ORAL PATHOLOGY: VESICULAR LESIONS [1]
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
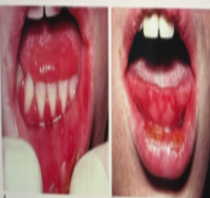
PRIMARY HERPETIC GINGIVOSTOMATITIS
CLINICAL FEATURES:
rarely occurs before 6 months
short, yellowish, fluid-filled vesicles develop
HISTOLOGIC FEATURES:
intraepithelial blisters filled with fluid
lipschutz bodies
degenerating cells show ballooning degeneration
MODE OF TRANSMISSION:
direct contact
droplet infection
TREATMENT:
unsatisfactory because disease is unalterable
antibiotic
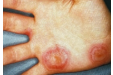
ERYHTEMA MULTIFORME
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME EXUDATIVUM
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME
CLINICAL FEATURES:
young adults, males
recurrence of disease over period of years is common
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
chicken pox
herpes zoster
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS
no specific
ACTH
seldom px’s life is endangered but chronic episode is disconcerting
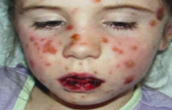
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME
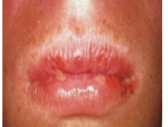
ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANE
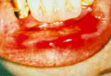
STOMATITIS VENENATA
DERMATITIS VENENATA
CONTACT DERMATITIS
CLINICAL FEATURES:
itching/burning sensation at site of contact → erythema → vesicle
if chronic: skin becomes thick and dry
ETIOLOGY:
dental or cosmetic preparations
dental materials
dental therapeutic agents
ORAL MANIFESTATIONS:
secondary infection is common
small vesicles form but transient and soon rupture to form erosions
TREATMENT:
discontinue contact with the offending material

STOMATITIS MEDICAMENTOSA
DRUG ALLERGY
DRUG IDIOSYNCRASY
DERMATITIS MEDICAMENTOSA
CLINICAL FEATURES:
skin lesions
fever
lymphadenopathy
ORAL MANIFESTATIONS:
common in gingiva, lips, palate, tongue
gingival lesion similar to ANUG
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS:
antihistamine
abstinence of particular drug involved
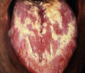
PEMPHIGUS
CLINICAL FEATURES:
equal distribution of occurrence in males and females
common among Jewish persons
HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES:
loss of cohesiveness between epithelial cells, because of this, clamps of epithelial cells called Tzanck cells are found
ETIOLOGY:
unknown
ORAL MANIFESTATIONS:
severe pain
profuse salivation
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
1. erythema multiform
2. bullous lichen planus
TREATMENT:
steroid and antibiotic (for secondary infection)
corticosteroids
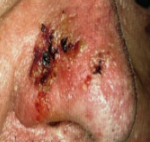
PEMPHIGUS VEGETANS
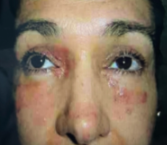
PEMPHIGUS FOLLACEUS
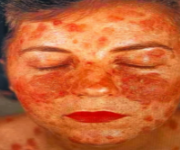
PEMPHIGUS ERYTHEMATOSUS OR SENEAR-USHER SYNDROME
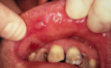
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS