Biodiversity changes over time
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
How far back does the fossil record of life on Earth extend
It extends back 3.5 billion years to a time when the most complex organisms were cyanobacteria
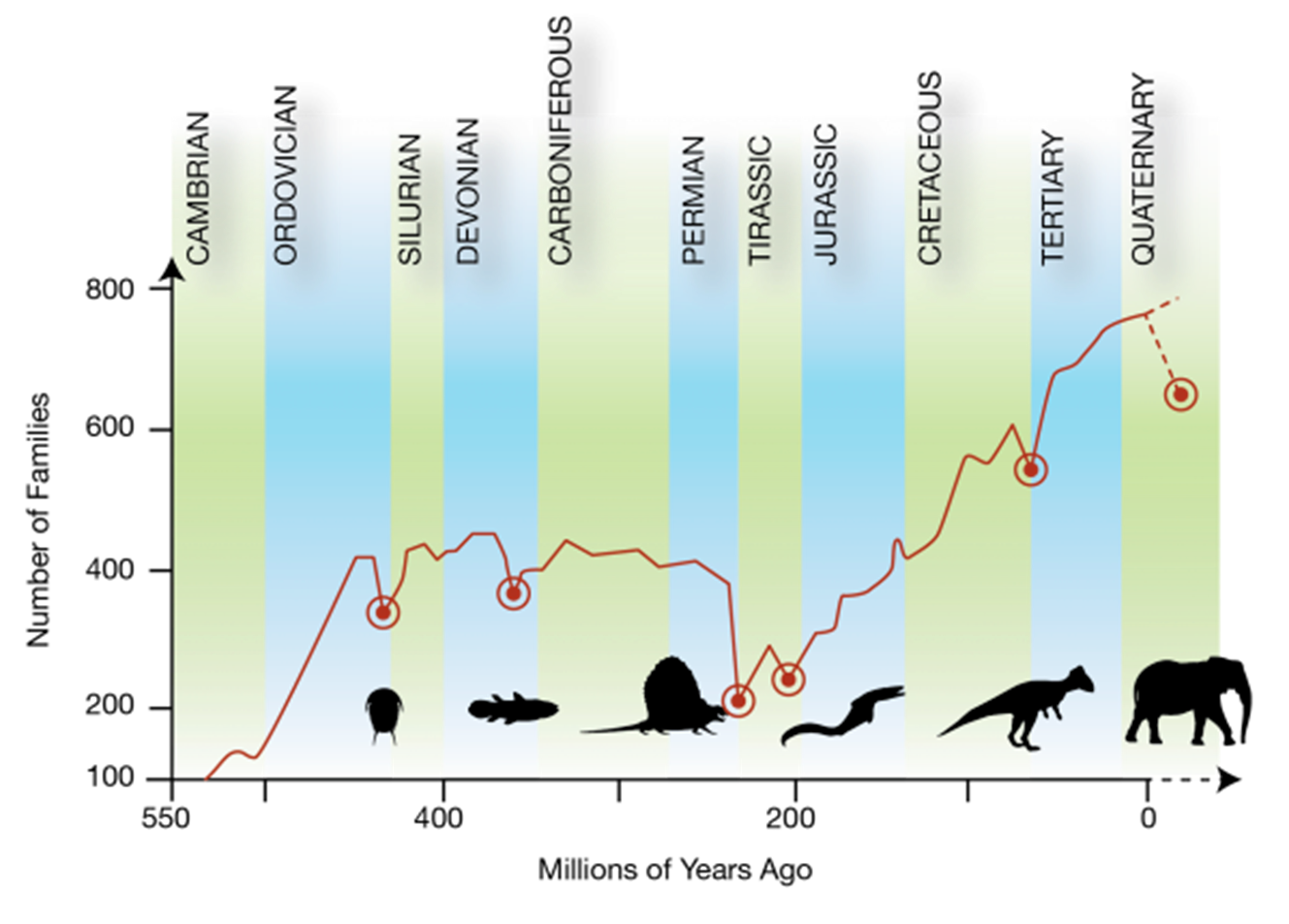
What patterns are observed in the fossil record
The fossil record is marked by major pulses of speciation and extinction
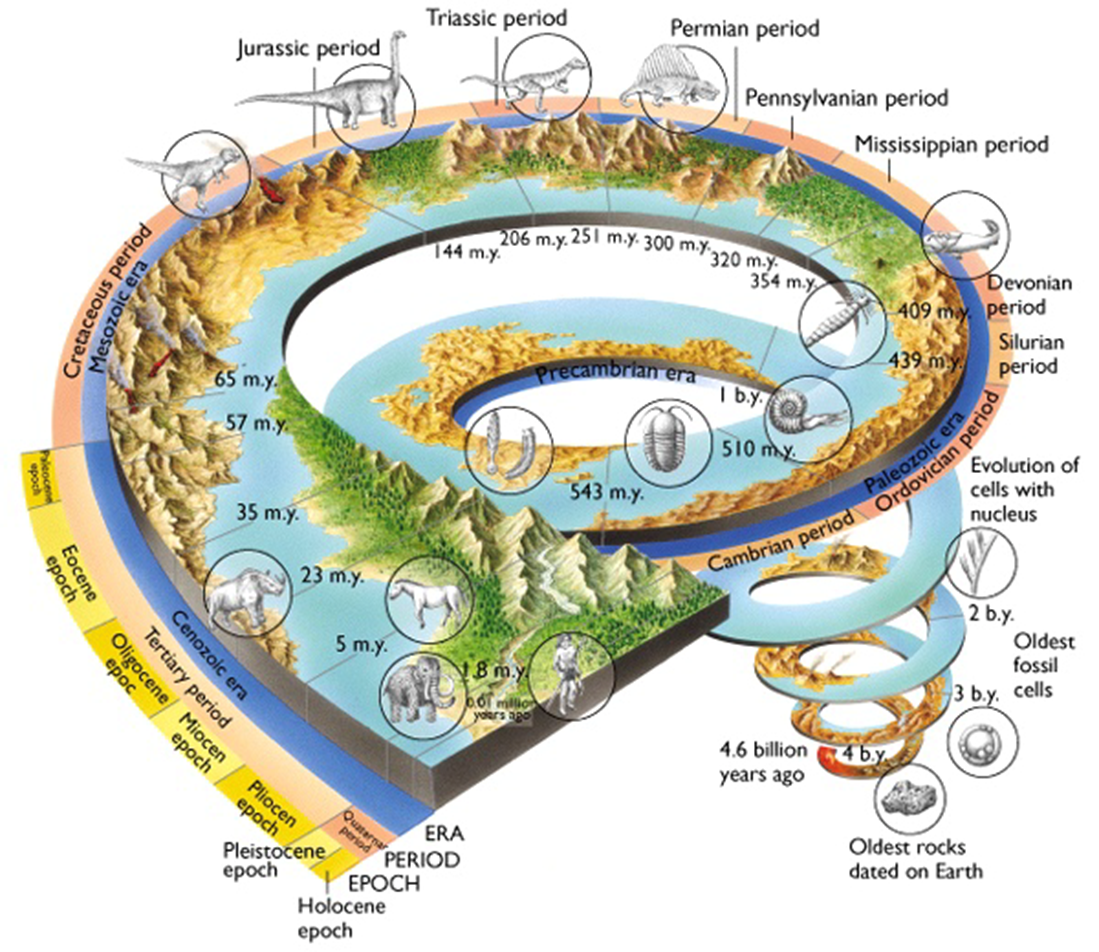
Approximately what percentage of all species that have ever lived are now extinct
Around 99% of the ~4 billion species that have evolved are extinct
What is background extinction
It is the continuous, low level of species extinction that has occurred throughout most of Earth's history
What determines Earth's biodiversity over time
The balance between the formation of new species and the extinction of existing ones
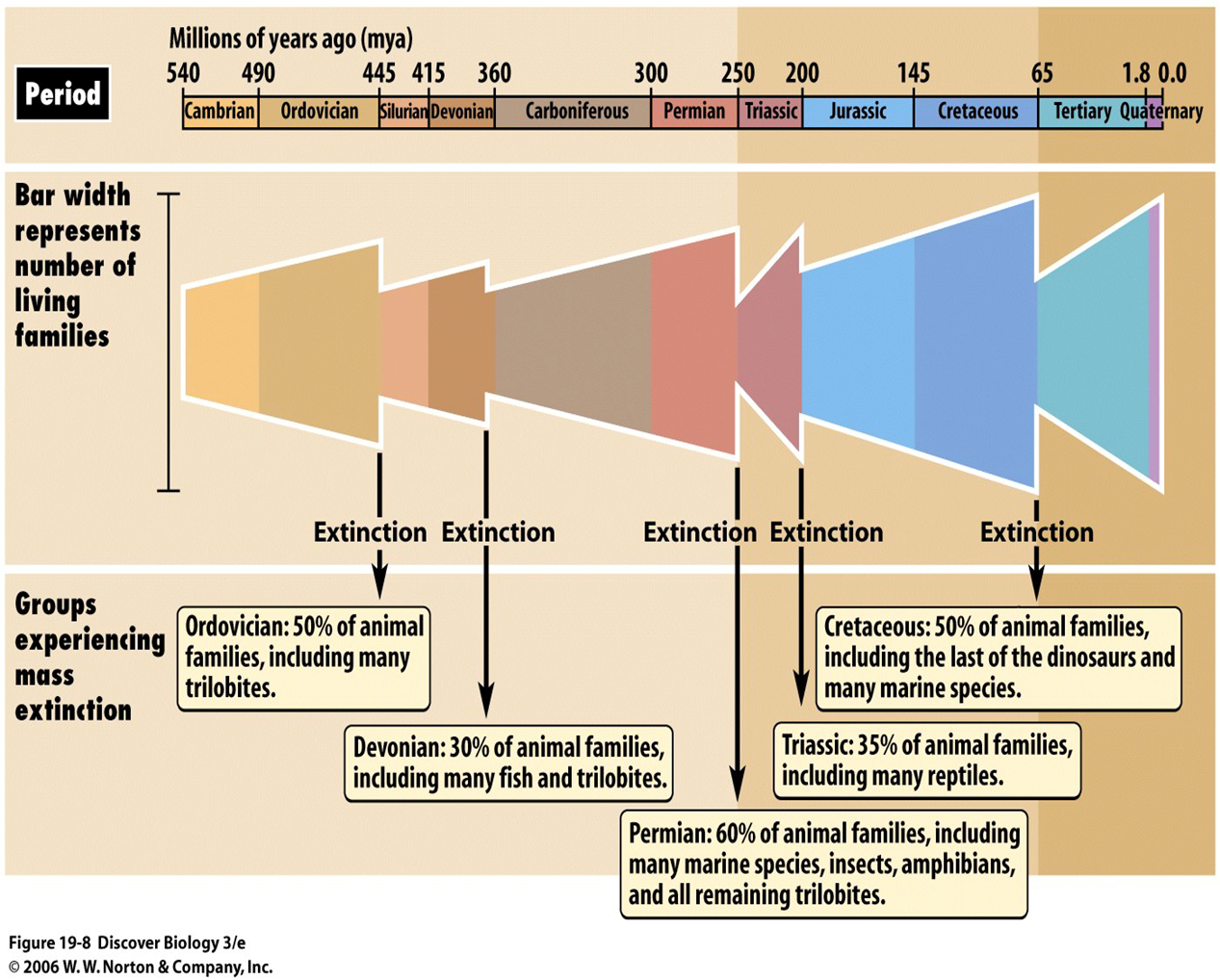
What is a mass extinction
A mass extinction is the extinction of many species in a relatively short geologic time period
How many mass extinctions has Earth experienced, and what percentage of species went extinct in them
Earth has experienced five mass extinctions, during which 50–95% of species went extinct
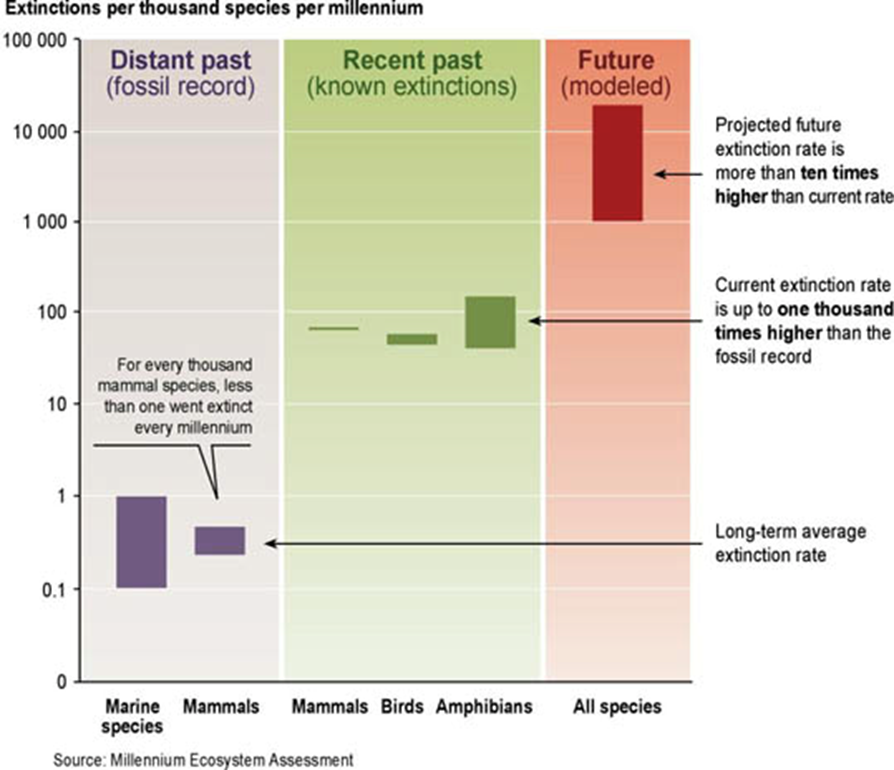
How has human activity affected biodiversity in modern times
Human encroachment has caused many species extinctions, reducing biodiversity and pushing Earth toward a sixth mass extinction
What are the ecological consequences of mass extinctions
They leave behind empty niches, which surviving or new species can exploit
What happens to species that exploit empty niches after a mass extinction
Natural selection acts on them, leading to better adaptation and often speciation
How do lineages evolve after mass extinctions
Isolated populations adapt to different niches, leading to diversification and adaptive radiation
What is an example of adaptive radiation after a mass extinction
After the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago, mammals diversified into many new niches
Which groups have the best fossil records for studying speciation
Marine bivalves, gastropods, plankton, and bryozoans have better fossil records than mammals or plants
What does the fossil record help us understand about speciation
It helps identify periods of rapid species diversification, especially after mass extinctions
What surprising discovery was made in 1980 about insects in tropical forests
In one study of 19 trees in Panama, 80% of the 1,200 beetle species discovered were new to science

What comparison highlights our limited knowledge of biodiversity
Scientists know more about the number of stars in the galaxy than the number of species on Earth
How fast are species becoming extinct compared to the background extinction rate
Currently 100 to 1,000 times faster, and potentially 10,000 times faster by the end of the century
According to the 2005 Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, what proportion of Earth's land surface has been disturbed by humans
At least half, possibly up to 83% (excluding Antarctica and Greenland)
What is local extinction
When a species disappears from a specific area but exists elsewhere
What is ecological extinction
When a species exists in such low numbers it no longer plays its ecological role
What is biological extinction
When a species is no longer found anywhere on Earth—extinction is permanent
How many species are officially listed as at risk of extinction
Around 30,000, though the actual number is likely much higher
Why are fish the most threatened group of species
Due to overfishing, habitat degradation, and pollution
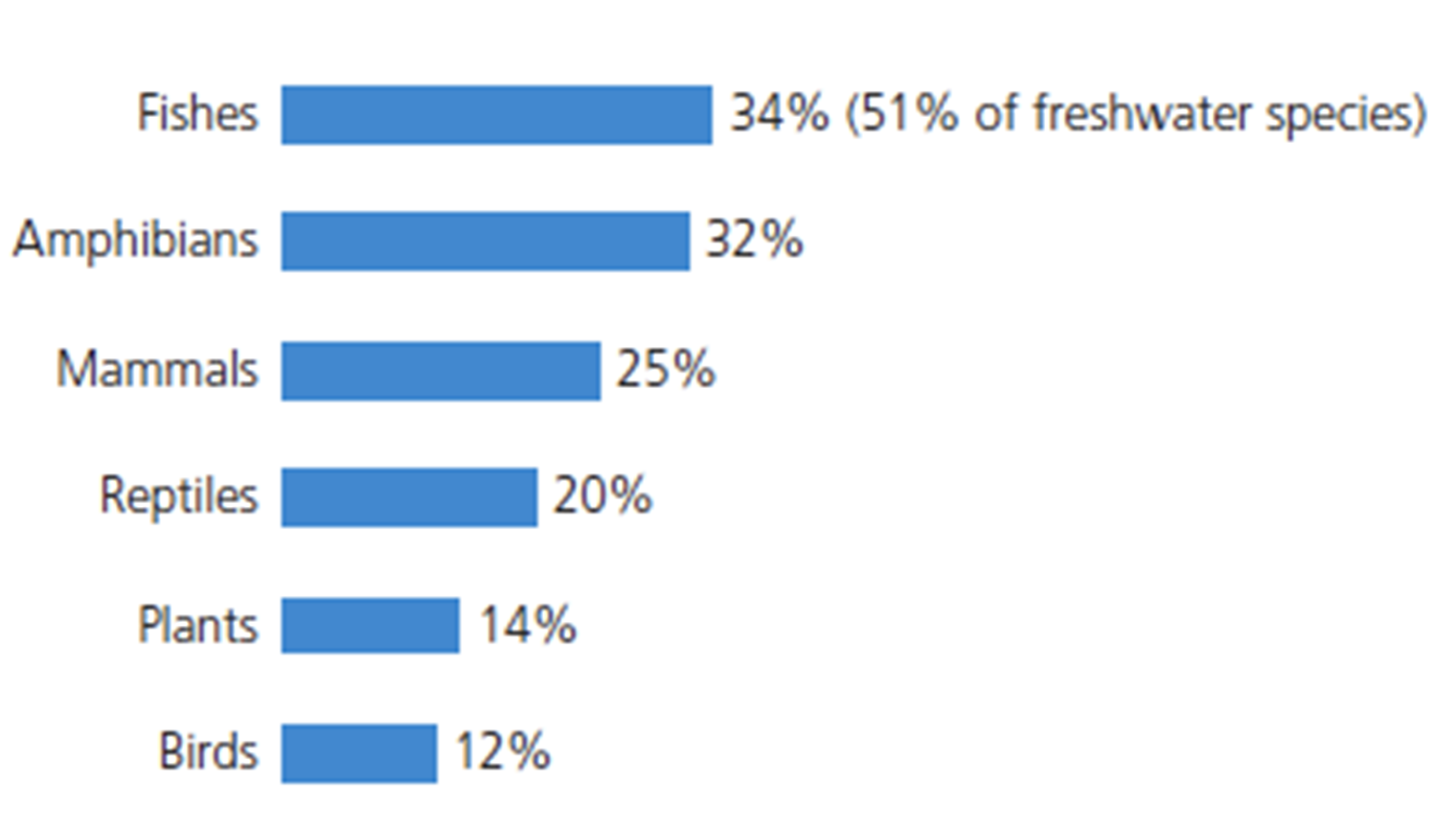
Why should we prevent premature extinction of species
Because of their ecological and economic services and their intrinsic right to exist
Name five human activities causing species extinction
Unsustainable hunting/harvesting
Habitat destruction (e.g., deforestation, urban sprawl)
Introduction of diseases, parasites, predators
Pollution (air, water, soil)
Climate change
How can short-term events like volcanoes or fires threaten biodiversity
They can devastate species with limited ranges, especially endemic species
How did fire affect the Leadbeater’s Possum
Fire worsened the species’ stress from habitat loss and reduced nesting sites
What are the effects of El Niño and La Niña on marine species
They can alter ocean temperatures, shifting the ranges of marine species
How has climate change affected fish distributions in Tasmania
Fish not previously recorded in Tasmania have now been found due to warming waters
How does continental drift affect biodiversity
It creates isolated environments that can lead to speciation over time
Why do tropical ecosystems have higher biodiversity
Stable, warm, and productive environmental conditions near the equator support more species
Why does Australia have so many endemic species
Due to its long-term geographic isolation after separating from Gondwana ~40 million years ago
What percent of Australia's vascular plants are endemic
92%
What percent of Australian mammals are endemic
83%
What are the endemism rates for birds, reptiles, and frogs in Australia
Birds: 45%
Reptiles: 89%
Frogs: 93%
What’s Australia’s record for species extinctions since European settlement
126 species extinct (83 plants, 43 animals including 19 mammals, 21 birds, 3 frogs)
What is a biodiversity hotspot
A biogeographic region with high levels of biodiversity that is under threat from humans
What is the fossil record
A collection of fossils showing extinct life and changes in life forms over time
What does the fossil record support
The theory of evolution, showing consistent appearance of organisms in a specific order
According to fossil evidence, what types of organisms appeared first
Prokaryotes before eukaryotes
Single-celled before multicellular
Invertebrates before vertebrates
Amphibians before dinosaurs
Ferns before flowering plants
Why are soft-bodied organisms rarely fossilized
Because they decay quickly and lack hard parts like bones or shells
How is the geological timescale organized
Into eons → eras → periods
What marks the boundaries between geological time intervals
Abrupt changes in fossil characteristics, such as mass extinctions or new species
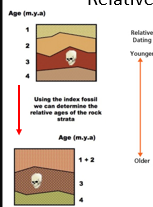
What is the principle of superposition
In undisturbed strata, the oldest layers are at the bottom and the youngest at the top

What is stratigraphy
Estimating the relative age of rock layers based on their position and index fossils
Why don’t igneous rocks contain fossils
Because they form from hot lava, which would destroy organic material
What kind of rock typically contains fossils
Sedimentary rock, formed by compression of mud, silt, or sand
What are index fossils
Fossils of species that lived for a short, known time and are used to date rock layers
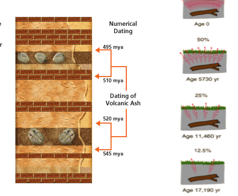
How does radiometric dating work
By measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes in igneous rock
Why can't radiometric dating be used on sedimentary rocks directly
Because the minerals in sedimentary rocks formed before the rock itself did
What is an isotope
An atom of an element with a different number of neutrons
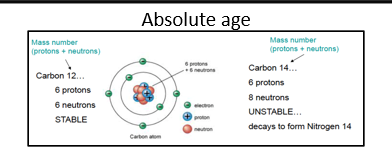
What is a radioactive isotope
An unstable atom that decays into a stable product (e.g. Carbon-14 → Nitrogen)
What is relative dating in geology
A method of determining the order of past events by comparing rock layers (strata), without determining their exact age. It uses principles like the law of superposition and index fossils
What is numerical (absolute) dating in geology
A method of determining the exact age of rocks or fossils in years using radiometric dating, based on the decay of radioactive isotopes in igneous rocks
What happens in the first stage of allopatric speciation
The parent population expands into new areas (due to factors like competition).
All individuals still share a common gene pool with regular gene flow.
How does allopatric speciation progress after expansion
Stage 2: Geographical isolation (e.g., by continental drift or sea level change) prevents gene flow.
Stage 3: Different environments lead to different selection pressures; populations become subspecies.
Stage 4: Reproductive isolation occurs; even if barriers are removed, genetic isolation is complete, and new species have formed.
What is sympatric speciation and how is it different from allopatric speciation
It's the formation of a new species within the same geographic area as the parent species. No physical separation occurs.
It's rarer in animals, but common in plants, often due to polyploidy, habitat preference, or food source changes.
What are the stages of sympatric speciation
Stage 1: A change in habitat or food preference (e.g., insect lays eggs on a new plant).
Stage 2: Reproductive isolation forms as the new group mates and raises offspring only within their new habitat.
Over time, these groups diverge into distinct species.
What does the global distribution of species suggest about their evolution
It suggests that modern species evolved from ancestral populations that radiated out into new environments.
Examples of this are seen on islands where isolation led to diversification:
Galapagos Islands
Cape Verde Islands
Tristan da Cunha