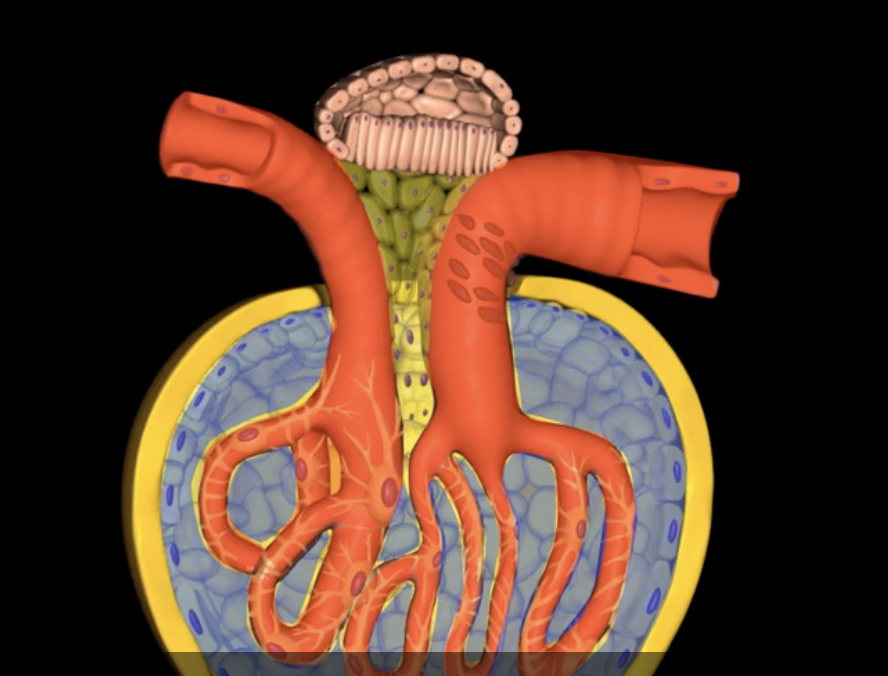
Podocytes
nephron
type of cell
Bowman’s capsule
Glomerular filtration involves pressured movement of fluid and solutes from the blood into ___ (blue arrows)
capillaries
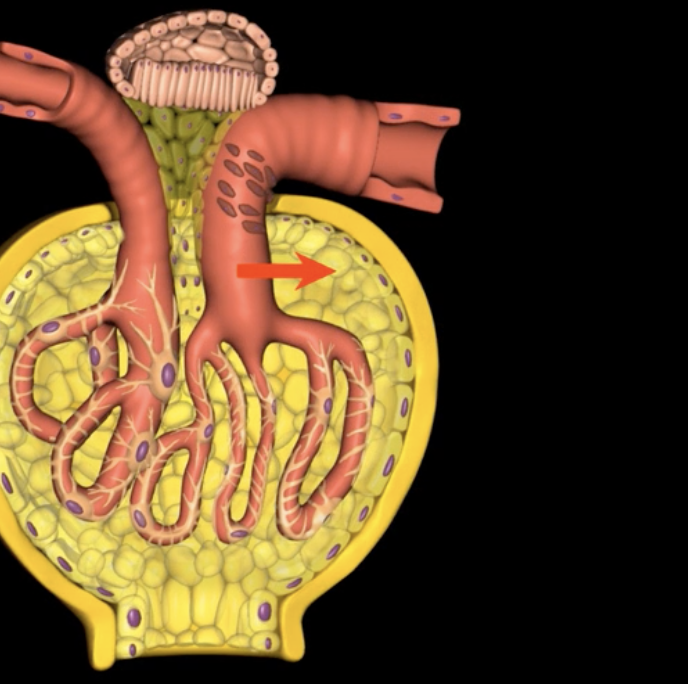
orange
Bowman’s capsule
green
endothelium
filtration membrane is composed of ____ (yellow)
visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule
purple
basement membrane
blue
afferent arteriole
green
visceral layer
orange cells
foot processes
purple
filtration slits/slit diaphrams
yellow
capsular space
outlined in blue
capsular space
blue space
the rate at which the nephrons push fluid from the glomerular capillaries
What is GFR?
fluid movement out of the blood and into the capsular space
Elevated Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (GHP) promotes … red arrow
proteins that remain in the glomerulus create glomerular oncotic pressure, which has a tendency to pull fluid back into the glomerular capillaries
Blood colloid osmotic pressure (HPc): red arrow
Filtrate with bowman’s capsule exerts capsular hydrostatic pressure which impedes additional movement of fluid from the glomerular capillaries into the capsular space
capsular hydrostatic pressure (HPc): red arrows
a decrease in blood volume with concomitant reduction in blood pressure
An increase in GFR resuts in increased urine production and ?
intrinsically and extrinsically
As the primary contributor to GFR, capillary hydrostatic pressure can be adjusted both ________ and _______ as needed to tightly regulate GFR.
which decreases HPg and GFR, and causes decreased urine volume
Vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole decreases blood flow into the glomerulus…..
which also decreased HPg and GFR, causing decreased urine volume
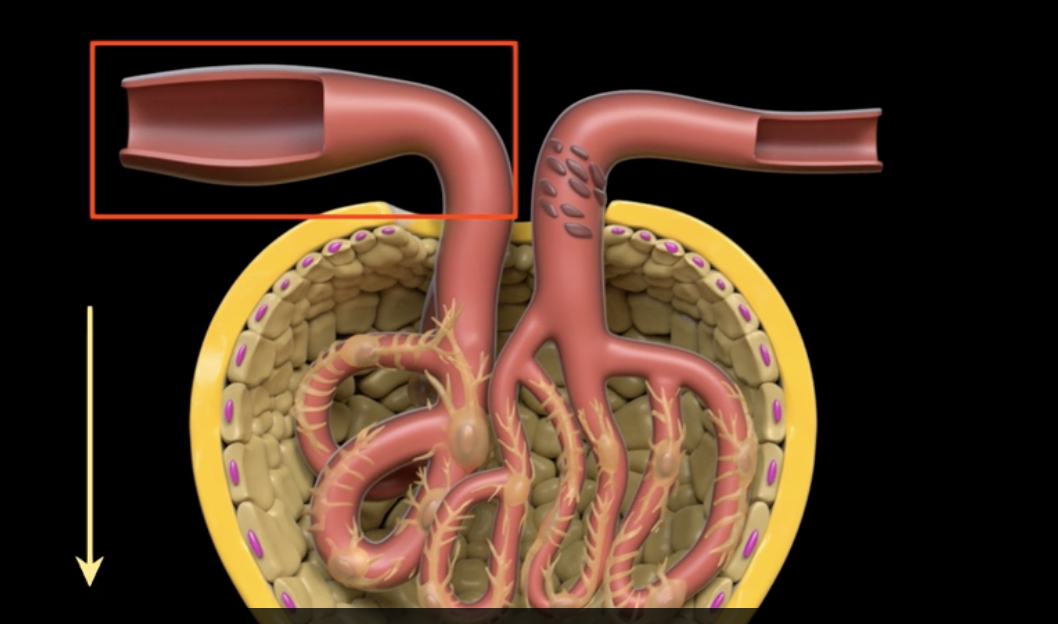
Vasodilation of the efferent arteriole increases flow out of the glomerulus…
macula densa cells stimulate afferent arteriole vasoconstriction to reduce GFR, slowing filtrate flow and optimizing reabsorption
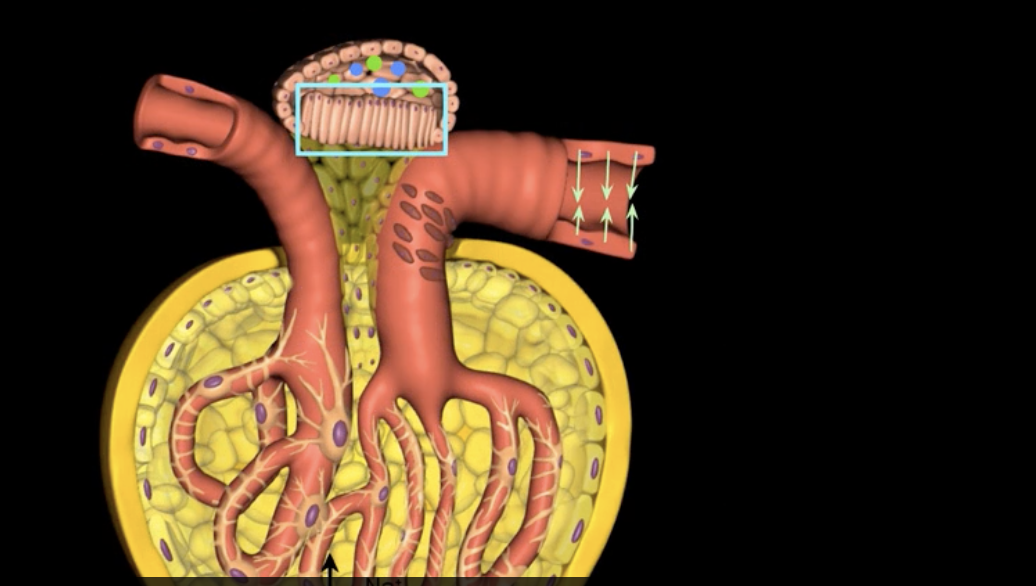
high concentrations of Na+ and Cl- in the filtrate indicate high flow rate with decreased reabsorption. causing?
sympathetic nervous system and hormones
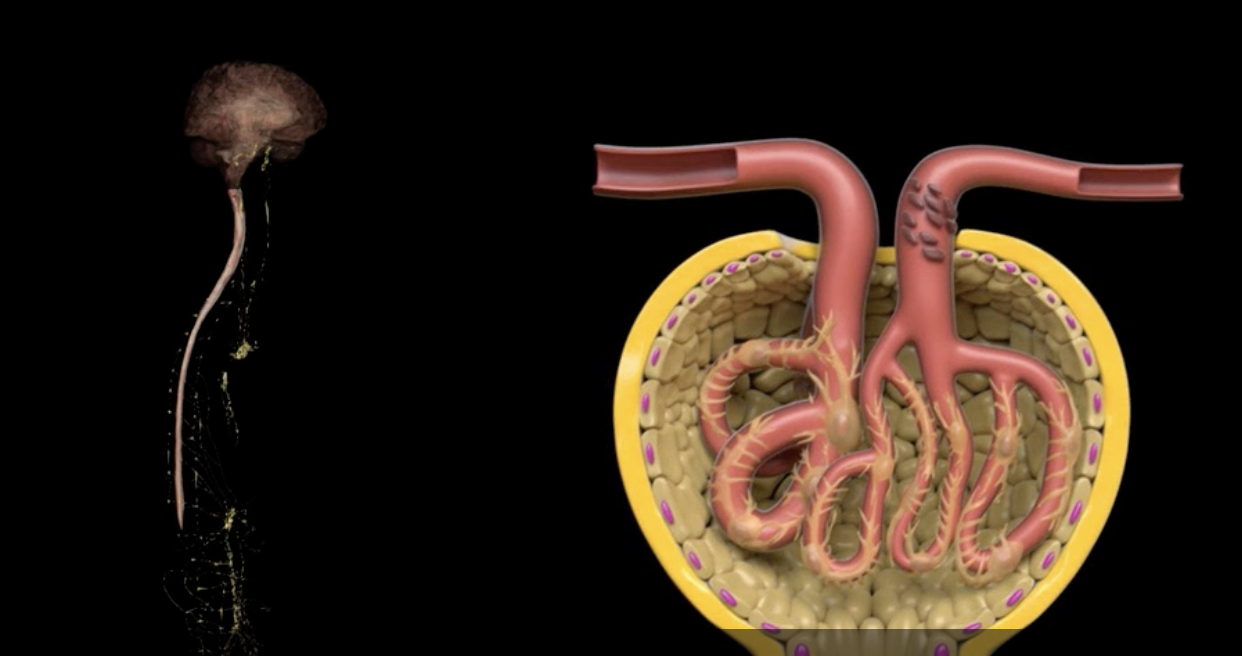
Extrinsic control of GFR maintains mean arterial pressure through activation of what?
decrease in GFR, and in turn increasing blood volume and systemic blood pressure
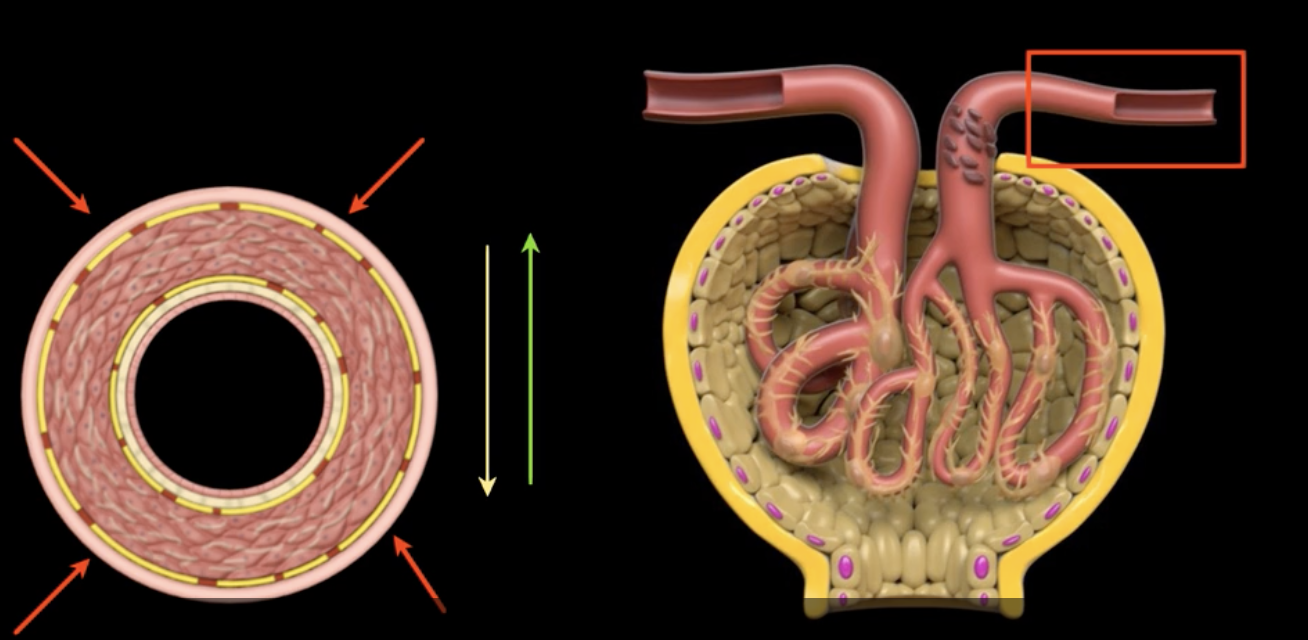
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system results in vasoconstriction throughout the body resulting in…
an enzyme secreted by the juxtaglomerular cells in response to a drop in blood pressure and initiates a cascade of events resulting in generalized increased in blood pressure
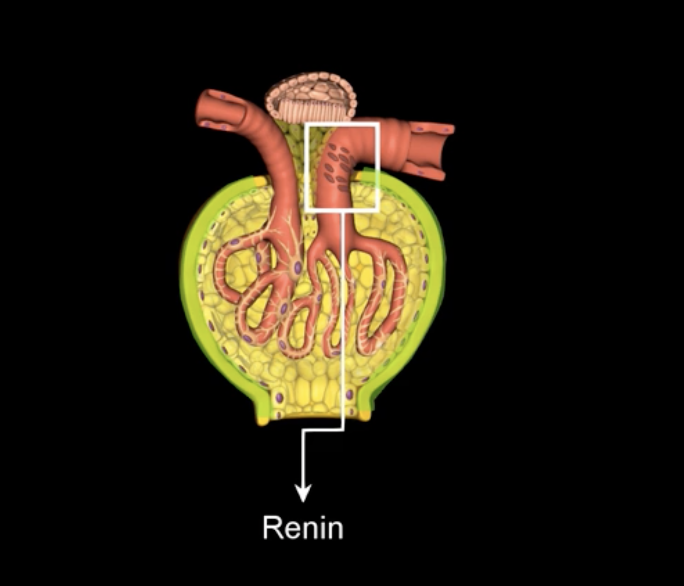
What is renin?
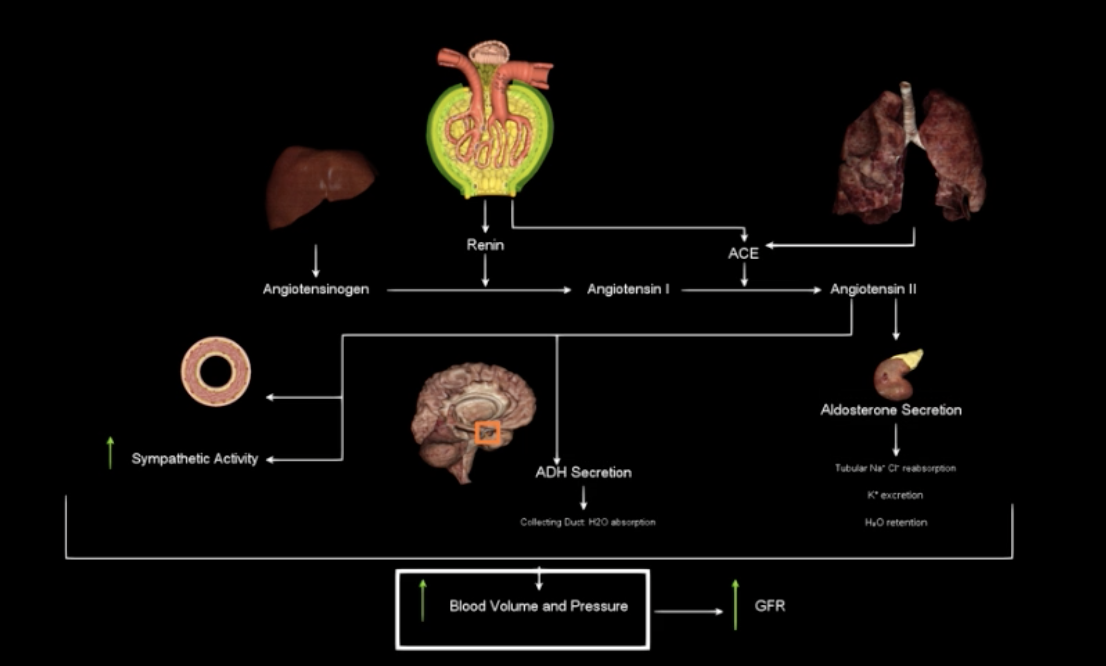
RAAS… know this .. mucha will def test this
What is this?
Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg)
Pressure within capillaries that pushes fluid out of blood
Blood colloid osmotic pressure (OPg)
Pulls fluid back into blood due to presence of proteins
Capsular hydrostatic pressure (HPc)
Opposes movement of fluid out of blood
microvilli = purple
proximal convoluted tubule = green
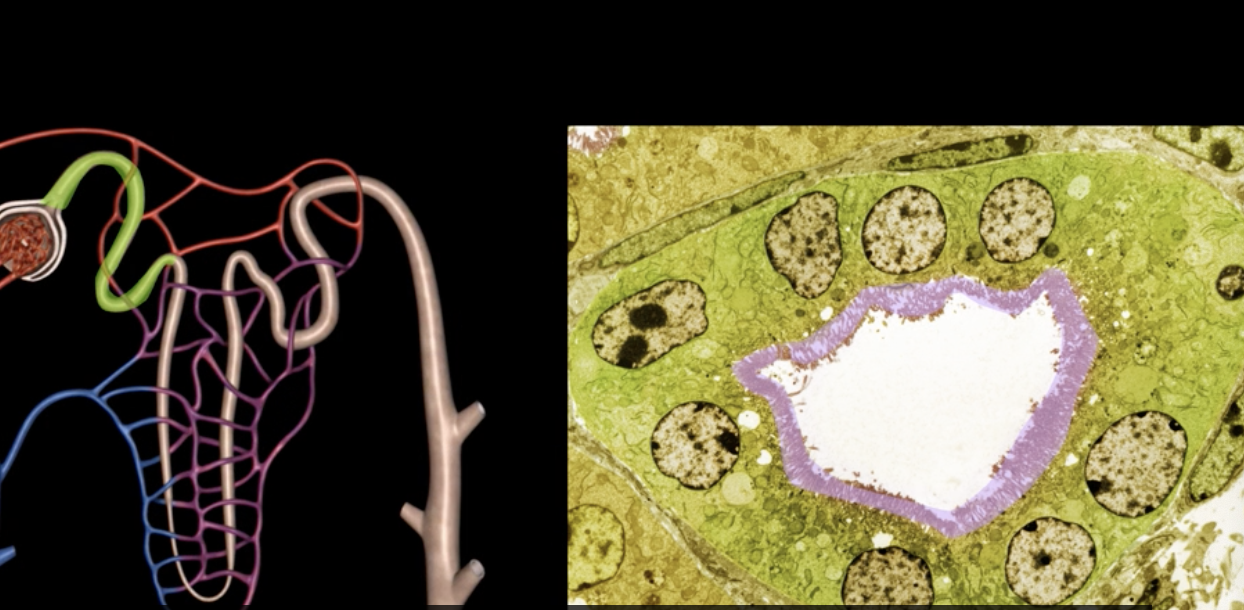
right image: purple and green
yellow arrow= transcellular reabsorption
red= basolateral surface
light blue ring= apical surface
neon blue arrow = paracellular reabsorption
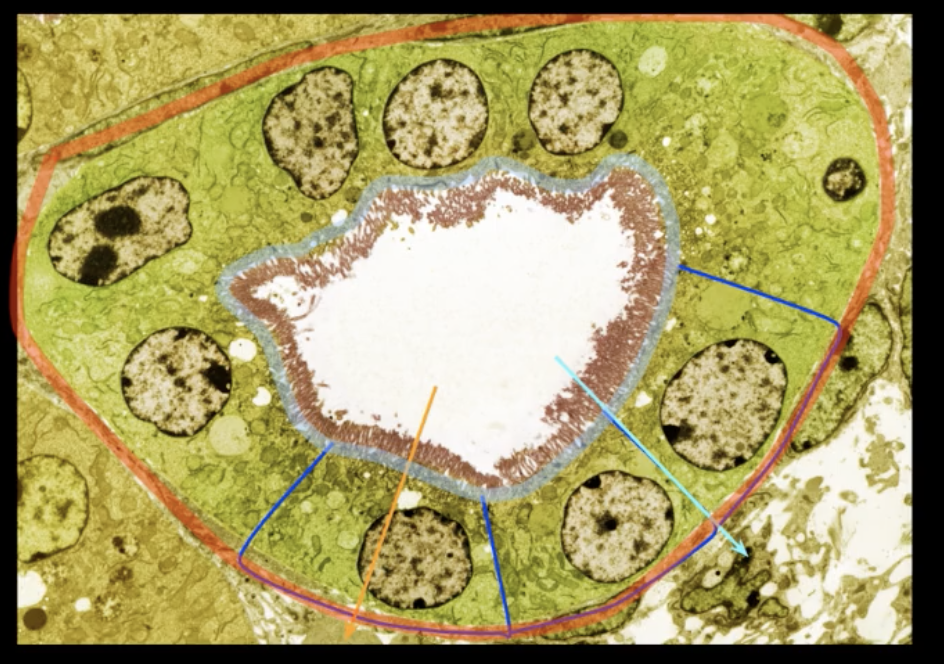
yellow arrow, red outer ring, light blue inner ring, and neon blue arrow
bowman’s capsule
orange
proximal convoluted tubule
green