AP Human Geography - Unit 3 Culture
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/91
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
1
New cards
culture
shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by the members of a society that are not the result of biological inheritance (socially constructed)
2
New cards
ethnicity
a group of people who share a common cultural identity
- social group that defines itself based on certain factors: culture, language, religion, tradition, etc.
- changeable through movement, assimilation, etc.
- social group that defines itself based on certain factors: culture, language, religion, tradition, etc.
- changeable through movement, assimilation, etc.
3
New cards
ethnicity examples
hispanic, german, italian, hmong, japanese
4
New cards
race
historical classification that is used to categorize human populations with shared physical traits (not culture)
social construct around biology of a person
social construct around biology of a person
5
New cards
race examples
american indian/alaska native, native hawaiian/pacific islander, black/african american, white, asian
6
New cards
culture trait
a single attribute of a culture, such as food preferences, architecture, and land use
- what members of local culture produce in material culture reflects beliefs and values of nonmaterial cultures
- what members of local culture produce in material culture reflects beliefs and values of nonmaterial cultures
7
New cards
material culture traits
things people construct: clothing, food, literature/art, house/public buildings
8
New cards
nonmaterial culture traits
beliefs, practices, aesthetics, values of group of people: language/religion, education systems, government/law systems, music/holidays
9
New cards
2 attitudes toward cultural differences
1. ethnocentrism
2. cultural relativism
2. cultural relativism
10
New cards
ethnocentrism
judging another culture based on the values of one's own culture (language, religion, customs)
11
New cards
cultural relativism
the idea that a person's beliefs, values, and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture, rather than be judged against the criteria of another
12
New cards
cultural landscape
combination of physical features, agricultural and industrial practices, religions and linguistic characteristics, sequent occupancy, traditional and postmodern architecture, and land use patterns
13
New cards
sequent occupance
the combined imprint on an area when it has been inhabited by a succession of cultures (ex. buildings, transportation systems, farms, irrigation, recreation facilities)
14
New cards
attitudes toward ____________ and ___________ shape the use of space in a society
ethnicity and gender
15
New cards
indigenous communities
the original settlers of an area (pre-invasion/colonialism) who have retained their culture apart from the colonizers (ex. Native Americans, First Nations, Aborigines)
16
New cards
ethnic enclave
an area within a city occupied by a distinctive minority culture (ex. Little Italy in NYC)
17
New cards
gender
social and cultural differences between males and females (not biological differences)
18
New cards
gender role
learned behaviors that are deemed appropriate to gender as determined by cultural norms
19
New cards
role of women in workforce
women engaged in paid work outside the home has increased substantially over the second half of the 20th century
20
New cards
gendered spaces
areas in which gender expression is either welcome or unwelcome
- Muslim society: public space (employment, politics) belong to men and private space (home) belongs to women
- U.S. society: public restrooms divided by gender
- Muslim society: public space (employment, politics) belong to men and private space (home) belongs to women
- U.S. society: public restrooms divided by gender
21
New cards
patterns of ________, __________, and ___________ shape the cultural landscape
language, religion, ethnicity
22
New cards
sense of place
term used to connote attachment to and comfort in a particular place with a strong identity that is deeply felt by inhabitants
STRONG sense of place: sense of place that is felt by visitors as well as inhabitants
STRONG sense of place: sense of place that is felt by visitors as well as inhabitants
23
New cards
place making
how a culture makes a place fit their identity by shaping the landscape to show what they believe and value (buildings, statues, sacred sites, etc.)
24
New cards
_________, _________, and ___________ are forces that can unite or divide a country
language, religion, and ethnicity
25
New cards
centripetal forces
forces that unite a country: custom/common language, ethnicity, religion
26
New cards
centrifugal forces
forces that divide a country: multiple competing ethnicities, languages, or religions
27
New cards
culture spreads through
diffusion
28
New cards
cultural diffusion
spread of an idea, innovation, cultural trend, or disease from its source area to other areas
29
New cards
relocation diffusion
type of cultural diffusion when an innovation or idea spreads by the actual movement of individuals who have adopted the idea and carry it to a new place (ex. spread of Christianity to New World, spread of Spanish and English to the New World)
30
New cards
expansion diffusion
type of cultural diffusion when an innovation or idea develops in a source area and remains strong there while also spreading outward the innovation or idea moves through fixed populations (wave-like)
NO MOVING PEOPLE
NO MOVING PEOPLE
31
New cards
3 types of diffusion
1. contagious
2. hierarchical
3. stimulus
2. hierarchical
3. stimulus
32
New cards
contagious diffusion
type of expansion diffusion where nearly all individuals are affected as it spreads outward (ex. spread of Islam)
33
New cards
hierarchical diffusion
type of expansion diffusion where particular (most connected) groups are affected as it leapfrogs over areas (ex. FAX machines, AIDS)
34
New cards
stimulus diffusion
type of expansion diffusion where a small portion of the population adopts an idea or modifies it (ex. veggie burgers in India)
35
New cards
culture changes and/or disappears over time through
interactions between groups
36
New cards
lingua franca
a language mutually understood by people who speak different languages, usually for the purpose of trade (ex. English as language of international business, Swahili as language of trade in East Africa, Arabic as language of trade in Southwest Asia)
37
New cards
creolization
2 or more languages mix - develop formal structure & vocab to create a new language (developed through settings of colonization/slavery)
blending of European, Amerindian, and African cultures in the New World as a result of colonialism to create something new (ex. Haitian Creole language in the Caribbean, Santeria religion in the Caribbean)
blending of European, Amerindian, and African cultures in the New World as a result of colonialism to create something new (ex. Haitian Creole language in the Caribbean, Santeria religion in the Caribbean)
38
New cards
historical processes impact
cultural patterns
39
New cards
cultural imperialism
dominance of one culture over another, historically, often occurred as a result of colonization (ex. Spanish and English cultures imposed on the Native People in the Americas, occurs in present day as pop culture, which is easily diffused and causes local traditions to become commercialized)
40
New cards
colonialism
policy of acquiring control over another country, occupying it with settlers and exploiting it economically (ex. English pilgrims landing in America, Spanish conquistadors landing in America)
when a powerful country establishes settlements in a less powerful country for economic/political gain
when a powerful country establishes settlements in a less powerful country for economic/political gain
41
New cards
neocolonialism
"new" colonialism - imperialism can be pursued through assertion of political, economic, cultural, influence rather than occupation
42
New cards
trade
people move from place to place around the world as they trade and come into contact with new ideas and cultural practices
43
New cards
culture is _______ constructed and change through both ______ scale and ______ scale processes
socially, small, large
44
New cards
culture is socially constructed
practices and beliefs (culture) that appear to be natural and obvious to people who accept it, but are actually learned behaviors (ex. race is not biological, but an agreed upon set of ideas about how humans are differentiated)
45
New cards
how does culture change?
through media, technological change, politics, economics, and social relationships
46
New cards
globalization
process of increased interconnectedness among countries most notably in areas of economics, politics, and culture
47
New cards
urbanization
refers to the movement of people to town/cities and the resulting expansion of the rural countryside to absorb increase in people
48
New cards
communication technologies are accelerating
interactions and changing cultural practices
49
New cards
time-space convergence
increasing connectivity between cultures that occurs as a result of communication technology (ex. internet)
50
New cards
cultural convergence
cultures become more alike as their interactions increase (ex. increasing use of English)
languages change through convergence: different languages have consistent spatial interaction = collapse 2 languages into 1
languages change through convergence: different languages have consistent spatial interaction = collapse 2 languages into 1
51
New cards
cultural divergence
tendency for culture groups to disassociate from others in order to protect or preserve their culture from influence or change (ex. Amish, Hutterite, Mennonite, Inuit)
52
New cards
local culture (folk culture)
culture traits of usually small, traditional, homogenous, rural communities (ex. Amish, Hutterite, Mennonite, Inuit)
53
New cards
why are there loss of indigenous languages?
consequence of colonialism and policies of assimilation
54
New cards
culture (language, religion, gender roles) spread from ________ ______
culture hearths
55
New cards
culture hearth
source of civilization: place where a civilization began and their ideas and practices spread to surrounding areas
56
New cards
civilization
society with an advanced state of social development possessing recordkeeping (writing), advanced cities (urbanization), technology, specialized workers, complex institutions (government, religion)
57
New cards
language
method of communication (spoke/written)
58
New cards
language family
group of languages with a shared but fairly distant origin
59
New cards
dialect
variant of a standard language along regional or ethnic lines (ex. differences in vocab, syntax, pronunciation, cadence, and pace)
60
New cards
world religions
belief systems that originated in a hearth and diffused
Christianity
Islam
Nonreligious
Hinduism
Chinese traditional religion
Buddhism
Animism - indigenous
African traditional
Sikhism
Judaism
Christianity
Islam
Nonreligious
Hinduism
Chinese traditional religion
Buddhism
Animism - indigenous
African traditional
Sikhism
Judaism
61
New cards
ethnic cultures
members that share cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language/dialect, symbolic systems (religion/mythology), rituals, cuisine, dressing styles, art, or physical appearance (ex. Greek, Spanish, Italian)
62
New cards
diffusion of language, religion, ethnic cultures can be represented on maps, charts, and toponyms
diffusion of language, religion, and ethnic cultures: trade, migration, invasion, conflicts, conquests, missions, and the spread of agriculture
63
New cards
toponym
place-names that can uncover historical information about a place and its origins, such as the language of the original inhabitants and succeeding settlement history and population dispersal (ex. Osceola County, Florida)
64
New cards
Indo-European language family
family of languages believed to all come from a single language (Proto-Indo European) that spread outward
65
New cards
conquest theory
source of Indo-European language lay somewhere in the steppes of present-day Ukraine and Russia more than 5000 years ago and spread by conquerors on horseback who moved westward from east
66
New cards
agriculture theory
source of Indo-European language lay somewhere in mountainous terrain of Anatolia in modern Turkey between 7000 and 9000 years ago and spread with diffusion of agriculture
established farming ----> reliable food supply ----> population increase ---> slow/steady wave of farmers dispersed into Europe and mixed with nonfarmers
established farming ----> reliable food supply ----> population increase ---> slow/steady wave of farmers dispersed into Europe and mixed with nonfarmers
67
New cards
diffusion of major religions
1. buddhism
2. islam
3. christianity
4. sikhism
5. hinduism
6. judaism
7. animism
2. islam
3. christianity
4. sikhism
5. hinduism
6. judaism
7. animism
68
New cards
universalizing religions
religions that actively seek converts because they view themselves as offering belief systems of universal applicability and appeal
buddhism
islam
christianity
sikhism
BICS
buddhism
islam
christianity
sikhism
BICS
69
New cards
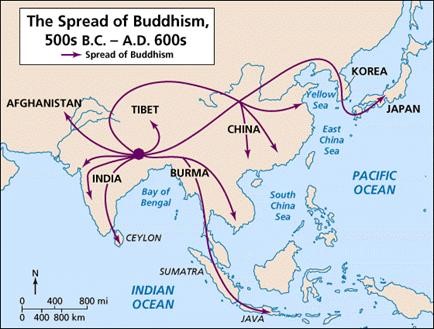
buddhism
culture hearth: south asia/northern india
distribution: southeast asia, east asia, south asia
- founded by Siddhartha Gautma in northern India with roots in Hinduism
- lost its following in India, becoming most widespread religion in East Asia
- spread by relocation diffusion to East Asia
- spread by expansion diffusion in China, Korea, Thailand, Burma, Japan
distribution: southeast asia, east asia, south asia
- founded by Siddhartha Gautma in northern India with roots in Hinduism
- lost its following in India, becoming most widespread religion in East Asia
- spread by relocation diffusion to East Asia
- spread by expansion diffusion in China, Korea, Thailand, Burma, Japan
70
New cards
islam
culture hearth: southwest asia/mecca
distribution: southwest asia, northern africa, and parts of southeast asia
- roots in Judaism
- based on one god belief Allah and Muhammad was Allah's prophet
- spread by expansion diffusion in Southwest Asia and North Africa
- relocation diffusion to Southeast Asia, Europe, and U.S.
- 2 major branches:
1. Sunni -- largest branch prominent through Southwest Asia and North Africa
2. Shiite (Shia) -- second largest in Iran and Iraq
distribution: southwest asia, northern africa, and parts of southeast asia
- roots in Judaism
- based on one god belief Allah and Muhammad was Allah's prophet
- spread by expansion diffusion in Southwest Asia and North Africa
- relocation diffusion to Southeast Asia, Europe, and U.S.
- 2 major branches:
1. Sunni -- largest branch prominent through Southwest Asia and North Africa
2. Shiite (Shia) -- second largest in Iran and Iraq
71
New cards
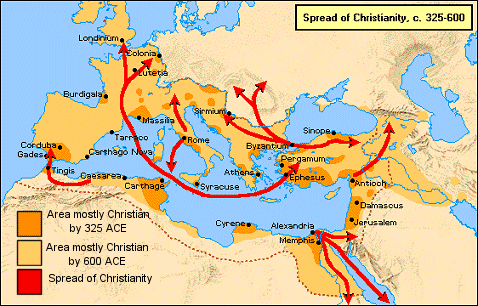
christianity
culture hearth: southwest asia/jerusalem/palestine/israel
distribution: australia, northern europe, north america, central and south america
MOST DOMINANT UNIVERSALIZING RELIGION
- roots in Judaism
- based on Old Testament and teachings of Jesus as told in New Testament
- spread by relocation and expansion diffusion throughout the world
- 3 major branches:
1. roman catholicism -- prominent in Europe, Americas
2. protestantism -- prominent in North America and England
3. eastern orthodox -- prominent in Eastern Europe and Russia
distribution: australia, northern europe, north america, central and south america
MOST DOMINANT UNIVERSALIZING RELIGION
- roots in Judaism
- based on Old Testament and teachings of Jesus as told in New Testament
- spread by relocation and expansion diffusion throughout the world
- 3 major branches:
1. roman catholicism -- prominent in Europe, Americas
2. protestantism -- prominent in North America and England
3. eastern orthodox -- prominent in Eastern Europe and Russia
72
New cards
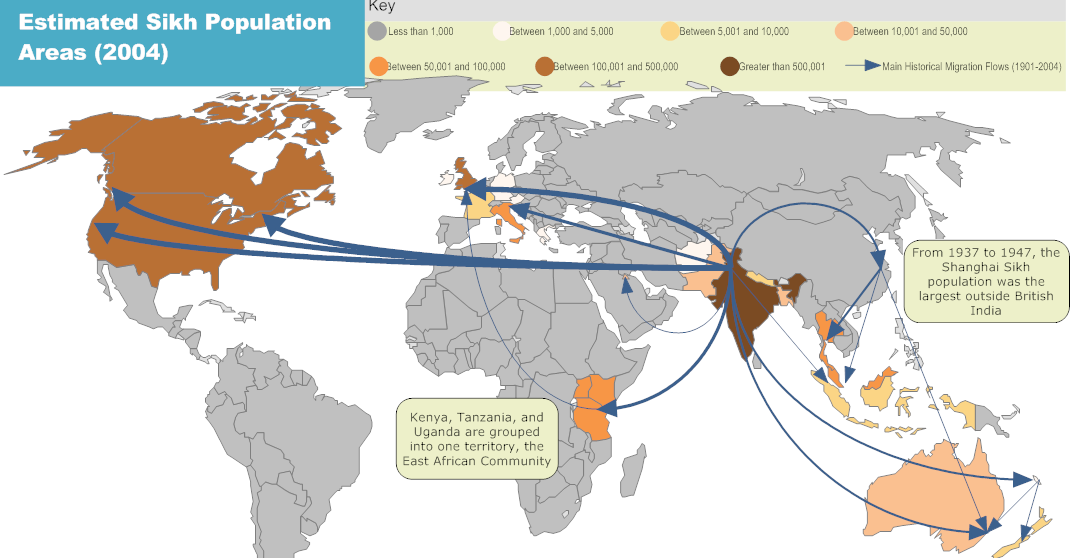
sikhism
culture hearth: south asia/india - punjab
distribution: India
- roots in Islam and Hinduism (reincarnation)
- founded in northern India
- based on teachings of Guru Nanak
- spread by expansion diffusion throughout India
- relocation to Southeast Asia, Europe, and North America
- spread through expansion in Middle East
- relocation North Africa, Europe, South East Asia, and U.S.
distribution: India
- roots in Islam and Hinduism (reincarnation)
- founded in northern India
- based on teachings of Guru Nanak
- spread by expansion diffusion throughout India
- relocation to Southeast Asia, Europe, and North America
- spread through expansion in Middle East
- relocation North Africa, Europe, South East Asia, and U.S.
73
New cards
ethnic religions
religions that do not actively seek converts and are generally found near the hearth or spread through relocation diffusion
judaism
animism
hinduism
JAH!
judaism
animism
hinduism
JAH!
74
New cards
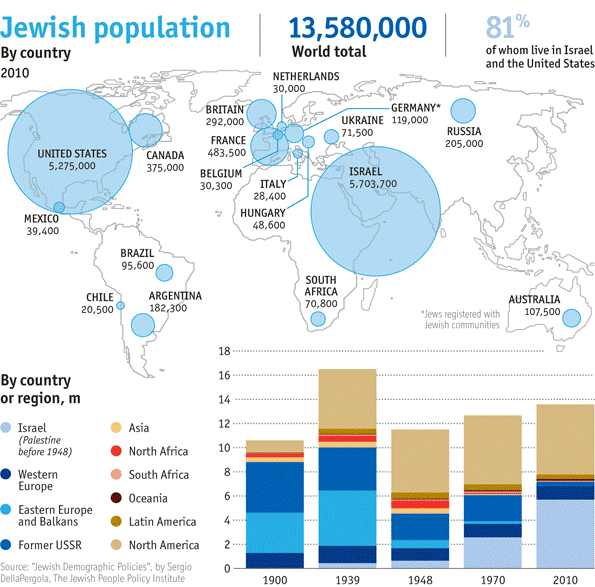
judaism
culture hearth: south asia/canaan
distribution: north america (U.S.), southwest asia (israel), europe, russia
- founded by Abraham in Southwest Asia
- first monotheistic religion (one god)
- spread by relocation diffusion due to Diaspora: scattering of Jews from homeland by Romans
- many Jews relocated back to Southwest Asia following WWII and creation of Israel
- highly concentrated today: 4/5 Jews live in U.S. and Israel (rest in Canada, France, UK, Germany, Russia, Argentina)
distribution: north america (U.S.), southwest asia (israel), europe, russia
- founded by Abraham in Southwest Asia
- first monotheistic religion (one god)
- spread by relocation diffusion due to Diaspora: scattering of Jews from homeland by Romans
- many Jews relocated back to Southwest Asia following WWII and creation of Israel
- highly concentrated today: 4/5 Jews live in U.S. and Israel (rest in Canada, France, UK, Germany, Russia, Argentina)
75
New cards
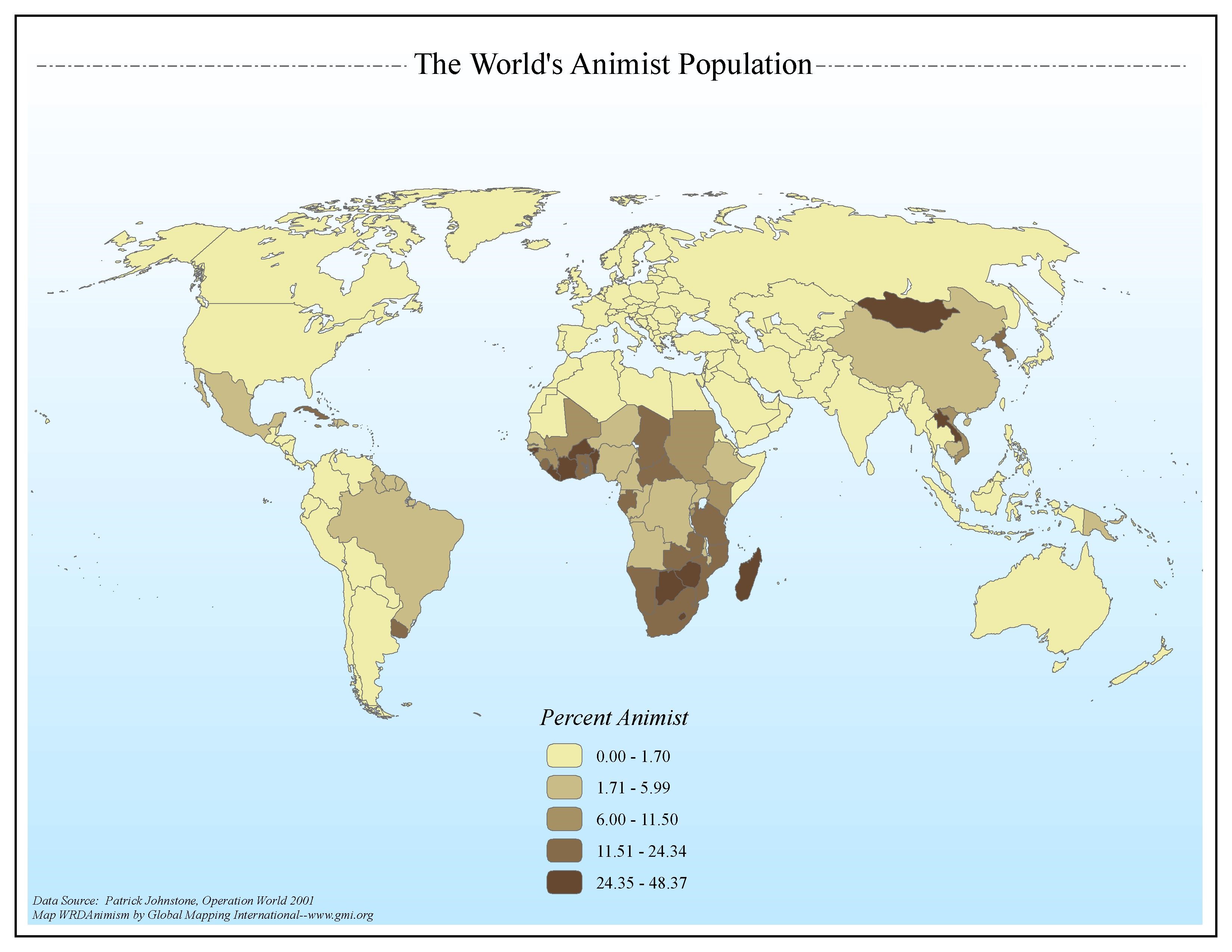
animism
- oldest religion pre-dating civilization and centered on belief that inanimate objects (mountains, rivers, trees) possess spirits and should be revered
- found among Native Americans in North and South America and among Africans and other indigenous groups globally
- found among Native Americans in North and South America and among Africans and other indigenous groups globally
76
New cards
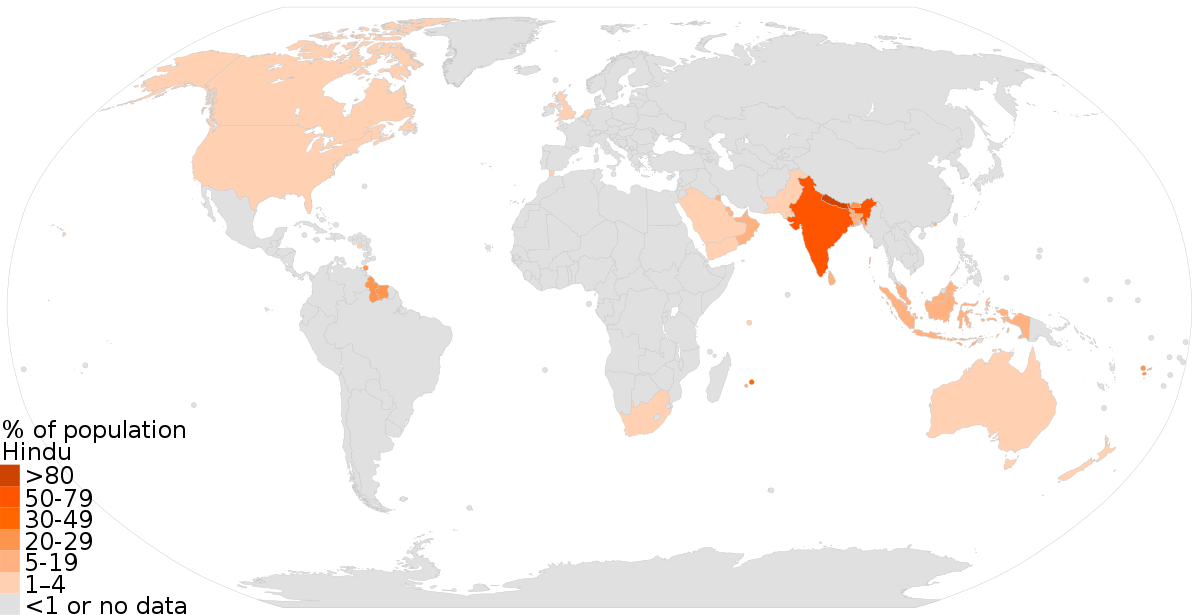
hinduism
culture hearth: south asia/india
distribution: indian subcontinent
- oldest major religion founded in India that can't be traced to 1 founder
- collection of religious beliefs strongly connected to Hindu culture based on reincarnation
- spread by expansion diffusion throughout India
- relocation diffusion to Southeast Asia, South Africa, North America and South America
distribution: indian subcontinent
- oldest major religion founded in India that can't be traced to 1 founder
- collection of religious beliefs strongly connected to Hindu culture based on reincarnation
- spread by expansion diffusion throughout India
- relocation diffusion to Southeast Asia, South Africa, North America and South America
77
New cards
effects of diffusion of culture
78
New cards
assimilation
process in which members of 1 cultural group adopt the beliefs and behaviors of another group, but still retain some original uniqueness; often occurs due to colonization or immigration (ex. native americans forced to learn english, chinese immigtant relocated and learns english)
79
New cards
acculturation
process by which a person or persons acquire the social and psychological characteristics of a group and can't be distinguished from anyone else (ex. european immigrants in america)
prolonged contact between 2 or more cultures when people in 1 culture adopt some traits from other cultures
prolonged contact between 2 or more cultures when people in 1 culture adopt some traits from other cultures
80
New cards
multiculturalism
maintaining a diversity of ethnic cultures within a community that are valued and respected for their unique differences (ex. New York City)
81
New cards
syncretism
development of a new cultural trait due to blending of 2 distinct but interacting cultures (ex. Americanized Chinese food, Americanized Mexican food)
82
New cards
placelessness
loss of distinct local features (uniqueness) in favor of standardized landscapes which happens as a result of pervasiveness of pop culture and mass production and availability of a wide variety of consumables (ex. strip malls)
83
New cards
pop culture
culture traits of large, heterogeneous, urban populations (usually rapid changing)
84
New cards
interfaith boundaries
conflict between world's major faiths
Islam and Judaism in Israel
Hinduism and Buddhism in Sri Lanka
Christians and Muslims in Sudan
Islam and Judaism in Israel
Hinduism and Buddhism in Sri Lanka
Christians and Muslims in Sudan
85
New cards
intrafaith boundaries
conflict within a single major faith, such as different denominations of Christianity or the two branches of Islam
Catholics/Protestants in Northern Ireland
Sunni/Shia in Iraq
Catholics/Protestants in Northern Ireland
Sunni/Shia in Iraq
86
New cards
sacred sites (spaces)
areas/places of religious/spiritual significance, including cathedrals, mosques, temples, and cemeteries
Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
Western Wall in Jerusalem
Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
Western Wall in Jerusalem
87
New cards
religions in U.S.
catholicism, protestantism, mixed
88
New cards
catholicism
northeastern states, southwestern states of arizona, new mexico, texas, florida
89
New cards
protestantism
baptist: southeastern states (Bible Belt region)
mormonism: utah
methodist: midland states
lutheran: upper midwest
mormonism: utah
methodist: midland states
lutheran: upper midwest
90
New cards
mixed
western states (large parts of cali, idaho, nevada, oregon, washington)
91
New cards
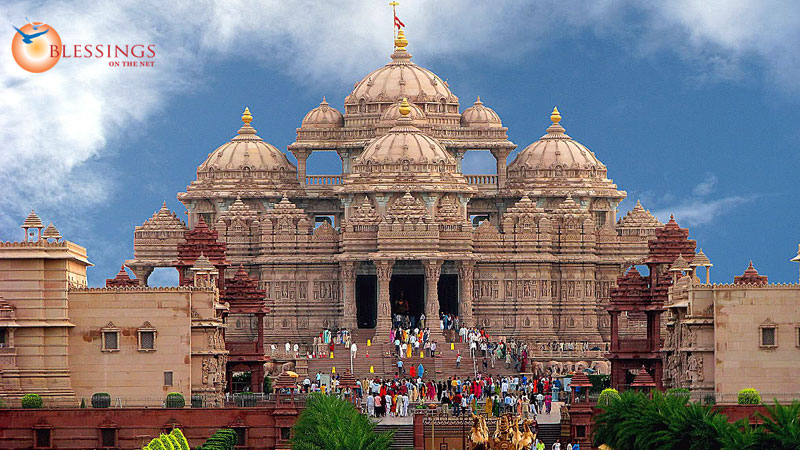
hindu architecture
colorful, ornate, multiple gods

92
New cards
buddhist architecture
far east: pagoda style, buddha, stupas
