Oral Communication Lecture Review
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering types of oral communication, modes of delivery, informative and persuasive speaking, and tips for presentation preparation and delivery.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Impromptu
Communication delivered without notes or formal preparation.
Extempore
Communication delivered with careful planning and preparation, often using notes or cue cards.
Memorization
Communication delivered by reciting a script from memory.
Reading
Communication delivered by reading directly from a prepared script.
Informal Oral Reports
Oral presentations that are more relaxed and involve a high degree of audience interaction, typically in a small-group setting.
Informative Speaking
Oral Presentations where audience learning is the primary goal; examples include explaining a concept, instructing an audience, or describing an event.
Persuasive Speaking
Oral presentations intended to influence what an audience thinks or does, such as to reinforce beliefs, change attitudes, or motivate action.
Preparation (for oral presentation)
Includes knowledge of the audience, knowledge of the subject, use of time, rehearsal, and personal appearance and grooming.
Presentation Delivery
Refers to being composed and enthusiastic, maintaining eye contact, using one's voice effectively, and managing time well during a presentation.
Visual Aids
Enhance a presentation by improving interest and understanding, but they must be relevant and well-designed to avoid detracting from the message.
Ideas are useless unless you communicate to someone else
True
oral presentations
can be formal or informal, depending upon their explicit and implicit purposes and the delivery situation
Examples of oral presentations
any report type, such as a design review, a proposal, or a conference talk.
Features of eeffective oral presesntation
carefully planned with your objectives in mind
pays close attention to the demands of your audience.
4 skills needed for effective oral communication
outlining and planning,
preparing overheads or other display media,
rehearsing and
delivery.
2 ways an oral report can be delivered?
may be delivered around a small table with just a few listeners (formal)
in a large
auditorium to hundreds of people (informal)
Characteristics of Oral Presentations
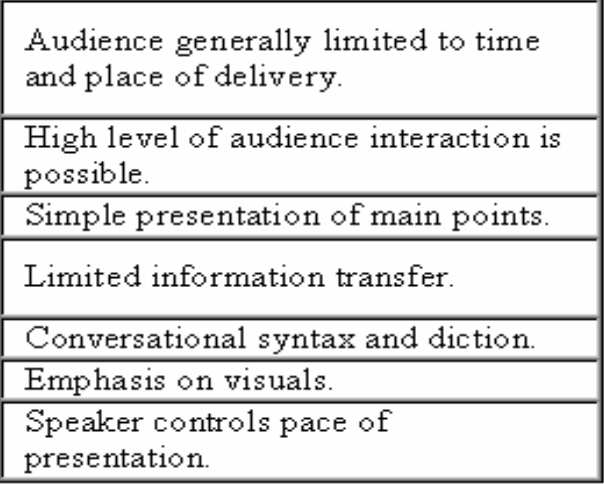
Characteristics of Written Documents
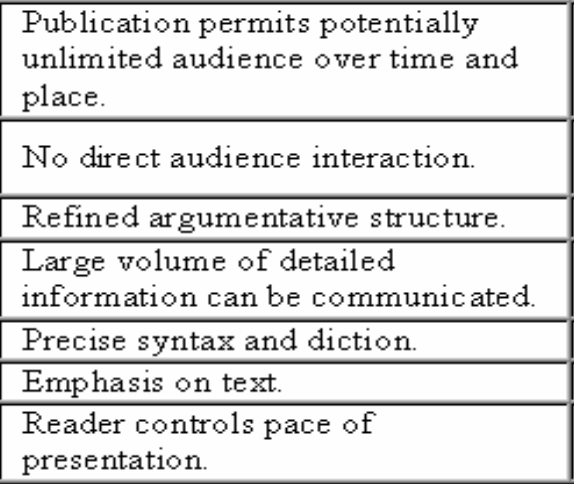
Informal oral reports characterized by
1. small- group settings
high degree ofaudience interaction and
relaxed manner of delivery and dress.
Informal oral presentations can foster
free exchange of ideas
Informal oral presentations are important for
producing action items
Oral presentations in professional environments generally fall into two categories:
informative speaking
persuasive speaking
What is the primary goal of informative speaking?
audience learning
4 things informative speaking achieve:
explain a concept
instruct an audience
demonstrate a process
describe an event.
4 forms of the informative speech:
• Individual or Group Report
• Oral Briefing
• Panel Discussion
• Oral Critique
Primary goal of persuasive speaking:
influence what an audience thinks or does
Goals of persuasive speaking:
to reinforce the attitudes, beliefs, and values an audience already holds
to inoculate an audience against counter persuasion
to change attitudes
to motivate an audience to act
4 delivery methods of oral presentations:
Extempore
Impromptu
Memorization
Reading
The extemporaneous method involves significant effort but
results in a degree of quality that tells your audience that you care about them.
Features of extemporaneous method:
The detailed laying out of the presentation from beginning to end.
Doing your homework to fill in your knowledge gaps.
use of 3 x 5 cue cards or similar method to jog your memory on specifics and keep your presentation on track.
Characteristics of the impromptu method:
1. poor organization and incompleteness,
It tells the audience that you are indifferent about them.
Disadvantages of memorization method:
it is risky; you can lose your place or leave something out and,in a panic, you might revert to the impromptu method, resulting in disaster.
Irrespective of the method of delivery, the presenter must consider the following 5 parameters in preparing for the presentation:
knowledge of the audience
knowledge of subject,
use of time,
rehearsal and
personal appearance and grooming.
What is an important element of any
effective presentation?
use of visual aids
What does knowing your audience entail?
• Do not patronize your audience!
Neither speak down nor speak up to your audience.
How much do they already know about your subject?
Know the age level of the audience as well as its members' leve l of educational sophistication and special interests.
Tailor your presentation accordingly.
Ho can you know your subject?
Whether you use notes, manuscript, or strictly memory, you must know your subject well.
If gaps exist, fill them up!
Ensure appropriate use of time + rehearsal by:
Time limits are to be observed!
Even if no time limit is given, you should strive to do justice to your subject in a little time as possible.
But not at the price of an incomplete presentation.
Maintain personal appearance by:
Your personal appearance affects your credibility.
Informal clothing is rarely appropriate for a professional presentation.
Pay significant attention to personal grooming.
4 components of presentation delivery:
Presentation Delivery
Poise and Enthusiasm
Eye Contact
Use of Voice
Use of Time
Poise & Enthusiasm Tips:
Be well prepared and strive for muscular control, alert attention, vibrant interest in the subject, and an eagerness to communicate.
Avoid distracting mannerisms, but don't stand in a "frozen" position. Moving about, if not excessive, can accentuate your enthusiasm.
Eye Contact Tips:
• During your presentation try to make eye contact with most and if possible every person
in the room.
Avoid fastening your gaze on your notes, on your chart or screen, or on some point in
space above the heads of your listeners
Voice Tips:
• Don't speak too softly, too fast, or mumble!
Your audience must be able to
(1) hear what you say
(2) understand what you say
Use of Time Tips:
Without adequate preparation, it is easy to become nervous and start rushing through a presentation.
Instead, use the pacing established during your many rehearsals.
Material of oral presentation should be:
concise
tell an interesting story.
Important Features of Formal Presentations:
Your voice - how you say it is as important as what you say•Body language - a subject in its own right and something about which much has been written and said.
In essence, your body movements express what your attitudes and thoughts really are.
Appearance - first impressions influence the audience's attitudes to you. Dress appropriately for the occasion.
True or False: As with most personal skills oral communication cannot be taught. Instructors can only point the way.
true
So as always, _____ is essential, both to improve your skills generally and also to make the best of each individual presentation you make
practice
What do you need to think about when preparing a written report?
the objectives of the talk
the main points you want to make
Make a list of these two things as your starting point
Write out the presentation in rough, just like a first draft of a written report.
Review the draft. You will find things that are irrelevant or superfluous - delete them.
Check the story is consistent and flows smoothly.
If there are things you cannot easily express, possibly because of doubt about your understanding, it is better to leave them unsaid.
Never read from a _____It is also unwise to have the talk written out in detail as a
_______ - the chances are you will not locate the thing you want to say amongst all the other text.
script, prompt sheet
You should know most of what you want to say - if you don't then you should not be
giving the talk! So prepare ____________
•Postcards are ideal for this.
Don't forget to number the cards in case you drop them.
cue cards which have key words and phrases (and possibly sketches) on them.
•Remember to mark on your cards the _____so that the right OHP or slide is shown at the right time
•Rehearse your presentation - to ________
visual aids that go with them, yourself at first and then in front of some colleagues.
•The initial rehearsal should consider ______
how the words and the sequence of visual aids go together.
First step of making oral presentations:
Greet the audience (for example, 'Good morning, ladies and gentlemen'), and tell them who you are.
Good presentations then follow this formula:
tell the audience what you are going to tell them,
then tell them,
at the end tell them what you have told them.
•Keep to the time allowed. If you can, keep it short. True or false: It's better to under-run than over-run.
True