PSY 350 Chapter 1
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions and Textbook Questions for Chapter 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
True or False: Unusual behavior is abnormal.
False.
Unusual or statistically deviant behavior is not necessarily abnormal. Exceptional behavior also deviates from the norm.
True or False: About one in 10 American adults suffers from a diagnosable mental or psychological disorder in any given year.
False.
It’s actually about one in four American adults.
True or False: Although effective treatments exist for some psychological disorders, we still lack a means of effectively treating most types of psychological disorders.
False.
The good news is that effective treatments exist for most psychological disorders
True or False: Psychological problems like depression may be experienced differently by people in different cultures.
True.
For example, depression is more likely to be associated with the development of physical symptoms among people in East Asian cultures than in Western cultures.
True or False: A night’s entertainment in London a few hundred years ago might have included gaping at the inmates at the local asylum.
True.
A night on the town for the gentry of London sometimes included a visit to a local asylum, St. Mary’s of Bethlehem Hospital, to gawk at the patients. We derive the word bedlam from Bethlehem Hospital.
True or False: Despite changing attitudes in society toward homosexuality, the psychiatric profession continues to classify homosexuality as a mental disorder.
False.
The psychiatric profession dropped homosexuality from its listing of mental disorders in 1973.
True or False: In a recent experiment, pain patients reported some relief from pain after taking a placebo pill, even though they were told the pill was merely a placebo.
True.
Placebo effects may occur even when participants are told they are taking a placebo.
True or False: Recent evidence shows there are literally millions of genes in the nucleus of every cell in the body.
False.
Although no one yet knows the precise number, scientists believe there are about 20,000 to 25,000 genes in the nucleus of each body cell, but certainly not millions.
True or False: Case studies have been conducted on dead people.
True.
Case studies have been conducted on people who have been dead for hundreds of years. One example is Freud’s study of Leonardo da Vinci. Such studies rely on historical records rather than interviews.
Psychological Disorders
Abnormal behavior patterns that involve a disturbance of psychological functioning or behavior.
Abnormal Psychology
The branch of psychology that studies abnormal behavior and ways of helping people who are affected by psychological disorders.
Medical Model Perspective
Views abnormal behavior as symptoms of an underlying illness or brain disorder.
(The term mental disorder or mental illness is derived from this model)
Criteria for Determining Abnormality
Unusualness → behavior that is unusual is often considered abnormal
Social deviance → violation of social norms
Family perceptions or interpretations of reality
Significant personal distress
Maladaptive or self-defeating behavior
Dangerousness
Legal Criteria for Determining Abnormality
Potential harm to oneself and potential harm to others.
Hysterical Paralysis
Paralysis of limb for psychological reasons. Common diagnosis during the Freudian era/model. Hyster- coming from womb/uterus/female (hysterectomy).
Is culture static?
No, abnormality charges as culture changes. This can lead to cultural friction between generations.
Demonological Model
Mental illness is a product of demonic possession.
Trephination/Trepanation
Drilling the skull to provide an outlet for those irascible spirits/demons (from the Demonological Model).
Humors
Health of the body and mind depended on the balance of humors, or vital fluids, in the body: phlegm, black bile, blood, and yellow bile.
Idea created by Hippocrates.
Phlegmatic
A lethargic or sluggish person was believed to have an excess of phlegm.
Melancholia
An overabundance of black bile was believed to cause depression.
Sanguine
An excess of blood created a sanguine disposition: cheerful, confident, and optimistic.
Choleric
An excess of yellow bile made people bilious and choleric - quick-tempered.
Mind/Body Dualism
Dualistic → exist as both physical (body) and nonphysical (humors affecting the mind)
Monistic → mind is body and body is mind
Malleus Maleficarum
“Witch’s Hammer”; manual used by inquisitors (used to interrogate women)
Why were women considered witches rather than men?
Women were seen as weaker and more vulnerable to the devil.
Moral Therapy
Treat hospitalized patients with care and understanding (associated with the Reform movement).
Who led the reform movement?
Jean-Baptiste Pussin & Philippe Pinel during the 18th & 19th century
What occurred after the reform movement?
“A step backward” - Latter half of 19th century and early 20th century
As moral therapy fell out of favor in the late 1800s, asylums returned to terrible “warehouse” conditions. Patients were locked away and not treated because they cared more about control than treatment.
What forms of treatment were used in the early 20th century?
Lobotomies and the rise of electroshock therapy occurred during this time.
Treatments were focused on experimental and scientific curiosity in order to publish papers.
Deinstitutionalization
A policy of shifting the burden of care from state hospitals to community-based treatment settings, which led to a wholesale exodus from state mental hospitals.
Community Mental Health Movement
Created community mental health centers for those released from the hospital under deinstitutionalization.
Goal was to get people out of state hospitals and into long-term or short-term care based on needs.
Helped by development of new classes of drugs (anti-psychotics) to treat serious disorders.
Wanted to make people self-sufficient.
What was the issue with the community mental health movement?
Psych patients left state institutions but did not get the support from the local communities due to a lack of funding for full support. These patients lacked social skills and self care after being taken care of in institutions, which led to widespread homelessness.
Where are we at today with mental health?
There is more acceptance of mental disorder as an illness, but within limits.
Considerable stigma attached to mental illness.
Limited support from health insurance.
Preference for cheaper drugs over expensive therapy.
Communities also lack good mental health infrastructure.
What are the four major steps in the scientific method?
Formulating a research question.
Framing the research question in the form of a falsifiable hypothesis.
Testing the hypothesis.
Drawing conclusions about the hypothesis. Support or revise theory
Existing Theory
Theoretical model → current understanding based on scientific research from before
Subject to change; always being worked on.
Hypothesis
A prediction tested in an experiment.
Why do we want a falsifiable hypothesis?
We gather data in a way that can prove yourself wrong. It is the difference between scientific and non-scientific ways.
Why was Andrew Wakefield’s study on autism considered bad research?
He studied the MMR vaccine and autism, found a casual connection. He published his findings (which clashed with the theoretical model) and caused a large uproar.
It is considered bad research because he had a very small sample, so he cannot generalize these findings to the larger population. He also had multiple malpractices within his study.
Researchers found that there is no trend in other datasets, but it takes a while to find this. By the time they publish there are already large amounts of anti-vax families.
Naturalistic Method
The investigator observes behavior in the field, where it happens.
Observe behaviors in natural environment, but not inferring causation (does not reveal why someone does a certain behavior).
Correlational Method
Involves the use of statistical methods to examine relationships between two or more factors that can vary, called variables.
Terms: correlation coefficient, positive correlation, negative correlation
Correlation Coefficient
The statistical measure used to express the association or correlation between two variables. Can vary along a continuum ranging from -1.00 to +1.00.
Positive Correlation
When higher values in one variable (negative thinking) are associated with higher values in the other variable (depressive symptoms), there is a positive correlation.
Variables move in the same direction, either both increase or both decrease.
Negative Correlation
If higher levels of one variable are associated with lower values of another variable, there is a negative correlation.
Variables move in opposite directions, one increases while the other decreases.
Epidemiological Method
Examines rates of occurrence of abnormal behavior in various settings or population groups.
Terms: survey method, incidence, prevalence
Survey Method
One type of epidemiological study which relies on interviews or questionnaires.
Incidence
The number of new cases occurring during a specific period of time.
Prevalence
The overall number of cases of a disorder existing in the population during a given period of time.
Case Study Method
Intensive studies of individuals. Typical for rare conditions or something new. Cannot be generalized to the population.
Kinship Studies
Attempt to disentangle the roles of heredity and environment in determining behavior.
What types of situations do kinship studies focus on?
Rely on family, adoption, and twin studies. Including twins separated at birth.
Monozygotic vs Dizygotic
Monozygotic → identical twins, share 100% of their genes in common
Dizygotic → fraternal twins, share 50% overlap of genes (same as any two other siblings)
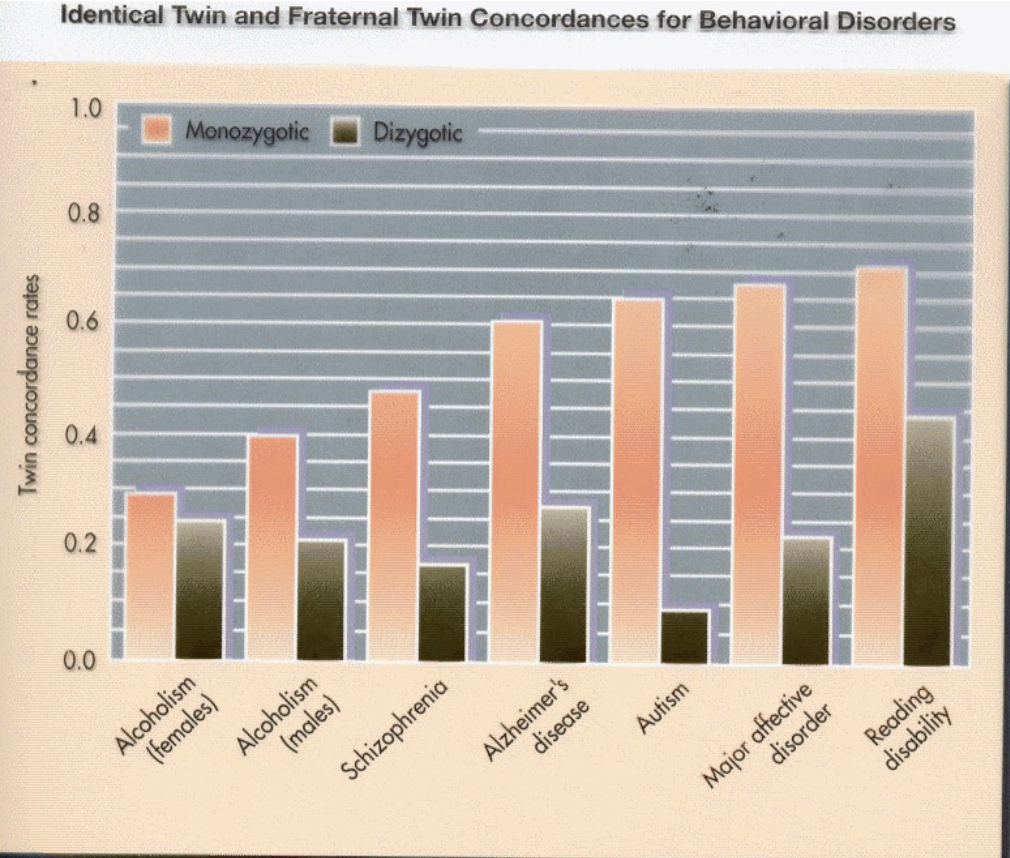
What kind of study is this?
What does it mean when the bars for the monozygotic and dizygotic are close to each other?
What does it mean if there is a larger gap between the two types of bars?
Study: Kinship study
Smaller gap: Suggests environment plays larger role (as seen in alcoholism)
Larger gap: Suggests genetics have larger impact (as seen in autism)
Experimental Method
Allows scientists to demonstrate casual relationships by manipulating the casual factor and measuring its effects under controlled conditions that minimize the risk of other factors explaining the results.
Another def: manipulate an independent variable to determine its effect on the dependent variable
Independent Variable
The factors or variables hypothesized to play a casual role are manipulated or controlled by the investigator.
(thing that we think impacts human experience)
Dependent Variable
The factors that are observed in order to determine the effects of manipulating the independent variable.
(human experience; measured but not manipulated)
Experimental Group vs Control Group
Experimental group is given the experimental treatment, whereas the control group is not.
Random Assignment
Randomly assigning research participants to either the experimental or control groups.
Why is it important to hold conditions constant for each group?
In order to determine the actual effect of the treatment and be confident in the results, all other variables must be held constant.
Otherwise, they could be providing inaccurate results based on uncontrolled factors.
Placebo
An inert drug that physically resembles the active drug (typically a sugar pill).
Placebo Effect
A beneficial effect produced by a placebo drug or treatment, which cannot be attributed to the properties of the placebo itself, and must therefore be due to the patient’s belief in that treatment.
Internal Validity
Occurs when the observed changes in the dependent variable(s) can be casually related to the independent or treatment variables.
Does manipulation cause changes?
External Validity
Refers to the generalizability of results of an experimental study to other individuals, settings, and times.
Can results be generalized?
Construct Validity
A conceptually higher level of validity. It is the degree to which treatment effects can be accounted for by the theoretical mechanisms or constructs represented in the independent variables.
Do the theoretical constructs really account for the results?
What is a challenge with the experimental method?
Population has lots of variability, so it is hard to run experiments while holding all variables steady.