Skin Physiology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
types of receptors in skin
free nerve endings (+tactile discs), corpuscles (tactile, lamellar, bulbous)
free nerve endings description
most common, terminals have ion channels and GPCRs
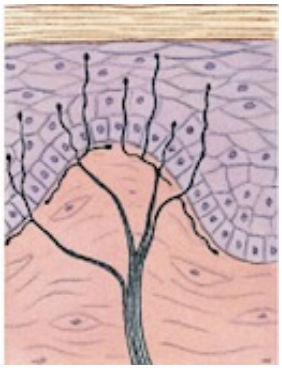
free nerve endings
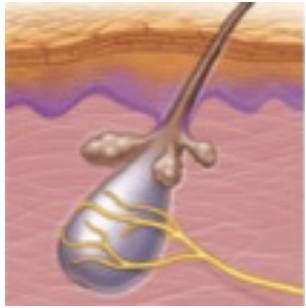
root hair plexus
different TRPs detect…
different temperature ranges
tactile merkel discs
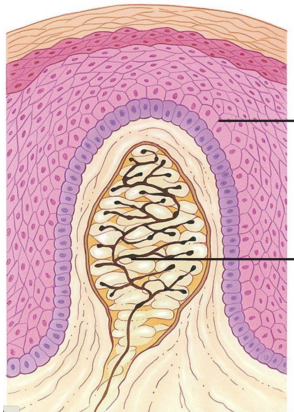
tactile meissner corpuscles
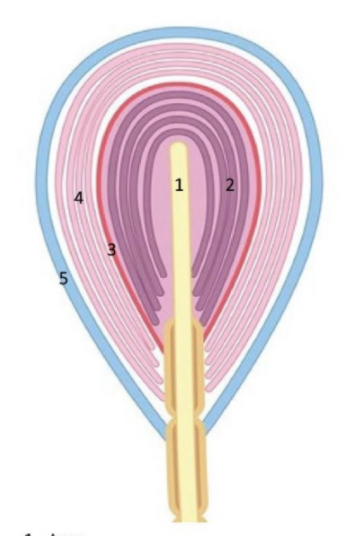
lamellar pacinian corpuscles
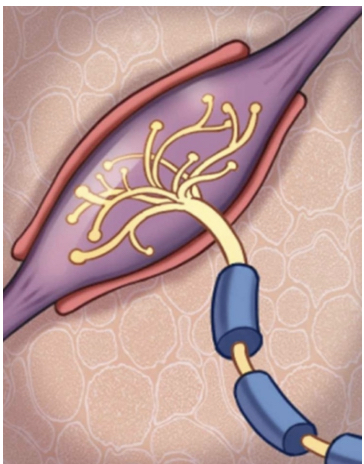
bulbous ruffini corpuscles
tactile discs description
specialised nerve endings associated tactile merkel cells in stratum basale
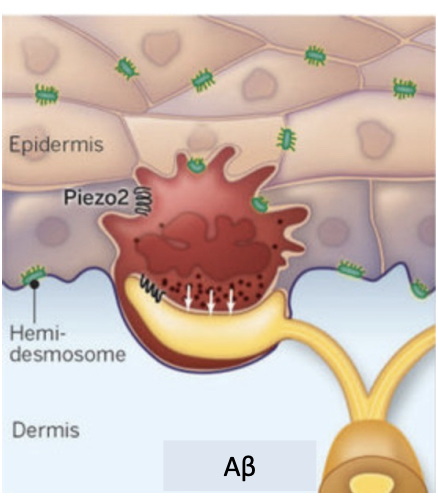
triggering action potentials in tactile merkel discs
mechanical stimulus opens piezo2 receptors in tactile cell
ions move into cell, causing release of neurotransmitters that depolarise nerve
tactile meissner corpuscles description
branched axon surrounded by specialised schwann cells inside connective tissue capsule
triggering action potentials in tactile meissner corpuscles
deformation of capsule triggers APs in axon
lamellar pacinian corpuscles description
single axon surrounded by layers of collagen, fibroblasts and schwann cells separated by gelatinous fluid
triggering action potentials in lamellar pacinian corpuscles
pressure/vibration transmitted through layers to axon, regaining shape quickly
A-delta fibres vs. C-fibres
A-delta = small diameter, myelinated, sharp fast pain
C = medium diameter, unmyelinated, dull aching pain
bulbous ruffini corpuscles description
branched axon intertwined with collagen fibres continuous with collagen of dermis surrounded by flattened capsule
triggering action potentials in bulbous ruffini corpuscles
force of stretching collagen transmitted to axon triggering AP
what do free nerve endings detect?
temperature, itching, pain, light touch
what do tactile merkel cells detect?
shape, edges, 5-15Hz vibration
what do tactile meissner corpuscles detect?
two point discrimination, light pressure, 10-50hz vibration
what do lamellar pacinian corpuscles detect?
deep pressure, vibration
what do bulbous ruffini corpuscles detect?
stretching in collagen (prorioception), deep pressure
where are tactile merkel discs most commonly found?
fingertips — have small receptive fields
where are tatile meissner corpuscles most commonly found (type of skin + layer of skin)
glabrous/hairless skin, papillary layer of dermis
what layers are lamellar corpuscles found in?
deep dermis and hypodermis
where are bulbous ruffini corpuscles most commonly found (skin type + layer + function)
deep dermis and hypodermis
fingertips (detect slippage) and joint capsules (proprioception)
how does sympathetic nervous system affect precapillary sphincters
release noradrenaline → alpha-1 adrenergic receptors on smooth muscle → vasoconstriction
how does sympathetic nervous system affect eccrine sweat glands?
particular nerves release acetylcholine → cholinergic mAchRs → sweating
what type of receptor are mAchRs?
muscarinic GPCRs
mechanisms of body temperature DECREASE
vasodilation, sweating, increased respiratory rate, behaviour
mechanisms of body temp increase (CONSERVATION)
vasoconstriction, counter-current exchange, goosebumps
mechanisms of body temp increase (GENERATION)
shivering, increased metabolism (adrenal medulla), brown fat cells burning stored energy, increased BMR (thyroxine)