Bio Chapter 7 - Cell Functions
Lesson 7.1 - Intro To Cellular Life
Study - New Technology allowed people to study the ==movement== and ==structure== of cells
Microscopes:
- Electron microscopes reveal details @@1000 times bigger@@ than visible in light microscopes
- Transmission electron microscopes are used to show cell structure and large protein molecules. Electrons go through and need to be %%cut into slices%%
- Scanning ^^electron^^ microscopes ^^create 3D images^^. Electrons bounce off of and ^^do not have to be cut^^ into small slices
Prokaryotes + Eukaryotes:
- Types of ==Cells== Include:
- Bacteria, @@plants@@, animals, fungi, protists
- All Cells Include:
- Cell Membrane
- %%Cytoplasm%%
- ^^Ribosomes^^
- ==DNA==
- @@Prokaryotes@@:
- Genetic material not contained
- No %%membrane-bound organelles%%
- ^^Smaller^^ than eukaryotic cells
- ==Bacteria==
- @@Eukaryotes@@:
- DNA is stored in the nucleus
- %%Long%% and %%complex%%
- Contain ^^dozens of structures and internal membranes^^
- Highly ==specialized==
- @@Plants, animals, fungi, protists@@
- Discovery of Cells
- %%James Hooke%% coined the term “cell”
- He was attempting to study ^^cork^^
- Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek observed microorganisms in ==pond water under a microscope==
- Matthias Scheider concluded that all plant tissue is made of cells and that cells are a @@basic unit of life@@
- Theodore Schwann concluded that all animal tissue is made of cells
- %%Properties%% of Cells/Cell Theory
- All organisms consist of ^^1 or more cells^^
- Cells are the ==basic unit of life== and ==structure== of all organisms
- All cells come from @@preexisting@@ cells
Lesson 7.2 - Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Eukaryotic Cell Structures:
- Organelles: %%Preform cell functions%%
- 2 Parts: ^^Nucleus + Cytoplasm^^
- Cytoplasm is ==outside the nucleus==
@@Plant@@ Cell:
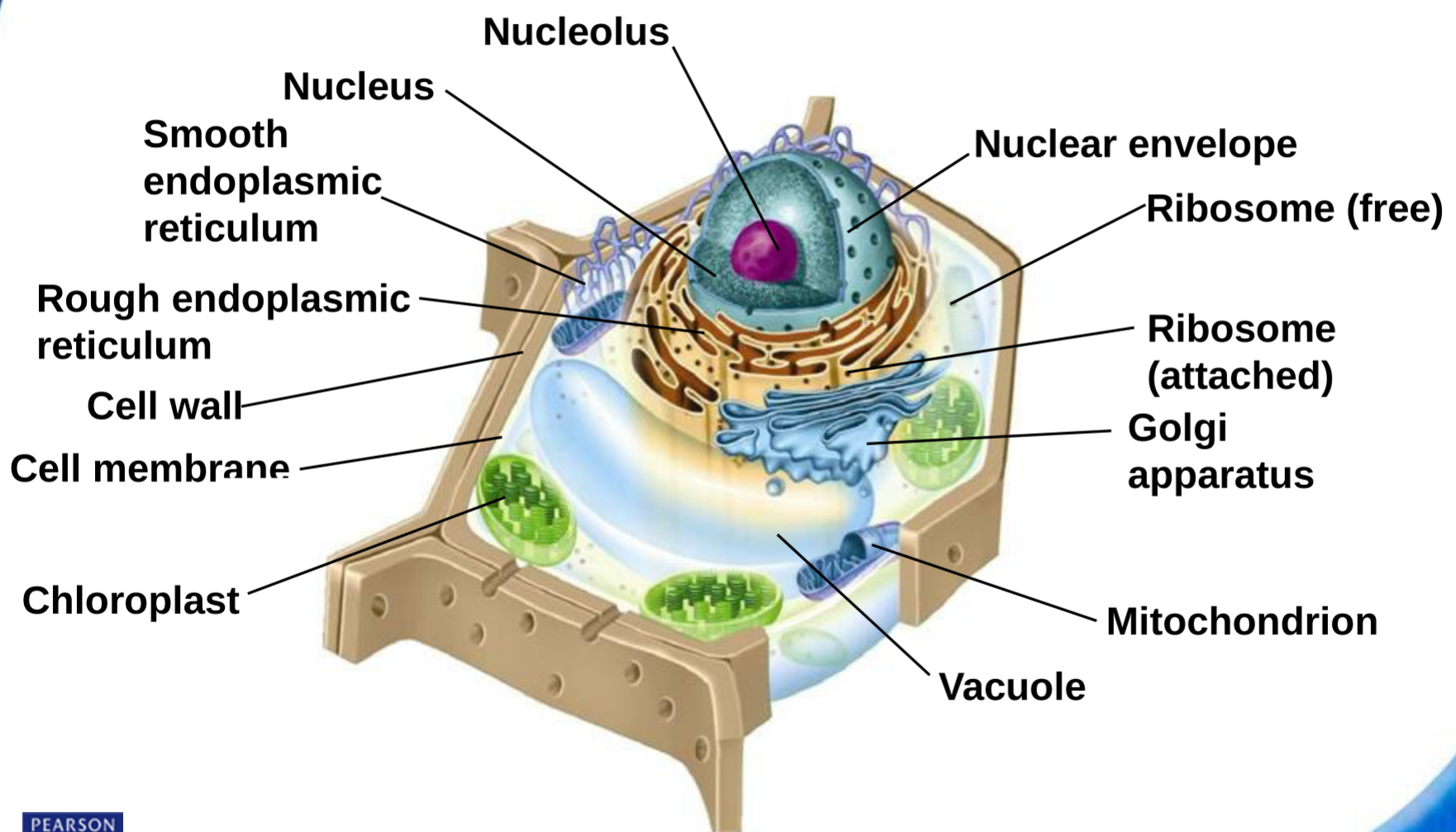
Animal Cell:
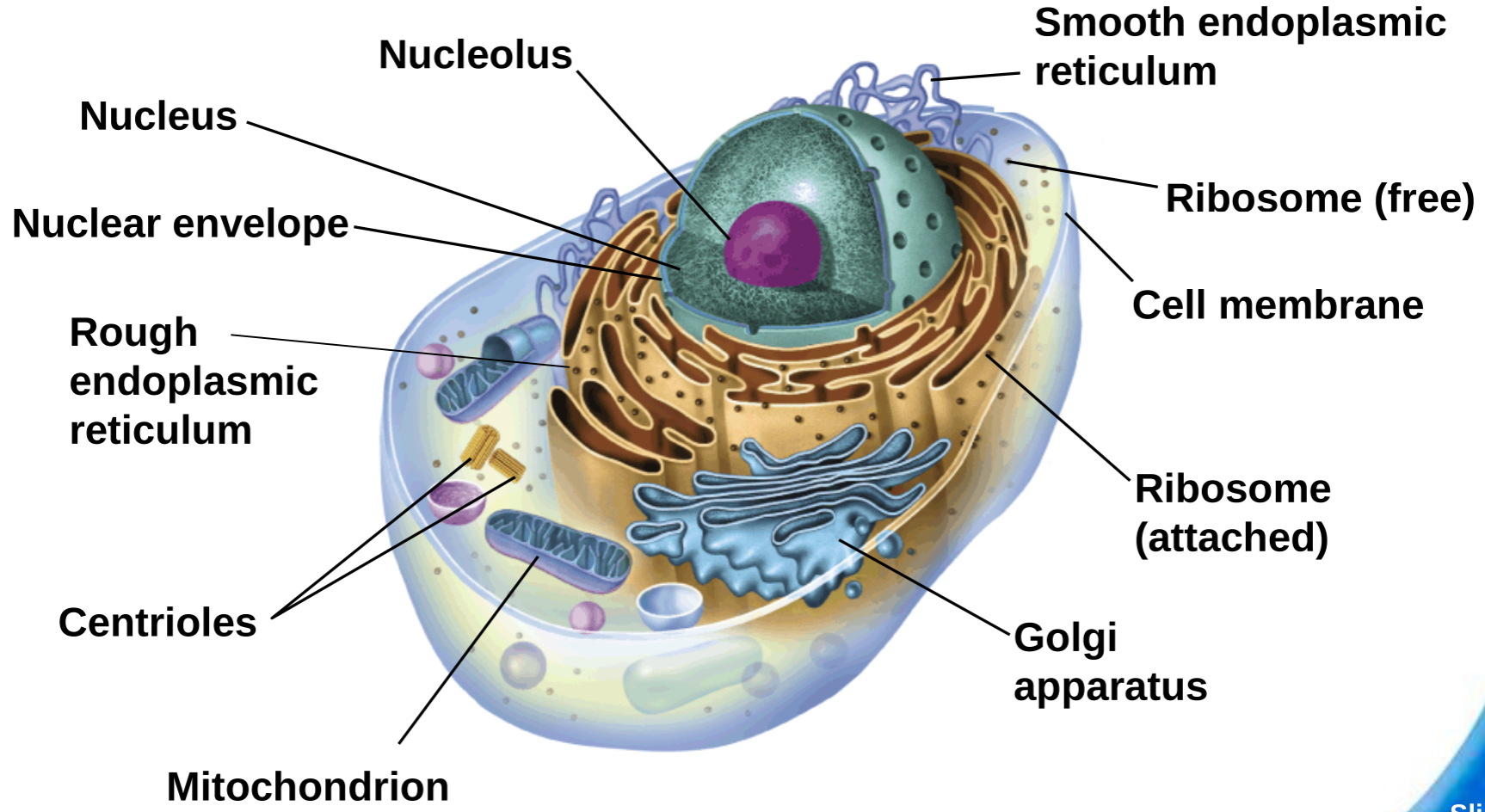
%%Endomembrane%% System:
- Nucleus - ^^Holds instructions^^
- Ribosomes - ==Build==
- ER - @@Shape@@
- Golgi - Modify/Sort/Package
- Vesicles - %%Ships%%
^^Nucleus^^:
- ==Control== center
- Holds @@instructions for making proteins@@
- Surrounded by 2 nuclear envelopes
- Envelopes contain %%pores that only RNA can pass through%%
- Granular material in the nucleus - ^^Chromatin^^
- Chromatin - ==made of RNA and protein==
- When a cell divides, @@chromatin condenses to become chromosomes@@. These contain @@genetic info@@
- The nucleolus only holds info to make more ribosomes
%%Ribosomes%%:
- Small particles of ^^RNA and protein^^ found ^^freely throughout the cytoplasm^^
- Create proteins in “==Protein Synthesis==”
- Follow @@instructions from the nucleus and RNA@@
ER:
- %%Rough%% ER (%%Part of protein synthesis%%) + %%Smooth%% ER (%%Not%% part of protein synthesis)
- ^^Ribsomones^^ on Rough ER are ^^found on the surface^^
- ==Rough== ER - ==Proteins are assembled== on ribosomes
- @@Smooth@@ ER- Creates @@lipids@@ and @@detoxifies@@ drugs
Golgi Apparatus:
- Proteins are %%moved from ER to Golgi%%
- ^^Modifies, Sorts, and Packages^^ proteins
- Sends to ==vesicles== which send to their ==necessary location==
Making @@Proteins@@:
- Nucleus
- Nuclear %%Pore%%
- ^^Ribosome^^
- ==Protein==
- @@Rough@@ ER
- Golgi Body
- %%Vesicle%%
- Cell ^^Membrane^^ + to a ^^new location^^
- ==Lysosomes==:
- Small @@organelles filled with enzymes@@
- Break down lipids, carbs, and proteins into things that can be used by the rest of the cell
- %%Breaks down organelles%% that %%no longer have a use%%
- ^^“Trash/Recycle”^^
- ==Vacuoles==:
- @@Saclike@@ structures
- Store water, salts, proteins, and carbs
- Holds %%pigments + toxins as defense mechanisms%%
- In ^^plant^^ cells - the ^^central vacuole is filled with liquid^^ that is used for ^^photosynthesis^^ + helps the ^^plant stand upright^^
- ==Unicellular== Organisms - ==filled with water== and have a ==pump to help from exploding==
- @@Mitochondria@@:
- Convert energy from food into compounds that can be used more conveniently by the rest of the cell
- Enclosed by %%2 membranes%%
- More ^^folds^^ = more ^^surface area^^ = more ^^energy^^ = more ^^ATP^^
- ==Choloplasts==:
- Capture @@energy from the sun@@ and @@convert it into chemical energy@@
- Photosynthesis
- Surronded by %%2 membranes%%
- Contain ^^chlorophyll^^
- ==Cytoskeleton==:
- Gives @@eukaryotic cells their shape@@
- A network of protein filaments
- Also involved in %%cell movement%%
- ^^Microfilaments^^:
- ==Thread-like== structures made of the ==protein actin==
- Make @@extensive networks in cells@@
- Make a tough, flexible framework that supports the cell
- Helps %%move cells%%
- ^^Microtubules^^:
- ==Hollow structures== that are made up of the ==protein tubulins==
- Help @@maintain cell shape@@
- Helps cells divide (mitosis+meosis)
- Build %%projections from the cell surface%% that enable %%cells to swim rapidly through liquids%%
- ^^Centrioles^^ are also formed from ^^tubulins^^
- These are ==located near the nucleus== and help ==organize cell division==
Lesson 7.3 - Cell Boundaries
All cells have a @@thin, flexible barrier@@ known as the @@cell membrane@@
Plants, fungi, bacteria + some protist cells also produce a stronger layer known as a cell wall
- The %%main function%% of the cell wall is to %%provide support and protection%% for the cell
- ^^No movement^^ - extra ^^padding^^
- Also ==attacks bacteria==
- Lies @@outside the cell membrane@@
- Porous enough to allow water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other substances to easily pass through
Cell %%Membrane%%
- Regulates what ^^enters and exits the cell^^
- Provides ==support and protection== for the cell
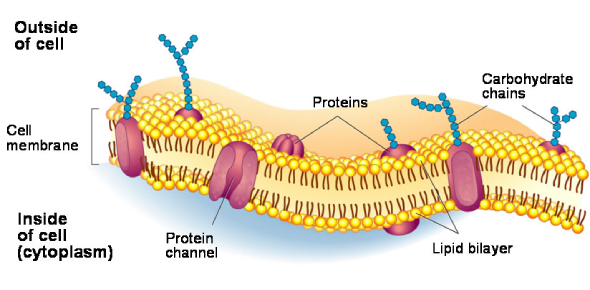
The composition of @@nearly all cell membranes@@ is made of a @@double-layered sheet@@ called a @@lipid bilayer@@
- Gives a flexible structure that forms a barrier between a cell and its surroundings
- Contains %%protein molecules%% embedded in the %%lipid bilayer,%% some of which have %%carb molecules attached to them%%
^^Diffusion^^ Through Cell Boundaries
- Every ==cell== lives in a ==liquid environment==
- The @@cell membrane regulates@@ the @@movement of diffusion@@ from the liquid on @@one side of the membrane to another@@
- Particles tend to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration
- This is the %%process of diffusion%%
- This will continue until a ^^state of equilibrium is reached^^
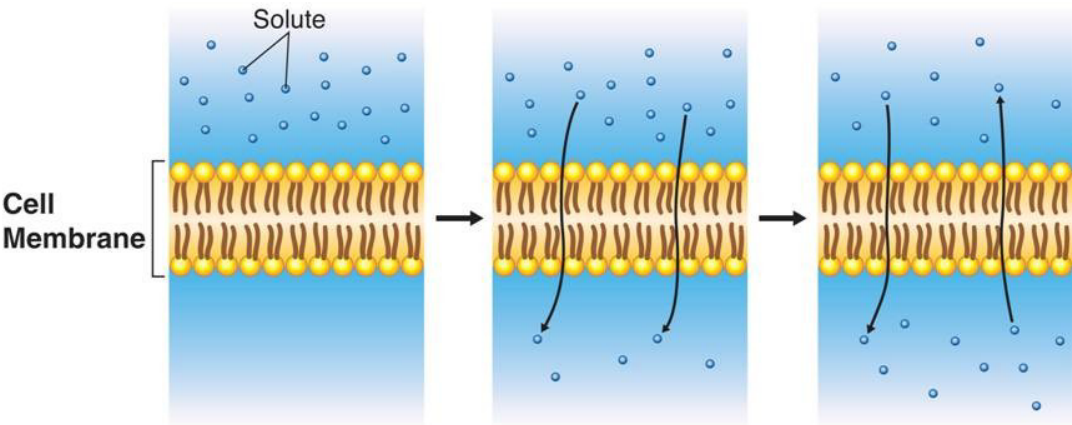
==Passive== Transport
- Depends upon @@random particle movements@@
- Substances diffuse across membranes without using energy
- This is called %%passive transport%%
^^Osmosis^^
- Diffusion of ==water== through a ==selectively permeable membrane==
- Water - @@solvent@@ - what is @@doing the dissolving@@
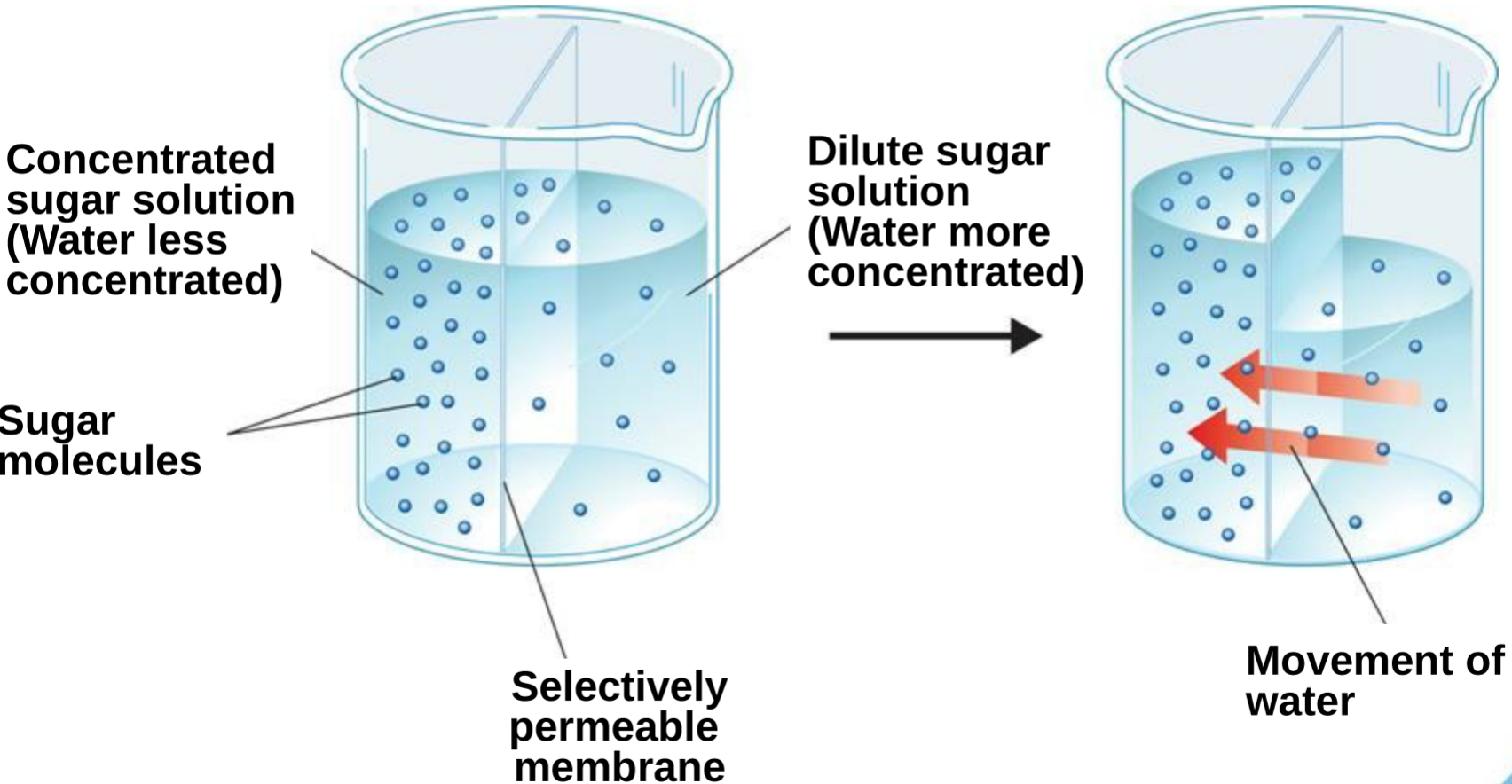
Levels of Concentration
- %%Water%% diffuses from %%areas of high to low concentration%%
- ^^More concentrated^^ solution - ^^Hypertonic^^
- Area of ==high concentration==
- Water with @@more sugar present@@
- Less concentrated solution - Hypotonic
- Area of %%low concentration%%
- Water with ^^less sugar present^^
- Water with ==equal parts sugar and water==
- @@Isotonic@@
- Osmosis is only concerned with water and its’ levels
- Particles %%never stop moving,%% as they must always %%work to maintain homeostasis%%
Osmotic ^^Pressure^^
- Occurs when ==water on the hypertonic side puts pressure on the membrane==
- The @@cell@@ is almost always @@hypertonic to fresh water@@
- If a cell has too much water, it is at risk of exploding or bursting (which leads to the death of the cell)
- Cells in %%large organisms%% and with %%cell walls%% are much %%less likely to burst%%
^^Facilitated^^ Diffusion
- Membranes contain ==integral proteins== that can ==assist in the movement of larger particles==
- The @@use of these proteins@@ is called f@@acilitated diffusion@@
- Protein channels are specific to certain particles only
- Ex. %%Glucose Transport%% - Only for %%glucose%%
- ^^Fast^^ and ^^Specific^^
- Still ==considered diffusion==
- Only occurs from @@high to low concentration@@
Active Diffusion
- Occurs when materials have to %%move from areas of low to high concentration%%
- ^^Against^^ the ^^concentration difference^^
- Requires ==energy==
- Ex. @@Stuffing things into a closet@@
Molecular Transport
- Small molecules are %%carried by proteins%%
- Allows movement from ^^low to high^^
- Requires ==energy==
@@Large Particle@@ Transport
- Occurs when particles are too large to be carried by proteins
- %%Active%% transport
^^Endocytosis^^
- Process of ==taking material into the cell by means of pockets of the cell membrane==
- A @@vacuole@@ is formed around the material that @@works to bring it into the cell@@
- This vacuole is from the cell membrane
%%Phagocytosis%%
- The ^^process of cytoplasm surrounding food^^
- This is then ==engulfed by the cell==
- Requires @@energy@@
- Collect
- Pinch Off
- Turns to Vesicle
- Engulfed by Cell
%%Pinocytosis%%
- The process of ^^cytoplasm surrounding waste^^
- This is then ==removed from the cell==
- Requires @@energy@@
- Collect
- Pinch Off
- Turns to Vesicle
- Released
%%Exocytosis%%
- The ^^release of waste from a cell^^
- Cell membrane ==fuses with waste from inside the cell==
- Then @@removes it from the cell@@
- Requires energy
Lesson 7.4 - Diversity of Cellular Life
- %%Unicellular%% Organisms
- Made of ^^only 1 cell^^
- ==Dominate life on Earth== because so ==many of them can fit== per any given space ==compared to multi==
- Includes: @@All bacteria@@ cells, @@certain eukaryotic organisms@@ (yeast + amebas)
- Multicellular Organisms
- Made of %%many cells%%
- ^^Great variety^^ in these cells
- Includes: ==All plant cells, all animal cells, most fungus cells, some protist cells==
- @@Specialized Animal@@ Cells
- Red blood cells transport oxygen
- Cells in the %%pancreas produce a protein%% (endomembrane systems)
- ^^Muscle^^ cells ^^allow for movement^^
- ==Specialized Plant== Cells
- Exchange @@carbon dioxide, oxygen, water vapor,@@ and other gases through @@stomata@@
- Guard cells surround the stomata and regulate the exchanges
- %%Levels%% of Organization
- ^^Individual^^ Cells - 1st level of organization
- ==Tissues== - ==Cells are grouped== and create these
- A @@group of similar cells that perform a particular function@@
- Organ
- Organ Systems
- Organism
- Ex. %%Muscle cell > Smooth muscle tissue > Stomach > Digestive System%%
- Types of ^^Tissue (Animals)^^
- ==Muscle - Moves==
- @@Skin - Epithelial@@
- Nervous - Neurons
- %%Connective - Ligaments/Cartlidge%%
- ^^Organs (Animals)^^
- Groups of ==tissues that work together to perform a specific function==
- Completes a @@series of specialized tasks@@
- Work together to create organ systems
- %%Nervous System%%
- %%Circulatory System%%
- %%Skeletal System%%
- %%Digestive System%%