final apes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
1
New cards
Specialists
advantage in habitats that remain constant
2
New cards
Generalists
advantage in habitats that are changing
3
New cards
K-selected species
large, few offspring, high parental care, long life spans
4
New cards
r-selected species
small, many offspring, minimal or no parental care, short life spans
5
New cards
Biotic potential
maximum reproductive rate of a population in ideal conditions
6
New cards
Most invasive species are this type
r-selected, generalists
7
New cards
Survivorship curve
graph that shows relative survival rates of a group of individuals of the same age
8
New cards
Type I survivorship
Low infant mortality, most individual die in old age. Typical of K-selected species.
9
New cards
Type II survivorship
Equal risk of death through the life span
10
New cards
Type III survivorship
High infant mortality, but those that survive live a long time. Typical of r-strategists.
11
New cards
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
12
New cards
overshoot
occurs when carrying capacity is exceeded. leads to resource depletion, causing famine, disease and/or conflict, and dieback of the population.
13
New cards
Things that limit population growth
available resources and space
14
New cards
Type of growth when resources are abundant
exponential growth
15
New cards
Type of growth when resources are limited
logistic growth
16
New cards
age structure diagram showing rapid growth
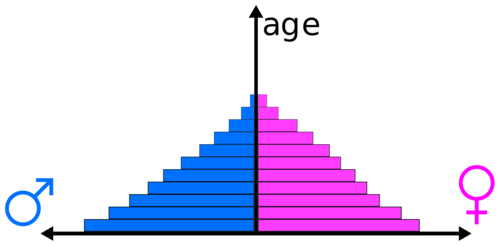
17
New cards
age structure diagram showing slow growth
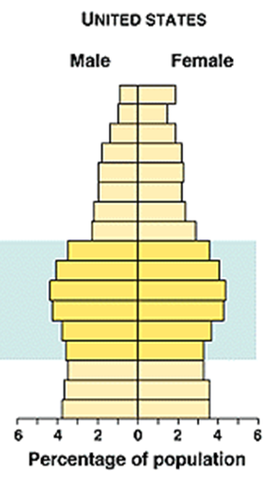
18
New cards
age structure diagram showing negative growth
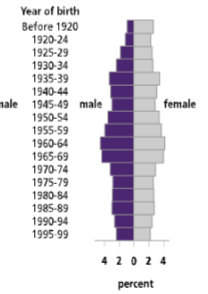
19
New cards
Total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
20
New cards
replacement fertility rate
the rate at which children must be born to replace those dying in the population (about 2.1 children per woman)
21
New cards
Factors affecting infant mortality
Prenatal and child healthcare, access to good nutrition
22
New cards
infant mortality
number of babies who die in their first year per 1000 live births
23
New cards
Factors that affect human population growth
birth rates, infant mortality rates, death rates, access to family planning, education, nutrition, and age at first marriage
24
New cards
Malthusian theory
The theory that population grows faster than food supply
25
New cards
Density independent limiting factors
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size (major storms, fires, heat waves, droughts)
26
New cards
density dependent limiting factors
limiting factor that depends on population size (access to clean water and air, food availability, disease transmission, territory size)
27
New cards
Doubling time of a population with 2% growth per year
35 years (use Rule of 70!)
28
New cards
Demographic transition
Industrialization of a country, and resulting transition from high birth and death rates in the preindustrial stage, to low birth and death rates in the post-industrial stage
29
New cards
Characteristics of less developed countries
high infant mortality rates, high TFR, more children in the workforce, more people dying of epidemic diseases
30
New cards
Characteristics of more developed countries
Strong economy, low TFR, low birth and death rates, more people dying of diseases of aging (diabetes, heart disease, cancer, etc.)
31
New cards
Demographic Transition Model
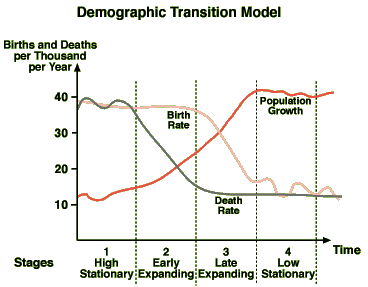
32
New cards
Equation to determine human impact
I = P x A x T
33
New cards
Population density
number of organisms per unit area
34
New cards
Population dispersion
how individuals are arranged in space - can be uniform, random, or clumped
35
New cards
Growth rate of a population of 1,000 that experiences 100 births, 90 deaths, 20 immigrants and 10 emigrants in a year
2% per year
36
New cards
Current human population on Earth
7.8 billion
37
New cards
A population has CDR = 7/1000, CBR = 19/1000, and net migration of 4/1000. What is the population of this country doing?
Growing/increasing
38
New cards
Carrying capacity of the Earth for humans
It depends on level of consumption per person
39
New cards
Major factor that limits food production on Earth for humans
There is only so much arable land on Earth, and some is being lost to erosion every year
40
New cards
Strategies for reducing TFR
education about and access to family planning, education and employment opportunities for women, eliminate government policies that reward having more children, encourage breastfeeding
41
New cards
Which of the following is an abiotic component? (choose all answers that apply)
c. A rock d. Rain
42
New cards
Which of the following is NOT true about ecosystems
They include no human components
43
New cards
Impacts of fracking include: I contamination of ground water, II increased use of coal, III lower natural gas prices
e. I & III only
44
New cards
There are 2.47 acres in 1 ha. How many acres are in 10 ha?
Selected: b. 24.7 acres
45
New cards
Common global scale environmental indicators include all of the following except
a. pollution in a local stream
46
New cards
A person's ecological footprint is
the land needed to support all of a person's activities
47
New cards
The first step in the scientific process is
a. observations and questions
48
New cards
If a device that measures water quality measures out 415ppm, 417ppm, 416ppm, 417ppm, and 415ppm in 5 trials and the target theoretical value is 400ppm, this device is:
a. precise, but not accurate
49
New cards
Challenges in the study of environmental science include all of the following except
d. dangers of studying natural systems
50
New cards
A control group is
A group with the same conditions as the experimental group except for the independent variable
51
New cards
Two atoms that are isotopes of one another have the same (select all that apply)
a. atomic symbol, \# of protons, atomic number
52
New cards
Which of the following is the most basic?
Bleach
53
New cards
Which of the following is not a macromolecule?
cell organelles
54
New cards
Which of the following is not an organic compound?
d. NaCl
55
New cards
Which of the following is not a property of water that allows it to support life?
b. High viscosity
56
New cards
The chemical bond that forms the attraction of sodium ions and chlorine ions in table salt is called
a. an ionic bond
57
New cards
A car traveling down the highway represents
c. kinetic energy
58
New cards
Which of the following will be most likely to return to a steady state after a disturbance?
c. A system with mostly negative feedback loops
59
New cards
Entropy is
c. randomness in a system
60
New cards
The concept of energy efficiency is used to quantify
c. the second law of thermodynamics
61
New cards
Ecosystem boundaries are
c. depend on many subjective factors
62
New cards
The average efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels is approximately
f. 10%
63
New cards
A giraffe is an example of
e. a primary consumer
64
New cards
Human construction of buildings and pavement affect the hydrological cycle by I. increasing runoff, II. increasing evaporation, III. increasing percolation
f. I & II only
65
New cards
Phosphorus
a. is a limiting nutrient in many aquatic systems
66
New cards
The net primary productivity of an ecosystem is
e. the energy captured after accounting for respiration
67
New cards
The largest carbon pool is found in
e. sedimentary rock
68
New cards
The intermediate disturbance hypothesis states that intermediate levels of disturbance will
d. increase species diversity
69
New cards
Which is a measure of how much a disturbance can affect the flows of energy and matter in an ecosystem?
c. Resistance
70
New cards
Which is not true about disturbances?
b. They occur only on short time scales
71
New cards
An ecosystem that rapidly returns to its original state after a disturbance is
a. Resilient
72
New cards
The precipitation line below the temperature line in a climate diagram (climatogram) shows
d. when plant growth will be limited by precipitation
73
New cards
A terrestrial biome is not defined by: I. annual precipitation, II. distrinctive animal species (fauna), III. distinctive plant species (flora)
b. II & III only
74
New cards
Permafrost (frozen soil) is an important factor in which of the following biomes?, I. Tundra, II. Boreal forest, III. Cold desert
c. I only
75
New cards
Which has an overall higher temperature? Seasonal or Tropical biomes?
d. Tropical
76
New cards
Most of the photosynthesis in lakes and ponds occurs in the
c. littoral zone
77
New cards
Aquatic biomes are categorized by which of the following? I. Dominant plant growth forms, II. Depth, III. Salinity
b. II & III only
78
New cards
Which biome contains the aphotic zone
b. Open ocean
79
New cards
Which of the following ecosystems experiences harsh conditions due to conditions from tides?
c. Intertidal zone
80
New cards
Which of the following is NOT an important ecosystem service provided by wetlands
b. seed dispersal
81
New cards
Two savanna communities both contain 15 plant species. In community A, each of the 15 species is represented by 20 individuals. In community B, 10 of the species are each represented by 12 individuals; the remaining 5 species are each represented by 3 individuals. Which statement best describes the two communities?
d. Community A has a higher species evenness
82
New cards
The change in the genetic composition of a population over time due to random mating is called
a. genetic drift
83
New cards
Which of the following processes create genetic diversity in a population? I. Mutation, II. Allele division, III. Recombination
a. I & III only
84
New cards
Phylogeny is
b. the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships
85
New cards
Which evolutionary effect results in reduced genetic variation in a community?
d. The founder effect
86
New cards
In a particular zoo, the population of spider monkeys has a higher proportion of individuals with light golden brown fur than spider monkeys in the wild. If the monkeys were recently captured from the wild and if fur color is largely determined by genetics, what evolutionary process is at work?
c. The founder effect
87
New cards
Which is the best definition of an adaptation?
c. A trait that improves an individual's fitness
88
New cards
Which of the following is often a cause of sympatric speciation?
a. Polyploidy
89
New cards
Which of the following would cause the most rapid evolution?
e. Artificial selection
90
New cards
The abiotic conditions under which a species can survive and reproduce is called its
b. fundamental niche
91
New cards
Which would be expected for a niche specialist?
a. A narrow fundamental niche
92
New cards
Which factors affect species richness (select all that apply)?
b. Latitude, Habitat size, d. Distance from other communities, e. Time
93
New cards
Which of the following is NOT typical of a keystone species
c. It is the least important species in a food chain
94
New cards
Resource partitioning
d. can occur through morphological differences between species
95
New cards
Which is true of primary succession?
c. It begins with colonization by algae, lichens, and mosses.
96
New cards
The process of succession in lakes without disturbance
a. results in a terrestrial ecosystem
97
New cards
Which is true of a population overshoot?
c. It is followed by a dieoff
98
New cards
An r-selected species characteristically has
d. a fast population growth rate
99
New cards
Which is true about a population's carrying capacity?
a. It depends on a limiting resource
100
New cards
The intrinsic growth rate of a population
c. only occurs under ideal conditions