AP Bio Unit 4: Cellular Energetics Vocab
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Energy is stored in ______ molecules.
Organic (carbs, lipids, proteins)
Endergonic
Energy enters the process
Exergonic
Energy exits the process
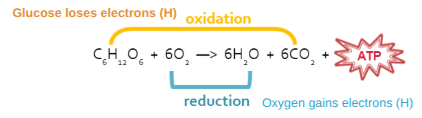
Oxidation
Loses electron
Adds O, removes H
Releases energy
Exergonic

Reduction
Gains electron
Removes O, adds H
Stores energy
Endergonic
Electron Carriers
Moves electrons by shuttling H atoms around, creating a gradient
When electrons move down the gradient through ATP synthase enzyme, ATP is generated
A phosphate group is added to ADP, storing energy in ATP
Each carrier is more electronegative than the previous (think of stairs), and is oixdation/exergonic
In the Calvin Cycle, NADPH oxidize to ______.
NADP+
In the Calvin Cycle, ATP reduces to ______.
ADP
In the Krebs Cycle, NAD+ reduces to _____.
NADH
In the Krebs Cycle, FAD reduces to _____.
FADH2
Photosynthesis
Converts light energy to chemical energy of food
Photosynthesis Products
ATP & NADPH (P for photosynthesis)
NADPH (in photosynthesis)
The electron carrier for photosynthesis (stores energy)
Mesophyll
The middle of a leaf, chloroplasts are found here
Stomata
Pores in the leaf and site of gas exchange (CO2 enters & O2 exits)
Thylakoids
The flat green “pancakes”. Stores chlorophyll and collect sun energy for the first part of photosynthesis.
Grana
Stacks of thylakoids and helps increase surface area
Stroma
The fluid that surrounds the thylakoids and is the site for the second half of photosynthesis. Also contains ribosomes & chloroplast DNA.
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Steps of Photosynthesis
LIGHT → Light reactions in thylakoids → ATP, NADPH → Calvin cycle in stroma → ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (carbs)
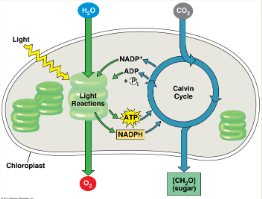
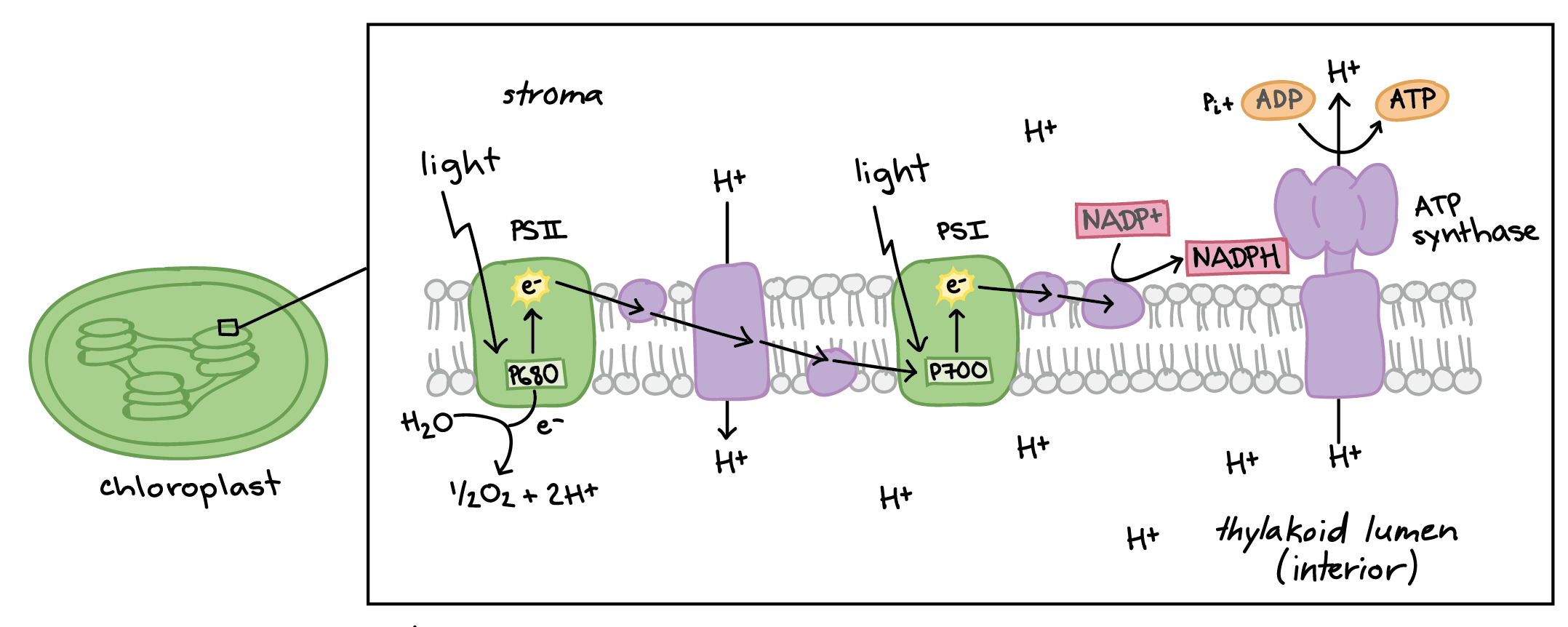
Light Reactions (Light Dependent)
Light energy converted into ATP & NADPH using electrons from H20
Calvin Cycle (Light Independent)
Takes the ATP from the light Reactions to power chemical reactions (with the enzymes) to convert CO2 and the H from H2O into glucose. Produces ADP & NADP+.
6 cycles = 1 molecule of glucose
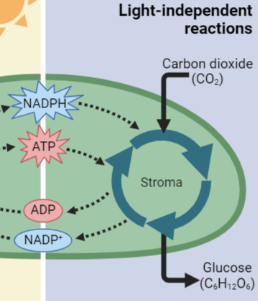
Calvin Cycle Products
ADP & NADP+
Carbon in the Calvin Cycle
R: 3 CO2 + 3 RuBP acceptors → P: 6 G3P
ATP in the Calvin Cycle
R: ATP → P: 9 ADP (6 in reduction, 3 in regeneration)
NADPH in the Calvin Cycle
R: 6 NADPH → P: 6 NADP+ (during reduction)
Rubisco
An enzyme in the Calvin Cycle that “fixes” the carbon dioxide into a carbohydrate during the Carbon Fixation stage
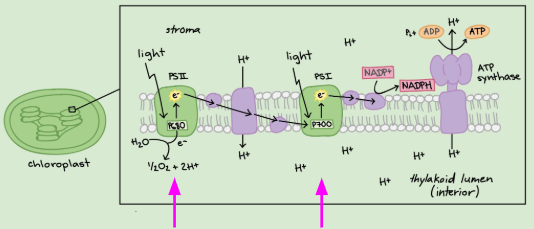
Photosystems (PS)
Large complexes of proteins and pigments (light-absorbing molecules) that are optimized to harvest light.
→ 2 types: PSI & PSII
PS II
Provides energy for ATP
Restored by splitting the water and releasing O2 & H+
First protein of the ETC
PS I
The second input of light re-energizes electrons
Provides energy to create NADPH
The third protein (after PSII & the cytochrome complex)
NADPH
Another form of stored energy (like ATP)
Electron Transport Chain (ETC in photosynthesis)
A cycle of oxidation & reduction to pass electrons on
Uses electrons’ energy to pump protons ( H+ ) into the thylakoid through active transport (against the gradient)
ATP Synthase (photosynthesis)
The enzyme in the ETC
Uses protein gradient (high H+ inside thylakoid & low H+ outside thylakoid) to make ATP
Passive diffusion of H+ provides energy to add phosphate back onto ATP
The three Calvin Cycle steps
Carbon Fixation, Reduction, & Regeneration
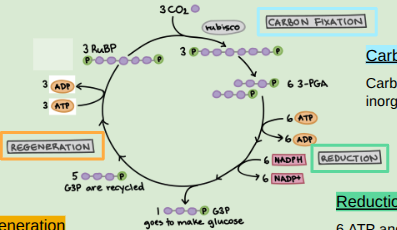
Carbon Fixation
Carbon dioxide is “fixed” into a carbohydrate by the enzyme Rubisco. Carbon dioxide is “fixed” from inorganic form into organic molecule
Reduction
6 ATP and 6 NADPH are used to make 6 G3P molecules
ADP and NADP go back to the light reactions to be reused and re-energized
Regeneration
1 G3P leaves the cycle while the other 5 G3P use 3 more ATP to regenerate 3 RuBP to repeat the cycle and the carbon dioxide can be “fixed” into a carbohydrate.
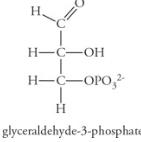
G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)
End product of the Calvin Cycle
Energy-rich, 3-carbon sugar
Exits chloroplast into cell’s cytoplasm and is an important intermediate to other molecules
2 G3Ps = 6-carbon glucose molecule, 6x cycle = 1 glucose molecule
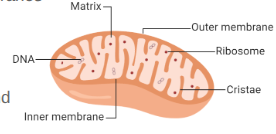
Mitochondria
Double membrane energy harvesting organelle
Structure:
Smooth outer membrane
Folded inner membrane (folds are the cristae, increasing surface area)
Intermembrane space: fluid-filled space between membranes
Matrix: inner fluid-filled space
DNA, Ribosomes
Enzymes: free & membrane-bound
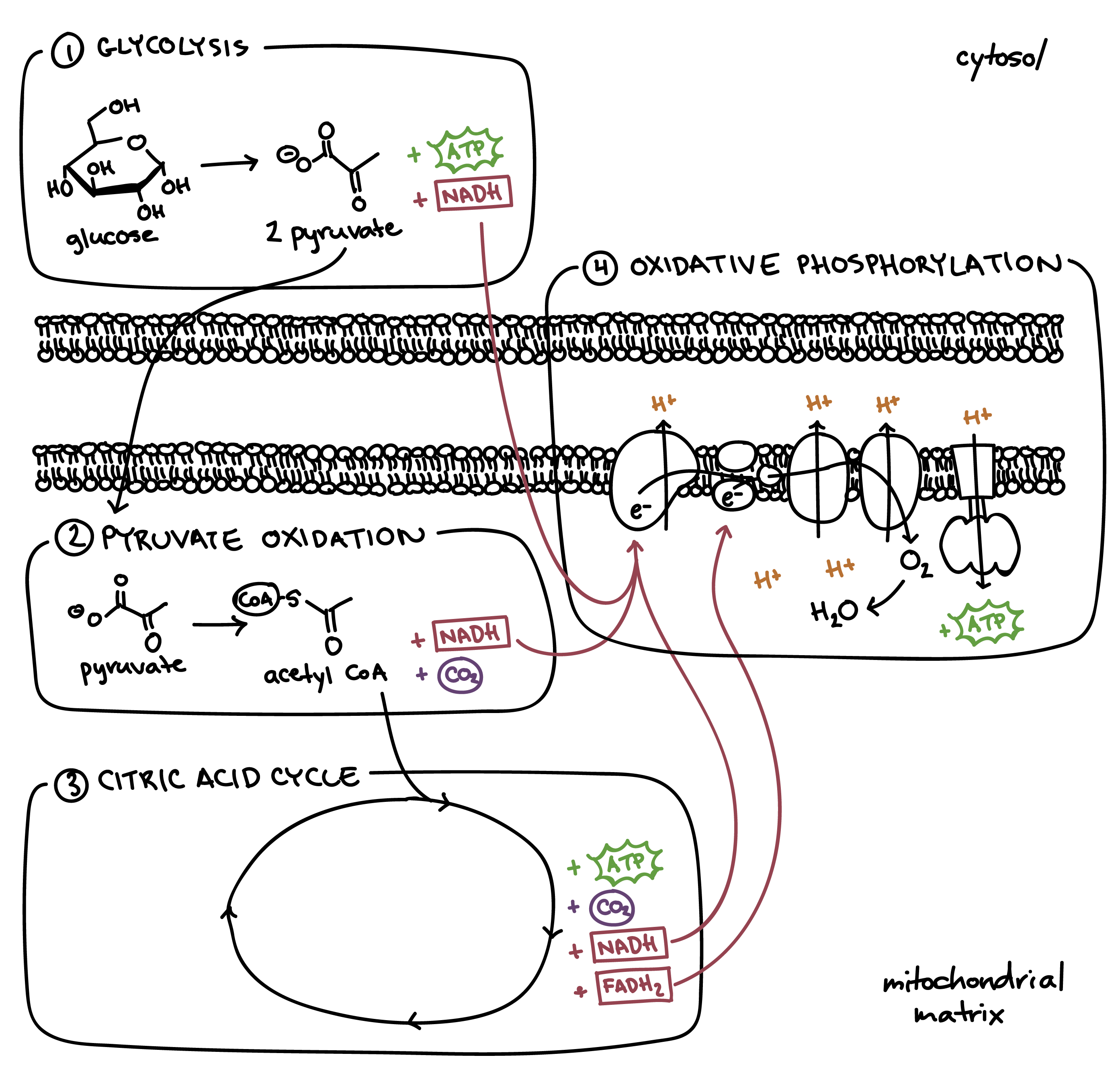
Cellular Respiration Stages
Glycolysis
Pyruvate Oxidation (link reaction)
Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain (oxidative phosphorlaytion)
Aerobic
With oxygen
Pyruvate oxidation
Krebs cycle
ETC
Glycolysis
Anaerobic
Without oxygen
Fermentation
Glycolysis (can occur w/ or w/o)
NADH
The electron carrier used in cellular respiration (stores energy)
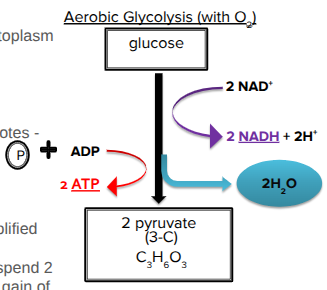
Glycolysis
Occurs outside of mitochondria in the cytoplasm
Can occur with or without O2
With: respiration
Without: fermentation
Partially oxidizes glucose (6C) to 2 pyruvates (3C)
Net gain: 2 ATP + 2NADH
Also makes 2H2O
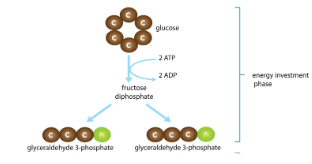
Glycolysis Steps: Energy Investment
Endergonic
Invest some ATP
Glucose is phosphorylated, rearranged, and split into 2 G3P molecules
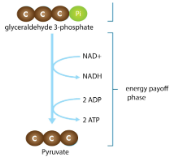
Glycolysis Steps: Energy Payoff
Exergonic
Harvest a little ATP and a little NADH
G3P gives H (is oxidized) to NAD+ (is reduced) to make NADH
G3P is broken down into pyruvate
An intermediate molecule (PEP) donates a P to ADP to make ATP
Substrate level phosphorylation - an enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a P from a substrate (PEP) to ADP to make ATP
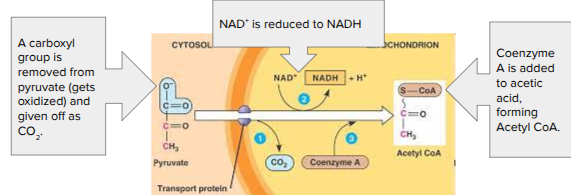
Pyruvate Oxidation
If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrial matrix
Pyruvate → Acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA = Coenzyme; a molecule that attaches to an enzyme’s active site to help catalyze a reaction
CO2, NADH, a 2 carbon sugar are produced (x2 since we start with 2 pyruvates)
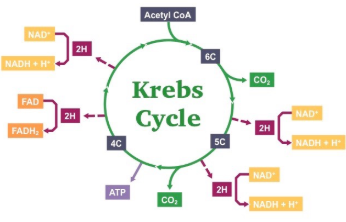
Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle
Occurs in mitochondrial matrix
Acetyl CoA (combines with oxaloacetate) —> Citrate —> many rxns —> CO2 + NADH + FADH2 released
Citrate is later broken down to make oxaloacetate so that it can combine with Acetyl CoA again (two Acetyl CoAs)
Glucose has been fully oxidized
Net gain:
2 ATP (produced by substrate-level phosphorylation)
6 NADH, 2 FADH2 (electron carriers)
CO2 released
Glucose is oxidized when
C6H12O6 → CO2
Single Cycle of the Krebs Cycle
2 x CO2
1 x ATP
1 x FADH2
3 x NADH + H+
Two Cycles of the Krebs Cycle
4 x CO2
2 x ATP
2 x FADH2
6 x NADH + H+
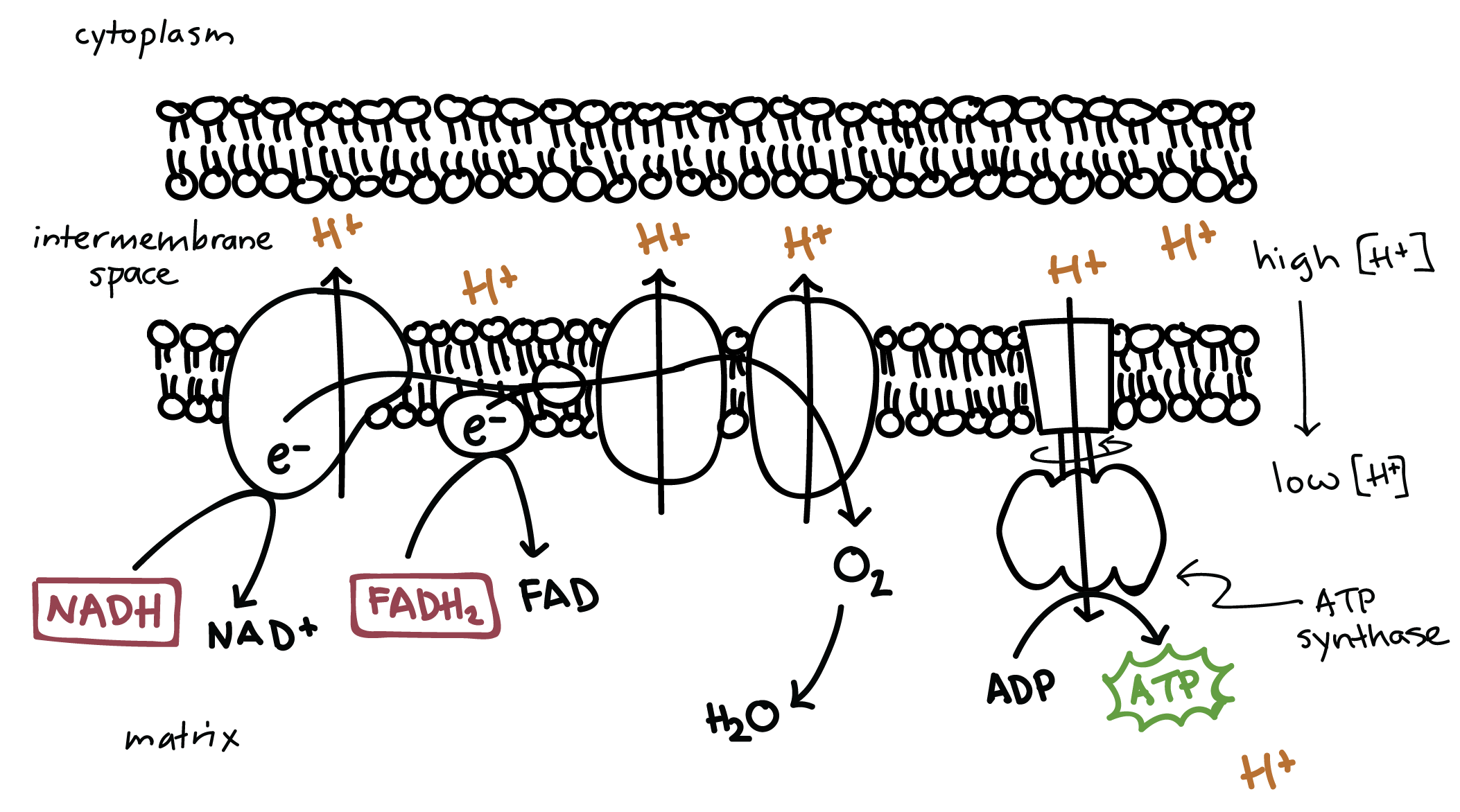
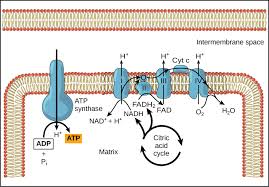
ETC (cellular resp)
Occurs along the cristae in the inner membrane of mitochondria
Produces 26-28 ATP
2 FADH2 and 10 NADH molecules produced in glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, donate high-energy electrons to energy carrier molecules
H+ ions pumped across inner mitochondrial membrane to the intermembrane space as the electrons pass from one carrier to another to create an H+ gradient
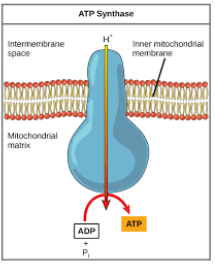
At the end, H+ diffuses down the gradient and through the ATP synthase (ADP → ATP) to the matrix, where they transfer their energy to ATP (chemiosmosis)
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the form of water
Chemiosmosis
The movement/diffusion of ions (H+) across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient
Chemiosmotic Theory
Explains the function of ETCs and how the transfer of electrons down an electron transport system through a series of oxidation-reduction reactions releases energy. The energy allows certain carriers in the chain to transport H+/protons across a membrane.
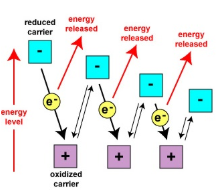
Oxidative Phosphorylation
A metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
H+
H → e- + H+
ATP synthase (cellular resp)
As the H+ ions pass through the enzyme, part of the enzyme rotates. This causes the other part of the enzyme to shift into its active form so that ADP and P can fit at the active site and be joined to make ATP.
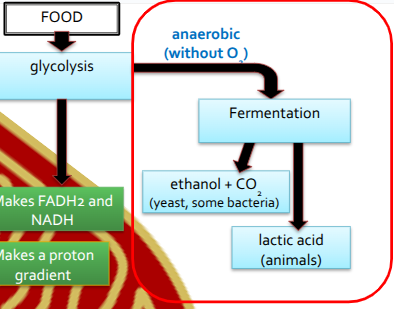
Fermentation
When glycolysis takes place without oxygen (anaerobic)
Fermentation is shown in two parts
Lactic Acid & Alcohol Fermentation
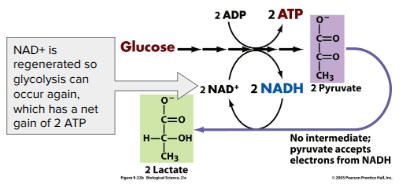
Lactic Acid Fermentation
(Glucose during glycolysis) → Pyruvate → Lactate
Ex. fungi, bacteria, human muscle cells
Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol
Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea)
Once oxygen is available, lactate is converted back to pyruvate by the liver
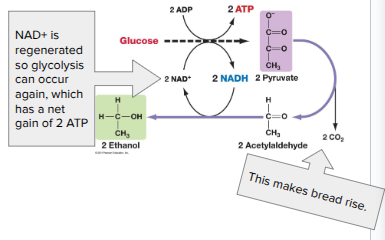
Alcohol Fermentation
(Glucose during glycolysis) → Pyruvate → Ethanol + CO2
Ex. bacteria, yeast
Used in brewing, winemaking, baking
Over time, the ethanol that is produced by this process kills the yeast and bacteria that do it
Metabolism
The set of chemical reactions that occur in the body’s cells to convert food into energy. Includes anabolic and catabolic reactions.
Anabolic Reactions
Forming bonds between molecules
Uses dehydration synthesis
Used to make macromolecules
Catabolic Reactions
Breaking bonds between molecules
Uses hydrolysis reactions
Used in digestion
Metabolic Pathways
Chemical reactions of life that are organized in complex pathways.
Divide chemical reactions into small steps
Increase efficiency, control, & options for intermediate branching points
ΔG
Change in free energy/ability to do work
Activation Energy
An initial input of energy required to break down large molecules
Large biomolecules are stable, so they must absorb energy for the bonds to be broken
Catalysts
Help reduce the amount of energy needed to start a reaction (activation energy)
Enzymes
Biiological catalysts
Generally made of proteins or RNA
Increases rate of reaction & reduces activation energy
Required for most biological reactions
Highly specific
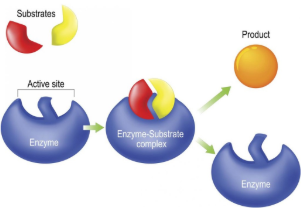
Substrate
Reactant that binds to an enzyme
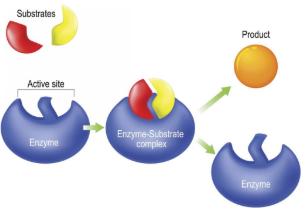
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Temporary association when a substrate is bound to an enzyme
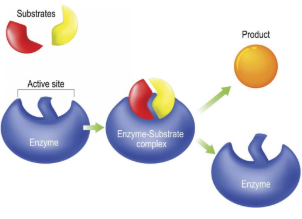
Active Site
Enzyme’s catalytic site; substrate fits into active site
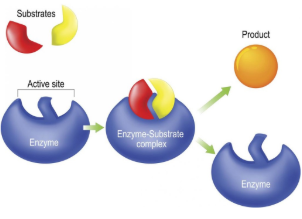
Product
The end result of a reaction
Properties of Enzymes: Reaction Specific
Each enzyme works with a specific substrate
Properties of Enzymes: Not consumed in reaction
Enzymes are unaffected by the reaction & can be used thousands of time per second
Properties of Enzymes: Affected by cellular conditions
Any condition that affects protein structure affects enzymes (pH, temp, etc)
Enzymes end in the suffix “_____”
-ase
Induced-Fit
Active site conforms to its substrate’s shape, bringing chemical groups in position to catalyze reactions.
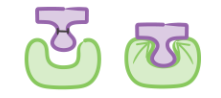
Enzymes in Synthesis Reactions
Active site orients substrates in correct position for reaction
Enzyme brings substrate closer together
Enzymes in Digestion Reactions
Active site binds substrate & puts stress on bonds that must be broken, making it easier to separate molecules
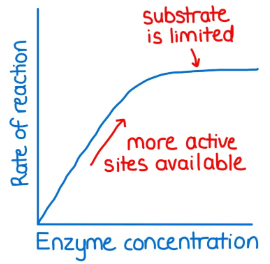
Enzyme concentration ______ (increases/decreases) reaction rate until all substrates are reacted.
Increases
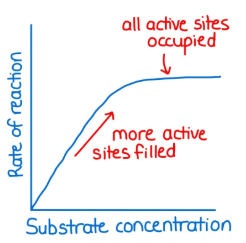
Substrate concentration ______ (increases/decreases) reaction rate until all enzymes are saturated.
Increases
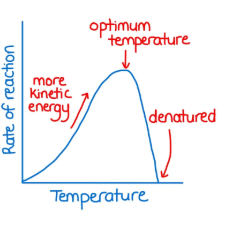
Above optimal temperature impact on enzyme activity
Activity decreases until the enzyme is denatured
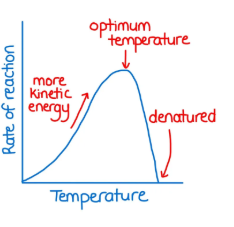
Optimal temperature impact on enzyme activity
Maximum rate
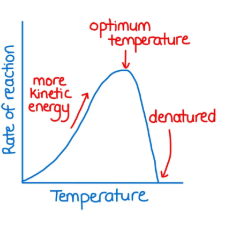
Below optimal temperature impact on enzyme activity
Molecules move slower (fewer collisions between substrate and enzyme) until enzyme becomes inactive or denatured
Above optimal pH impact on enzyme activity
Rate decreases; lower [H+] interferes with enzyme shape
![<p>Rate decreases; lower [H+] interferes with enzyme shape</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/785e58f1-d9e6-4af6-9838-d4367b35da39.png)
Optimal pH impact on enzyme activity
Maximum rate
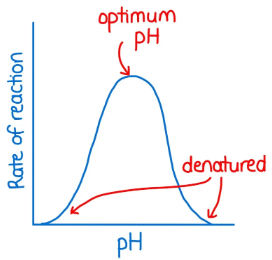
Below optimal pH impact on enzyme activity
Rate decreases; higher [H+] interferes with enzyme shape (denatures)
![<p>Rate decreases; higher [H+] interferes with enzyme shape (denatures)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3cdc79e-e116-4cb3-8cad-8bd58a569c80.png)
Activators
Increases enzyme’s activity - coenzymes & cofactors
changes enzyme’s shape so it works faster
helps enzyme bind to substrate
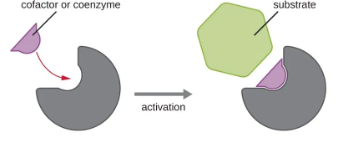
Coenzymes
Non-protein, organic molecules that bind to the enzyme near the active site
Cofactors
Non-protein, small inorganic compounds & ions
Inhibitors
Decrease or block the activity of enzymes, slowing down reaction rates - competitive, noncompetitive/allosteric, & feedback inhibition
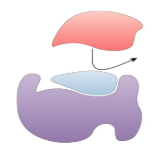
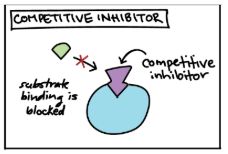
Competitve Inhibitor
Inhibitor & substrate “compete” for active site
Can overcome inhibition by increasing substrate concentration so it out-competes the inhibitor for the active site on the enzyme
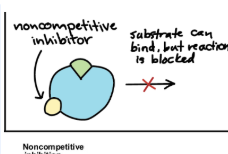
Non-Competitive Inhibitor
Binds to site other than active site (allosteric site)
This causes conformational change that disrupts enzyme function even though substrate still binds
Irreversible Inhibition
Inhibitor permanently binds to enzyme
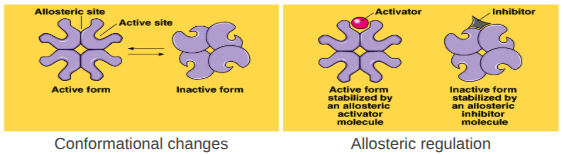
Allosteric Regulation
Conformational changes by regulatory molecules
Inhibitors - keeps enzyme in inactive form
Activators - keeps enzyme in active form
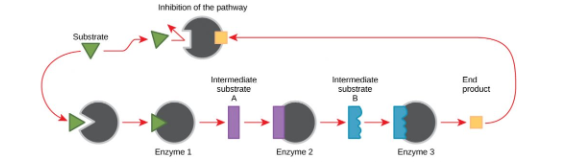
Feedback Inhibition
Each product becomes the reactant for the next step.
When enough final product has been made, the cell needs a way to slow or stop production to avoid wasting energy.
The final product acts as an allosteric inhibitor of an enzyme early in the pathway.
Photosynthesis ETC
Cellular Respiration ETC