Stereoisomerism and Chirality
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
conformations
different 3D shapes a molecule can adapt by rotating around single (sigma) bonds—-no bonds are broken
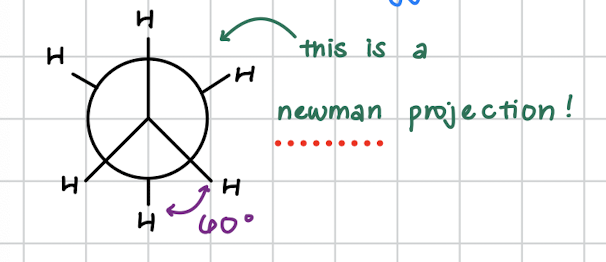
newman projections
look. atconformation sby looking straight down the bond axis
staggered conformation
H atoms are as far apart as possible
minimal electron repulsion
most stable conformation
all negihtboring H atoms are at 60 degrees
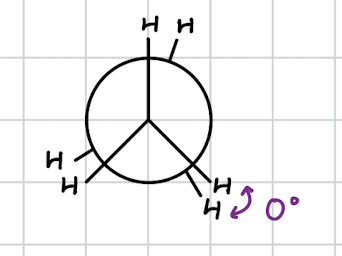
eclipsed conformation
hydrogen overlap when viewed down the bond
increased electron repulsion
less stable
all neighboring Hydrogen atoms are aligned
What conformation (staggered and eclipsed) is high energy vs. low energy?
Spaced (staggered)
Lies (low)
Ease (energy)
Eavesdropping (eclipsed)
Heats (high)
Everything (energy)
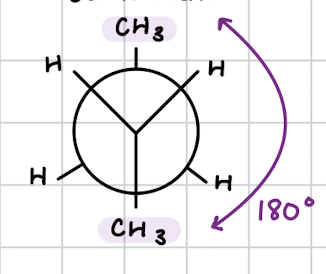
anti-conformation
form of staggered conformation
groups are opposite (180 degrees apart)
most stable
THINK: “distance makes the heart grow fonder”
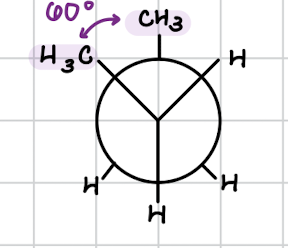
gauche conformation
form of staggered conformation
groups are next to each other
less stable because of steric hindrance
steric hindrance: slowing down/prevention of a chemical reaction because of bulky or crowded molecules involved
groups are 60 degrees apart
eclipsed
groups align
very high energy
0 degrees apart
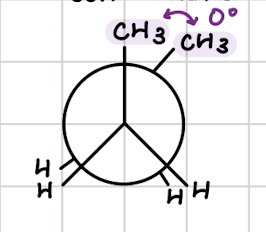
chair conformation
most stable in molecules like cyclohexane
no angle strain or torsional strain
angle strain: increase in potential energy in a molecule because of bond angles deviating from ideal values
torsional strain:: increase in energy in a molecule because of repulsion between electron clouds which are separated by 3 bonds
occurs when in eclipsed conformation
substituents are axial (up and down) or equatorial (around the belt)
THINK: if you’re in a chair, you have no discomfort and are just chilling
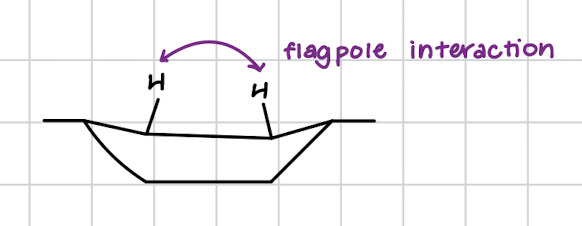
boat conformation
hydrogens clash and there are flagpole interactions
less stable in molecules like cyclohexane
THINK: if you were squeezed in a boat, you’d be rocking back and forth and uncomfortable
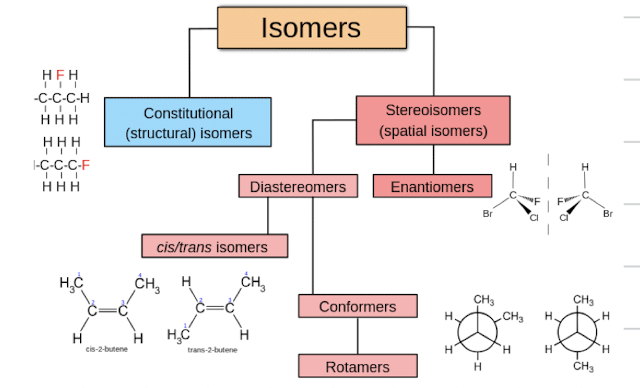
constitutional isomers
same molecular formula but are connected differently
THINK: fraternal twins who wear same outfits but go to different clubs (chess vs. nightclub)

stereoisomers
same formula and same connections but different arrangements in 3D space
THINK: identical twins everyone mixes up—until they talk. One’s bubbly and the other is emo
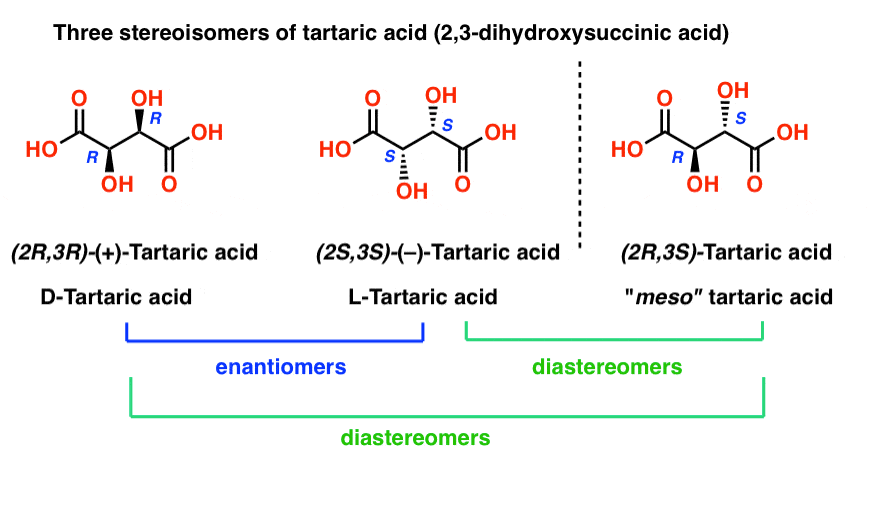
what are the 2 main types of stereoisomers?
enantiomers and diastereomers
enantiomers
a pair of molecules that are mirror images of each other but can’t be placed on top of each other
same everything but opposite vibes
R spins right
S spins left
have identical physical properties (melting point and boiling point)
differ in ways they interact with chiral things (enzymes, receptors, light)
THINK: can’t tell them apart until they enter a chiral club—one stands in line and other is VIP
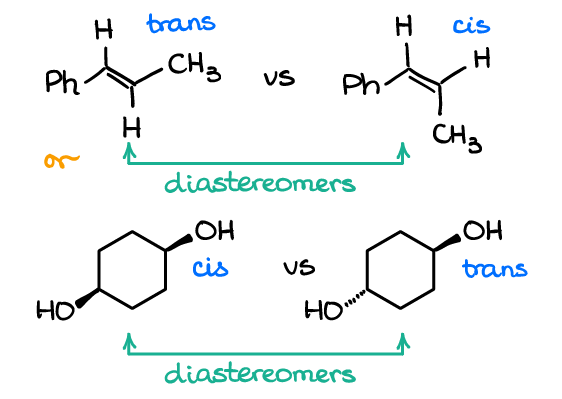
diastereomers
same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangements
have different properties
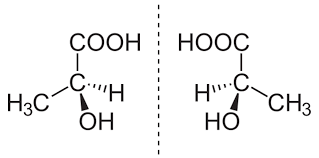
meso compounds
has a stereocenter but isn’t chiral because of internal symmetry
what is the family tree of isomers and how are they all related?
chiral center
(aka a stereocenter) a carbon bonded to 4 different groups
makes 2 non-superimposable mirror images
checklist for knowing if it is a chiral center
Is it bonded to 4 other atoms/groups?
Are all 4 groups different?
Is it sp³ hybridized? (aka only has single bonds?)
Is there no symmetry surrounding it?
If all are true, it is a chiral center and is asymmetric
What is not a chiral center?
Carbon in double bond or triply bond (sp² or sp)
Carbon bonded to 2 of same group
Carbon In a symmetrical environment