describe the role of micro-organisms in disease (TEAS 7)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
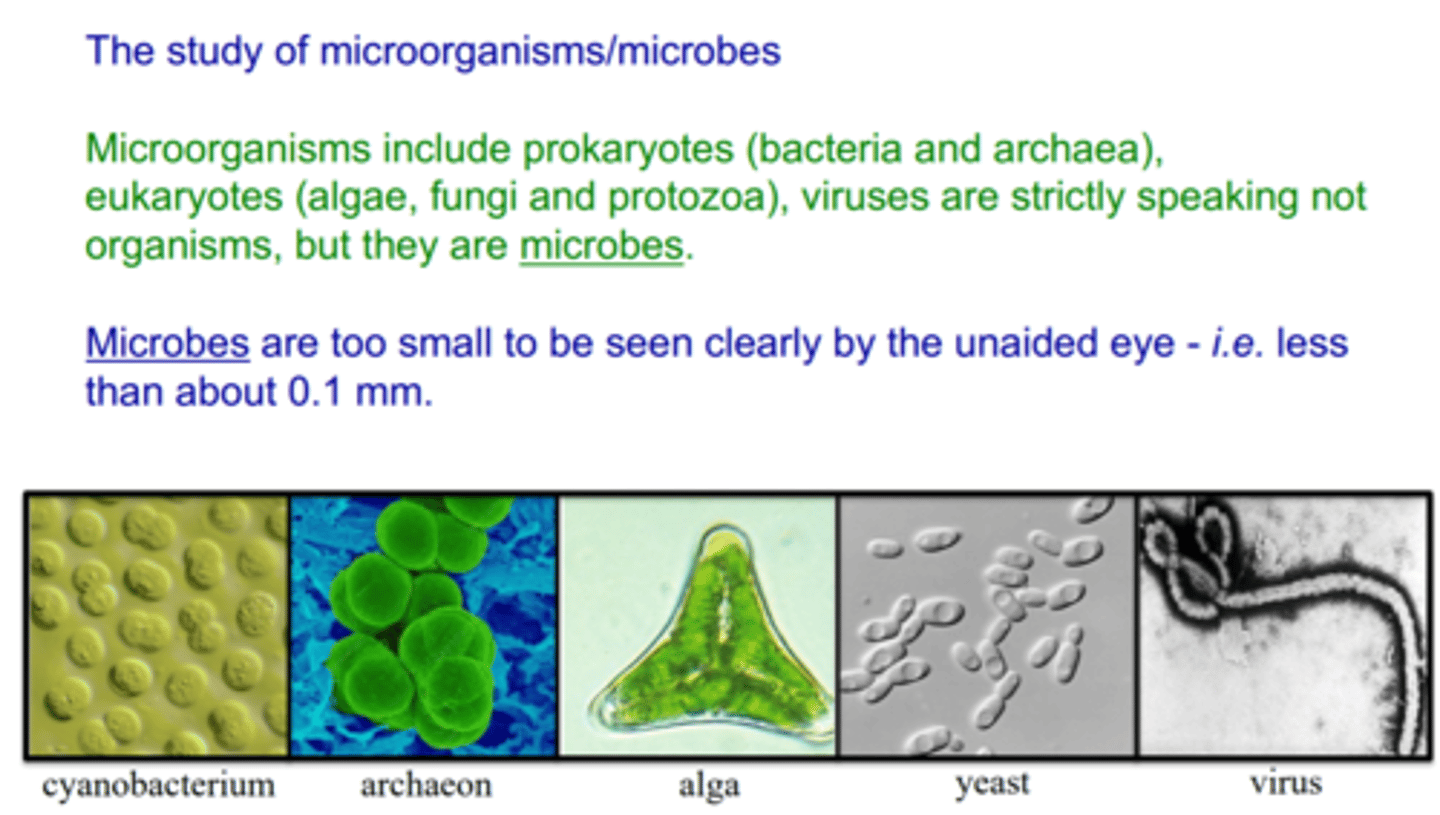
Microbes (microorganisms)
organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye and may be classified as bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa (including algae), or animals
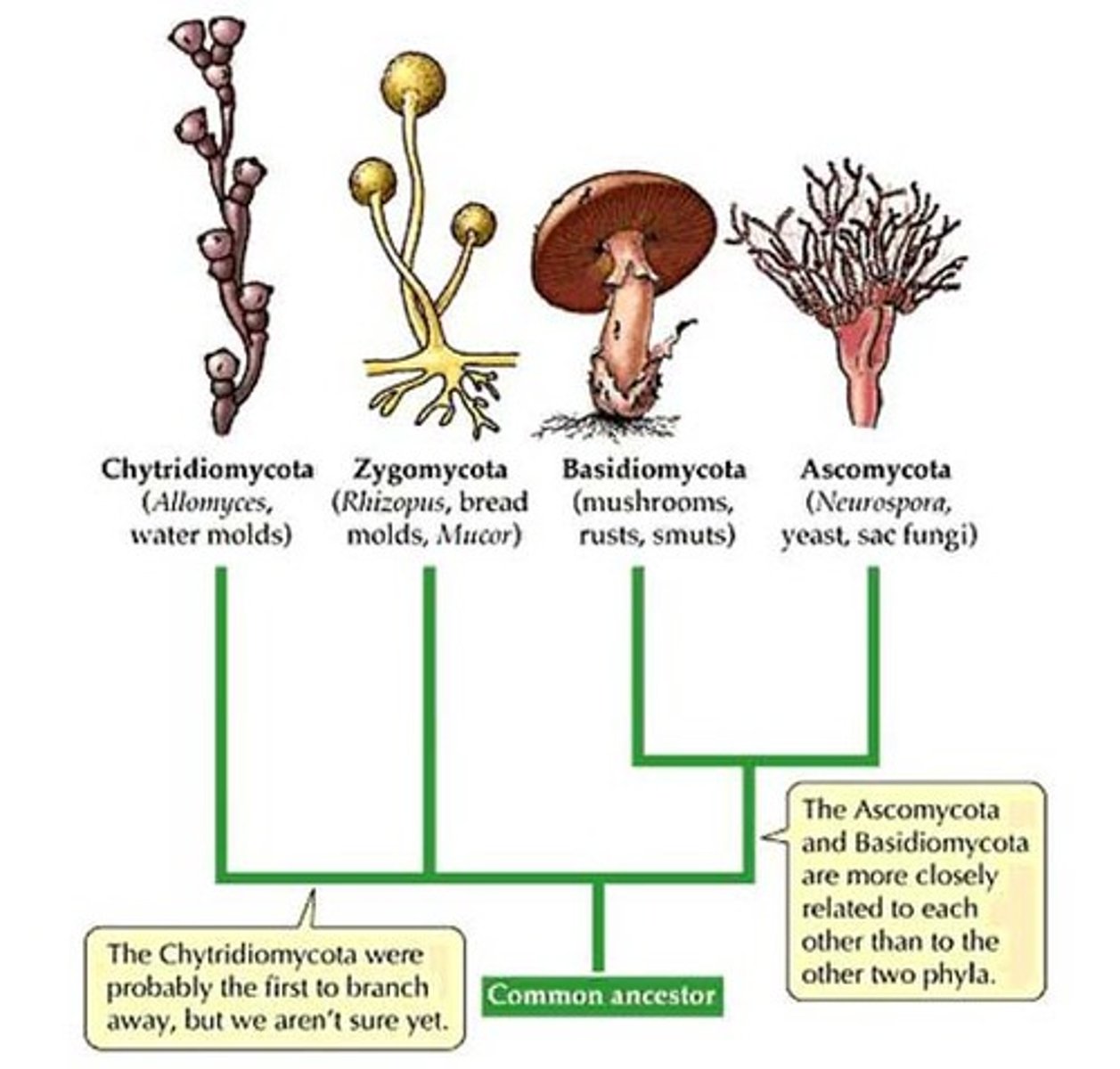
fungi
eukaryotic organisms obtain nutrients by absorbing material from their environment (decomposer) through symbiotic relationships with plants or harmful relationships with a host.
infectious/communicable disease
diseases that spread from one person to another; caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and protazoans.
example: cholera, chickenpox, and COVID-19
noninfectious disease/noncommunicable disease
A disease that cannot spread from one individual to another
examples: non-infectious diseases are diabetes, cancer and asthma.
protozoans/protists
unicellular aerobic eukaryotes. they are the largest group of organisms in the world in terms of numbers, biomass, and diversity.
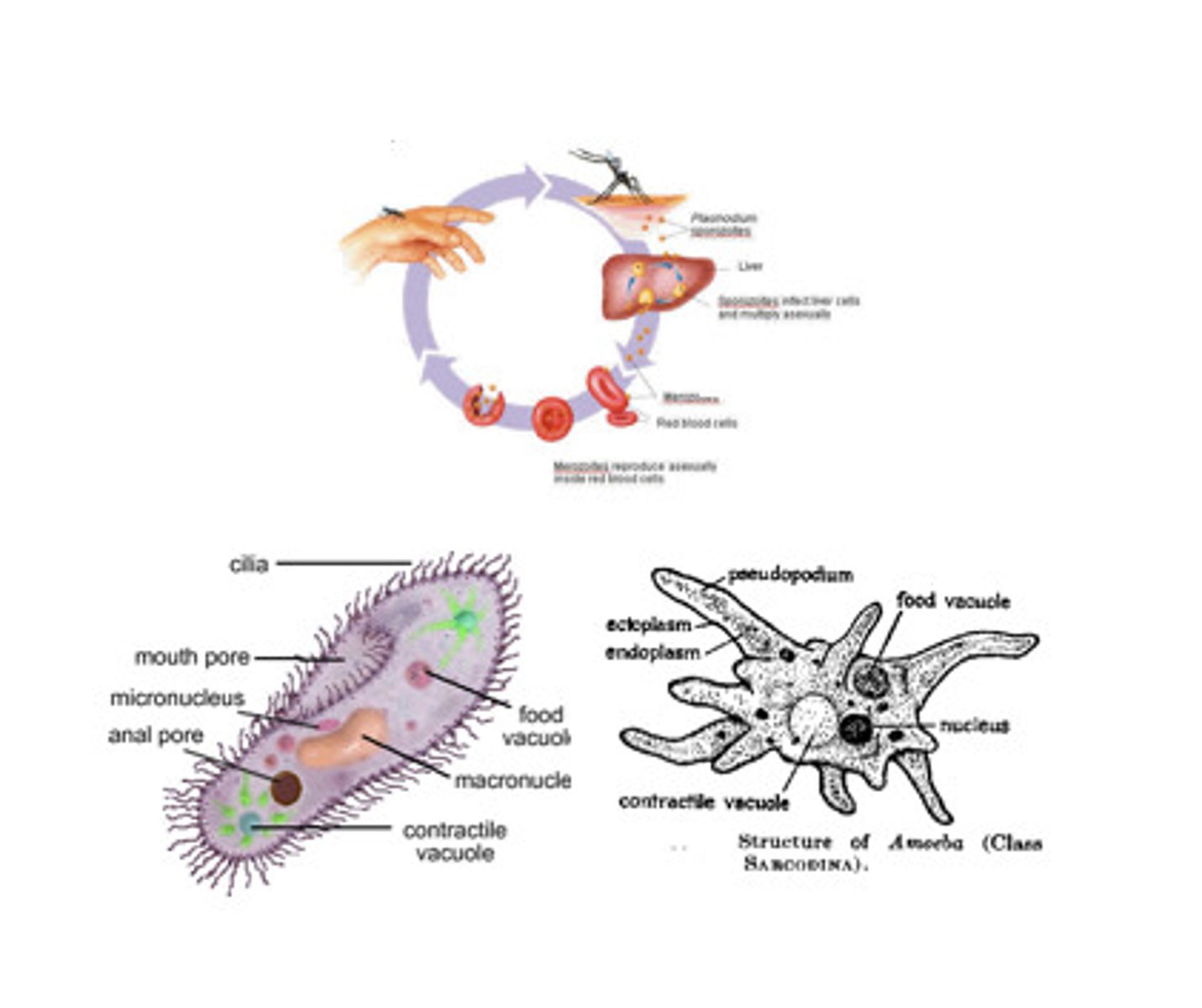
parasites
microbes that are not free-living and must find a host from which to gain nutrients
host
a larger organisms on whose body a parasite lives.
pathogen
an infectious agent
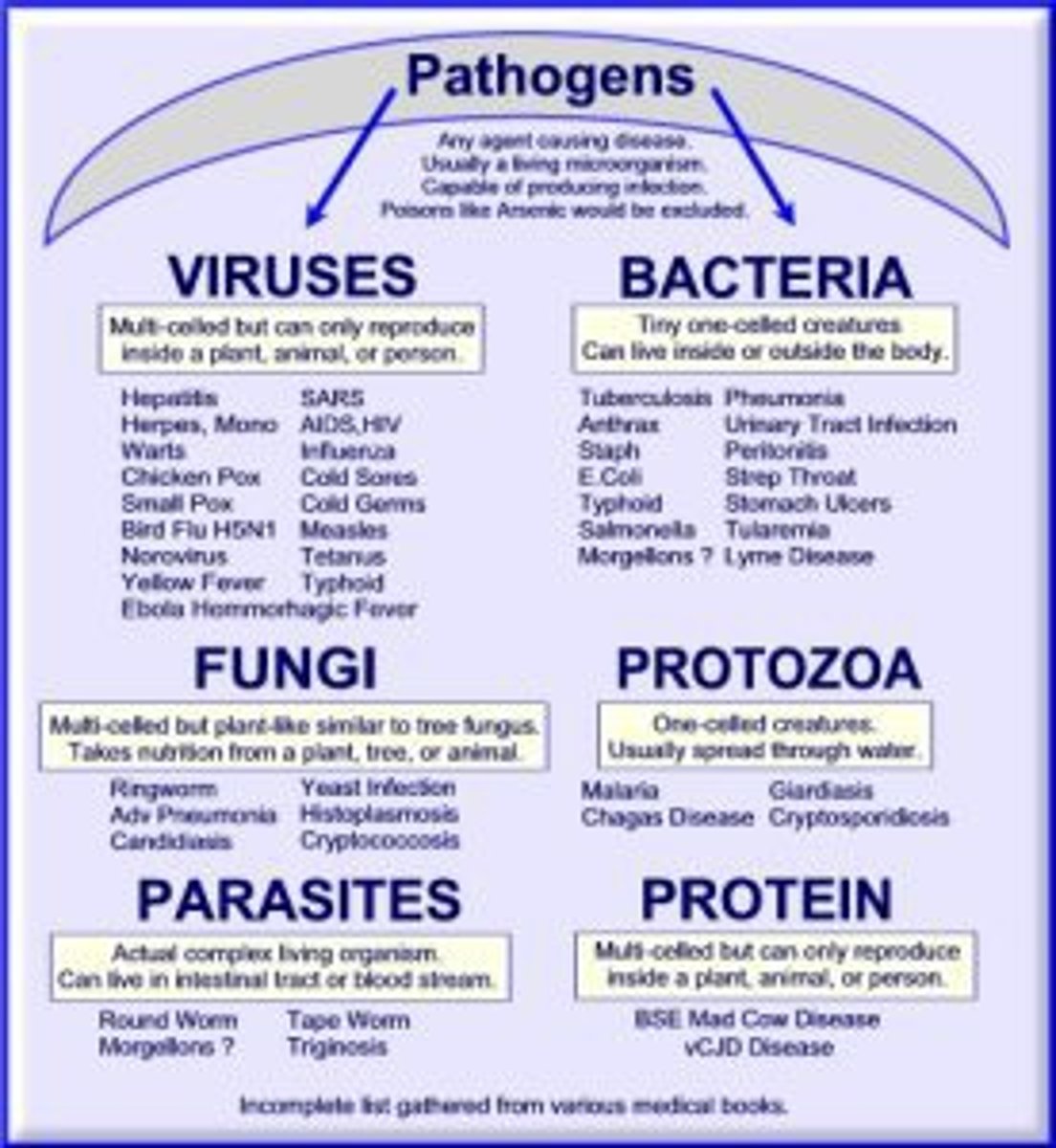
microorganisms are beneficial in producing
oxygen, decomposing organic material, providing nutrients for plants, and maintaining human health.
Bacteria
are unicellular organisms capable of causing diseases such as tuberculosis, meningitis, food poisoning, and many more.
-they are prokaryotic because they lack a nucleus

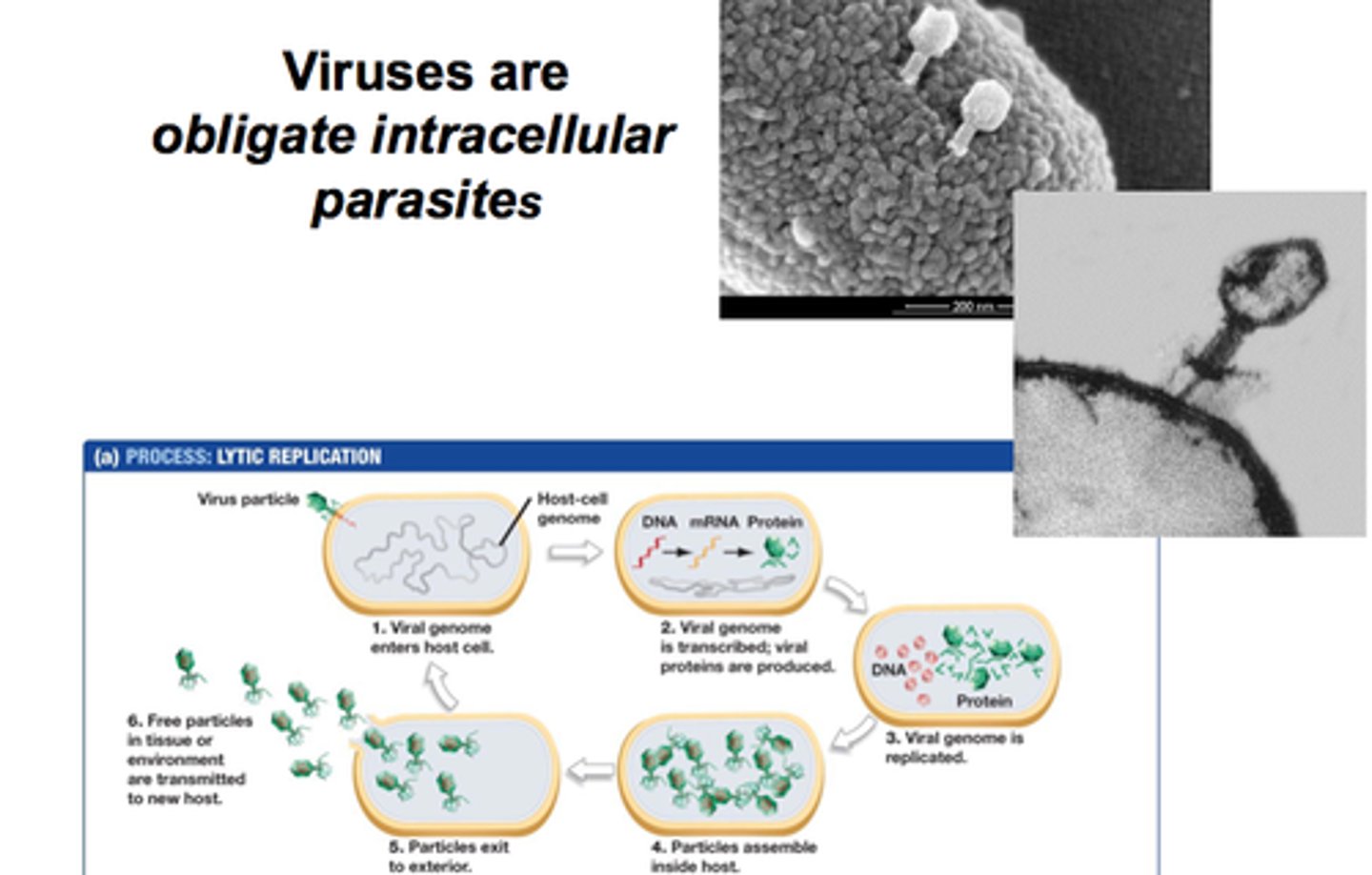
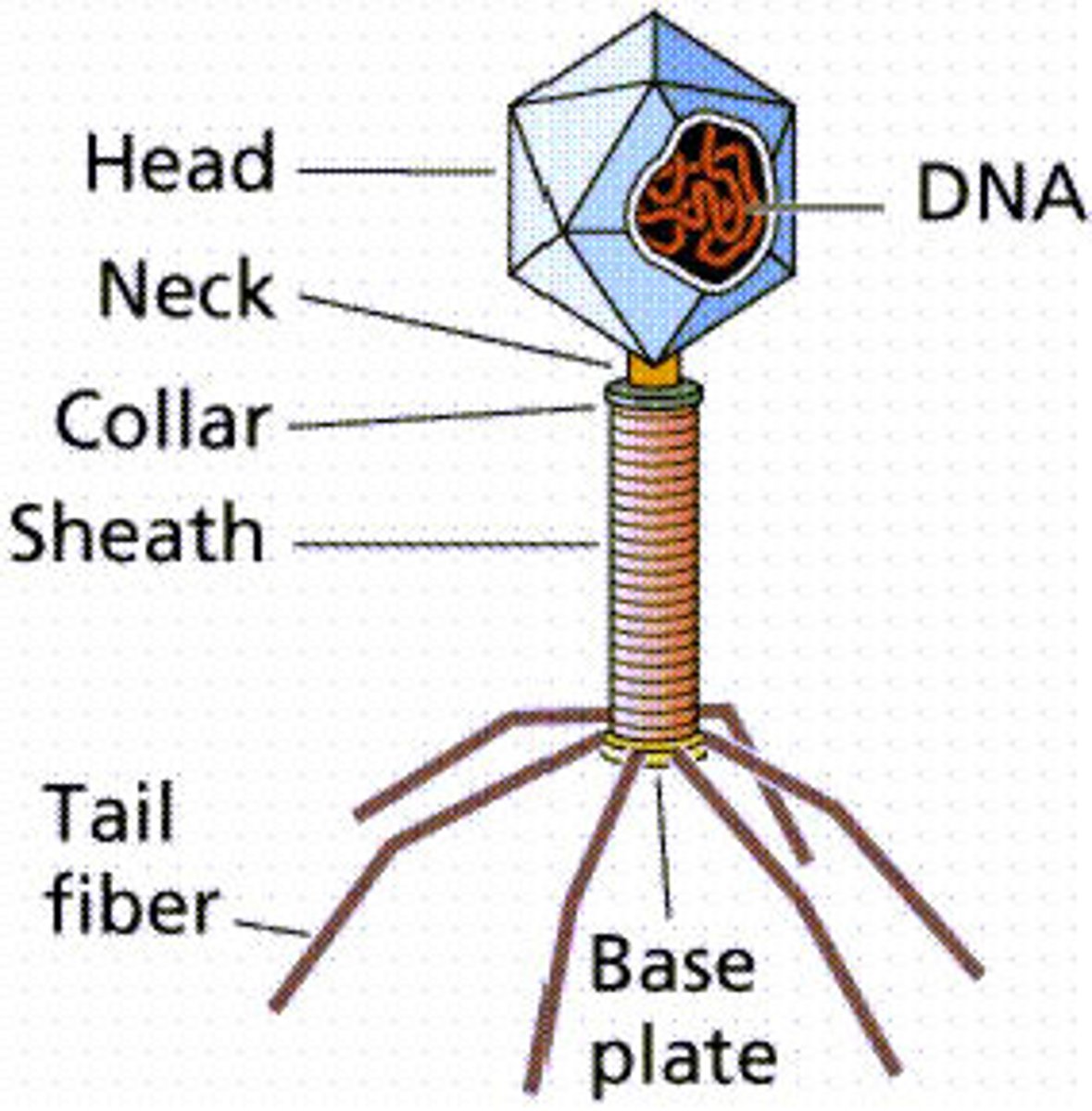
viruses
are noncellular entities that consist of a nucleic acid core (DNA and RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
examples: influenza, measles, mumps, HIV, and COVID-19
animals such as
parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large enough for people to see with the naked eye, and they can live in many areas of the body.
example: flatworms (tapeworms) and roundworms
electron microscope
a magnification instrument that forms an image using a beam of electrons that travel at high speeds and form wavelike patterns.
