AP Environmental Science (All Units)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Ecology
The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment.
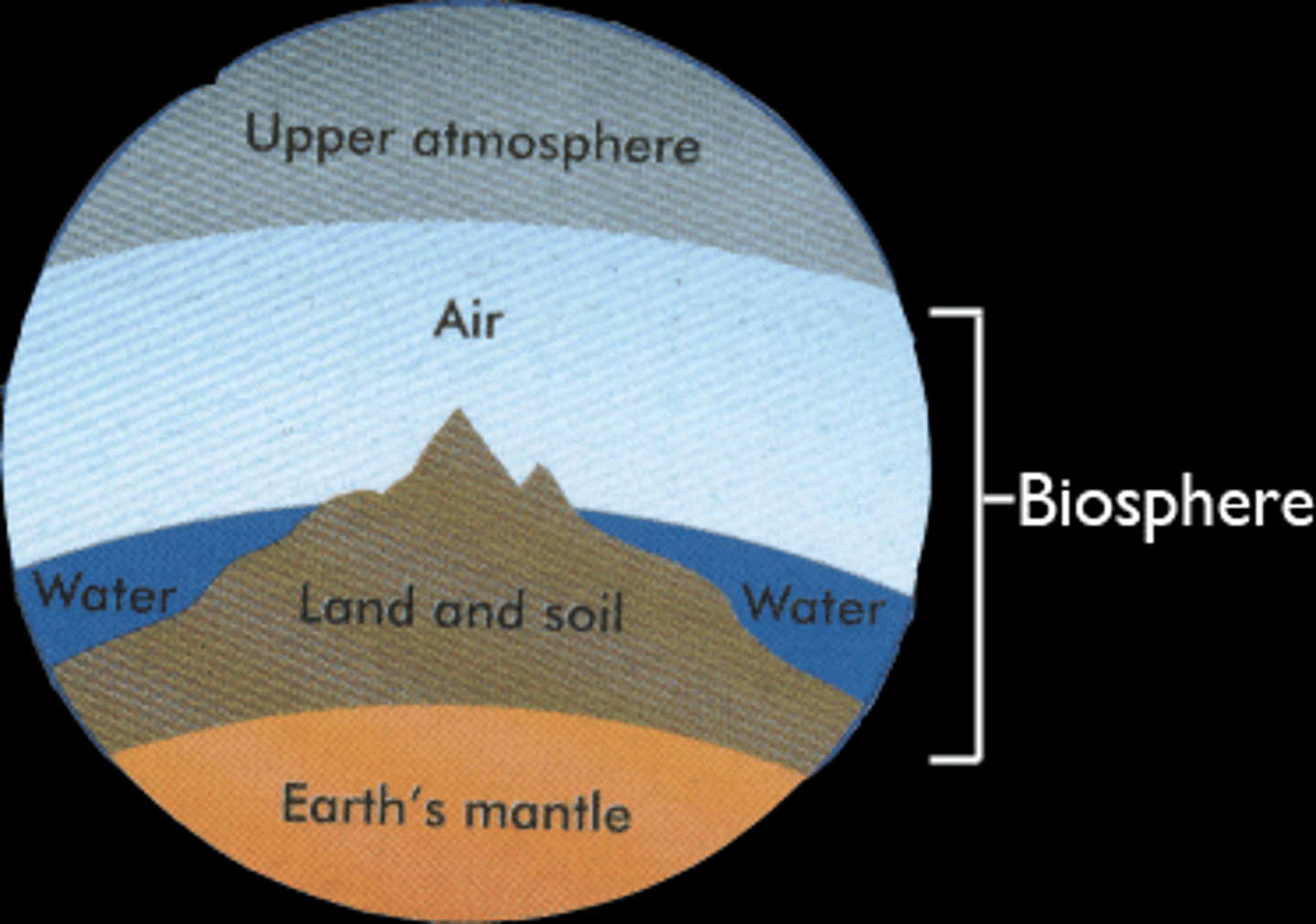
Biosphere
Parts of the earth's air, water, and soil where life is found.
Ecosystem
A community of different species interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment of matter and energy.

Community
The population of different species living in a particular place, and potentially interacting with each other.

Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a particular place.

Organism
An individual, living thing.

What are the three types of symbiotic relationship?
Mutualism.
Commensalism.
Parasitism.
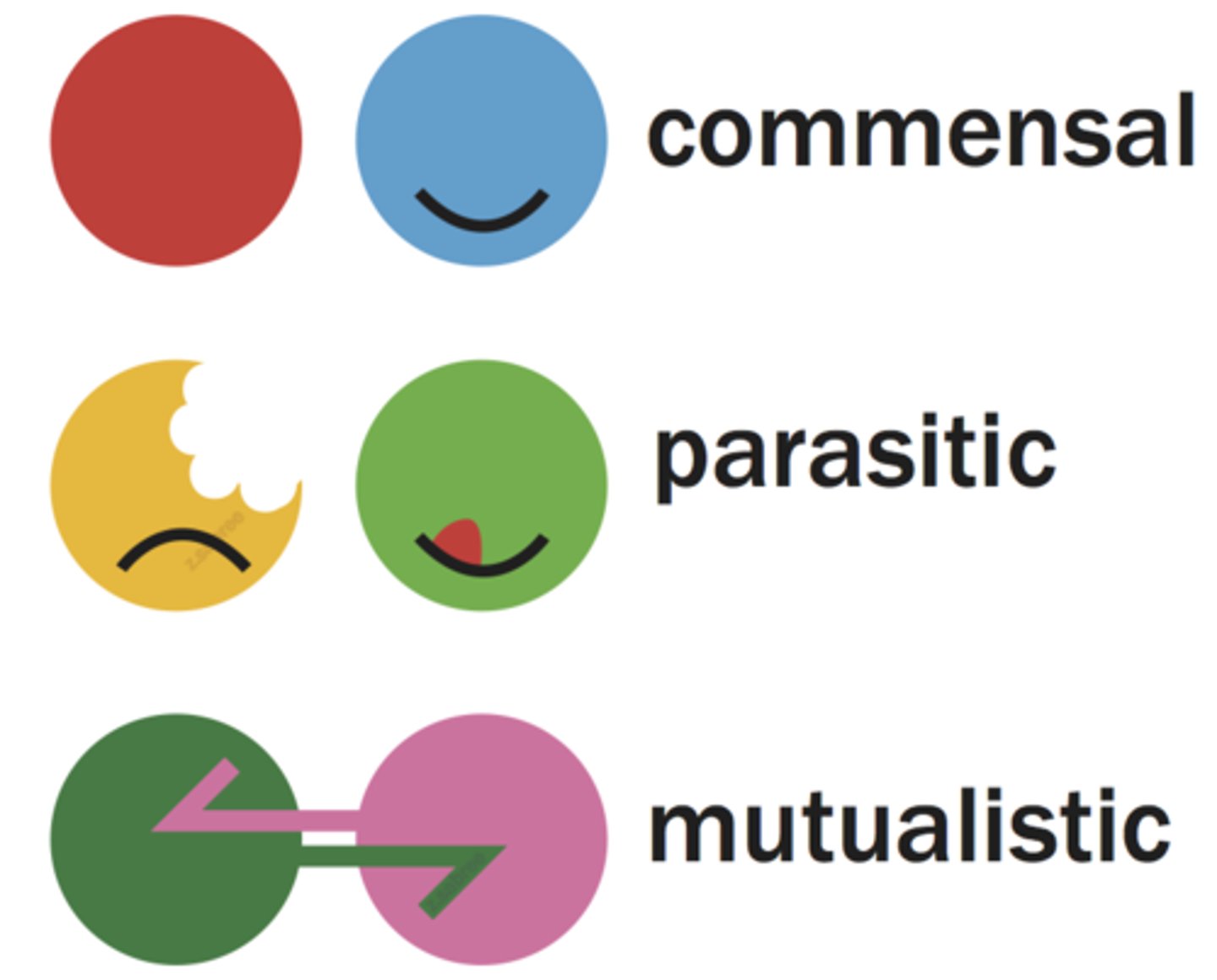
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit.
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected.
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed.
Niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
(Ex. Preferred habitat, position in the food web, mating, and eating behaviors).
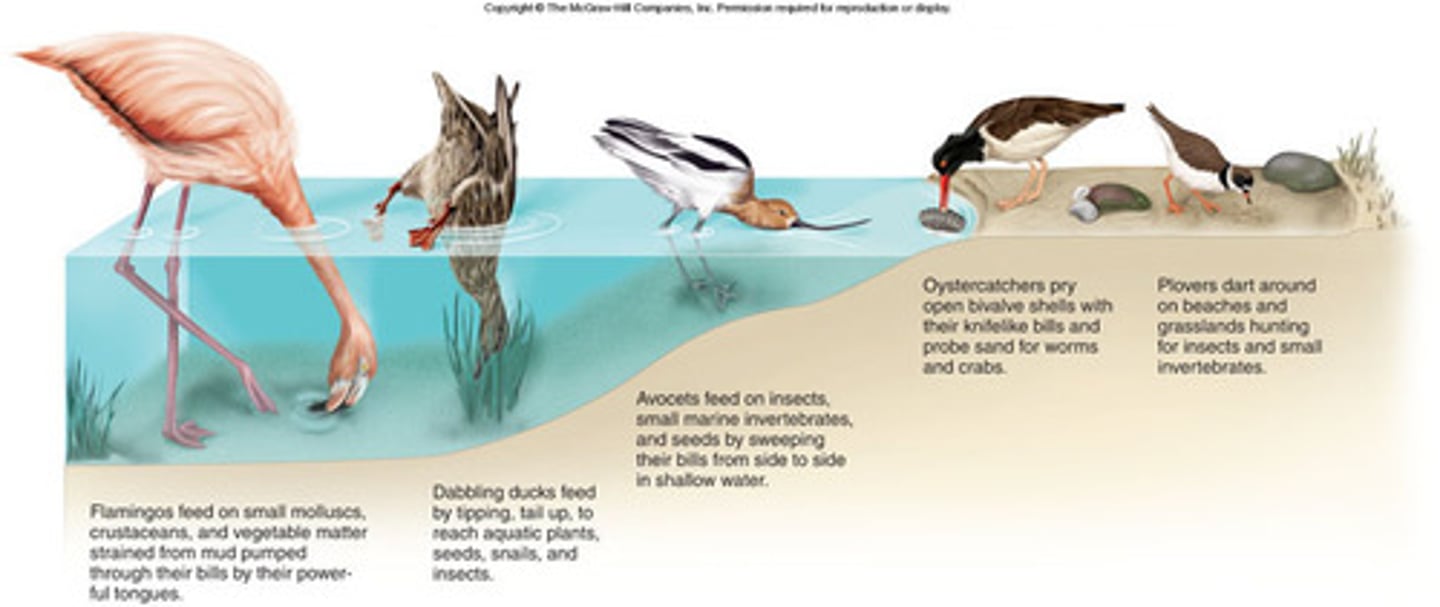
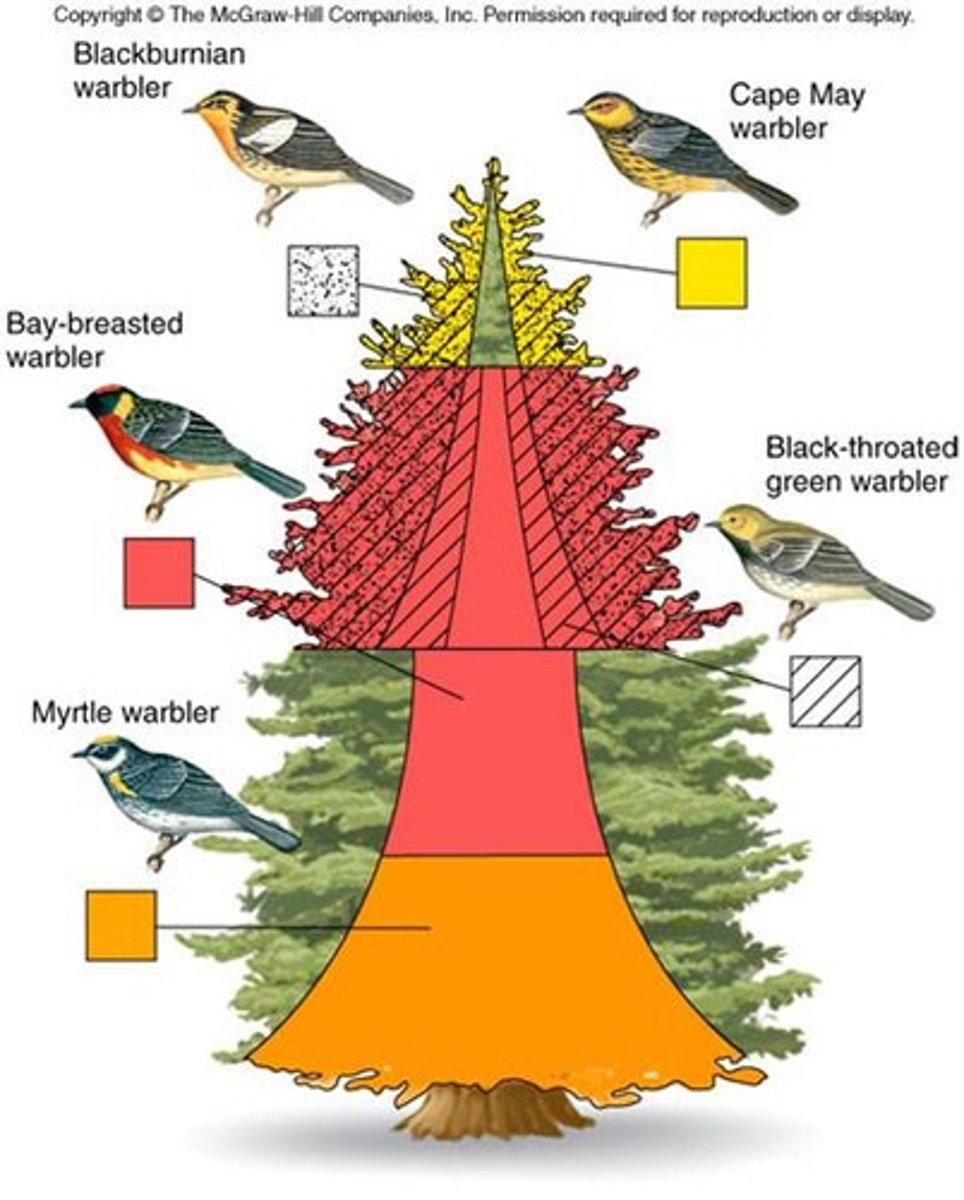
Resource Partitioning
When species avoid competition by dividing the use of resources.
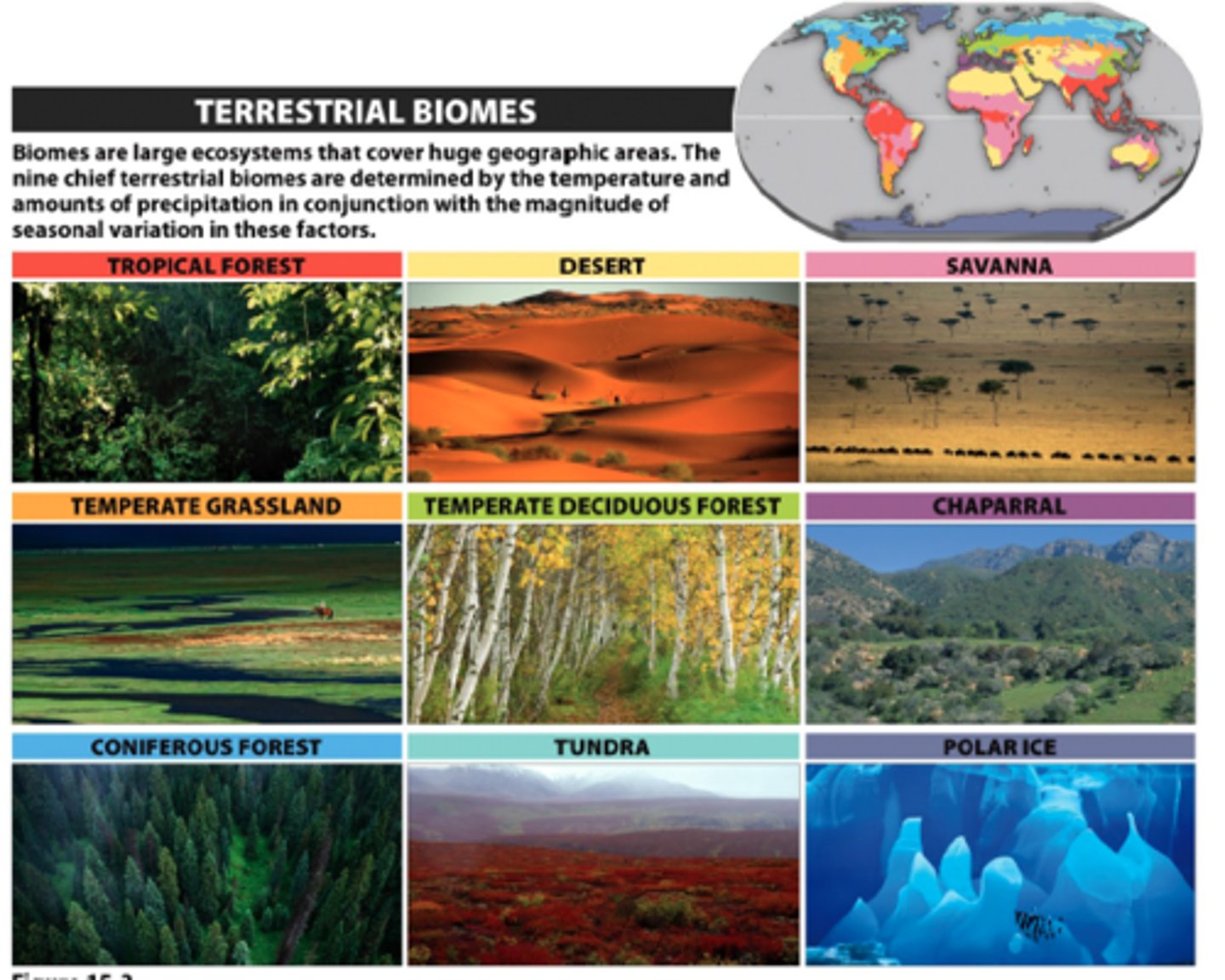
Terrestrial Biomes
Tropical forest.
Savanna.
Desert.
Chaparral.
Temperate Grassland.
Temperate Deciduous Forest.
Coniferous Forest.
Tundra.
Polar ice.
Tropical Rainforest
Biggest land biodiversity.
Occurs near the equator.
Plenty of light at the canopy.
Little light on the forest floor.
Plants: mosses, vines, bromeliads, orchids, etc.
Animals: monkeys, birds, snakes, amphibians, etc.

Polar Ice
A terrestrial biome that includes regions of extremely cold temperature and low precipitation.
Half the year= 24 hours light.
Half the year= 24 hours dark.
Little to no rainfall.
Below freezing temperatures year-round.
Plants: no plant life.
Animals: penguins and polar bears.

Savanna
Warm climate with alternating wet and dry seasons.
Grassland.
Plants: Scattered trees.
Animals: zebras, kangaroos, lions, cheetahs, and hyenas.

Desert
An extremely dry area.
Alternates between hot days and cold nights.
Little to no rainfall.
Animals and plants have evolved to need little water or to store water.
Plants: Scattered shrubs and cacti.
Animals: Camels, lizards, and snakes.
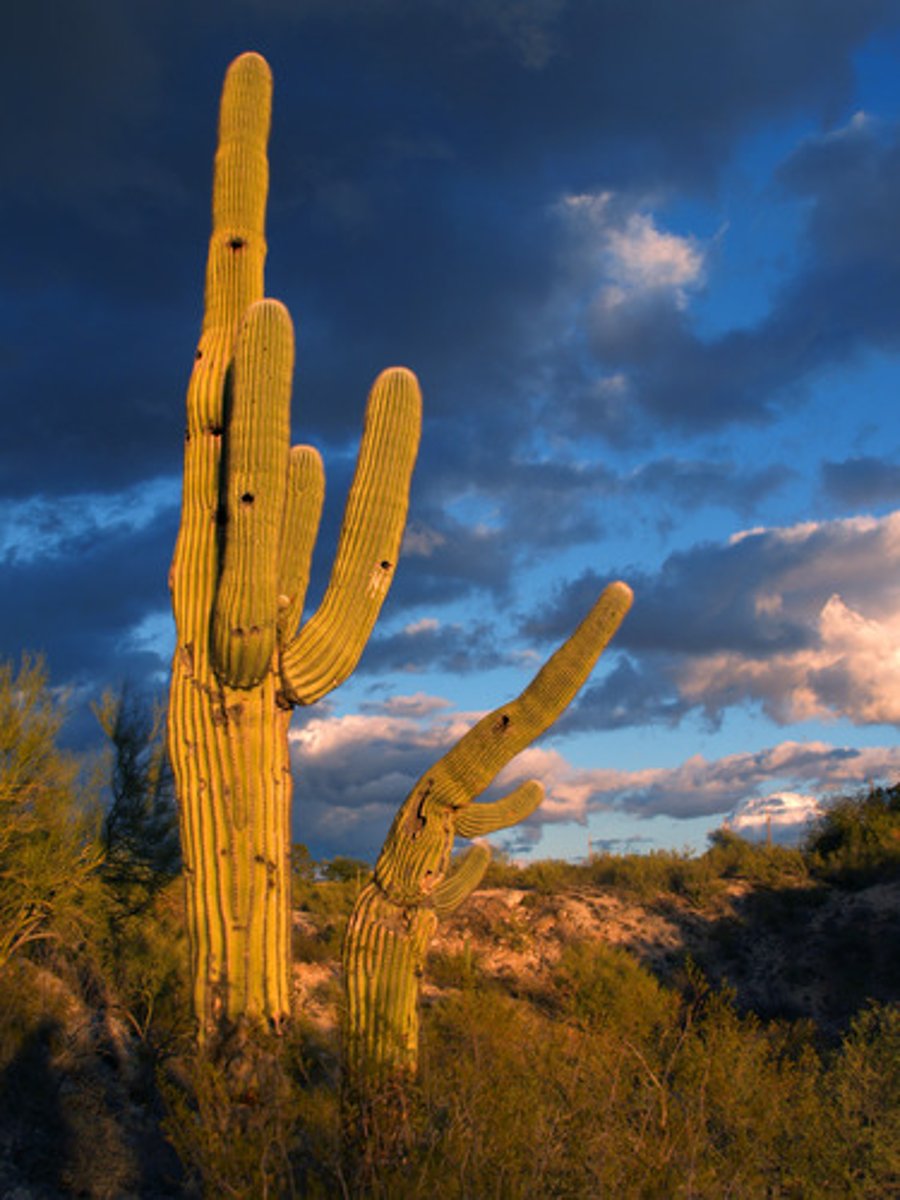

Coniferous Forest
Cone-bearing evergreen trees.
Also known as the Taiga.
Long cold winters with heavy rainfalls.
Plants: Pines, spruce, fir trees.
Animals: Moose, elk, hares, wolves, and bears.
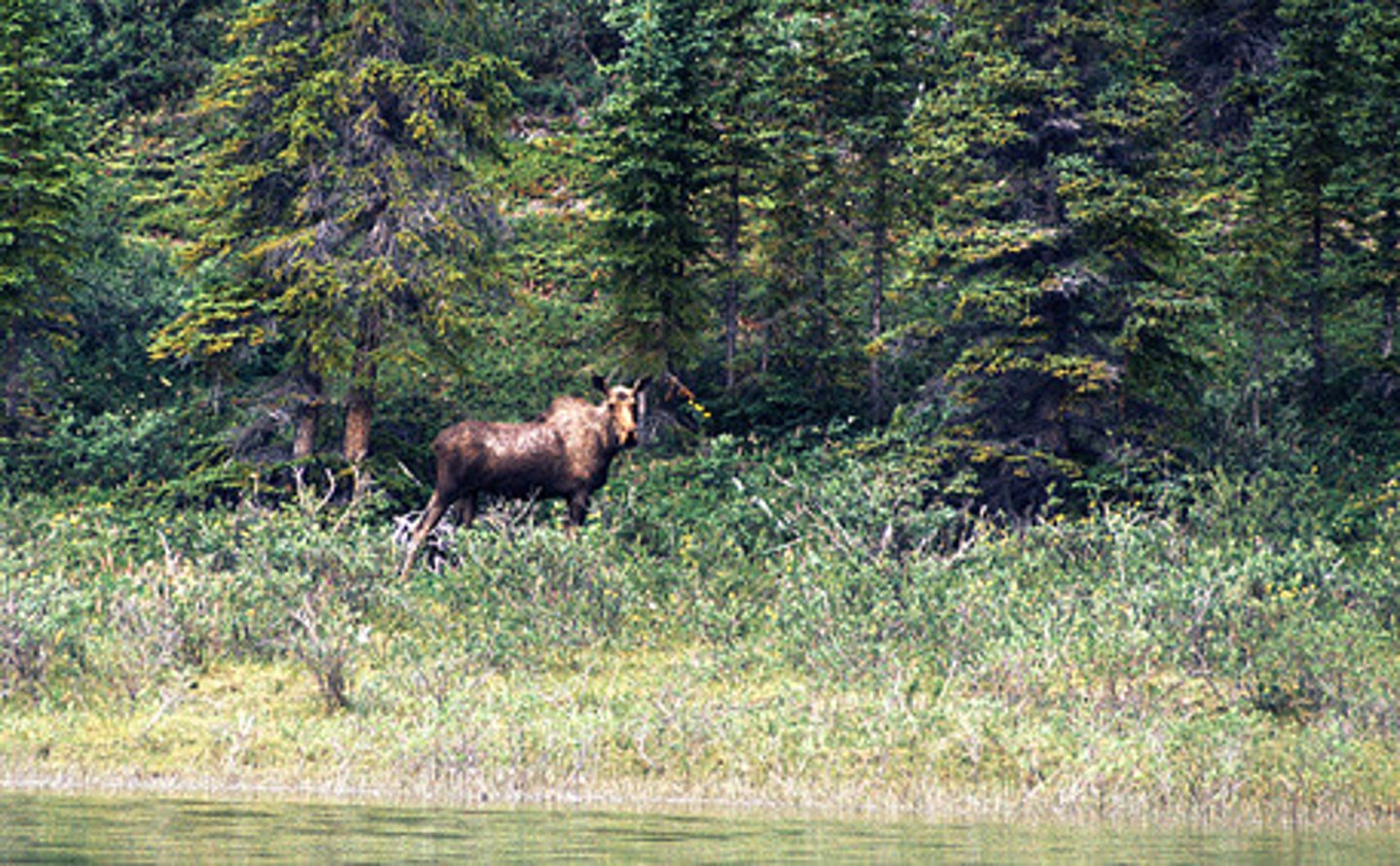

Temperate Deciduous Forest
Trees drop their leaves annually.
Cold winters, hot summers.
Tree leaves change color during the autumn months.
Plants: Maples, oak, beeches, and hickory.
Animals: Deer, squirrels, foxes, and bears.

Chaparral
Dense evergreen shrubs.
Rainy winters, dry summers.
Adopted to survive periodic bush fires.
Plants: Poison oak, chamise.
Animals: Deer, rodents, lizards, snakes.

Temperate Grassland
Deep nutrient-rich soil.
Cold winters.
Also known as Prairies.
Seasonal droughts, occasional fires.
Grazing animals such as bison.
Plants: different grasses like buffalo grass, purple needlegrass.
Animals: Coyotes, snakes, lizards, and insects.

Tundra
A vast treeless plain in the arctic regions.
Cold temperatures, long winters, high winds.
Contains permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil).
Short summer season.
Plants: No large plants due to permafrost just mosses, lichens, and grasses.
Animals: Caribou, snowy owl, arctic hare.

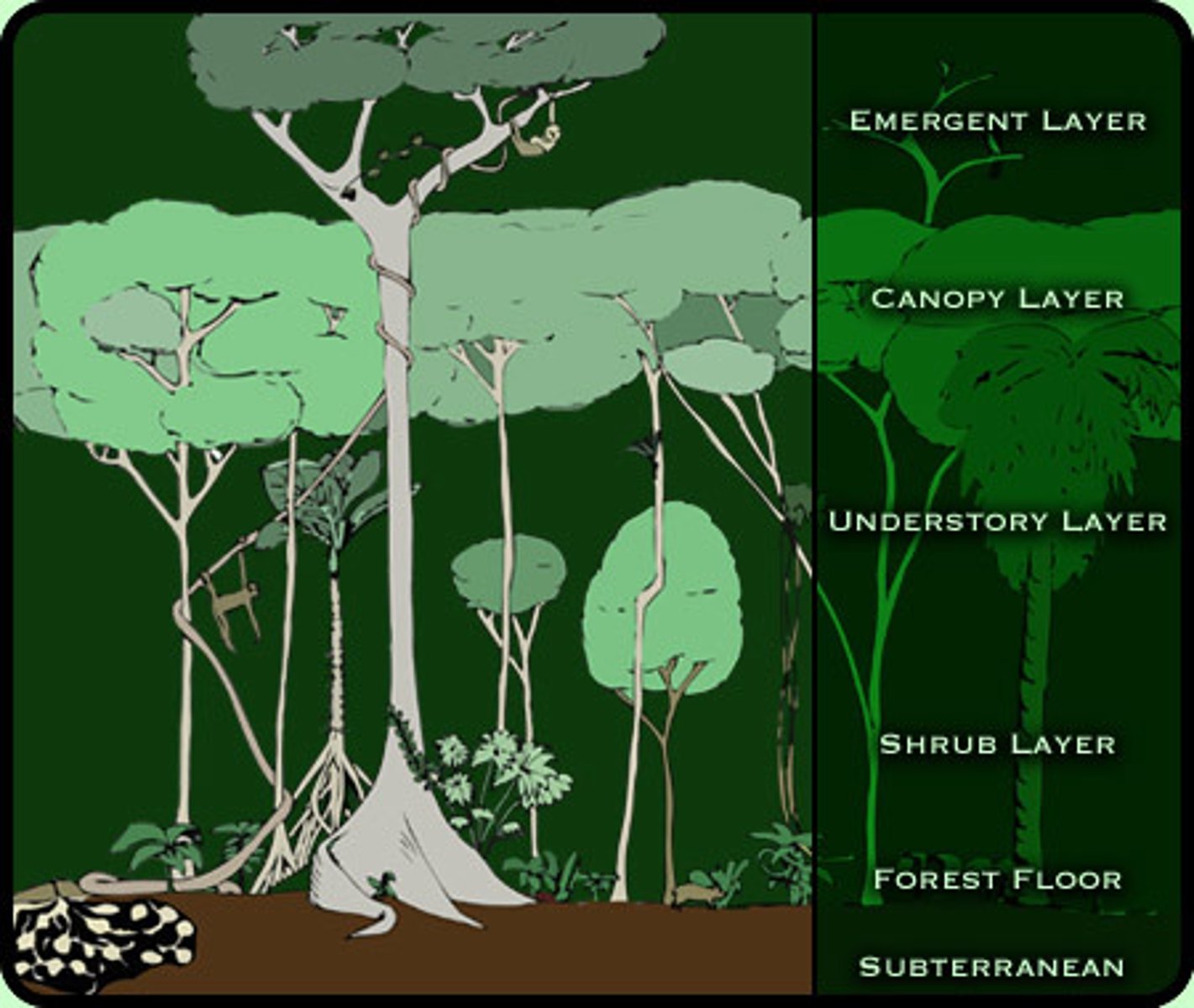
Canopy
Dense covering formed by the leafy tops of tall rainforest trees.
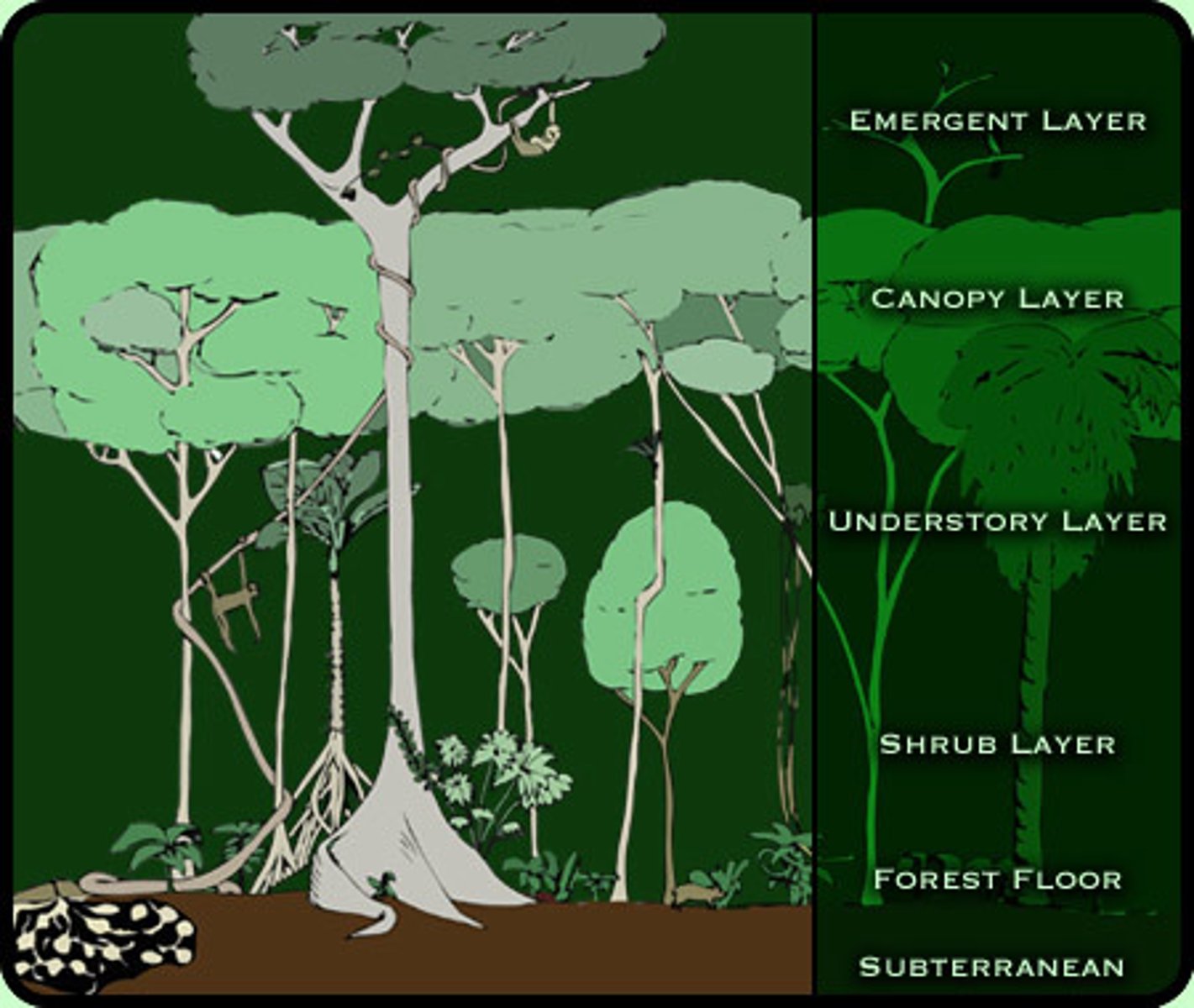
Understory
A layer of shorter plants grows in the shady area below the canopy.
World's Largest Forests
Largest non-polar desert on earth is the Sahara Desert in North Africa.
Largest in the United States: The Great Basin Desert.
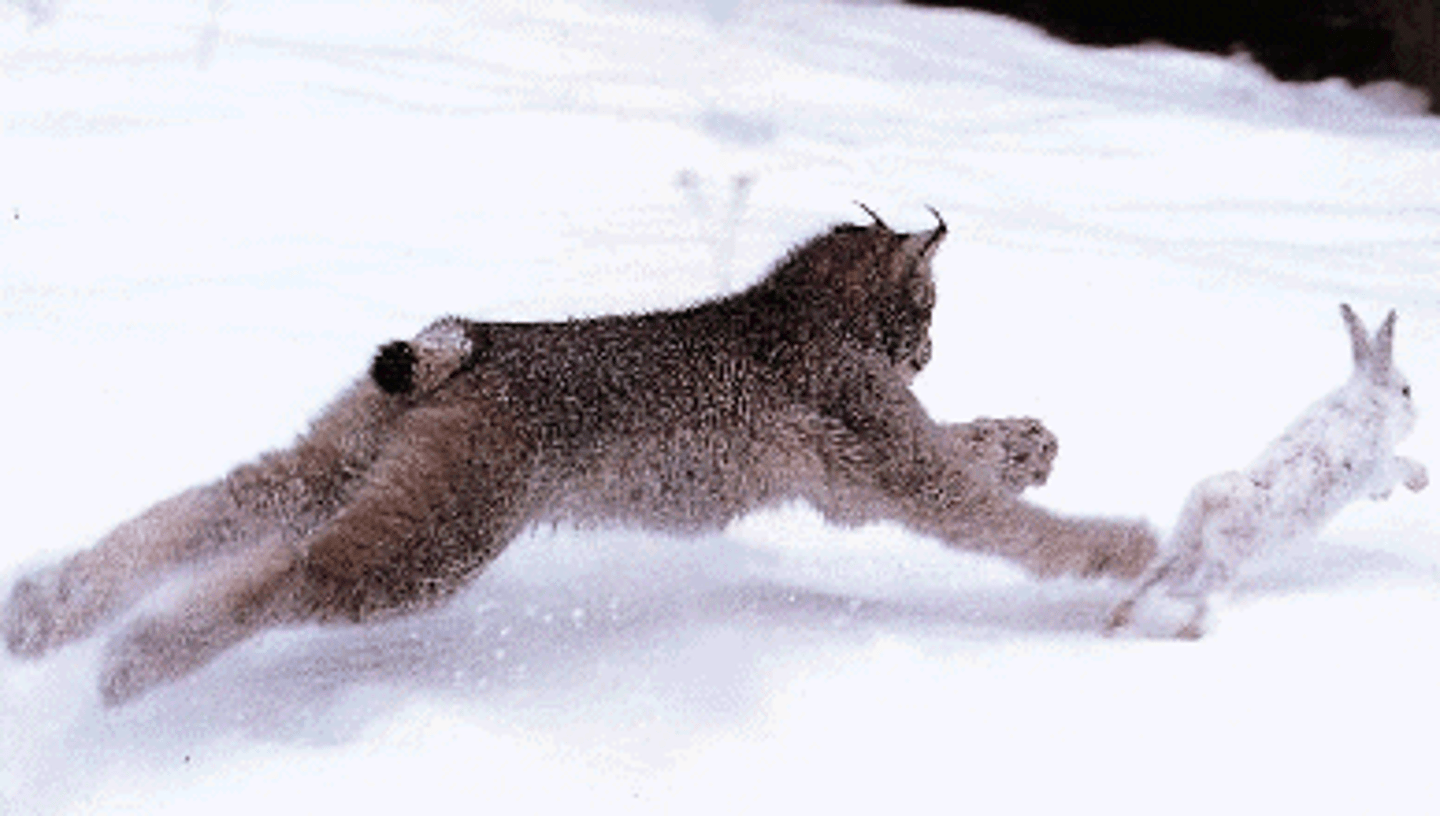
Predator-Prey Relationship
The predator is an organism that eats another organism the prey.

Climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time.
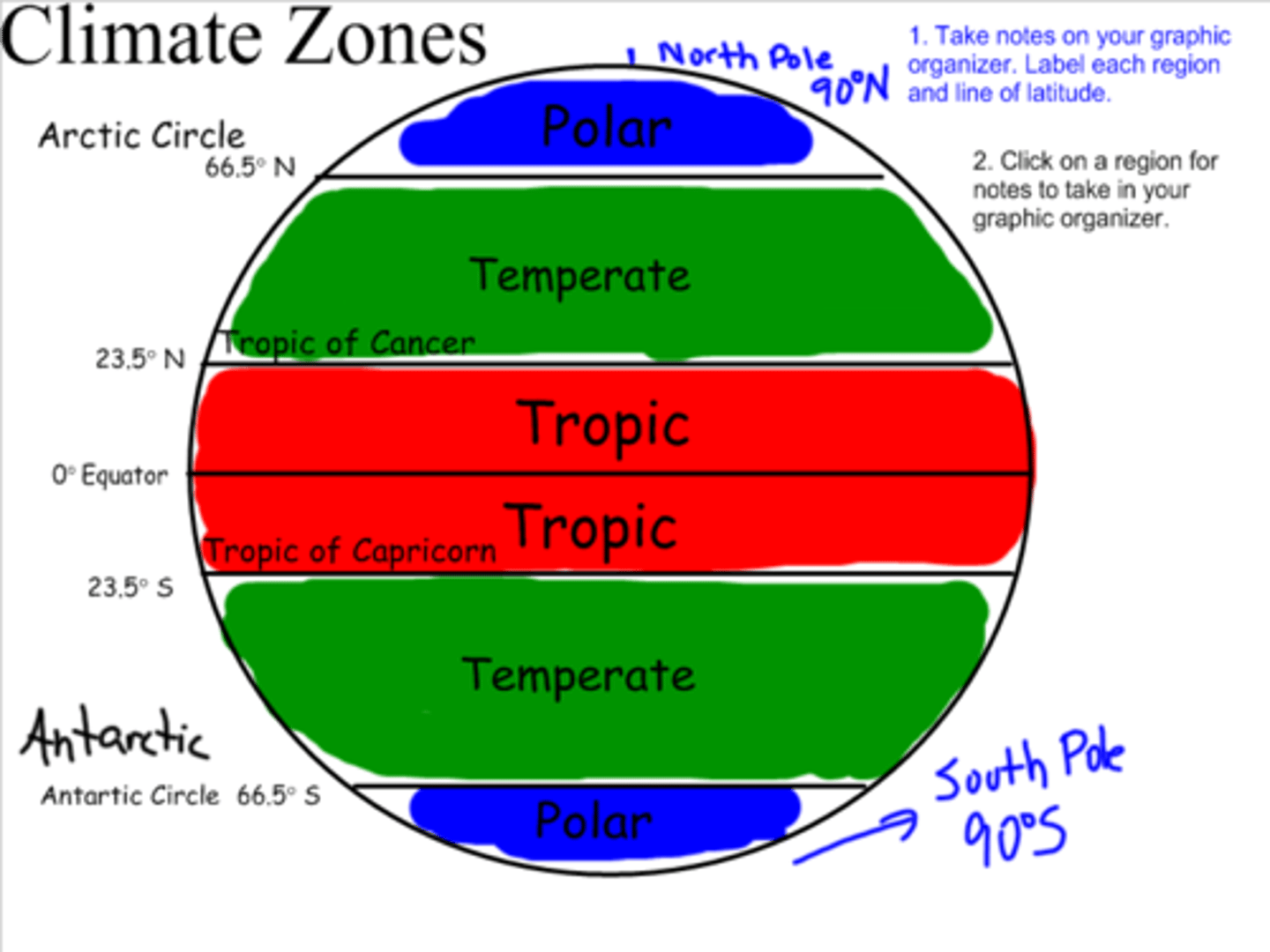
Climate Zones
Due to the spherical shape heat's earth's surface unevenly.
Near the equator, receives direct sunlight = Tropic Zones.
Least direct sunlight = Polar Zones.
Between tropic and polar zone = Temperate Zone.
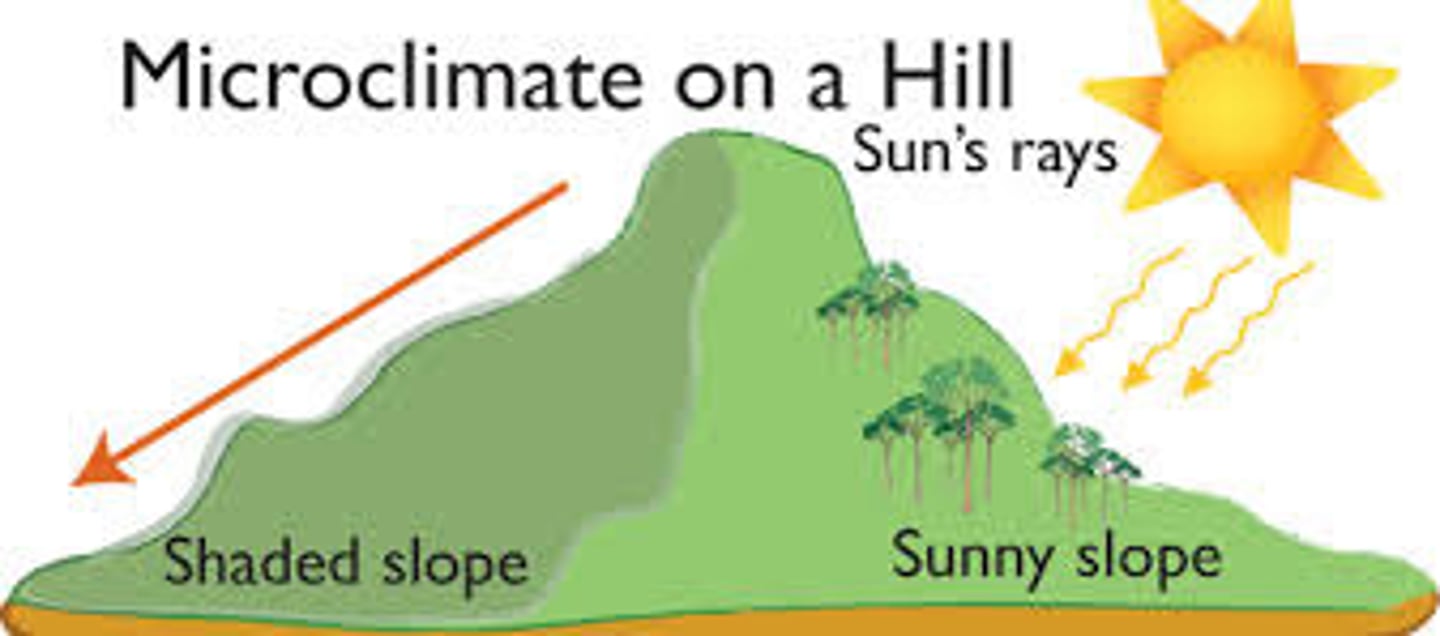
Microclimate
The climate within a small area that differs significantly from the climate of the surrounding area.
Biomes
Are characterized by the communities of plants, animals, and other organisms that are adopted to its climate and other abiotic factors.
Why are ecosystem services are important?
Pollination.
Clean water.
Seed Dispersal.
Soil Fertility.
Decomposition of Organic Waste.
Pest Control.
Flood Control.
Climate Regulation.
Cycling of nutrients.
Aquatic Biomes
Fresh Waters:
Streams.
Rivers.
Ponds.
Lakes.
Wet Lands.
Marine:
Open Ocean.
Shorelines.
Estuaries.
Coral Reef (biggest aquatic biodiversity).
Kelp Forest.
(Largest ocean on earth is the Pacific ocean).

Freshwater Ecosystem
Flowing Water: Rivers.
Standing Water: Lakes, ponds.
Flowing Water From Largest to Smallest
Rivers, Streams, Creeks, Brooks.
How Do Rivers Change?
Rivers flow downhill from source to mouth.
Near the source, water is cold, low on nutrients, and clear.
Far from source, water is warmer, fun on nutrients, looks dirty.
Algae is the producer in most river food chains.
Down Stream
The river becomes wider and deeper.
Water is warmer and murkier (dirty, gloomy).
More phytoplankton (think of photosynthesis) and other organisms.
Marches and other wetlands are common.

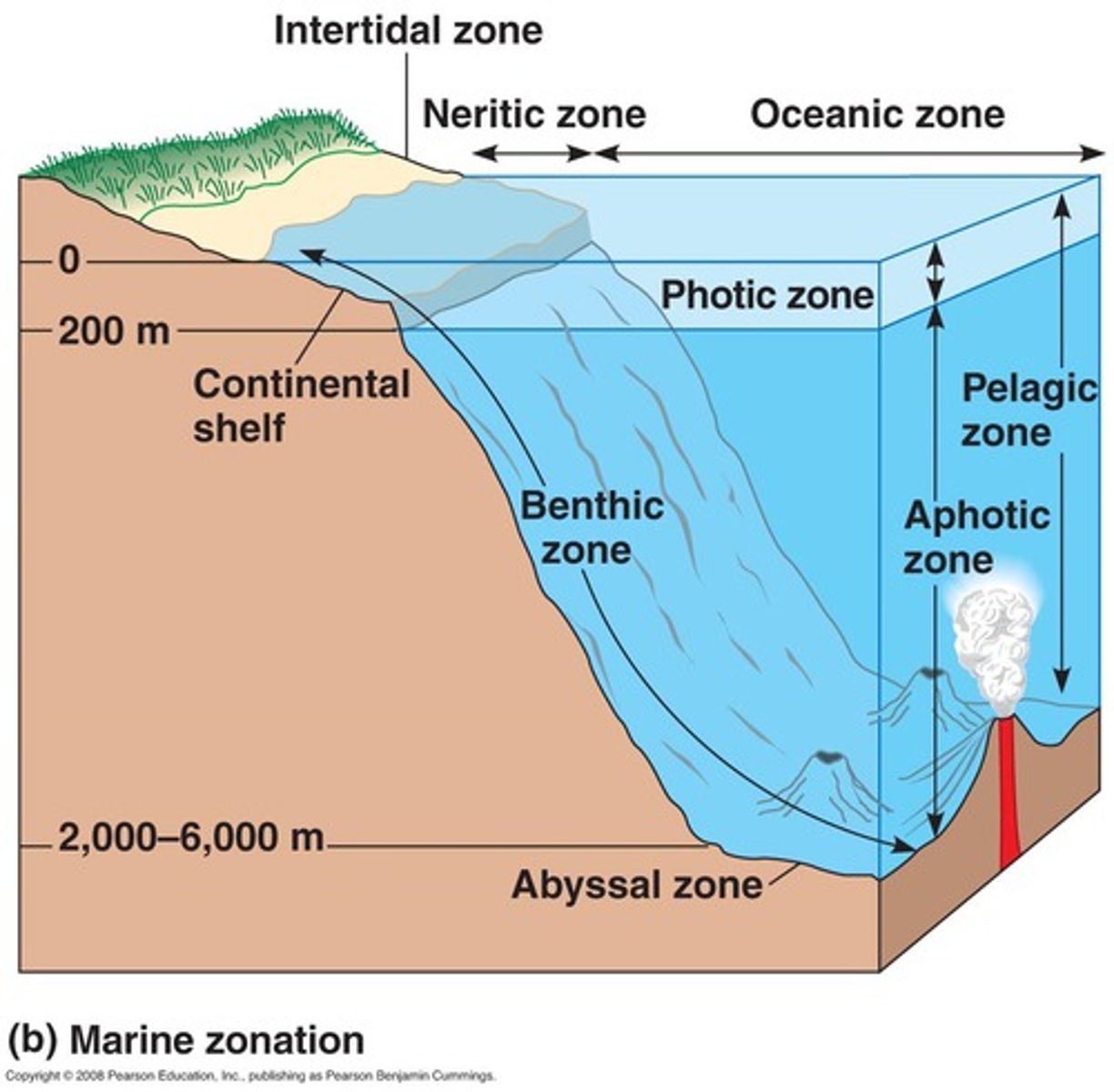
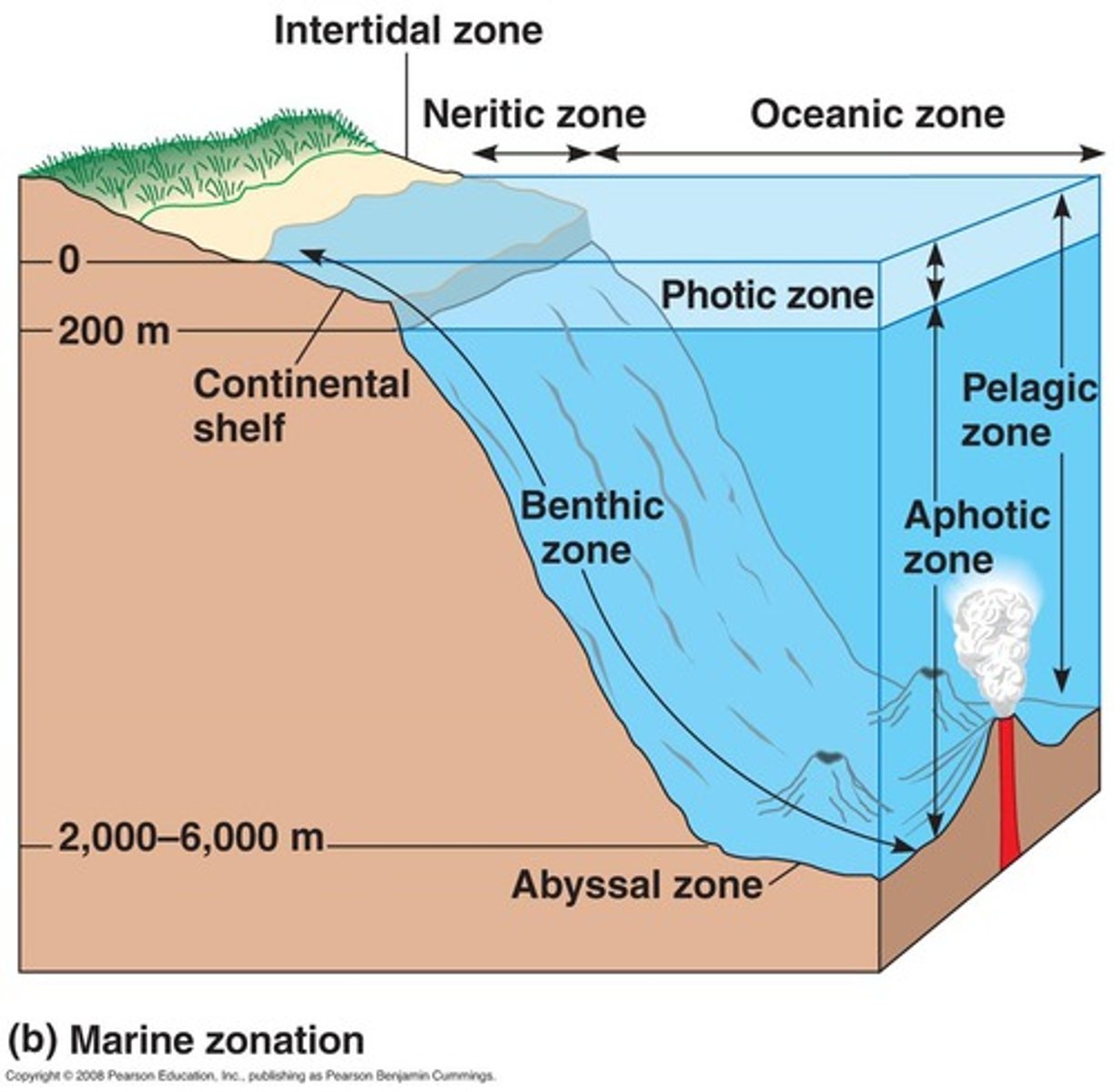
Photic Zone
Photic = Light, Sun.
Shallow water close to shore and the upper zone of water away from shore make up the photic zone where light is available for photosynthesis.
Freshwater Wetlands
Swamp: Support woody plants and trees.
Marshes: Support reeds and grasses.
Bogs: Support fungi, moss, and small shrubs.
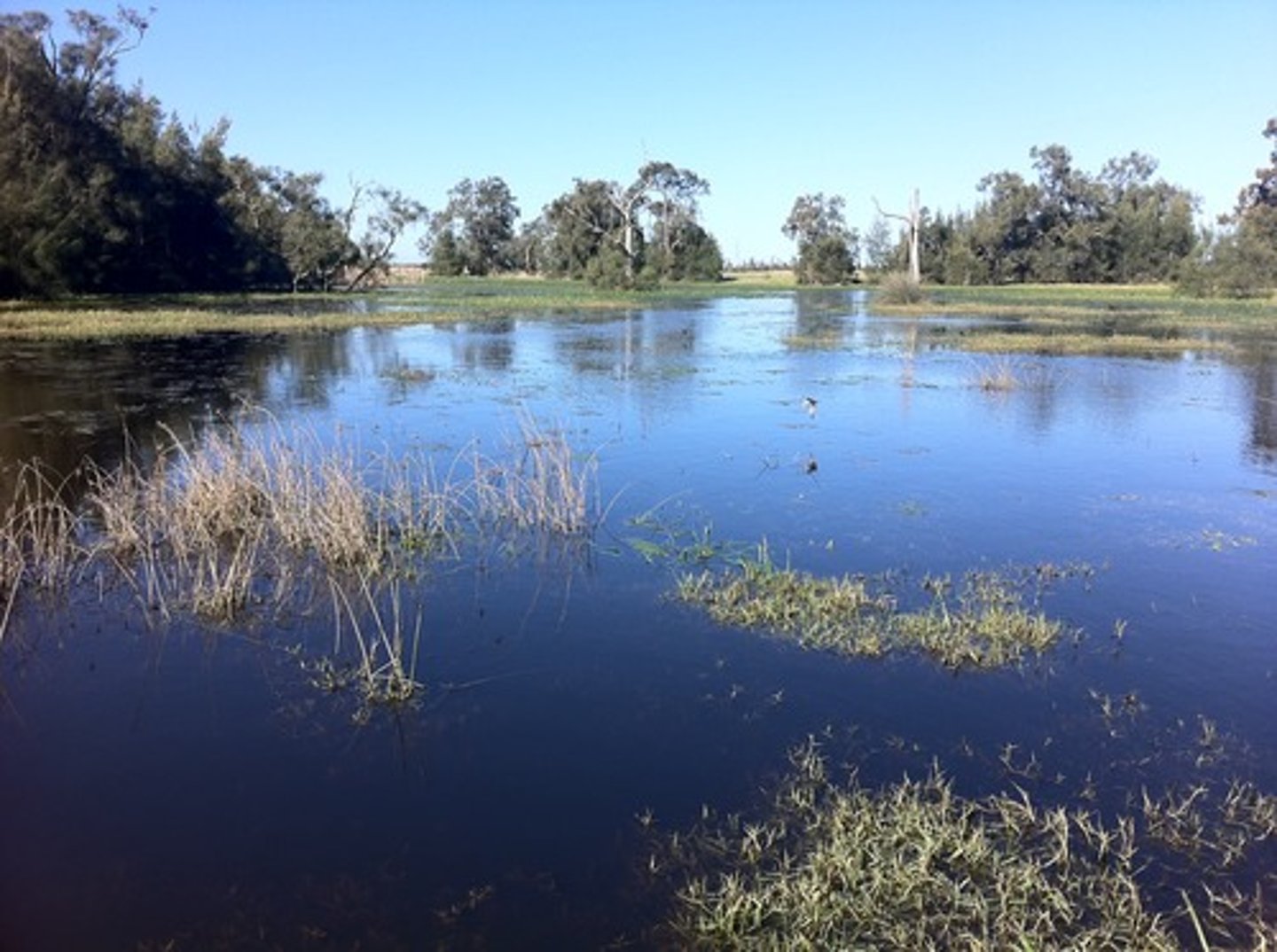

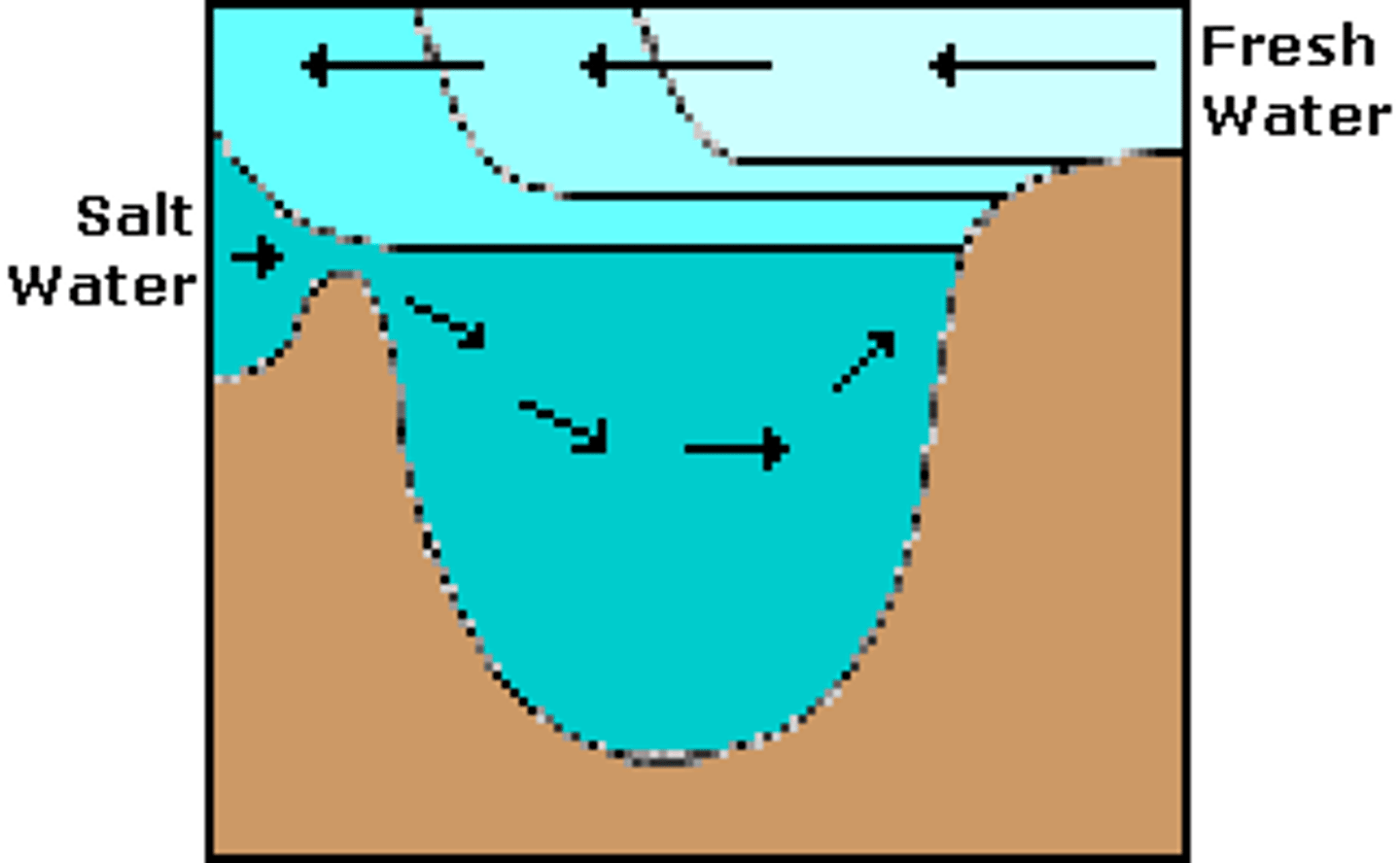
Estuaries
Wetlands formed where rivers meet the ocean.
Contains brackish water (a mixture of salt water and fresh water).
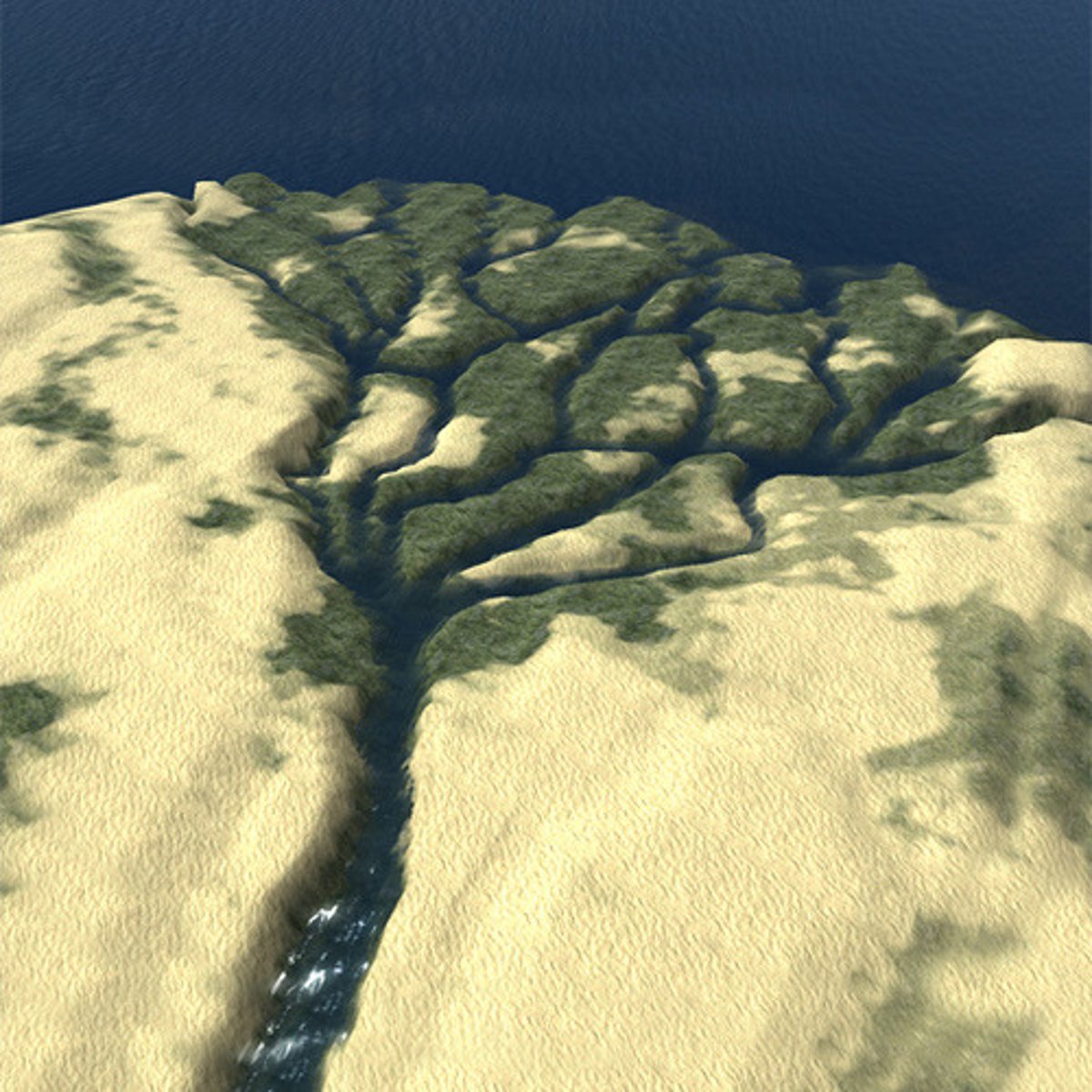
River Delta
As the river slows down it doesn't have the ability to carry sediment. The sediment is deposit at the mouth of the river forming a delta. Delta = 1 type estuary ecosystem.

Ocean Zones by Depth
Photic Zone = Light.
Aphotic Zone = No Light.
Benthic Zone = Covers ocean floor at all depths.
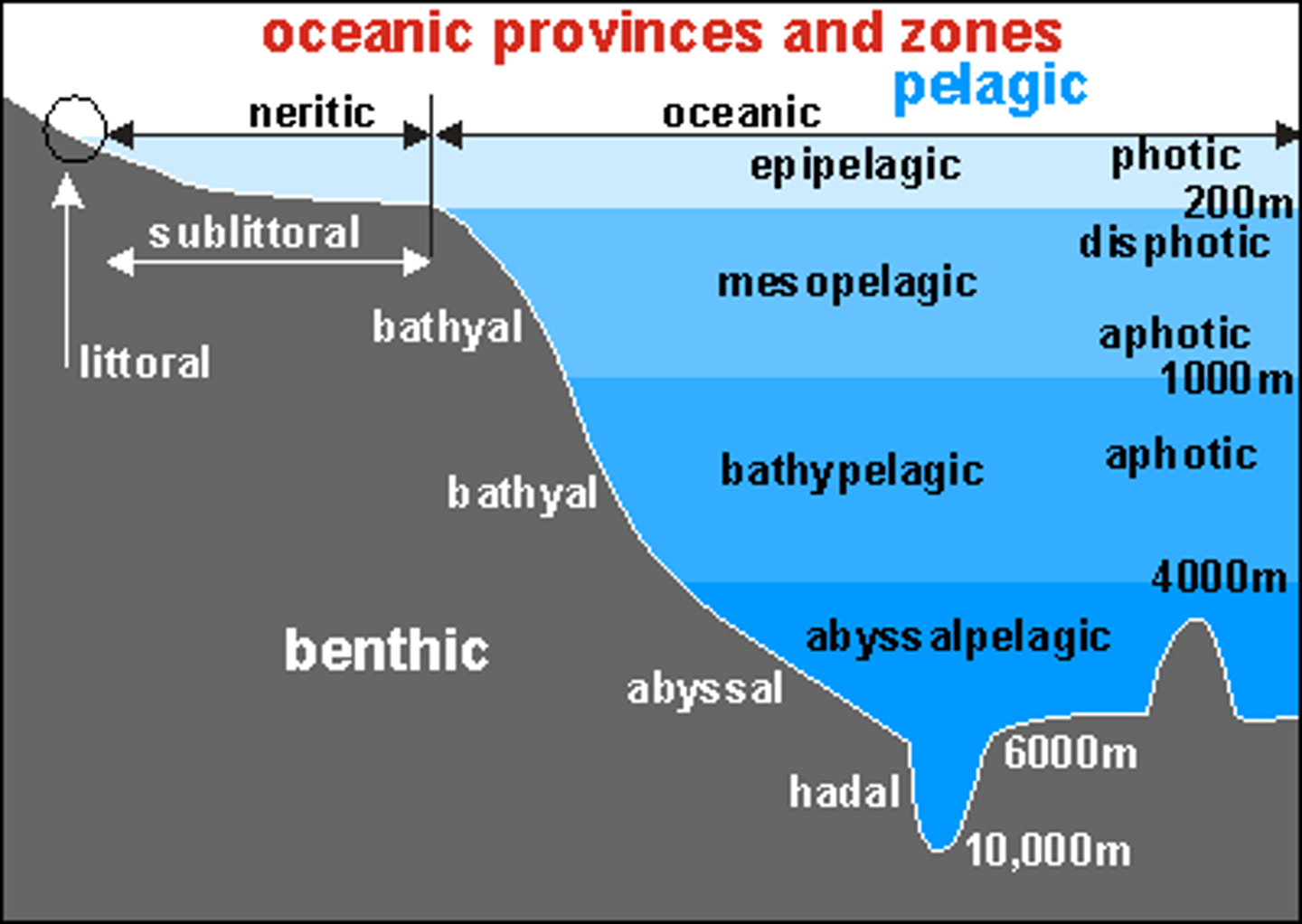
Ocean Zones by Distance
Intertidal Zone = Between high and low tide.
Hit by waves during high tides and exposed to sun and wind during low tide.
(Ex. Organisms = barnacles, crabs, sea stars, some seaweed).
Coastal or Neritic Zone = Between low-tide line and the edge of the continental shelf.
Shallow, some light reaches the bottom in most areas.
Coral reef and kelp forest (releases oxygen) can be found.
(Ex. Organisms = phytoplankton, mollusks, sponges, turtles, and fish).
Coral reefs are found in warm, shallow waters of tropical coastal oceans.
All invertebrates phyla are found in the coral reef ecosystem.
Open ocean or oceanic zone = Beyond the continental shelf.
Abundant phytoplankton and zooplankton provide food for organisms.
Deep-sea vents.
Hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor release hot gases and minerals from the earth's interior.
Unique ecosystems near these vents are adapted to high temperatures, pressure, and dissolved mineral contents.
(Ex. Organisms = dolphins, whales, squid, and many species of fish).
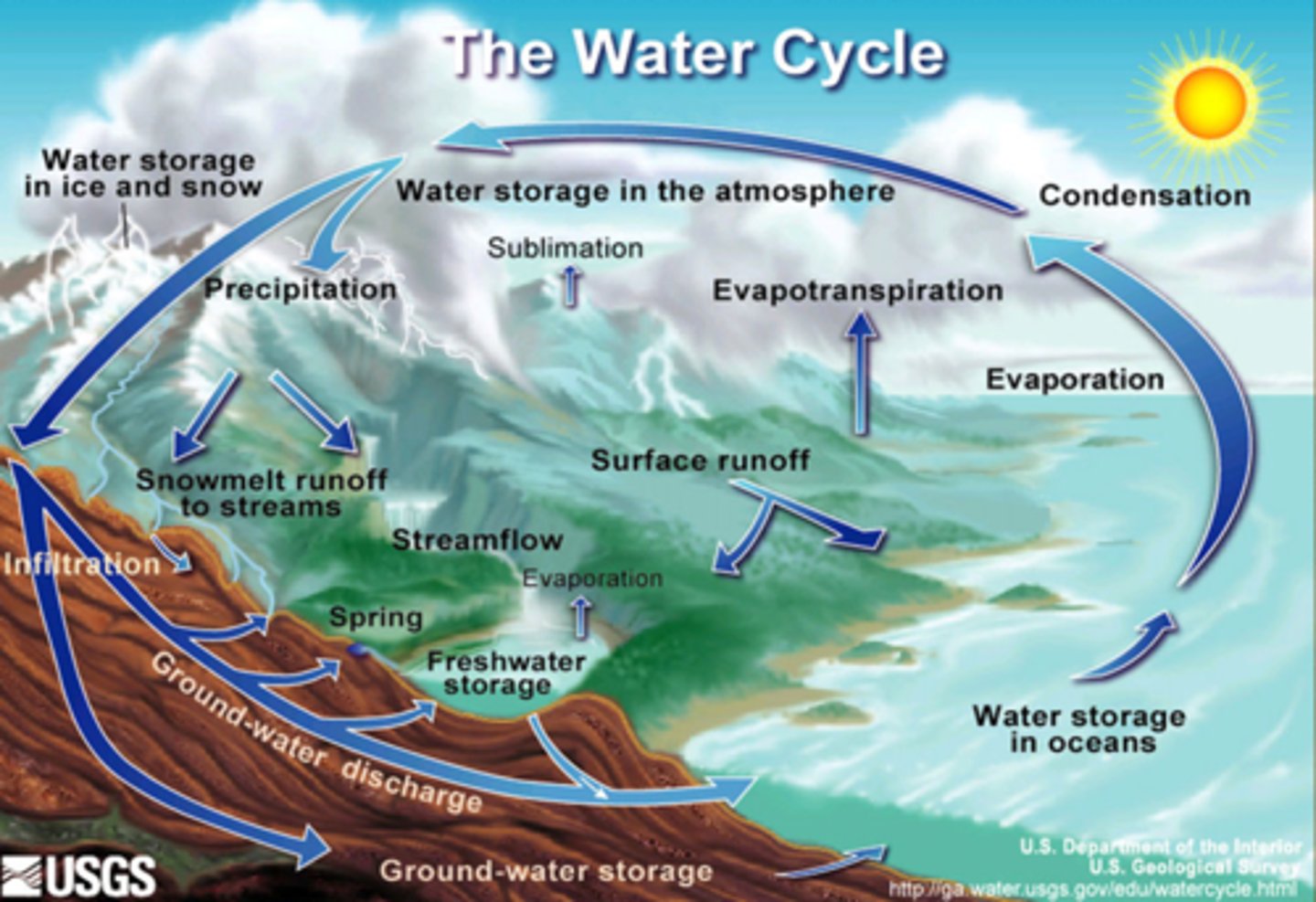
Water's Importance
Vital for all life, moderates climate, sculps the land, removes waste and water pollutants, moves continually through the hydrologic cycle.
Flows/Throughouts
Transfer process (location change) infiltration, runoff, plant uptake/transpiration, seepage, precipitation, consumption (drinking), percolation.
Transformation Process (Phase Change)
Snowmelt, evaporation, sublimation, freezing, condensation, fog drip.
Climate Change Effects
Precipitation increases/decreases = drought/flooding.
Sea level rise, loss of ice habitat/ freshwater sources (glaciers), groundwater depletion.

Other Human Effects
Pollution: chemicals, toxic metals, endocrine disruptors, eutrophication (excess nutrients), thermal pollution.
Stocks Isotopes/ Reservoirs
Ocean (largest), lakes, rivers, snow, clouds/atmosphere, biota, groundwater.
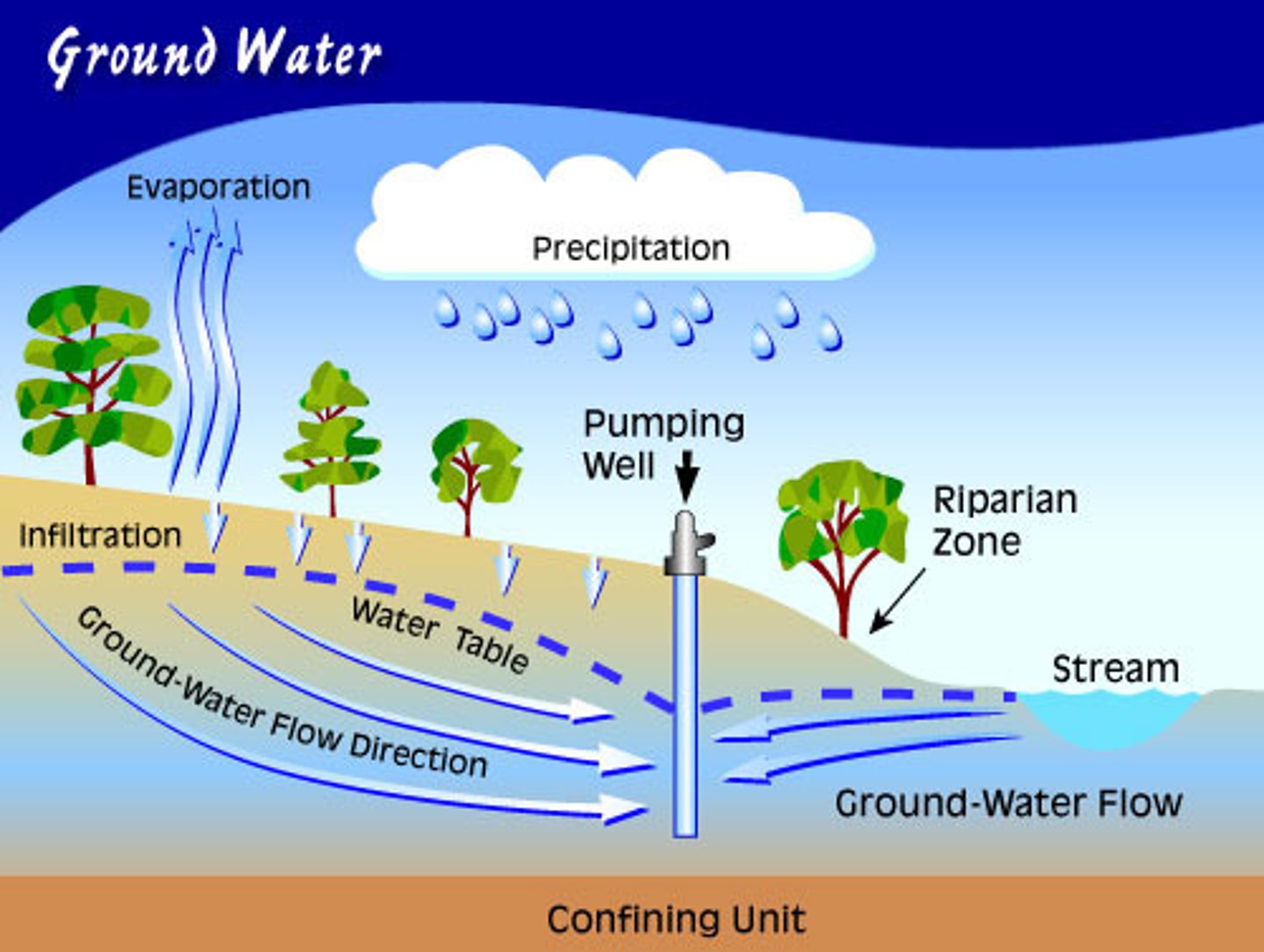
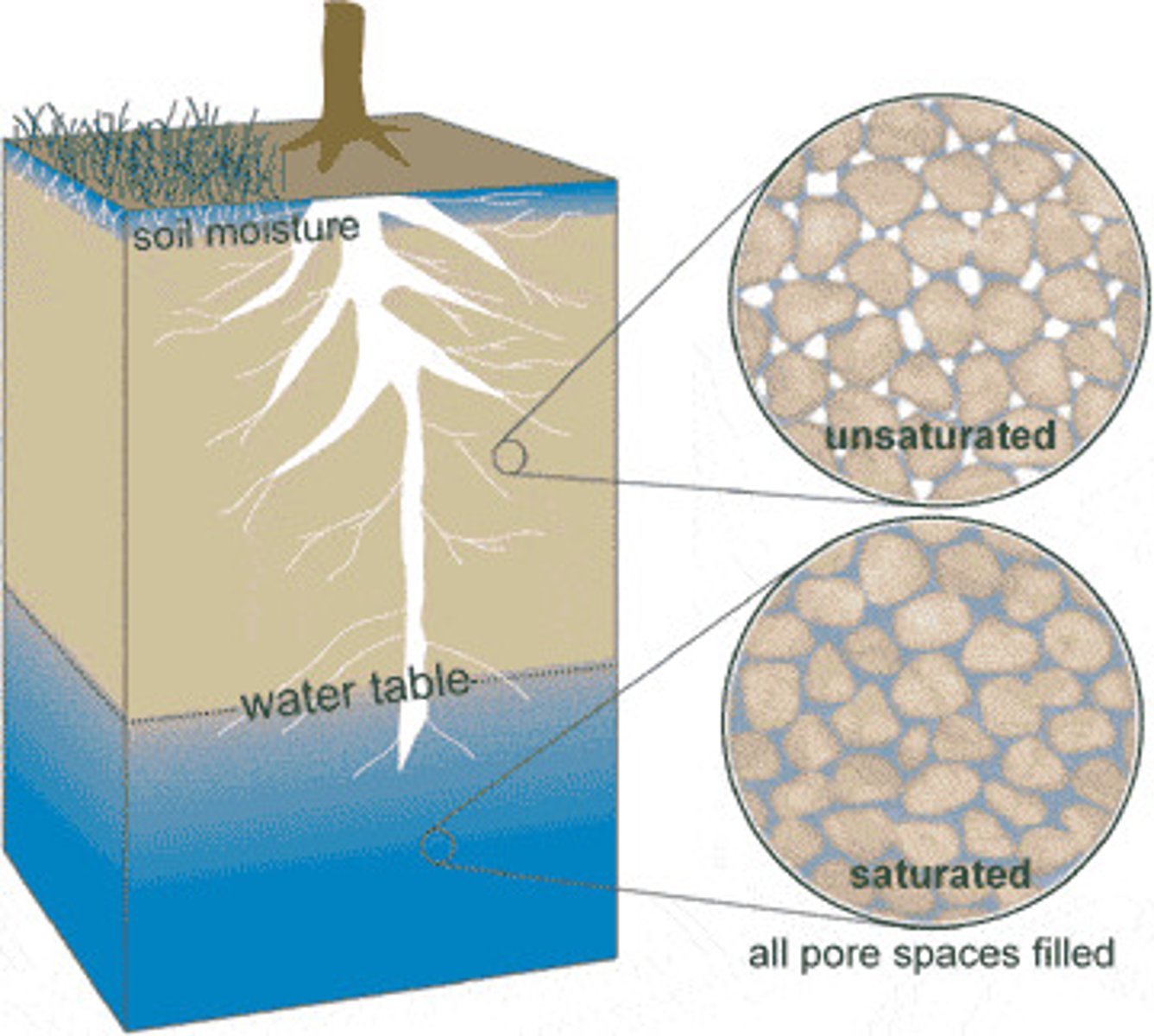
Groundwater
Precipitation that seeps into the ground and is stored in tiny holes, or pores, in soil and rocks.
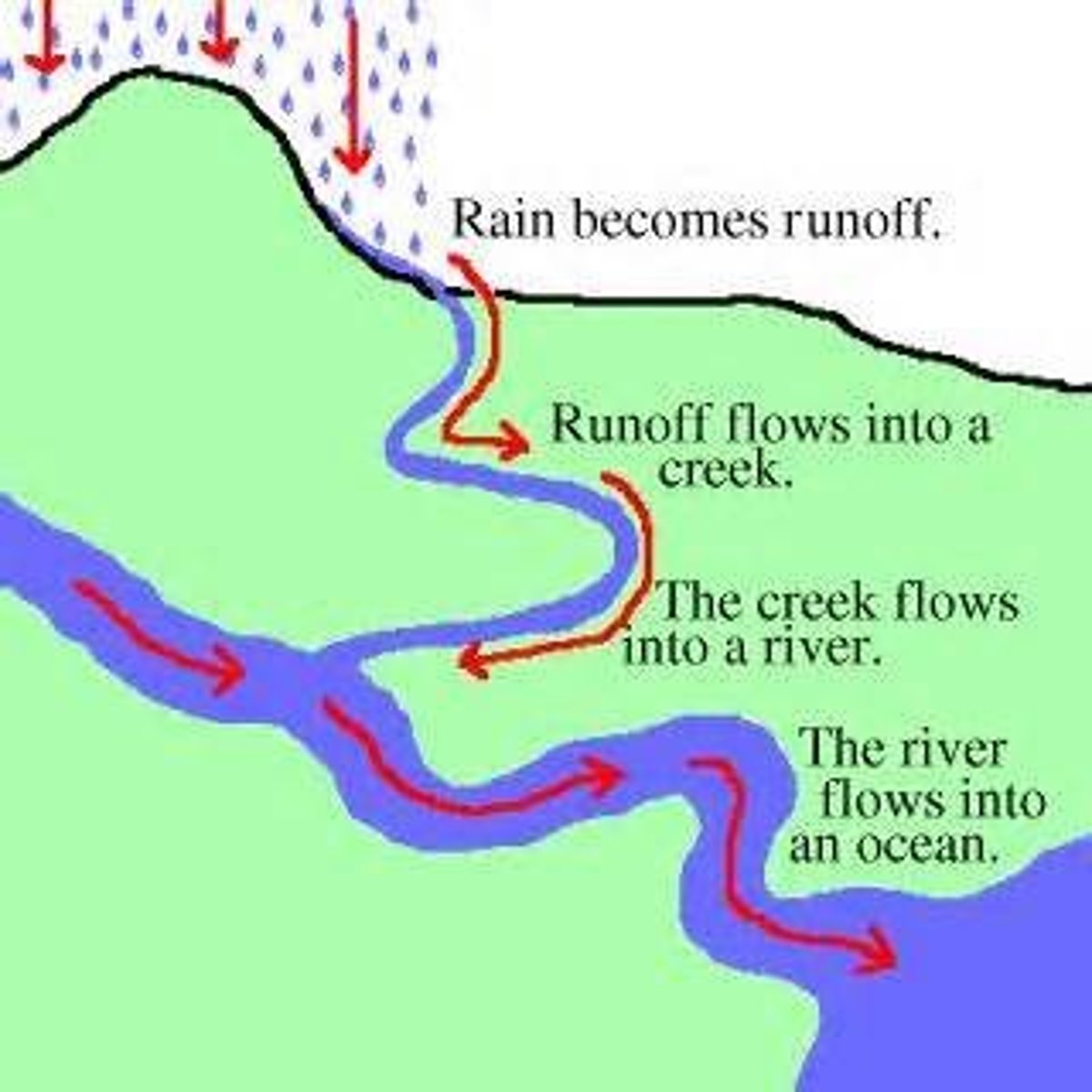
Surface Runoff
Water that does not sink into the ground or evaporate into the air runs off into bodies of water.
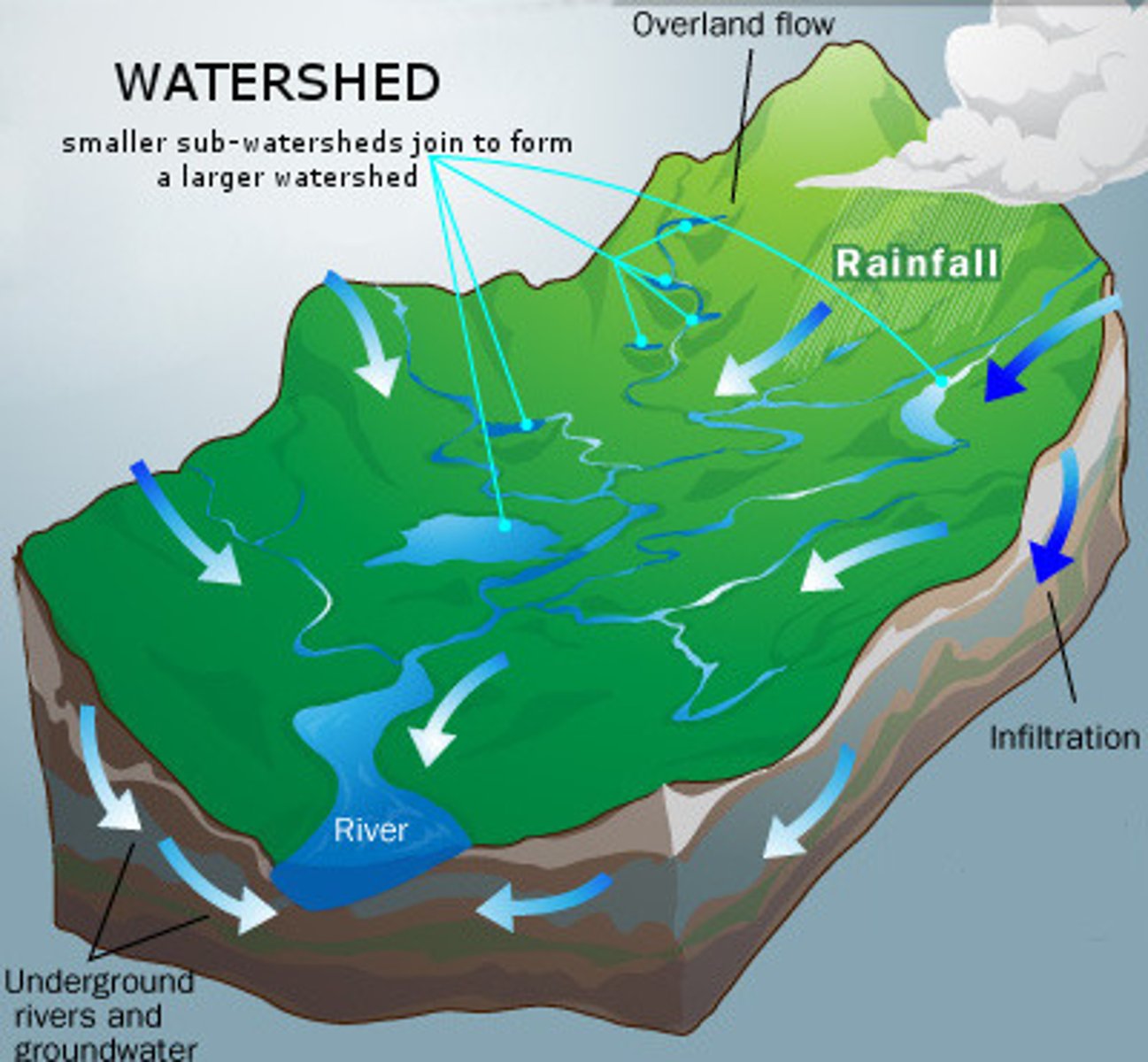
Watershed
An area of land where all water flows into a specific body of water, such as a stream, river, lake, or ocean
Characteristics of a watershed:
Area: Reflects volume of water.
Length: Can be measured in different ways.
Slope: Momentum of runoffs.
Vegetation: Adds organic matter to the soil, etc.
Divides: Peaks and ridge lines with line connecting highest points.
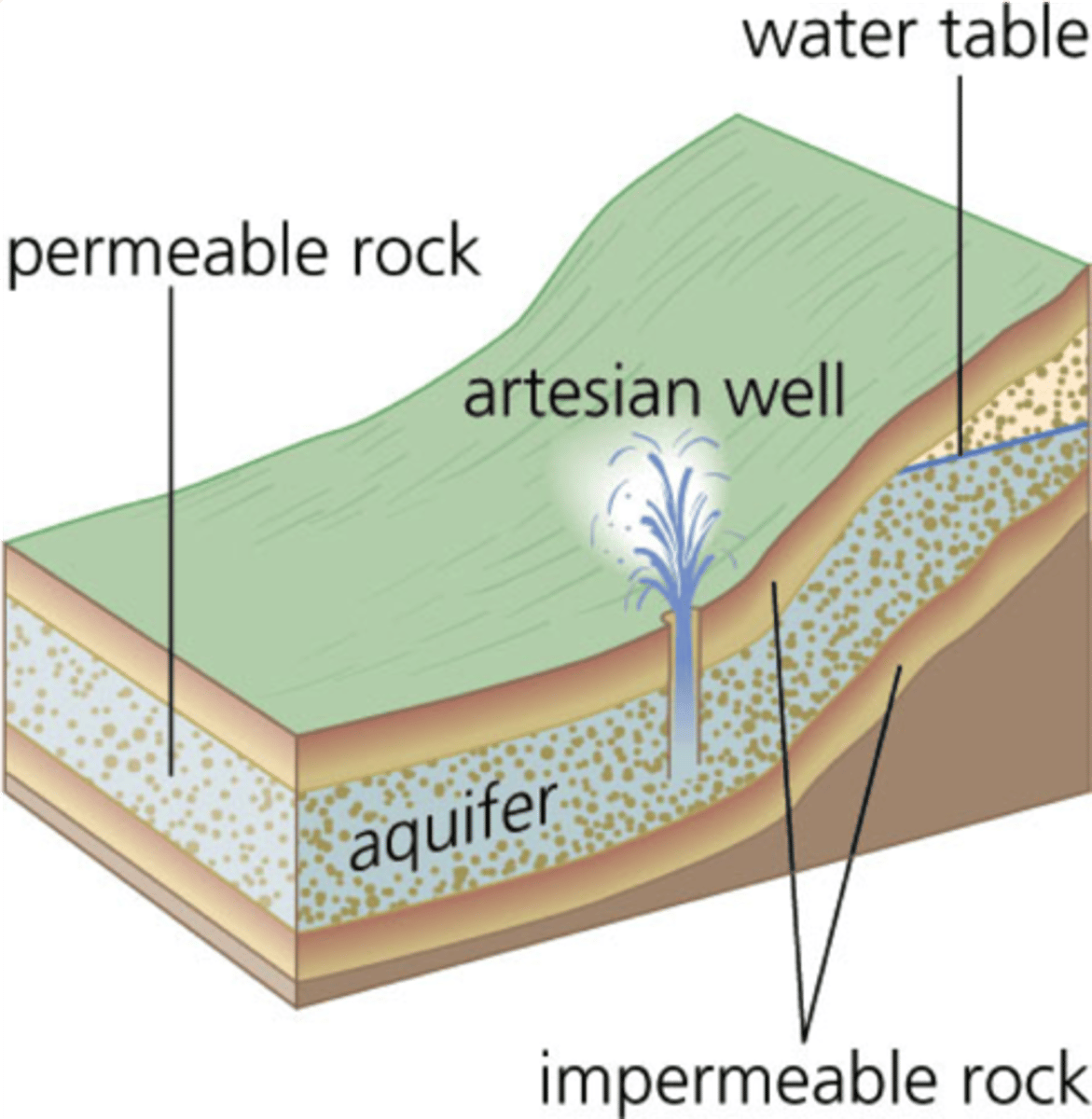
Aquifer
underground layers of permeable rock or sediment that hold and transmit water
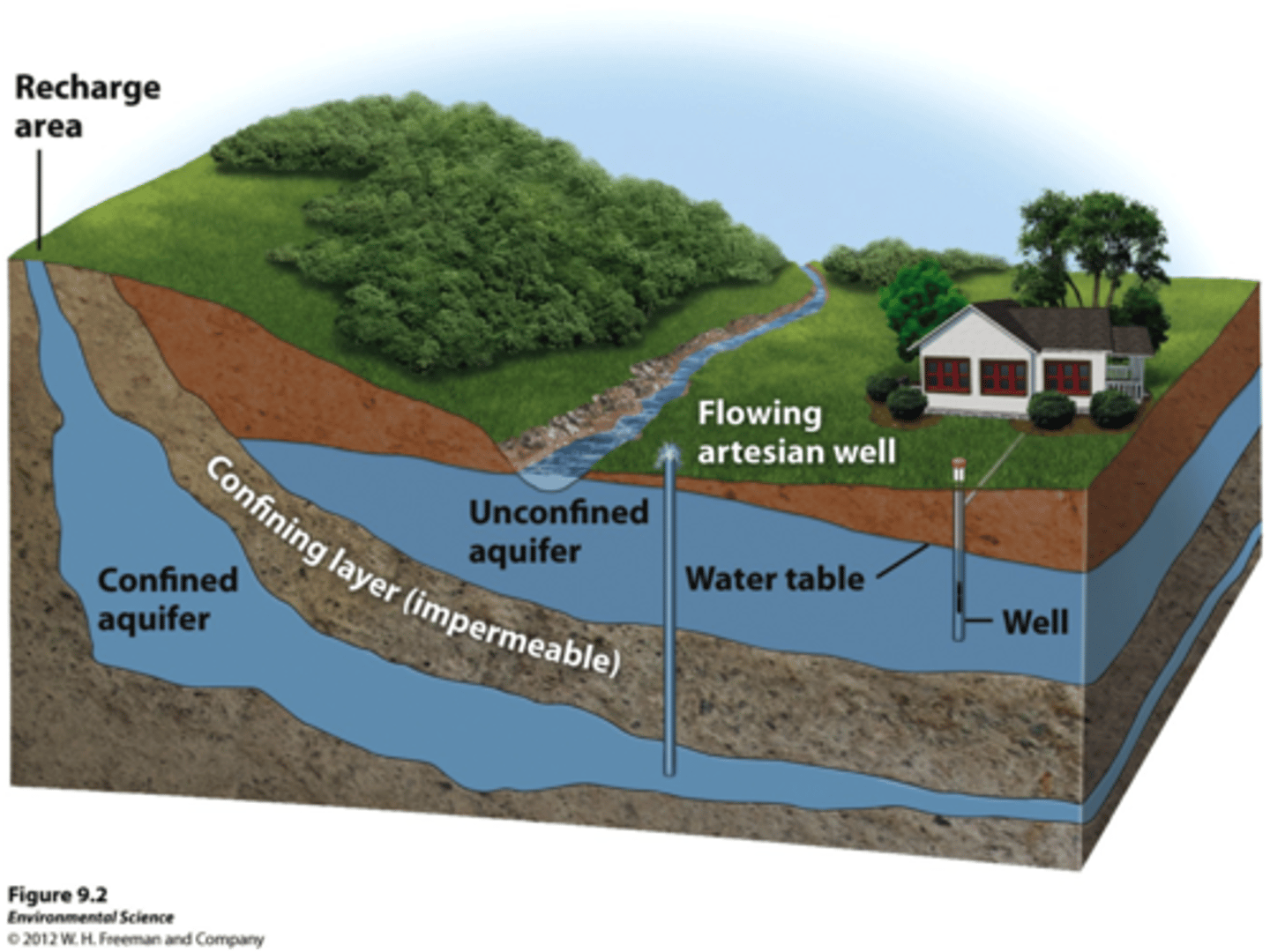
Water Table
The upper surface of the ground where the soil or rock is completely filled with water.
Unconfined Aquifer
An aquifer made of porous rock covered by soil out of which water can easily flow.
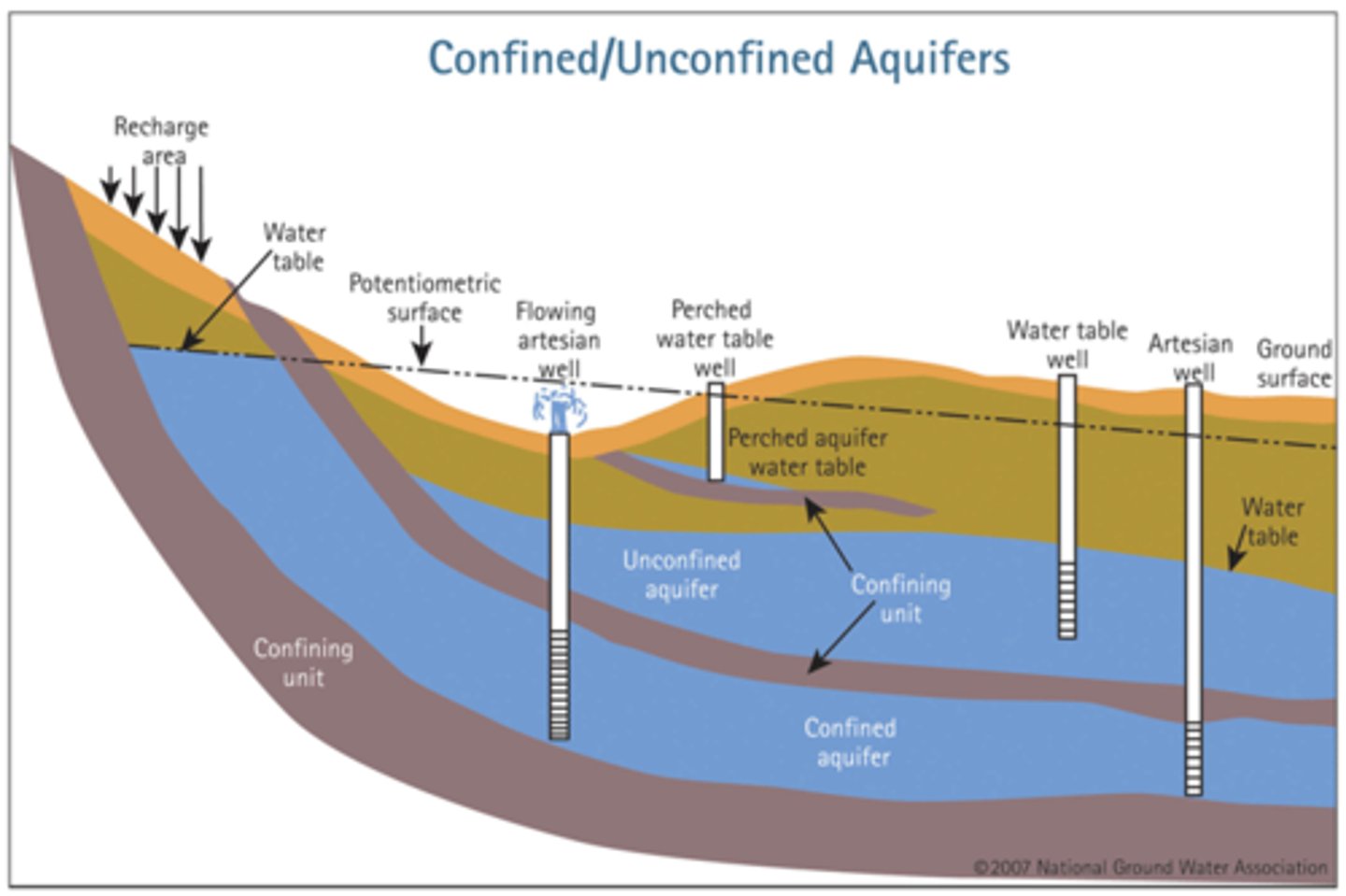
Confined Aquifer
Aquifers covered by an impermeable and confining layer impeding water flow in or out.
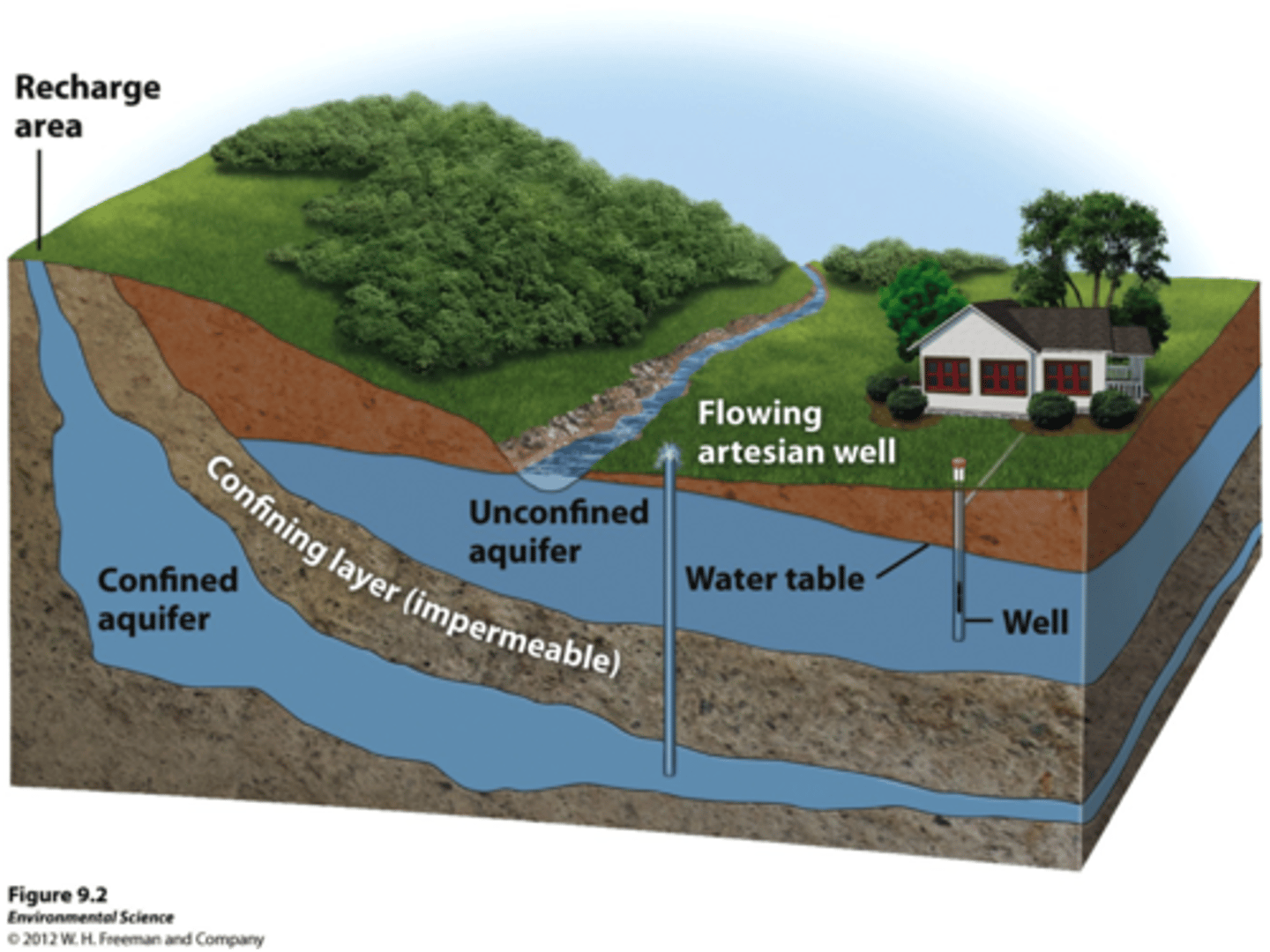
Artesian Well
Pressure from the confined aquifer pushes water up at a location without a pump.
Biogeochemical Cycles
The elements and compounds that make up nutrients move continually through air, water, soil, rock, and living organisms in ecosystems and in the biosphere in cycles.
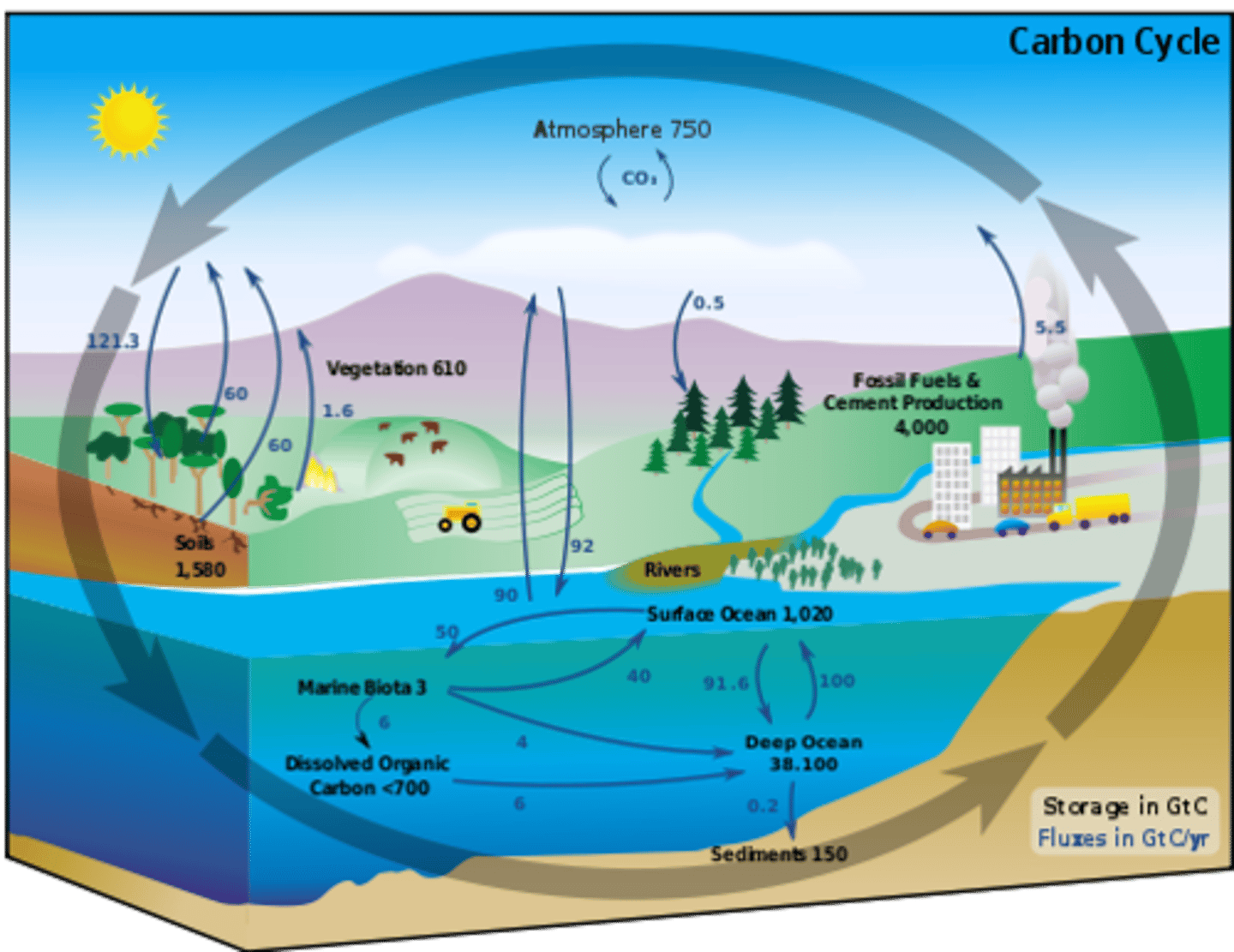
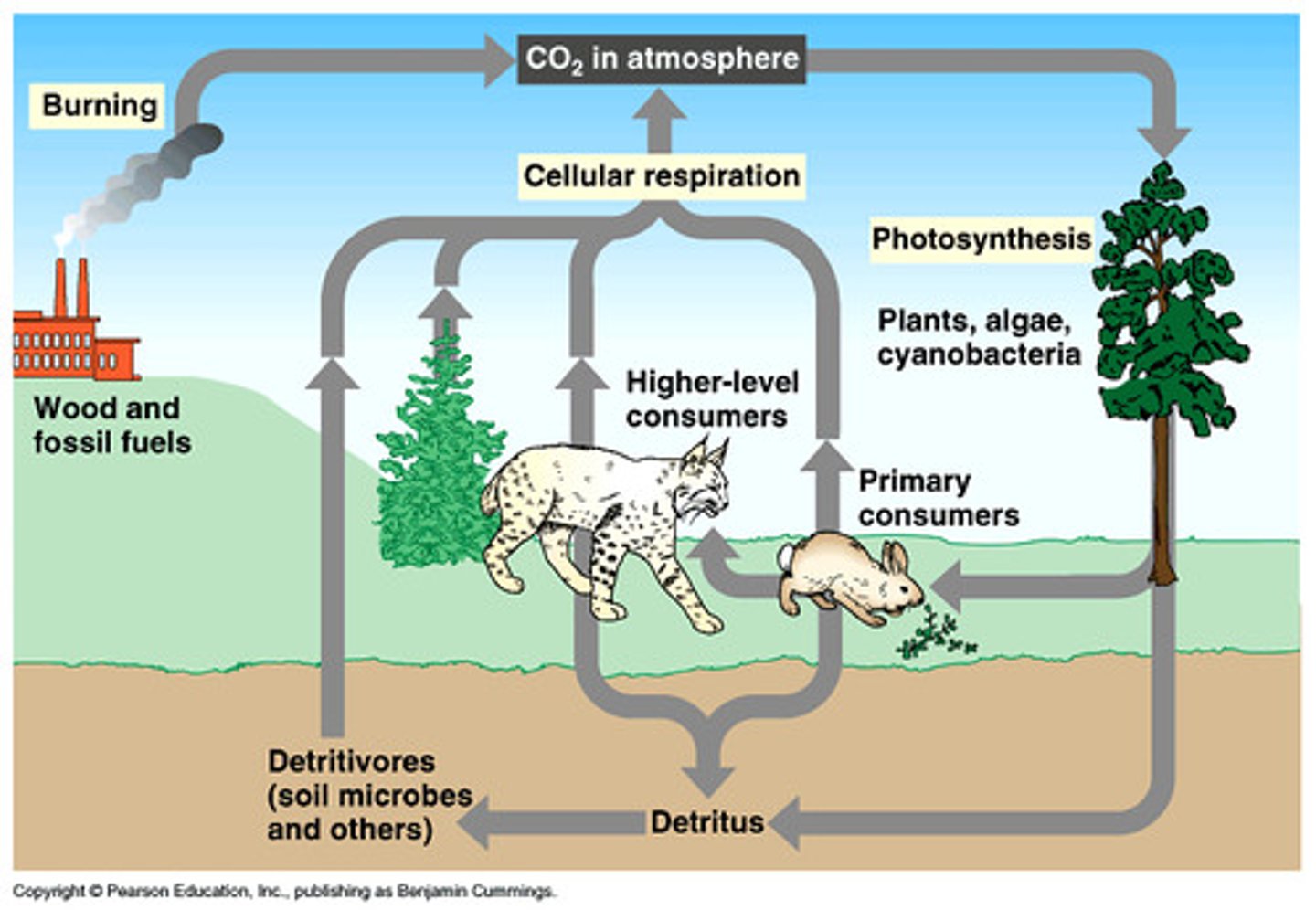
Carbon
Is the element of life.
Abiotic environment.
Carbon enters the biotic world through photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
Carbon returns to the atmosphere and water by cellular respiration (reverse of photosynthesis) burning, decay.
Produces C02 if oxygen is present.
Produces CH4 if oxygen isn't present.
Hydrologic Cycle
The continuous movement of water in the air, the surface of and below the earth.
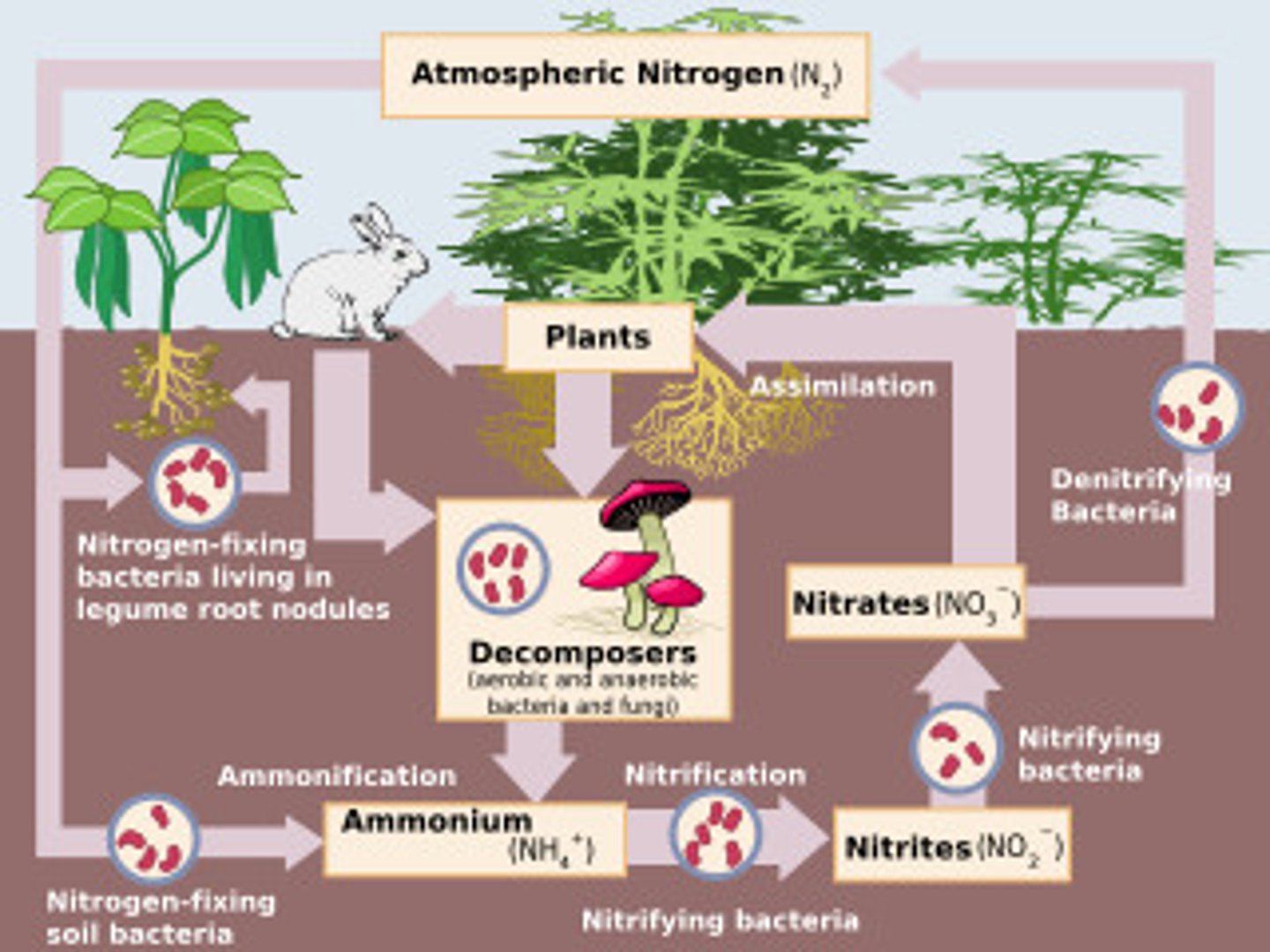
Nitrogen Cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere.
Need nitrogen and phosphates to build proteins and nucleic acids.
Nitrogen Fixation = Nitrogen gas to Ammonium.
Nitrification = Ammonia is converted to nitrate ions (NO3-).
Nitrification = The process by which nitrites and nitrates are produced by bacteria in the soil.
Carbon Cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again.
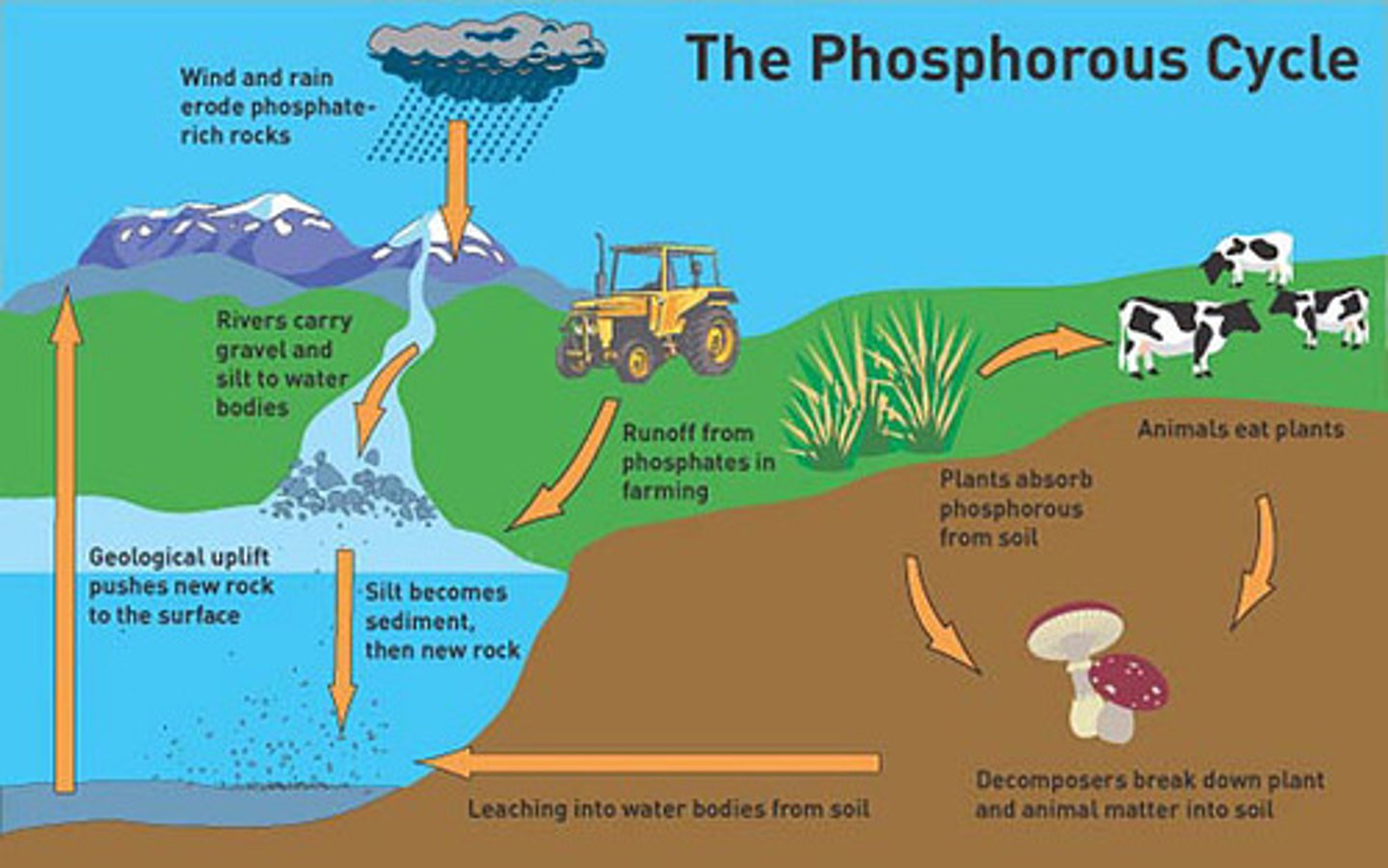
Phosphorus Cycle
The movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks.
Detritus
Dead organic matter.
Humus
Material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter.
Kinetic Energy
The energy an object has due to its motion.
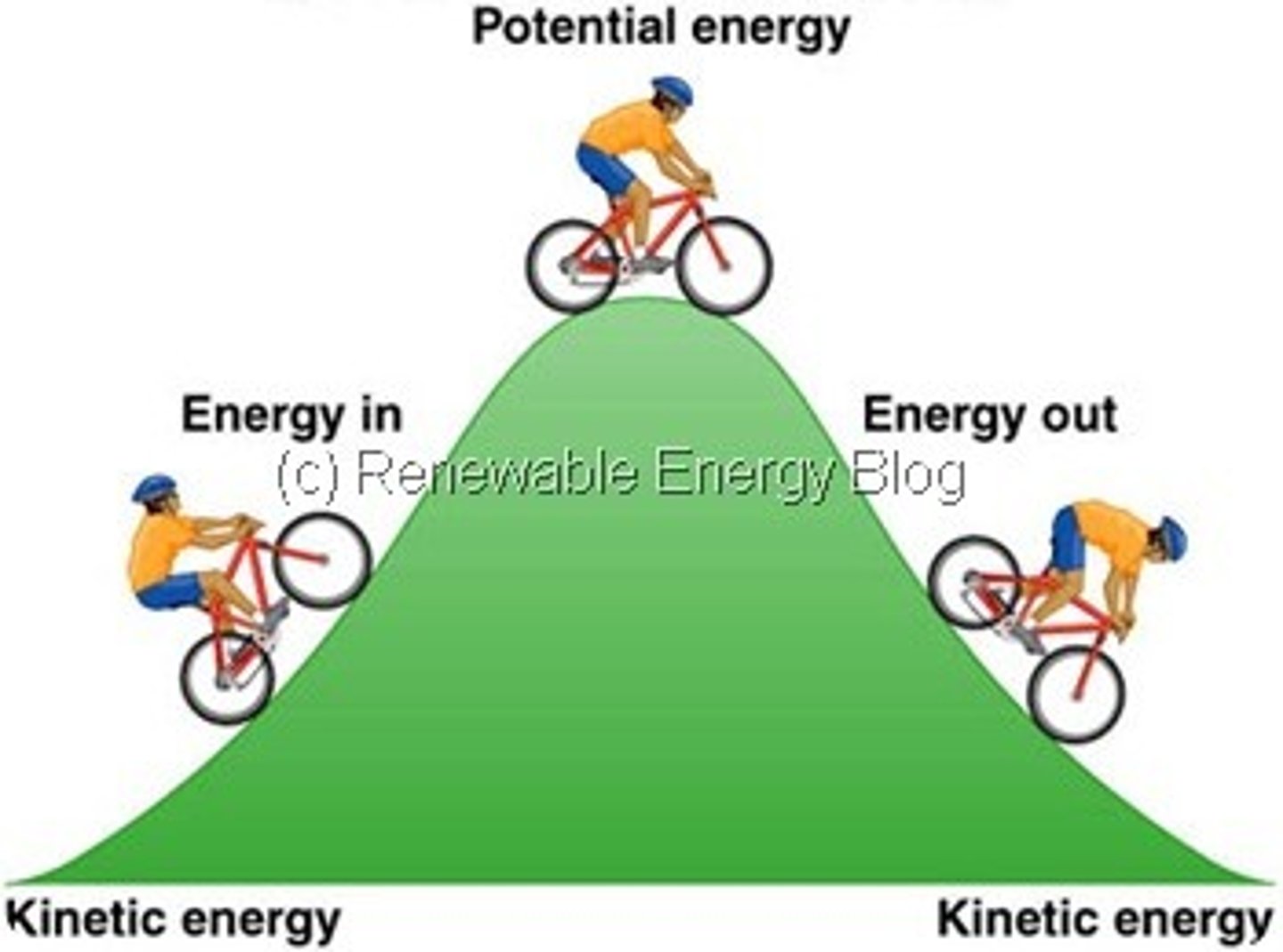
Potential Energy
Stored energy.
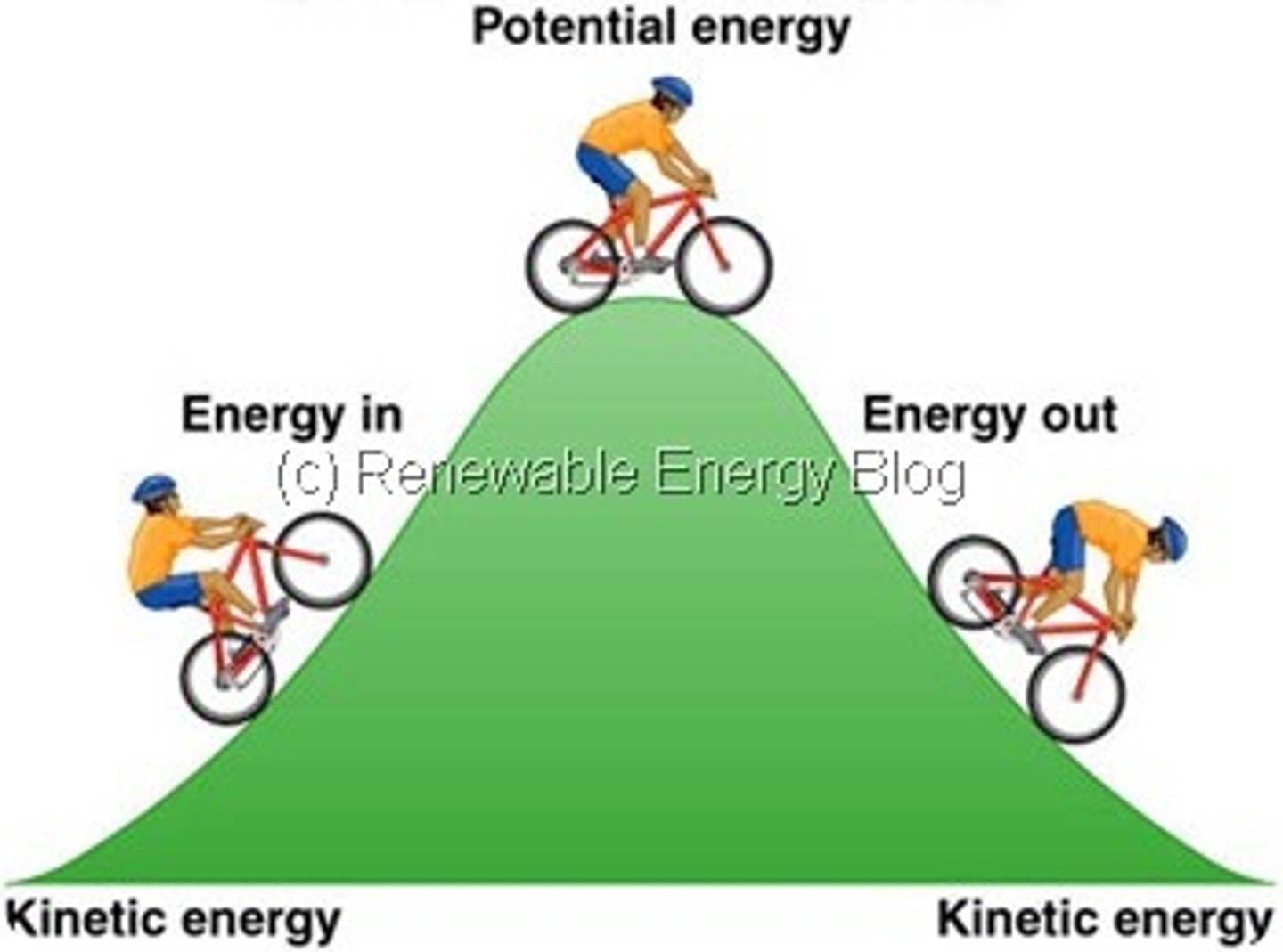
The First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
(Ex. It can change from one form to another.)
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
The increase of entropy when energy changes form it is always degraded to a more dispersed form.
Consumer
Heterotroph, not able to produce its own food.
Producer
Autotroph, able to produce its own food.
Decomposers
Organisms that break down wastes and dead organisms and return raw materials to the environment.
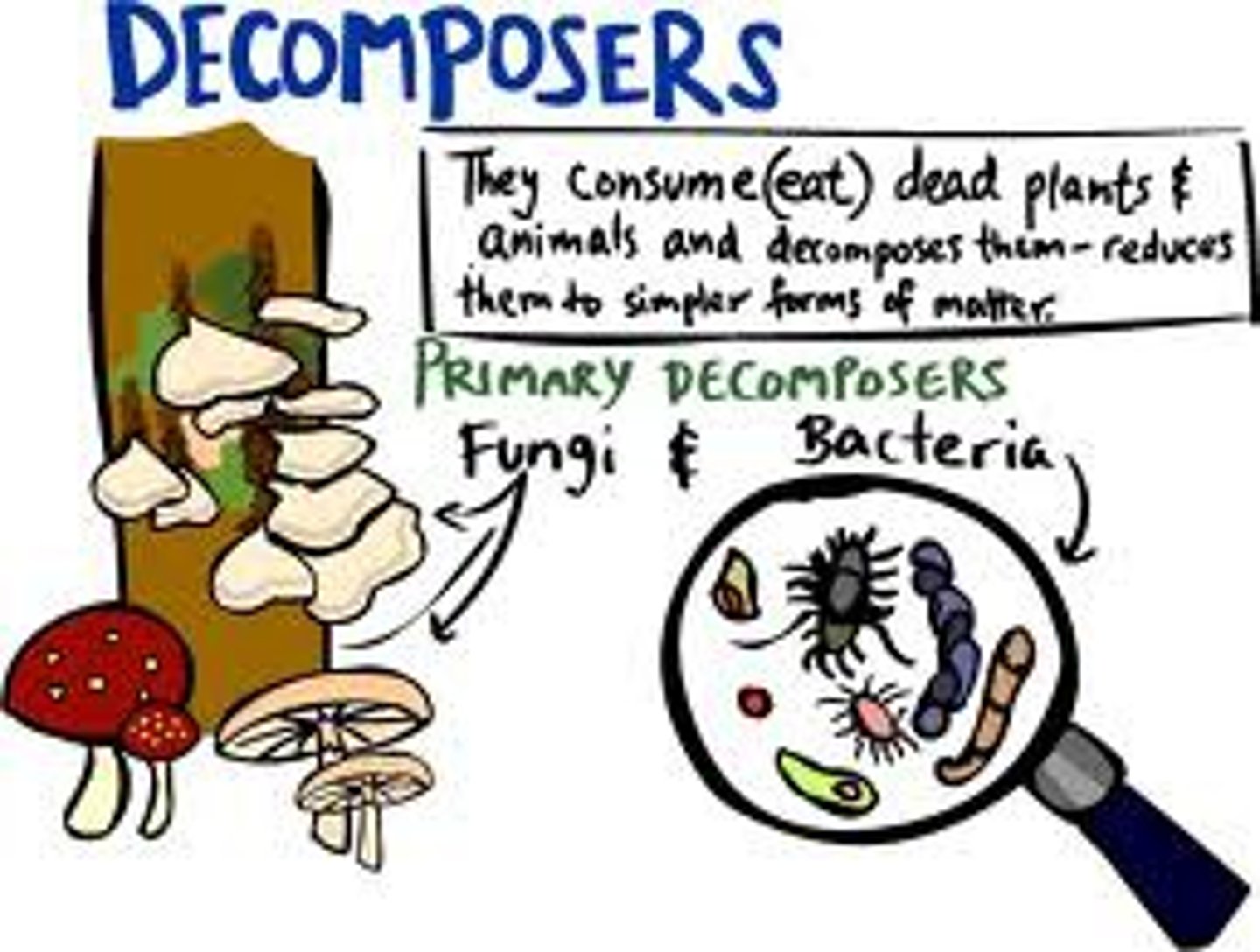
Detritivore
An organism that feeds on plant and animal remains and other dead matter.

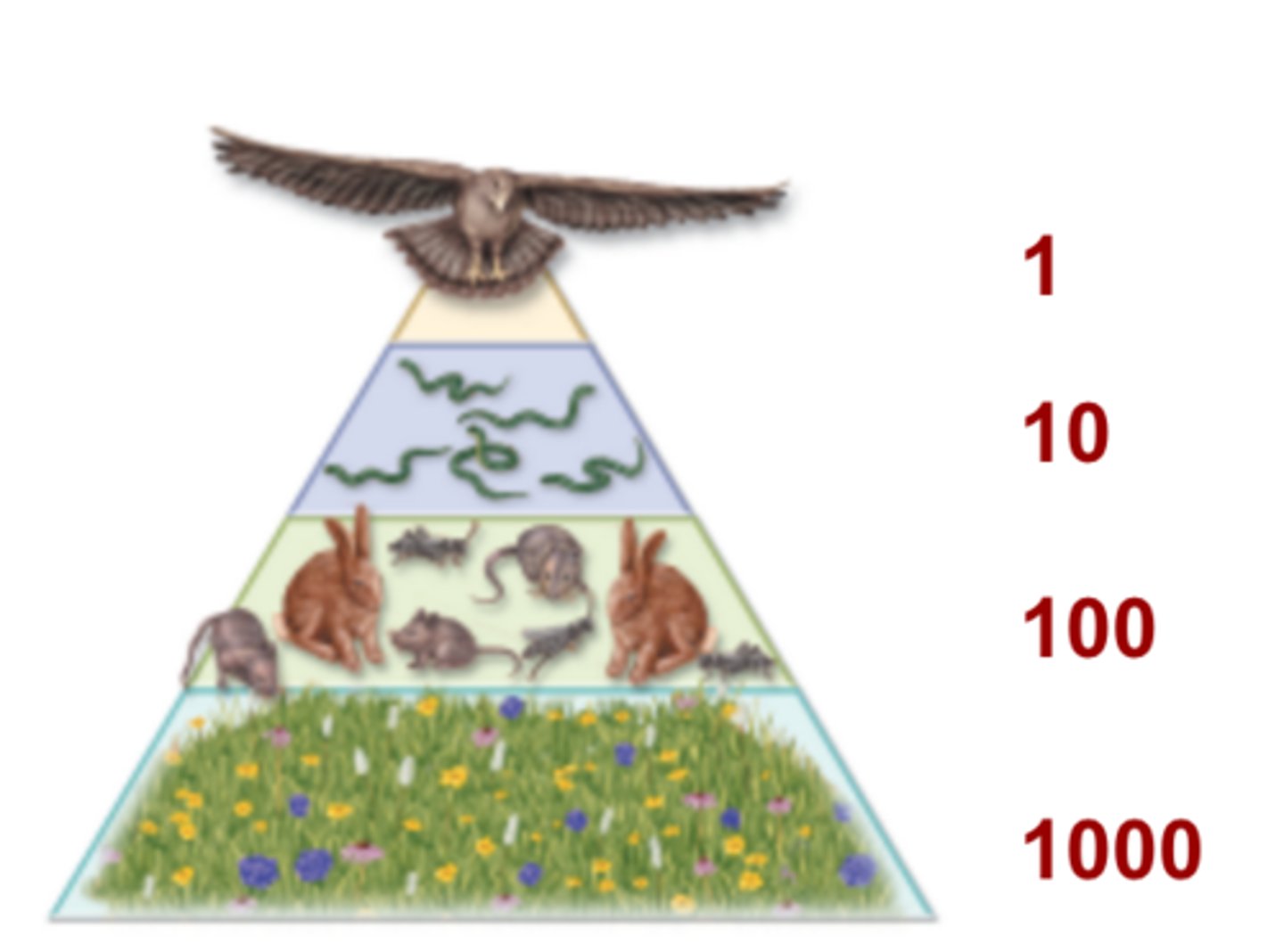
Ecological Pyramids
Energy Pyramid (sometimes called Trophic Pyramid), Biomass Pyramid, Pyramid of Numbers.
*Pyramid of energy cannot be inverted like the other two pyramids.
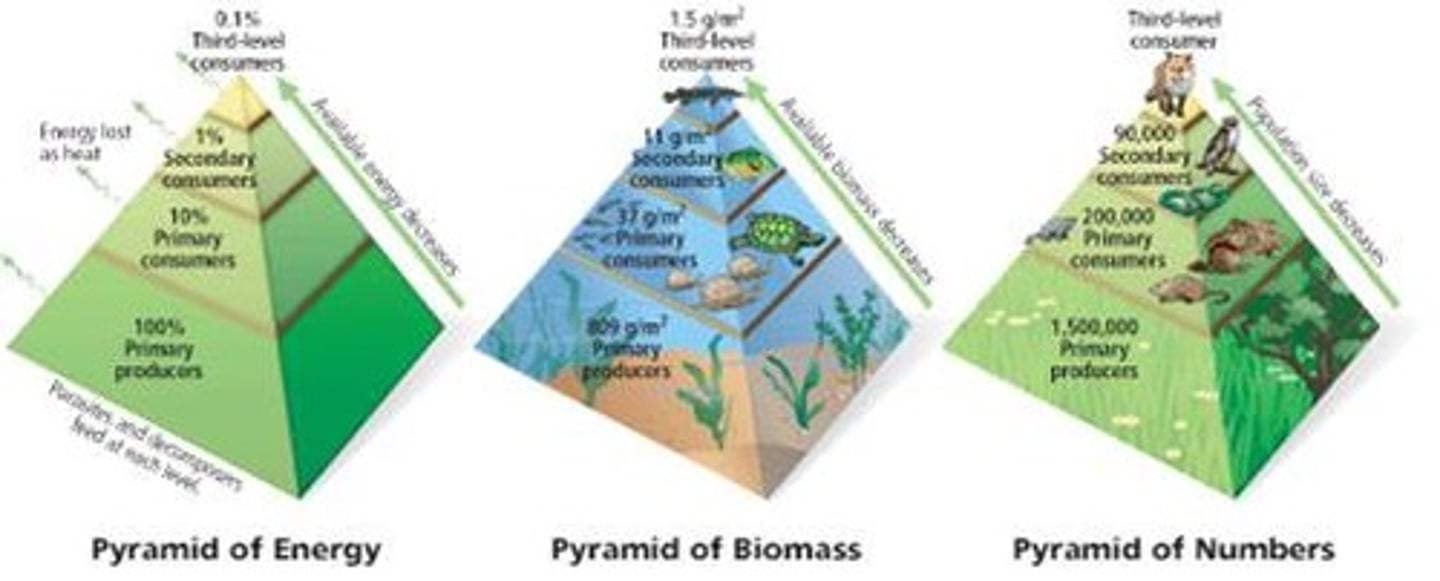
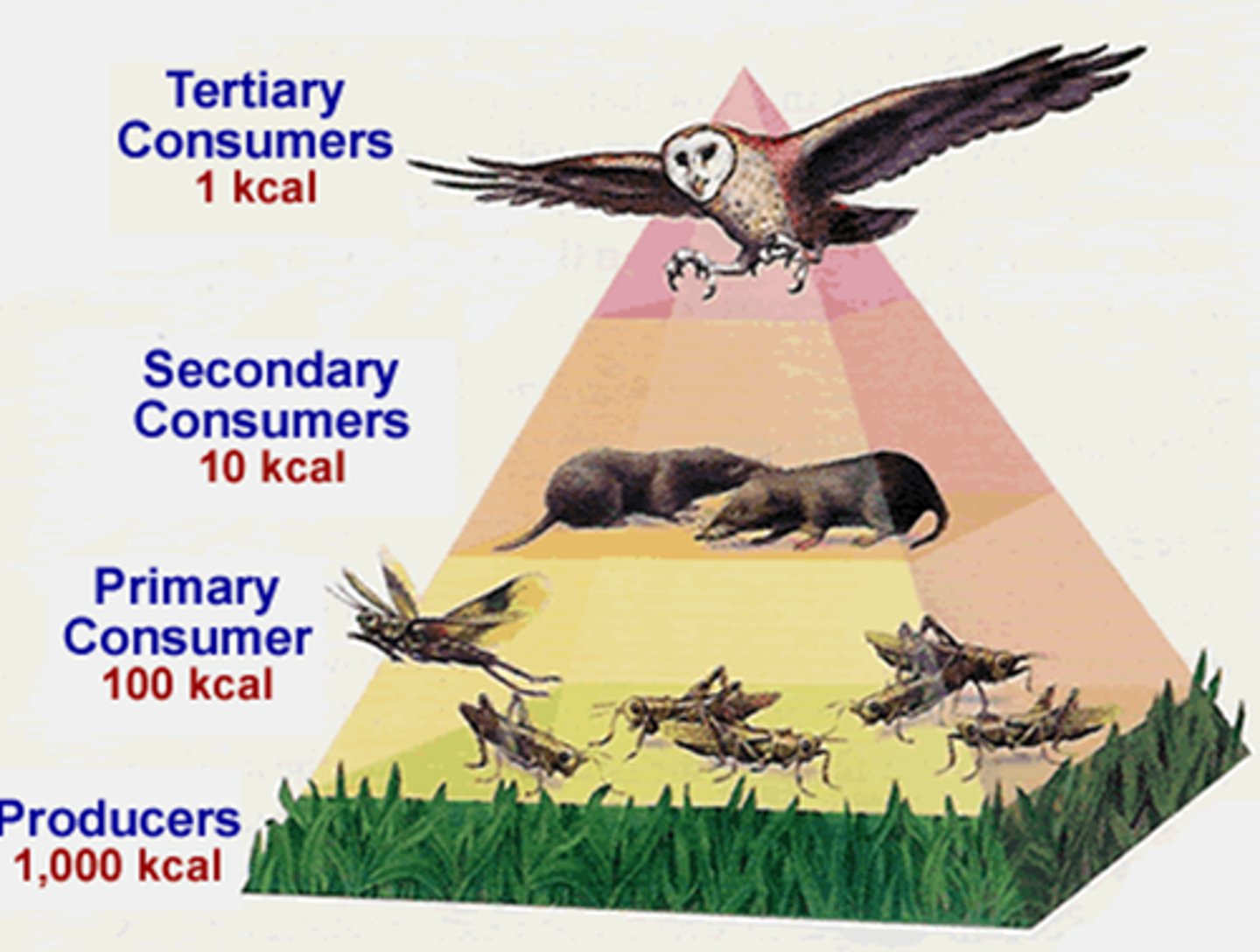
Energy Pyramid (10% Rule)
Only 10% flows from one level up to the next; the other 90% is lost as waste heat.
*Remember the 10% rule for each trophic layer.
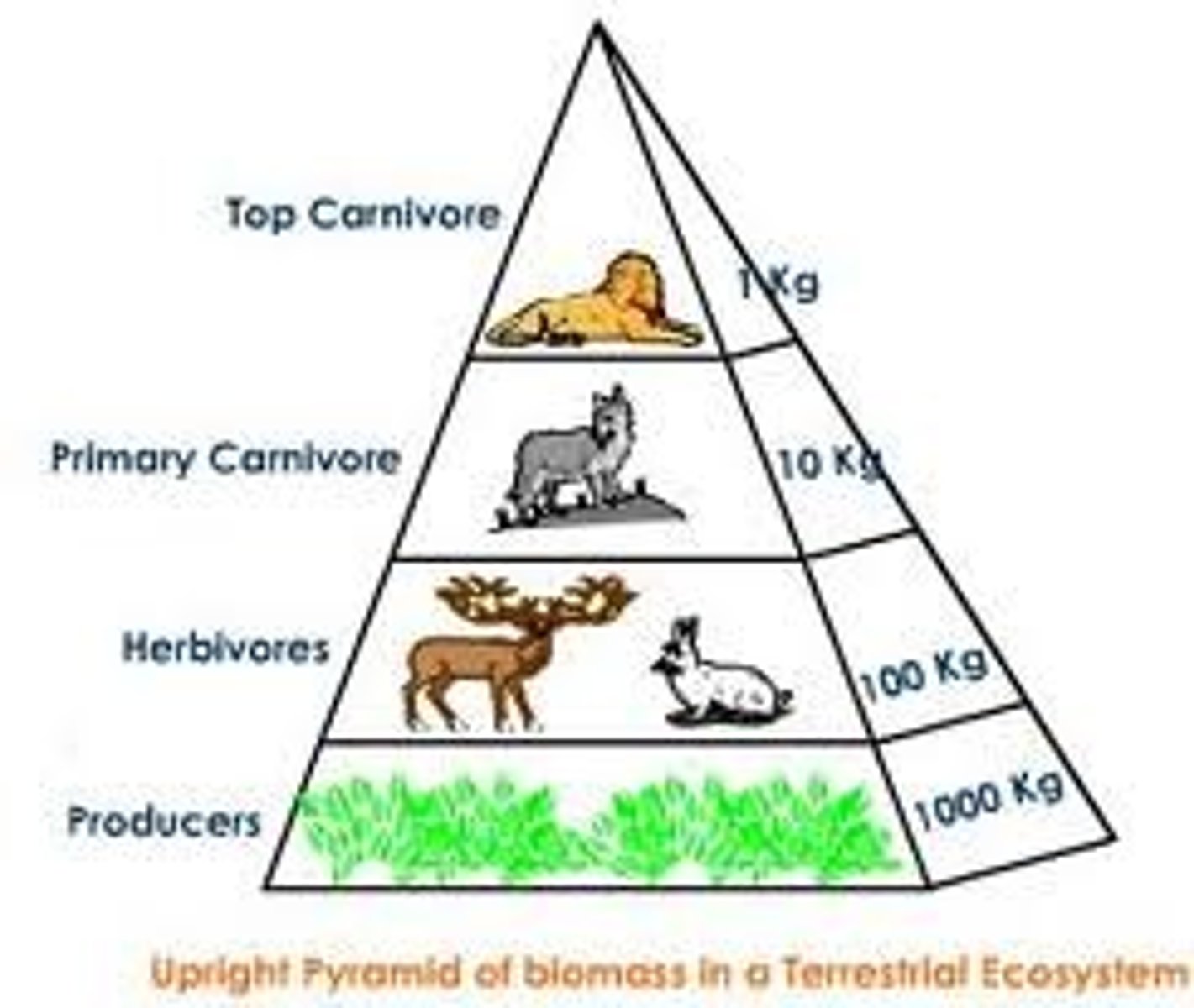
Biomass Energy Pyramid
Biomass energy pyramids show the relationship between biomass and trophic level by quantifying the amount of biomass present at each trophic level, typical units for a biomass pyramid are grams per square meter or calories per square meter.
Pyramid of Numbers
Representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem.
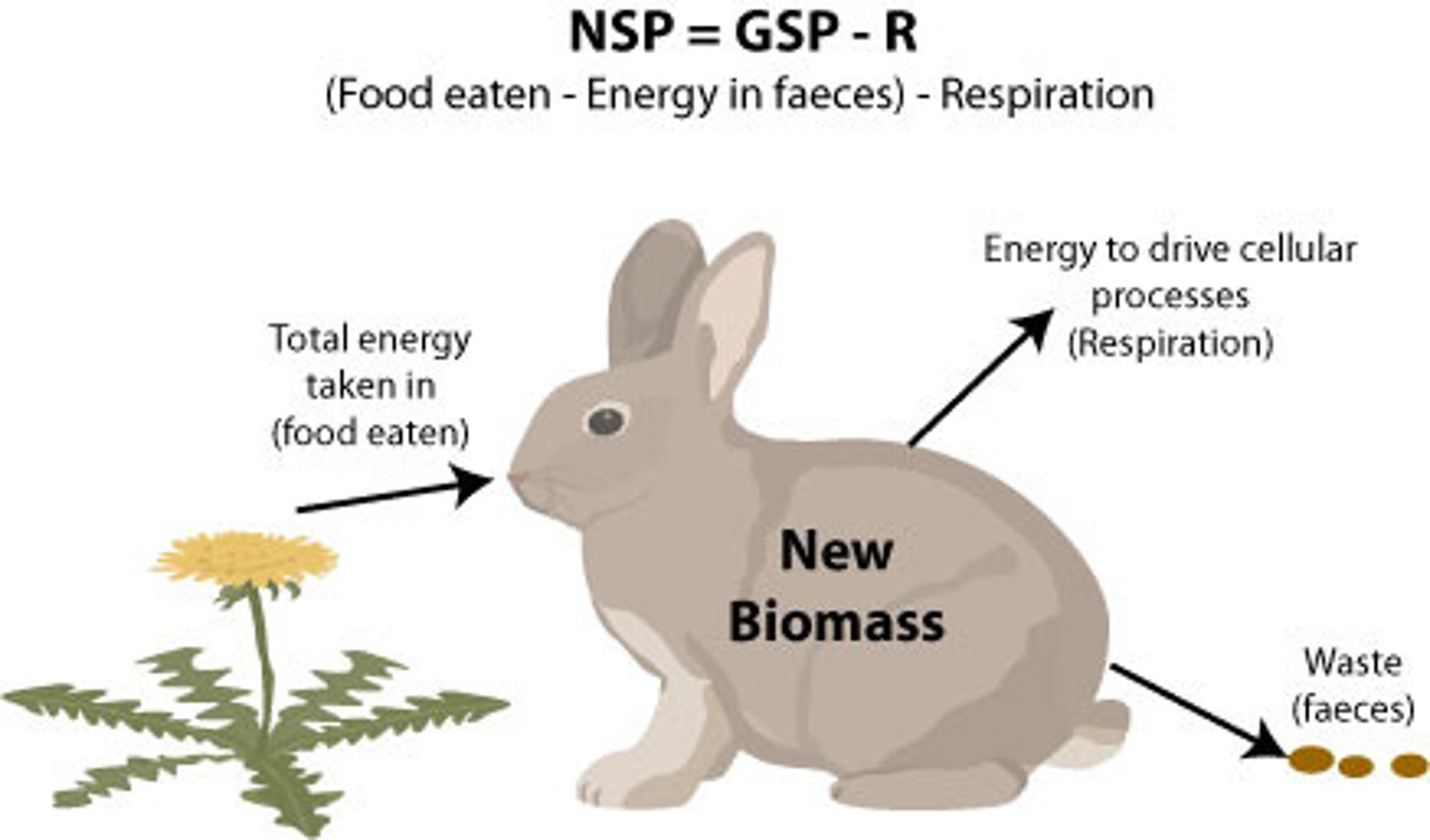
Primary Productivity
Rate at which autotrophs synthesize new biomes.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total rate of photosynthesis in a given area.
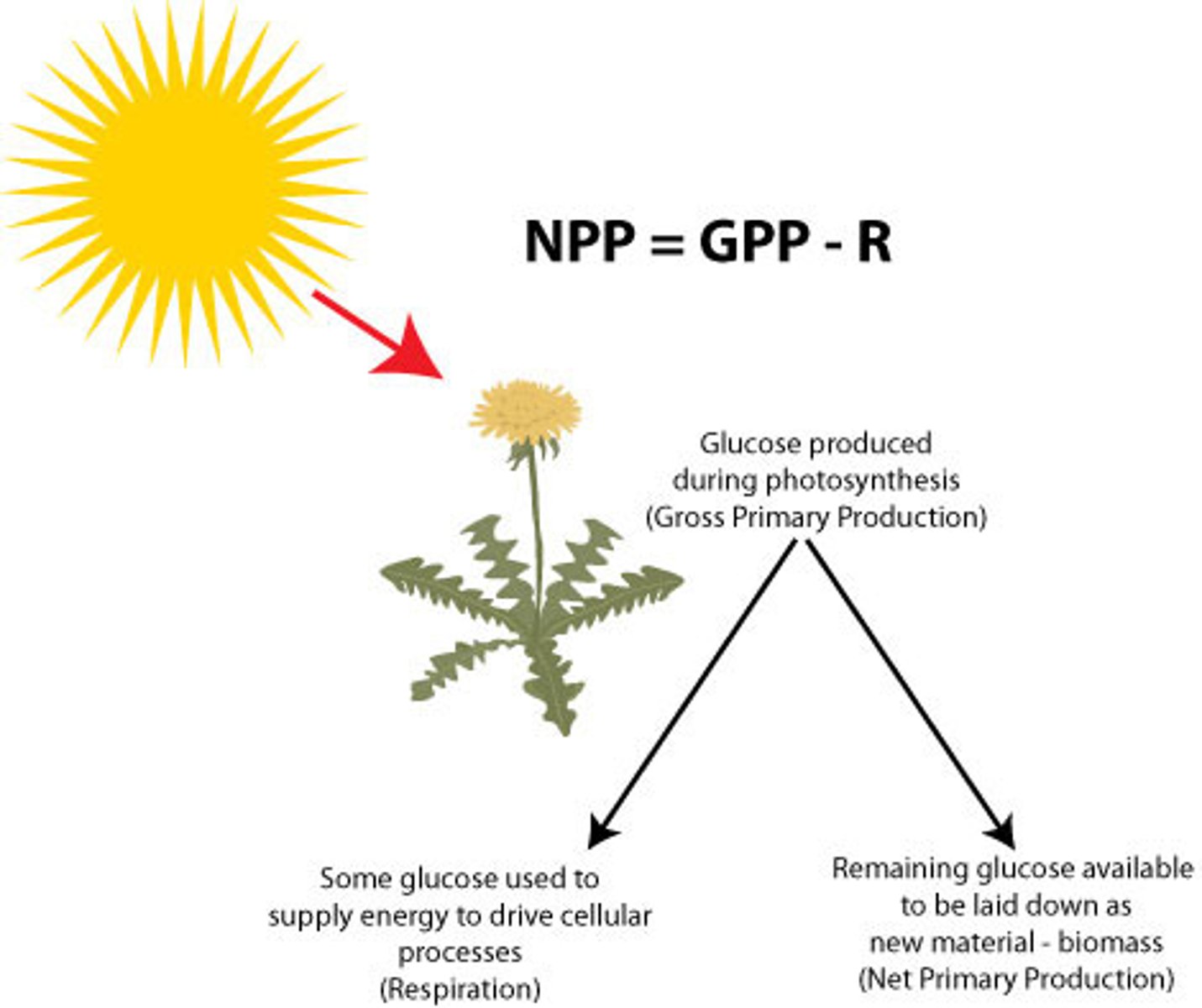
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The energy is available to consumers determined by subtracting the energy by plants from the total energy transformed by the process of photosynthesis.
Formulas: NPP=GPP-R GPP=NPP+R

Factors That Affect Primary Productivity
Solar Radiation: Quality/Quantity.
Temperature: Warmer temps correlate to higher productivity. High temps can denture enzymes.
CO2.
H2O.
*Most productive ecosystems are those with high temperatures, lots of water, light, and nutrients.
Marine Producers
Algae: Macro-algae, phytoplankton.
Plants: Seagrasses.
Bacteria: Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), chemosynthesizing, archaebacteria (no light needed).

Freshwater Producer
Algae.
Aquatic Plants: Waterlilies, cattails, duckweed.
Bacteria: Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae).
What are the three scales of biodiversity?
Genetic Diversity, Species Diversity, Ecosystem Diversity.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic Variation among individuals within a population.

What are the 2 environmental stressors?
Physical stress and Biological stress.
Physical Stress
Natural Disasters, Wildfires, Pollution, Thermal Stress, Radiation, Climatic (light, temperature).
Biological Stress
Predation, Competition, Parasitism, Lack of Mates.
Bottleneck Effect
A drastic and sudden reduction in the size of a population leads to a change in the genetic pool.
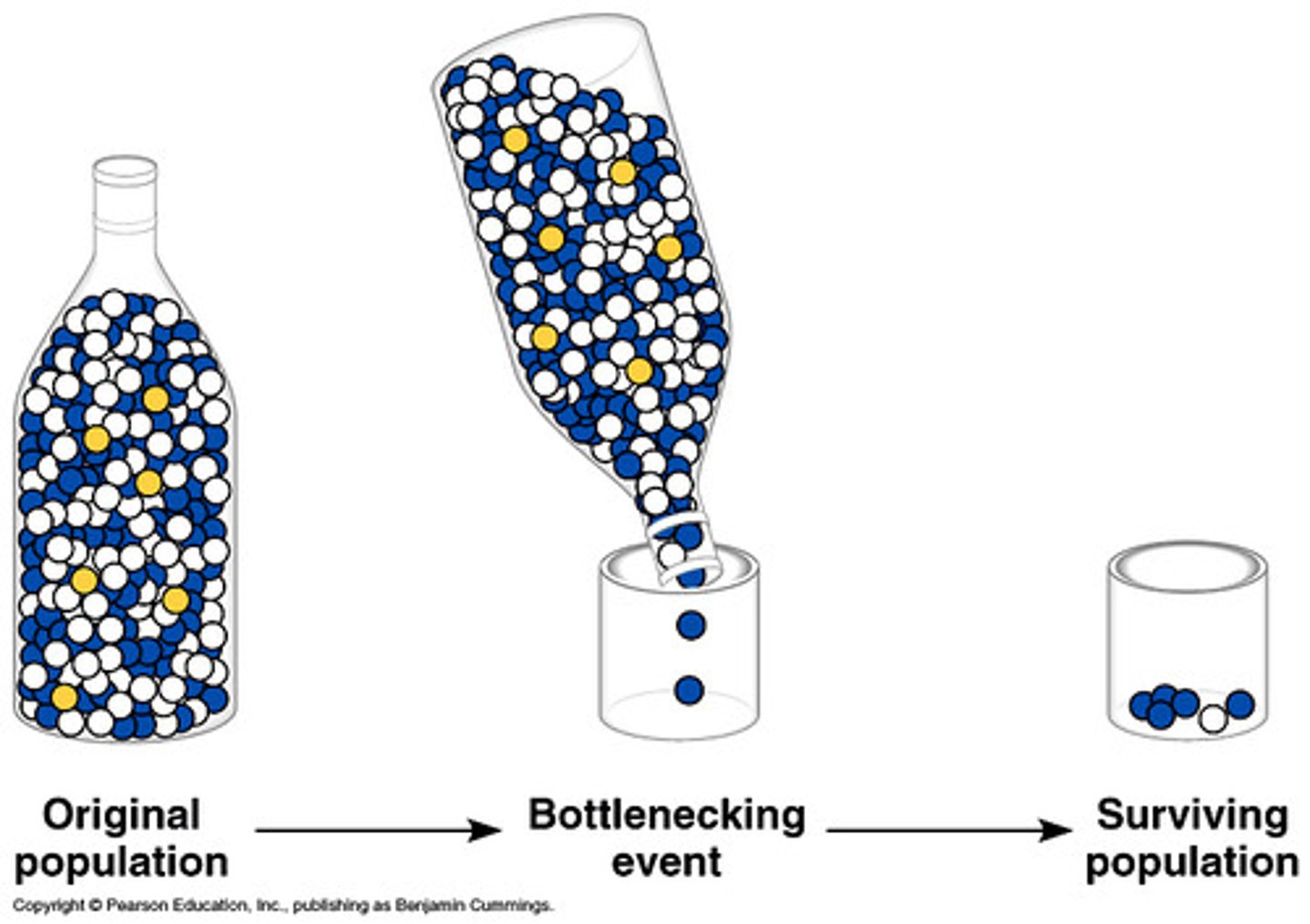
Species Diversity
The number of species in a region or habitat (in a community or ecosystem).

What is the most common animal on earth?
Nematode worms.
4-5 are nematode worms.
What is the most common organism?
The bacterium pelagibacter ubique (1/3rd of all single-celled ocean organisms).
Ecosystem Diversity (Habitat)
The variety of habitats that exist within a given region.
Generalist Species
Can live under a wide range of biotic (abiotic conditions can adopt anywhere).
Specialist Species
Live under a very narrow range of conditions or feed on one or a very small group of species (specialize on something, can't adopt to something new).
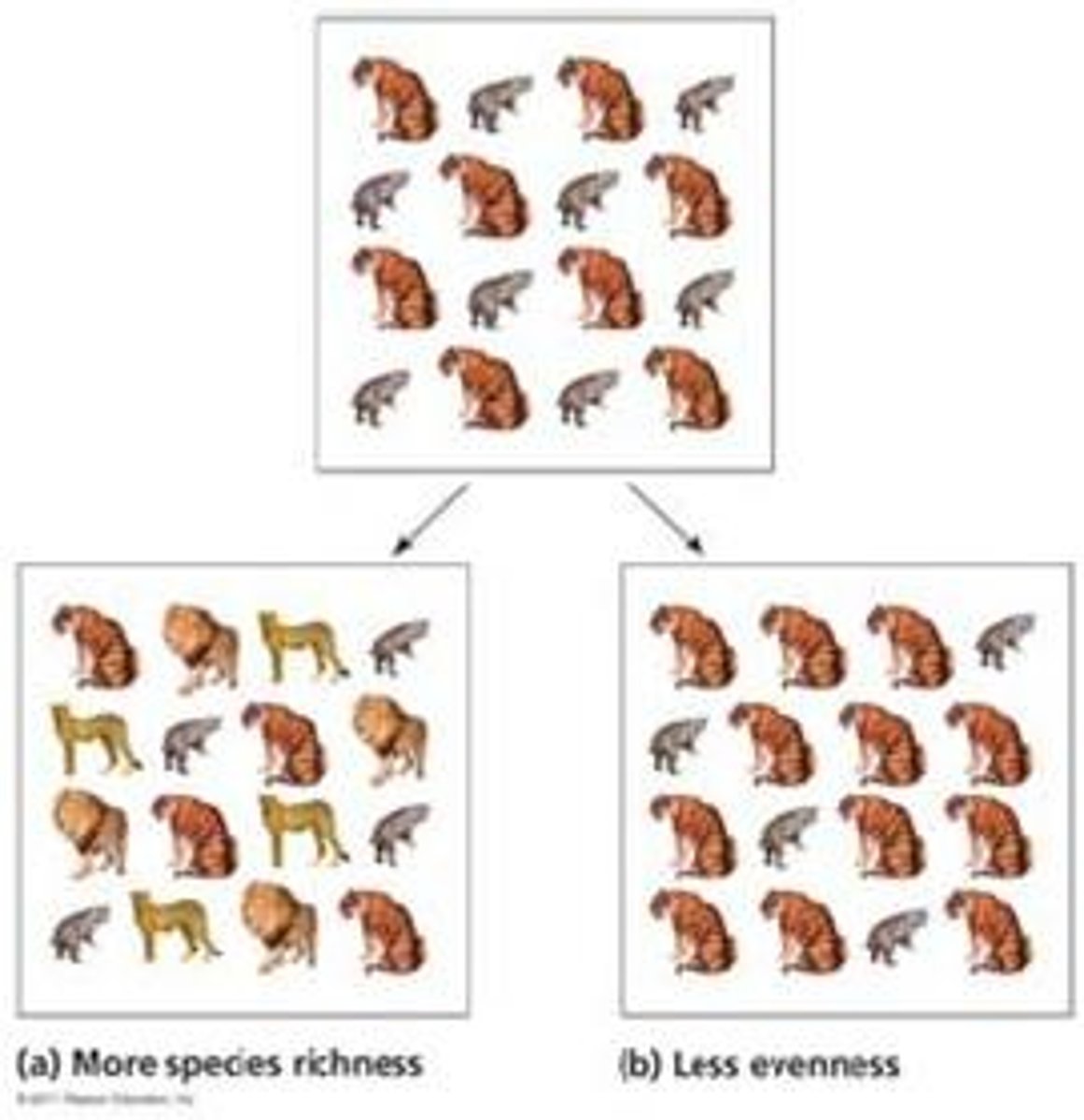
Species Evenness
The abundance of individuals within each species contained in a community.
Intrinsic Value
Ecosystems have their own value independent from the needs and desires of humans.
Moral obligations.
Often related to religion and or philosophy.
Instrumental
Has worth in terms of goods and services.
Provisioning Services (Ecosystem service)
Goods that humans use directly --> Lumbar, Food Crops, Rubber, Fur, Medicinal Plants (Taxol).

Regulating Services (Ecosystem service)
4 Gigatons of carbon removed by phytoplankton and plants --> Nutrients and water cycles.

Support Systems (Ecosystem service)
Pollination, Water Filtration, Natural Pest Control.