Unit 6 Micronutrients
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
B vitamins
Essential nutrients that act as coenzymes in energy metabolism or amino acid metabolism.
Thiamin (B-1) Food Sources
Pork, legumes, whole grains, enriched cereals, sunflower seeds

Thiamin Deficiency
Beriberi
Riboflavin Deficiency
Inflammation of the mouth & tongue; cracks at corner of mouth
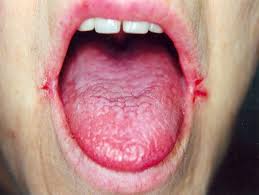
Riboflavin (B-2) Food Sources
Dairy, eggs, and leafy greens

Why is milk not packaged in clear containers?
Because riboflavin is broken down when exposed to light.
Niacin (B-3) Food Sources
Meat, fish, and poultry, enriched grains

Niacin Deficiency
Pellagra
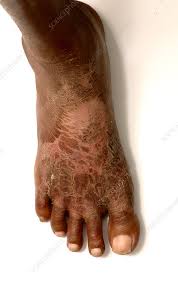
Niacin Toxicity
Flushing of skin
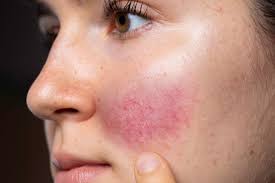
Pyridoxine (B-6) Food Sources
Animal proteins, potatoes, spinach, bananas, avocados, fortified cereals
Pyridoxine Deficiency
Dermatitis, anemia, convulsions, confusion, & depression
Pyridoxine Toxicity
Only from supplements - skin lesions & irreversible nerve damage
Folate Food Sources
Leafy green veggies, liver, legumes

Folate Deficiency
Anemia & Neural tube defects
What can high dose folic acid supplements mask?
B-12 deficiency
What is folic acid?
Synthetic form of folate, available in supplements
The highest folic acid dose is recommended for whom?
Early pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects

Cobalamin (B-12) Food Sources
Animal foods, fortified cereals
Cobalamin Deficiency
Pernicious anemia due to decreased intrinsic factor & Neurological symptoms (loss of concentration/memory; tingling)

What does intrinsic factor do with B-12?
Allows for B-12 to be absorbed
Vegans are at higher risk for what deficiency?
Cobalamin (B-12)
Can the body store B-12 even though it’s water soluble?
Yes! It’s stored in the liver, so it can take quite a while for a deficiency to reveal itself.
Pantothenic Acid
B Vitamin found in various foods
Pantothenic Acid Deficiency
Rare; weakness, fatigue, GI issues
Biotin Deficiency
Rare - dermatitis, conjunctivitis, hair loss, nervous system issues
Choline Food Sources
Eggs, meat, fish, milk

Choline
Vitamin-like substance
Choline Function
Precursor for acetylcholine (neurotransmitter)
Choline Toxicity
Fishy body odor
Iodine Chemical Symbol
I
Iodine Food Sources
Iodized salt, saltwater fish, seaweed

Iodine Function
Thyroid hormone synthesis
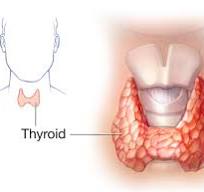
Iodine Deficiency
Goiter; Cretinism
Iodine Toxicity
Inhibits thyroid function
Chromium Chemical Symbol
Cr
Chromium Food Sources
Eggs, liver, whole grains, beans, meats, dark chocolate
Chromium Function
Enhances insulin action (blood glucose regulation)
Chromium Deficiency
Glucose intolerance, nerve damage, weight loss
Manganese Chemical Symbol
Mn
Manganese Food Sources
Nuts, legumes, whole grains, leafy greens, coffee, tea
Manganese Function
Cofactor in metabolism & antioxidant systems
Manganese Deficiency
Poor growth, skeletal abnormalities, impaired metabolism
Manganese Toxicity
Nervous system disorders (stiffness, tremors)
Sulfur Chemical Symbol
S
Sulfur Food Sources
Protein food sources (sulfur is part of some amino acids)
Sulfur Function
Stabilizes protein structure; acid-base balance